467595fede319461317d93dae42b7ed4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48

Scaleable Windows. NT? • Jim Gray Microsoft Research Gray@Microsoft. com http: //research. Microsoft. com/~Gray 1

Outline • What is Scalability? • Why does Microsoft care about Scale. Up • Current Scale. Up Status? • NT 5 & SQL 7 & Exchange 2
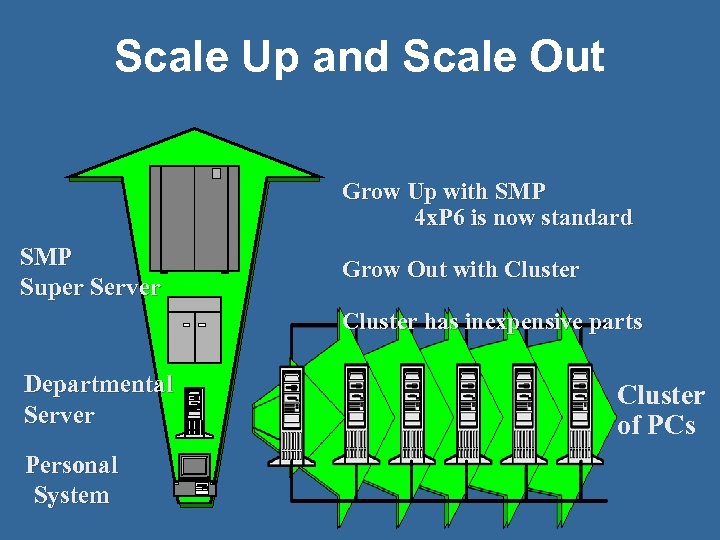
Scale Up and Scale Out Grow Up with SMP 4 x. P 6 is now standard SMP Super Server Grow Out with Cluster has inexpensive parts Departmental Server Personal System Cluster of PCs
Billions Of Clients • Every device will be “intelligent” • Doors, rooms, cars… • Computing will be ubiquitous
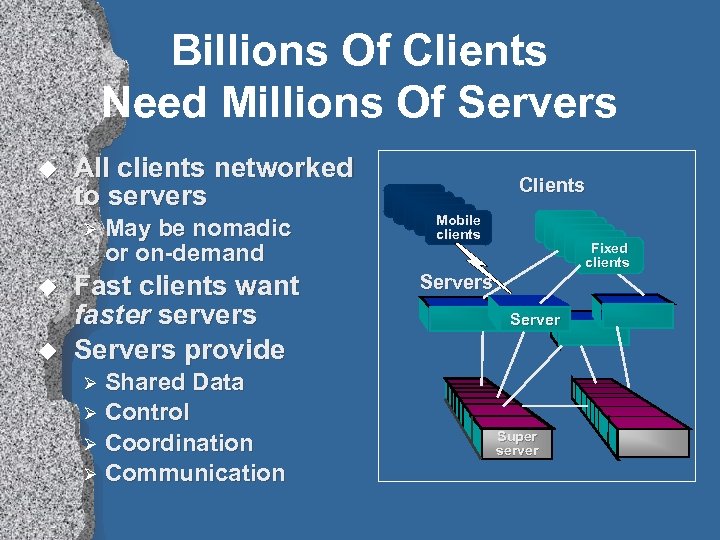
Billions Of Clients Need Millions Of Servers u All clients networked to servers Ø u u May be nomadic or on-demand Fast clients want faster servers Servers provide Shared Data Ø Control Ø Coordination Ø Communication Clients Mobile clients Fixed clients Server Ø Super server

Thesis Many little beat few big $1 million Mainframe 3 1 MM $100 K Mini $10 K Micro Nano 1 MB Pico Processor 10 pico-second ram 10 nano-second ram 100 MB 10 GB 10 microsecond ram 1 TB 14" u u 9" 5. 25" 3. 5" 2. 5" 1. 8" 10 millisecond disc 100 TB 10 second tape archive Smoking, hairy golf ball How to connect the many little parts? How to program the many little parts? Fault tolerance? 1 M SPECmarks, 1 TFLOP 106 clocks to bulk ram Event-horizon on chip VM reincarnated Multiprogram cache, On-Chip SMP

Outline • What is Scalability • Why does Microsoft care about Scale. Up • Current Scale. Up Status? • NT 5 & SQL 7 & Exchange 7
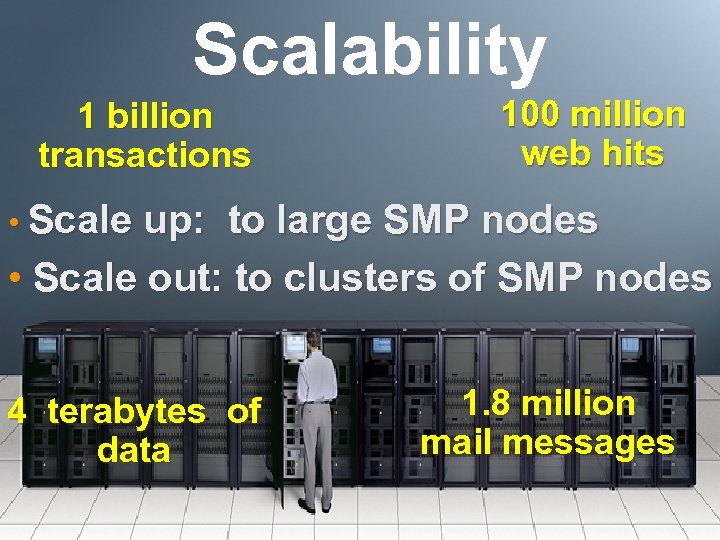
Scalability 1 billion transactions 100 million web hits • Scale up: to large SMP nodes • Scale out: to clusters of SMP nodes 4 terabytes of data 1. 8 million mail messages 8

“Commercial” NT Clusters • 16 -node Tandem Cluster » 64 cpus » 2 TB of disk » Decision support • 45 -node Compaq Cluster » 140 cpus » 14 GB DRAM » 4 TB RAID disk » OLTP (Debit Credit) • 1 B tpd (14 k tps) 9
Tandem Oracle/NT • 27, 383 tpm. C • 71. 50 $/tpm. C • 4 x 6 cpus • 384 disks =2. 7 TB 10
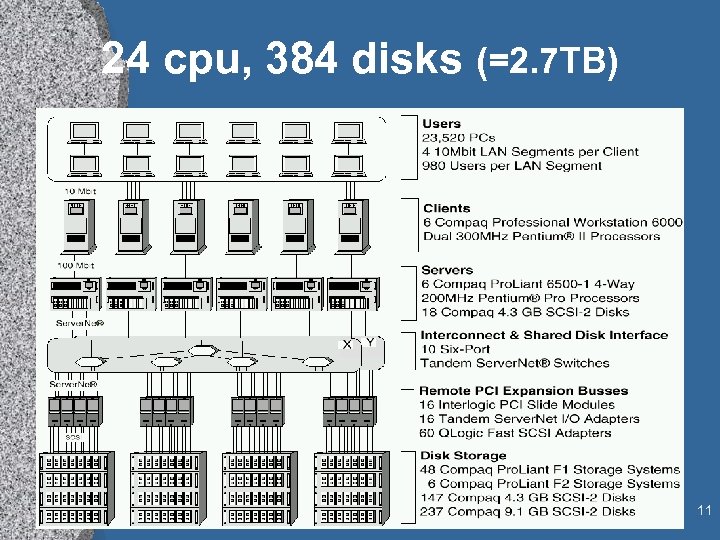
24 cpu, 384 disks (=2. 7 TB) 11

Billion Transactions per Day Project • • Built a 45 -node Windows NT Cluster (with help from Intel & Compaq) > 900 disks All off-the-shelf parts Using SQL Server & DTC distributed transactions Debit. Credit Transaction Each node has 1/20 th of the DB Each node does 1/20 th of the work 15% of the transactions are “distributed”
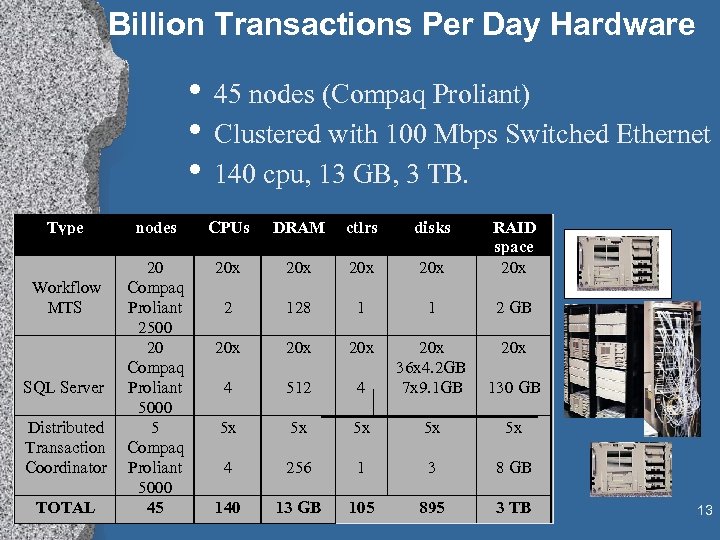
Billion Transactions Per Day Hardware • 45 nodes (Compaq Proliant) • Clustered with 100 Mbps Switched Ethernet • 140 cpu, 13 GB, 3 TB. Type Workflow MTS SQL Server Distributed Transaction Coordinator TOTAL nodes CPUs DRAM ctlrs disks 20 Compaq Proliant 2500 20 Compaq Proliant 5000 5 Compaq Proliant 5000 45 20 x 20 x RAID space 20 x 2 128 1 1 2 GB 20 x 20 x 4 512 4 20 x 36 x 4. 2 GB 7 x 9. 1 GB 130 GB 5 x 5 x 5 x 4 256 1 3 8 GB 140 13 GB 105 895 3 TB 13
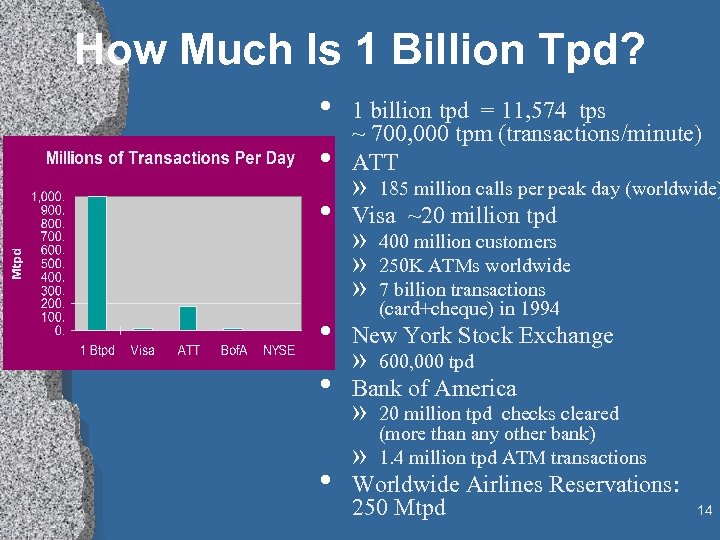
How Much Is 1 Billion Tpd? • 1 billion tpd = 11, 574 tps ~ 700, 000 tpm (transactions/minute) • ATT » 185 million calls per peak day (worldwide) • Visa ~20 million tpd » » » 400 million customers 250 K ATMs worldwide 7 billion transactions (card+cheque) in 1994 • New York Stock Exchange » 600, 000 tpd • Bank of America • » » 20 million tpd checks cleared (more than any other bank) 1. 4 million tpd ATM transactions Worldwide Airlines Reservations: 250 Mtpd 14
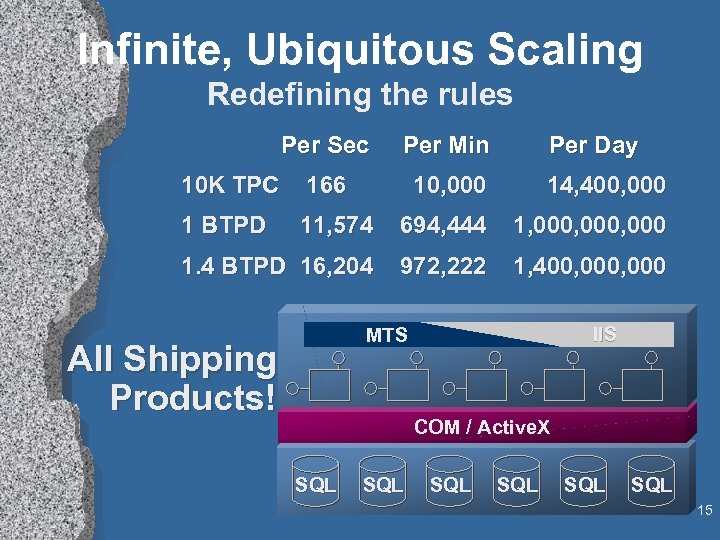
Infinite, Ubiquitous Scaling Redefining the rules Per Sec Per Min Per Day 10 K TPC 166 10, 000 14, 400, 000 1 BTPD 11, 574 694, 444 1, 000, 000 1. 4 BTPD 16, 204 972, 222 1, 400, 000 IIS MTS All Shipping Products! COM / Active. X SQL SQL SQL 15
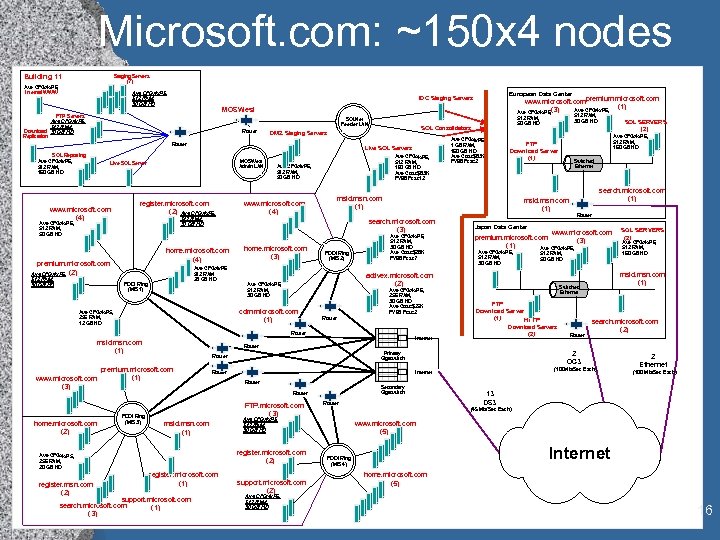
Microsoft. com: ~150 x 4 nodes Building 11 Staging Servers (7) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, Internal WWW Ave CFG: 4 x. P 5, 512 RAM, 30 GB HD FTP Servers Ave CFG: 4 x. P 5, 512 RAM, Download 30 GB HD Replication SQLNet Feeder LAN Router Live SQL Servers MOSWest Admin LAN Live SQL Server www. microsoft. com (4) register. microsoft. com (2) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 512 RAM, 160 GB HD Ave Cost: $83 K FY 98 Fcst: 12 Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 512 RAM, 50 GB HD www. microsoft. com (4) premium. microsoft. com (2) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6 512 RAM 28 GB HD FDDI Ring (MIS 1) home. microsoft. com (3) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 512 RAM, 30 GB HD Ave Cost: $28 K FY 98 Fcst: 7 Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 256 RAM, 30 GB HD Ave Cost: $25 K FY 98 Fcst: 2 Router msid. msn. com (1) www. microsoft. com (3) Router www. microsoft. com premium. microsoft. com (3) (1) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 512 RAM, 30 GB HD 512 RAM, 50 GB HD FTP Download Server (1) HTTP Download Servers (2) Router SQL SERVERS (2) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 512 RAM, 160 GB HD msid. msn. com (1) Switched Ethernet search. microsoft. com (2) Secondary Gigaswitch support. microsoft. com search. microsoft. com (1) (3) Router support. microsoft. com (2) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 512 RAM, 30 GB HD 2 Ethernet (100 Mb/Sec Each) 13 DS 3 (45 Mb/Sec Each) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 5, 512 RAM, 30 GB HD register. microsoft. com (2) register. microsoft. com (1) (100 Mb/Sec Each) Internet Router FTP. microsoft. com (3) msid. msn. com (1) 2 OC 3 Primary Gigaswitch Router Ave CFG: 4 x. P 5, 256 RAM, 20 GB HD register. msn. com (2) search. microsoft. com (1) Japan Data Center Internet Router premium. microsoft. com (1) FDDI Ring (MIS 3) Switched Ethernet Router home. microsoft. com (2) SQL SERVERS (2) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 512 RAM, 160 GB HD FTP Download Server (1) activex. microsoft. com (2) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 512 RAM, 30 GB HD cdm. microsoft. com (1) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 5, 256 RAM, 12 GB HD FDDI Ring (MIS 2) 512 RAM, 30 GB HD msid. msn. com (1) search. microsoft. com (3) home. microsoft. com (4) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 1 GB RAM, 160 GB HD Ave Cost: $83 K FY 98 Fcst: 2 msid. msn. com (1) 512 RAM, 30 GB HD Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 512 RAM, 50 GB HD Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 512 RAM, 30 GB HD www. microsoft. com premium. microsoft. com (1) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, (3) Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 512 RAM, 50 GB HD SQL Consolidators DMZ Staging Servers Router SQL Reporting Ave CFG: 4 x. P 6, 512 RAM, 160 GB HD European Data Center IDC Staging Servers MOSWest www. microsoft. com (5) Internet FDDI Ring (MIS 4) home. microsoft. com (5) 16

NCSA Super Cluster http: //access. ncsa. uiuc. edu/Cover. Stories/Super. Cluster/super. html • National Center for Supercomputing Applications • • • University of Illinois @ Urbana 512 Pentium II cpus, 2, 096 disks, SAN Compaq + HP +Myricom + Windows. NT A Super Computer for 3 M$ Classic Fortran/MPI programming DCOM programming model 17
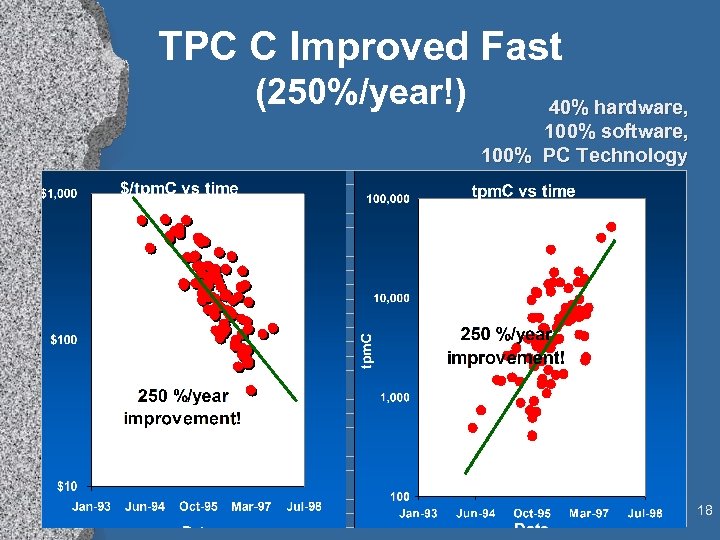
TPC C Improved Fast (250%/year!) 40% hardware, 100% software, 100% PC Technology 18
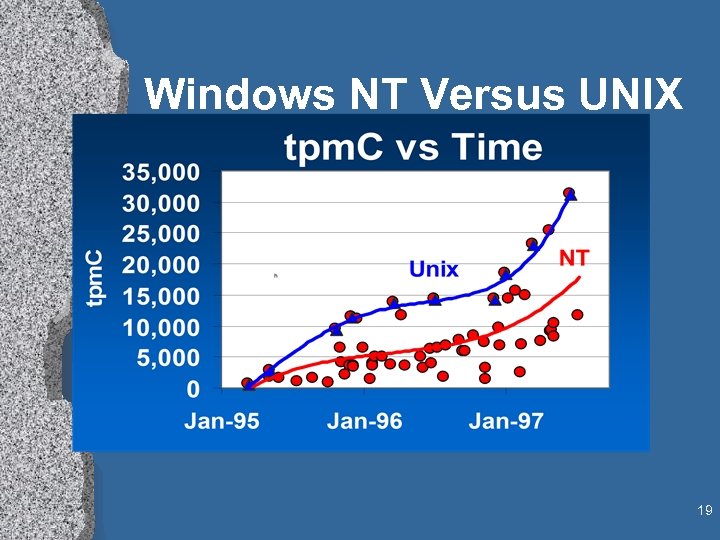
Windows NT Versus UNIX 19
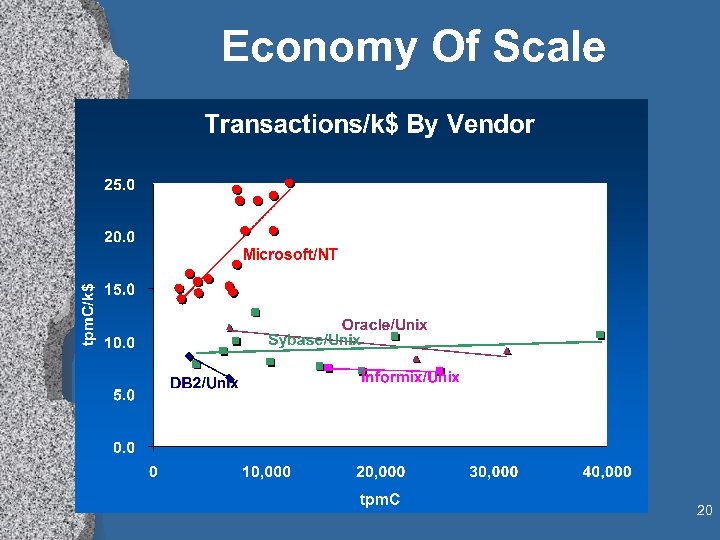
Economy Of Scale 20

Microsoft Terra. Server: Scaleup to Big Databases • • Build a 1 TB SQL Server database Data must be • Loaded • • On the web (world’s largest atlas) Sell images with commerce server. » 1 TB » Unencumbered » Interesting to everyone everywhere » And not offensive to anyone anywhere » 1. 5 M place names from Encarta World Atlas » 3 M Sq Km from USGS (1 meter resolution) » 1 M Sq Km from Russian Space agency (2 m) 21
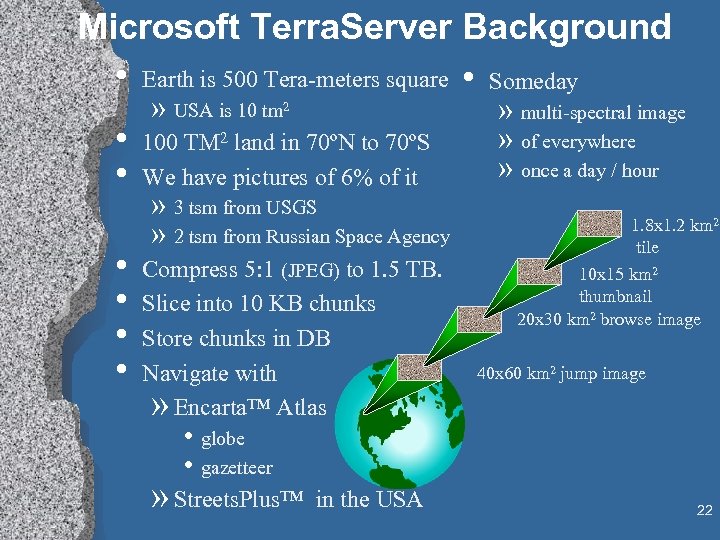
Microsoft Terra. Server Background • Earth is 500 Tera-meters square • Someday • • • » USA is 10 tm 2 100 TM 2 land in 70ºN to 70ºS We have pictures of 6% of it » 3 tsm from USGS » 2 tsm from Russian Space Agency Compress 5: 1 (JPEG) to 1. 5 TB. Slice into 10 KB chunks Store chunks in DB Navigate with » Encarta™ Atlas » multi-spectral image » of everywhere » once a day / hour 1. 8 x 1. 2 km 2 tile 10 x 15 km 2 thumbnail 20 x 30 km 2 browse image 40 x 60 km 2 jump image • globe • gazetteer » Streets. Plus™ in the USA 22

Demo • navigate by coverage map to White House • Download image • buy imagery from USGS • navigate by name to Venice • buy SPIN 2 image & Kodak photo • Pop out to Expedia street map of Venice • Mention that DB will double in next 18 months (2 x USGS, 2 X SPIN 2) 23

The Microsoft Terra. Server Hardware • Compaq Alpha. Server 8400 • 8 x 400 Mhz Alpha cpus • 10 GB DRAM • 324 9. 2 GB Storage. Works Disks » 3 TB raw, 2. 4 TB of RAID 5 • STK 9710 tape robot (4 TB) • Windows. NT 4 EE, SQL Server 7. 0 24
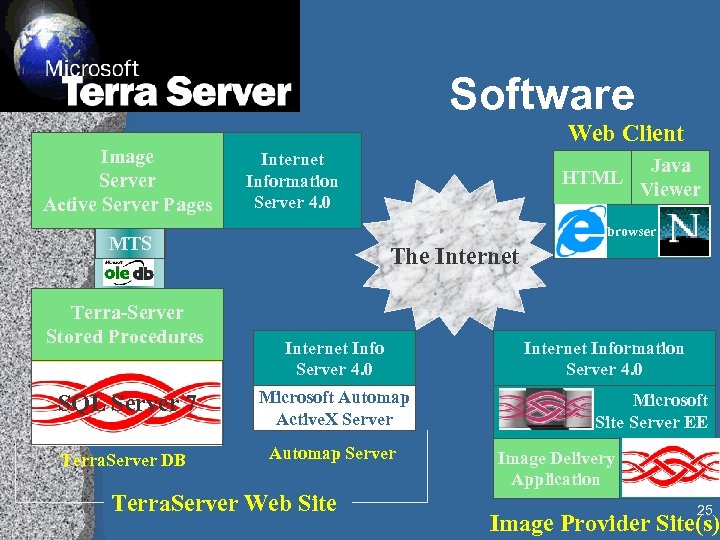
Software Image Server Active Server Pages Web Client Internet Information Server 4. 0 Java Viewer browser MTS Terra-Server Stored Procedures HTML The Internet Info Server 4. 0 SQL Server 7 Microsoft Automap Active. X Server Terra. Server DB Automap Server Terra. Server Web Site Internet Information Server 4. 0 Microsoft Site Server EE Image Delivery SQL Server Application 7 25 Image Provider Site(s)
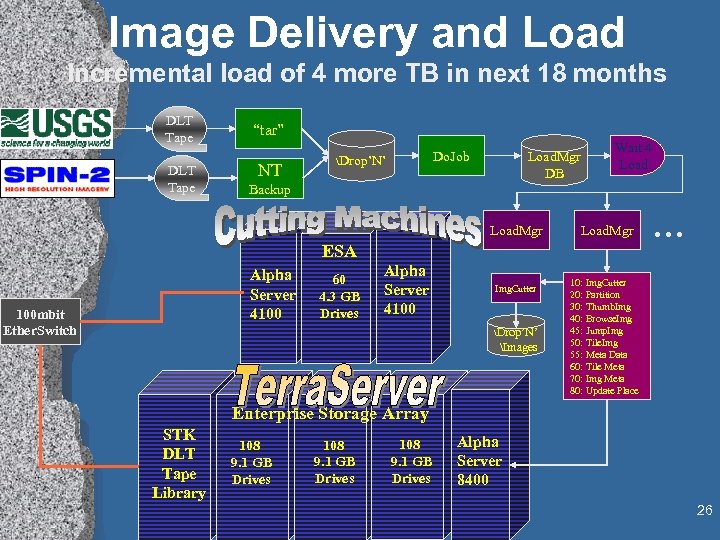
Image Delivery and Load Incremental load of 4 more TB in next 18 months DLT Tape “tar” NT Do. Job Drop’N’ Load. Mgr DB Wait 4 Load Backup Load. Mgr ESA Alpha Server 4100 100 mbit Ether. Switch 60 4. 3 GB Drives Alpha Server 4100 Img. Cutter Drop’N’ Images . . . 10: Img. Cutter 20: Partition 30: Thumb. Img 40: Browse. Img 45: Jump. Img 50: Tile. Img 55: Meta Data 60: Tile Meta 70: Img Meta 80: Update Place Enterprise Storage Array STK DLT Tape Library 108 9. 1 GB Drives Alpha Server 8400 26
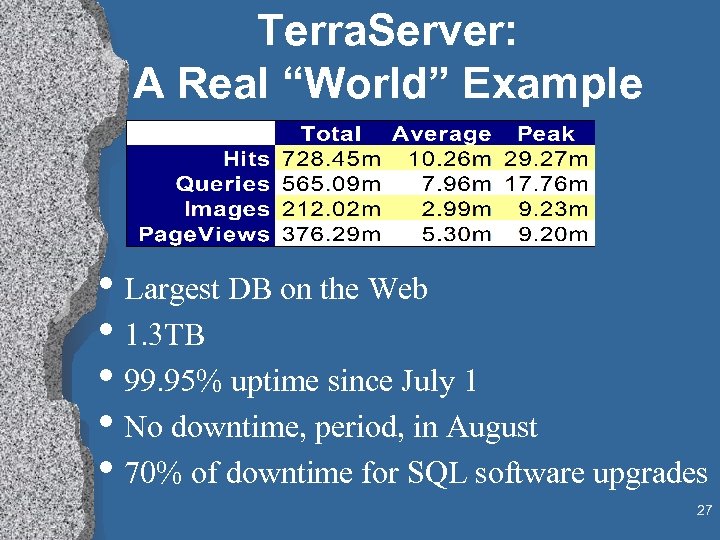
Terra. Server: A Real “World” Example • Largest DB on the Web • 1. 3 TB • 99. 95% uptime since July 1 • No downtime, period, in August • 70% of downtime for SQL software upgrades 27

NT Clusters (Wolfpack) • Scale DOWN to PDA: Windows. CE • Scale UP an SMP: Terra. Server • Scale OUT with a cluster of machines • Single-system image » Naming » Protection/security » Management/load balance • Fault tolerance » “Wolfpack” • Hot pluggable hardware & software 28
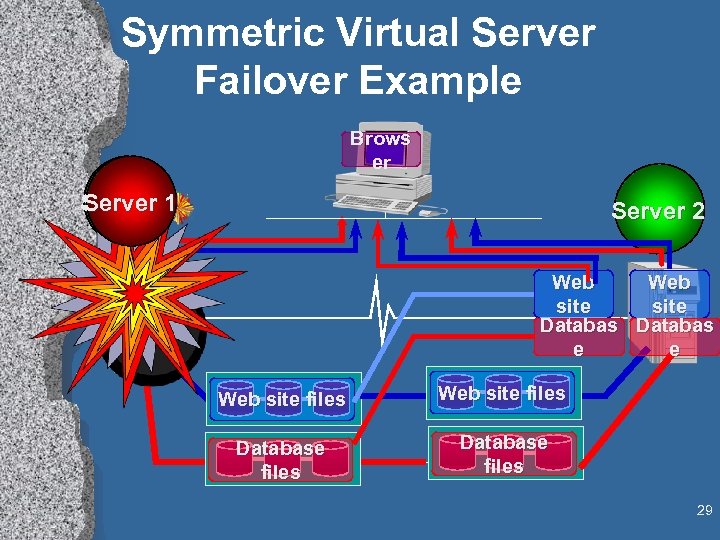
Symmetric Virtual Server Failover Example Brows er Server 1 Server 2 Web site Databas e e Web site files Database files 29

Windows NT 5 (scalability features) • Better SMP support • Clusters: » 16 x packs (fault tolerant clusters) » 100 x mobs: arrays for manageability » SAN/VIA support • 64 bit addressing for data » Apps like SQL, Oracle, will use it for data » 64 bit API to NT comes later (in lab now). • Remote management (scripting and DCOM) • Active Directory • Veritas volume manager • Many 3 rd party HSMs • Batch support 30

Microsoft SQL Server 7. 0 • Fixes the famous performance bugs » dynamic record locking » online backup, quick recovery…. • 64 bit addressing buffer pool • SMP parallelism and better SMP support • Built in OLAP (cubes and MOLAP) • Scale down to Win 9 x • Improved management interfaces • Data transform services (for warehouses) 31

Outline • What is Scalability • Why does Microsoft care about Scale. Up • Current Scale. Up Status? • NT 5 & SQL 7 32
end Other slides would be interesting, but. . . 33

Interesting “other slides” No time for them but. . . • How much information is there? • IO bandwidth in the Intel world • Intelligent disks • SAN/VIA • NT Cluster Sort 34
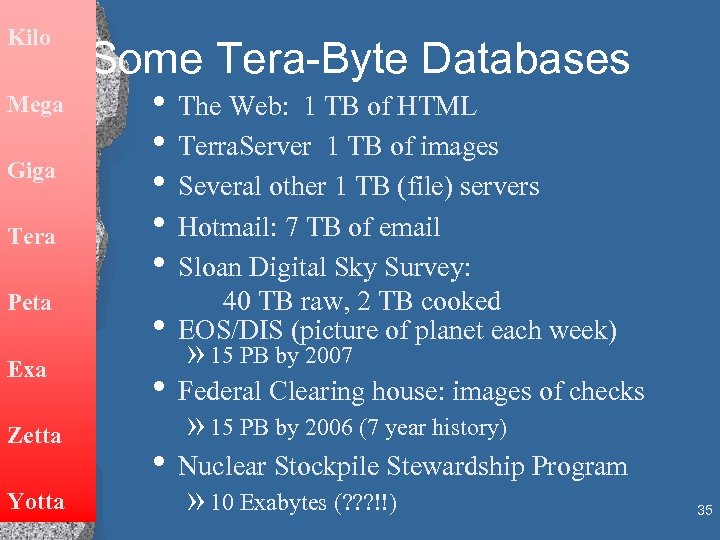
Kilo Mega Giga Tera Peta Exa Zetta Yotta Some Tera-Byte Databases • The Web: 1 TB of HTML • Terra. Server 1 TB of images • Several other 1 TB (file) servers • Hotmail: 7 TB of email • Sloan Digital Sky Survey: 40 TB raw, 2 TB cooked • EOS/DIS (picture of planet each week) » 15 PB by 2007 • Federal Clearing house: images of checks » 15 PB by 2006 (7 year history) • Nuclear Stockpile Stewardship Program » 10 Exabytes (? ? ? !!) 35

Kilo A letter A novel Info Capturerecord • You can Mega Giga A Movie • Tera Library of Congress (text) • Peta Lo. C (image) Video Audio Read or write: everything you see or hear or read. What would you do with it? How would you organize & analyze it? 8 PB per lifetime (10 GBph) 30 TB (10 KBps) 8 GB (words) Exa All Disks Zetta All Tapes See: http: //www. lesk. com/mlesk/ksg 97/ksg. html Yotta 36

Michael Lesk’s Points www. lesk. com/mlesk/ksg 97/ksg. html • Soon everything can be recorded and kept • Most data will never be seen by humans • Precious Resource: Human attention Auto-Summarization Auto-Search will be a key enabling technology. 37
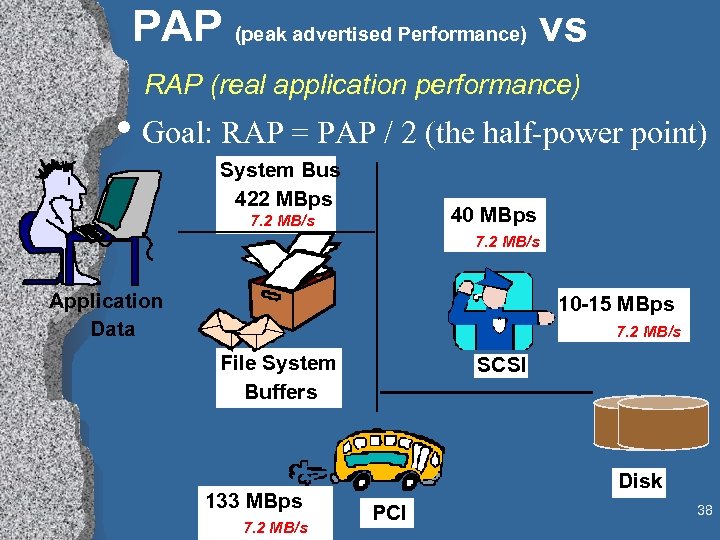
PAP (peak advertised Performance) vs RAP (real application performance) • Goal: RAP = PAP / 2 (the half-power point) System Bus 422 MBps 40 MBps 7. 2 MB/s Application Data 10 -15 MBps 7. 2 MB/s File System Buffers 133 MBps 7. 2 MB/s SCSI Disk PCI 38
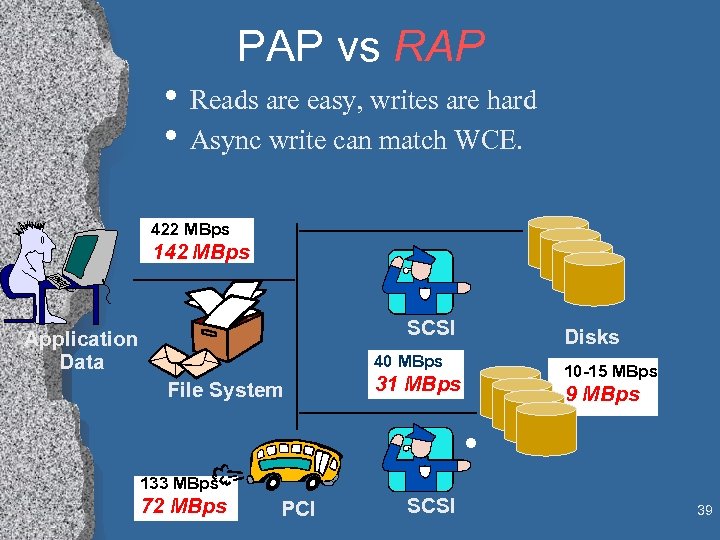
PAP vs RAP • Reads are easy, writes are hard • Async write can match WCE. 422 MBps 142 MBps SCSI Application Data Disks 40 MBps File System 10 -15 MBps 31 MBps 9 MBps • 133 MBps 72 MBps PCI SCSI 39
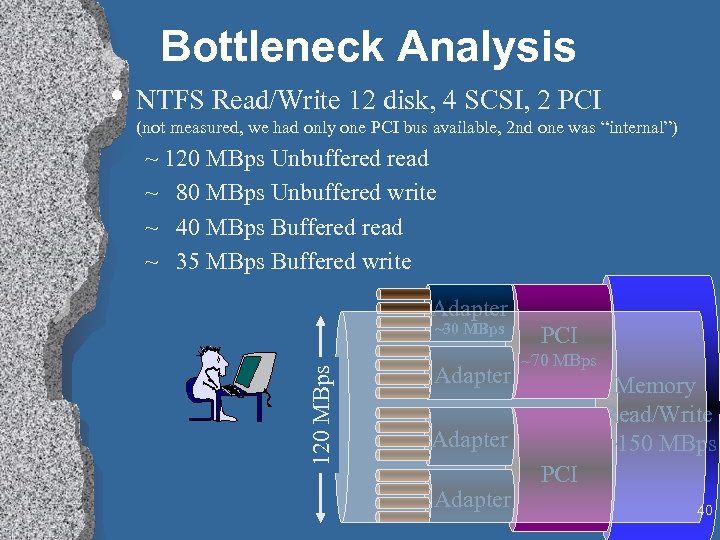
Bottleneck Analysis • NTFS Read/Write 12 disk, 4 SCSI, 2 PCI (not measured, we had only one PCI bus available, 2 nd one was “internal”) ~ 120 MBps Unbuffered read ~ 80 MBps Unbuffered write ~ 40 MBps Buffered read ~ 35 MBps Buffered write Adapter 120 MBps ~30 MBps Adapter PCI ~70 MBps Memory Read/Write ~150 MBps Adapter PCI 40

Year 2002 Disks • Big disk (10 $/GB) » 3” » 100 GB » 150 kaps (k accesses per second) » 20 MBps sequential • Small disk (20 $/GB) » 3” » 4 GB » 100 kaps » 10 MBps sequential • Both running Windows NT™ 7. 0? (see below for why) 41
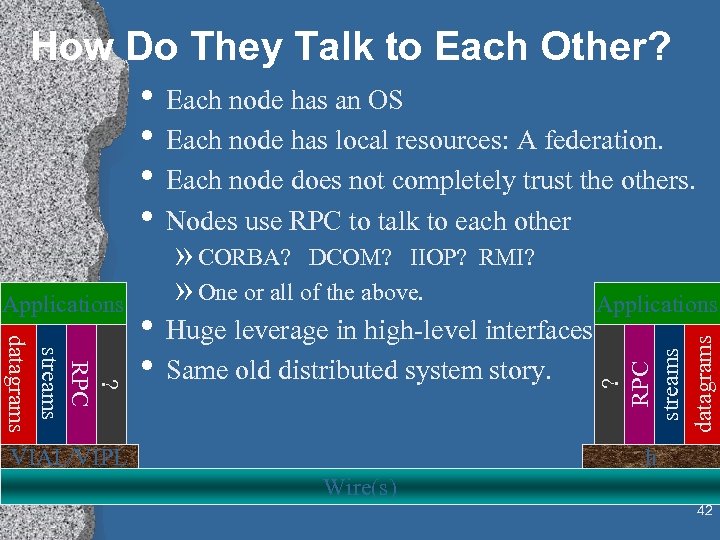
How Do They Talk to Each Other? • Each node has an OS • Each node has local resources: A federation. • Each node does not completely trust the others. • Nodes use RPC to talk to each other RMI? Applications ? RPC streams datagrams • Huge leverage in high-level interfaces. • Same old distributed system story. ? RPC streams datagrams Applications » CORBA? DCOM? IIOP? » One or all of the above. VIAL/VIPL h Wire(s) 42
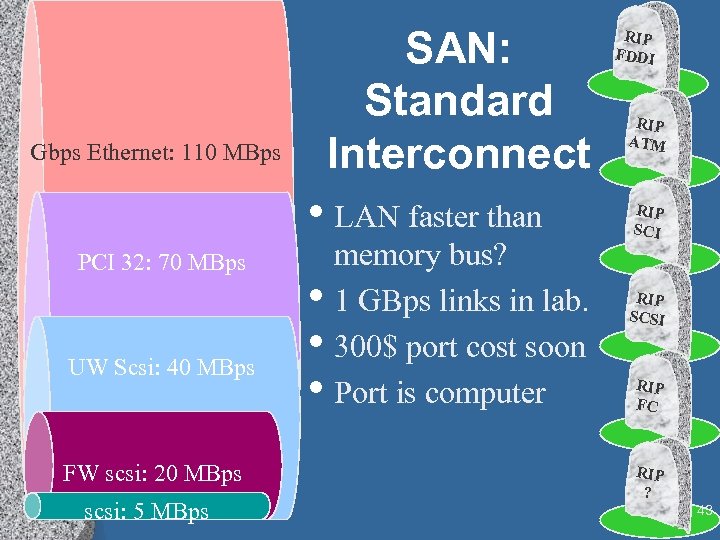
SAN: Standard Interconnect Gbps Ethernet: 110 MBps • LAN faster than PCI 32: 70 MBps UW Scsi: 40 MBps FW scsi: 20 MBps scsi: 5 MBps • • • memory bus? 1 GBps links in lab. 300$ port cost soon Port is computer RIP FDDI RIP ATM RIP SCI RIP SCSI RIP FC RIP ? 43
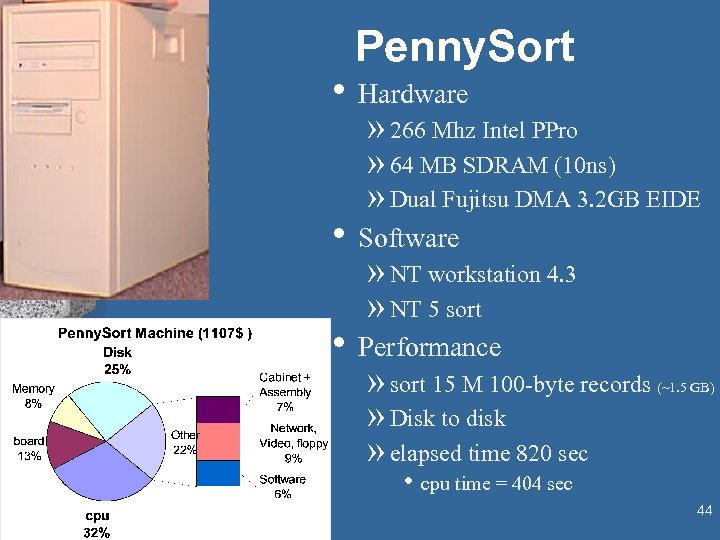
Penny. Sort • Hardware » 266 Mhz Intel PPro » 64 MB SDRAM (10 ns) » Dual Fujitsu DMA 3. 2 GB EIDE • Software » NT workstation 4. 3 » NT 5 sort • Performance » sort 15 M 100 -byte records » Disk to disk » elapsed time 820 sec (~1. 5 GB) • cpu time = 404 sec 44
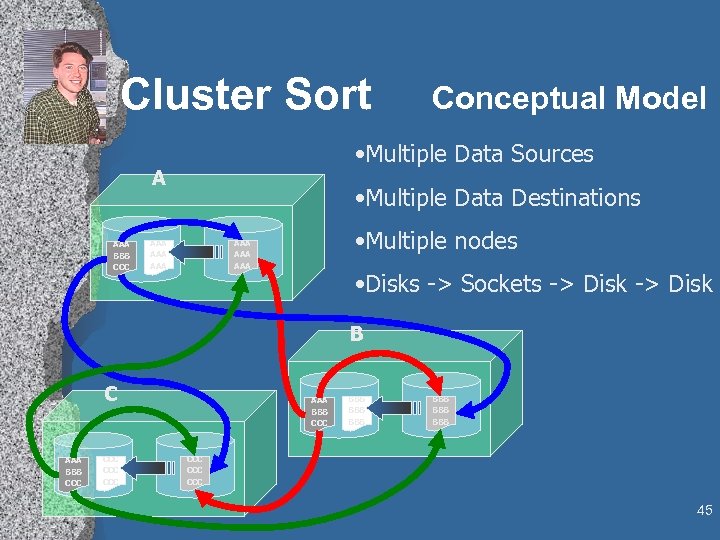
Cluster Sort • Multiple Data Sources A AAA BBB CCC Conceptual Model • Multiple Data Destinations AAA AAA • Multiple nodes AAA AAA • Disks -> Sockets -> Disk B C AAA BBB CCC CCC AAA BBB CCC BBB BBB BBB CCC CCC 45

Cluster Install & Execute • If this is to be used by others, it must be: • Easy to install • Easy to execute • Installations of distributed systems take time and can be tedious. (AM 2, Glu. Guard) • Parallel Remote execution is non-trivial. (GLUnix, LSF) How do we keep this “simple” and “built-in” to NTCluster. Sort ? 46
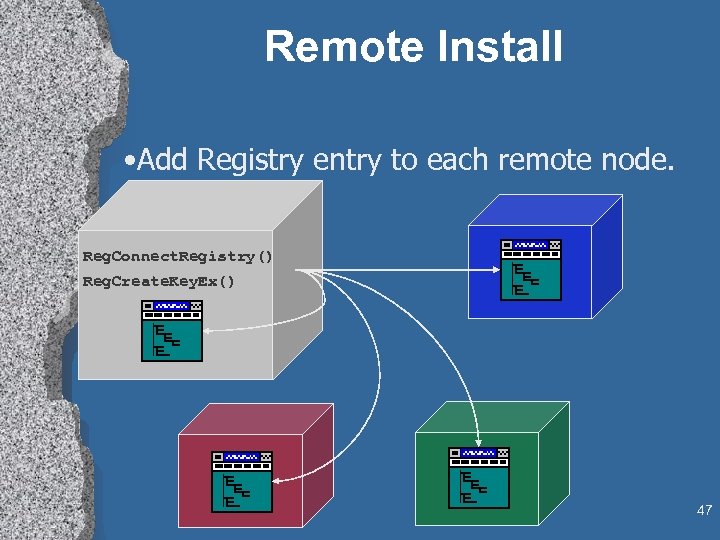
Remote Install • Add Registry entry to each remote node. Reg. Connect. Registry() Reg. Create. Key. Ex() 47
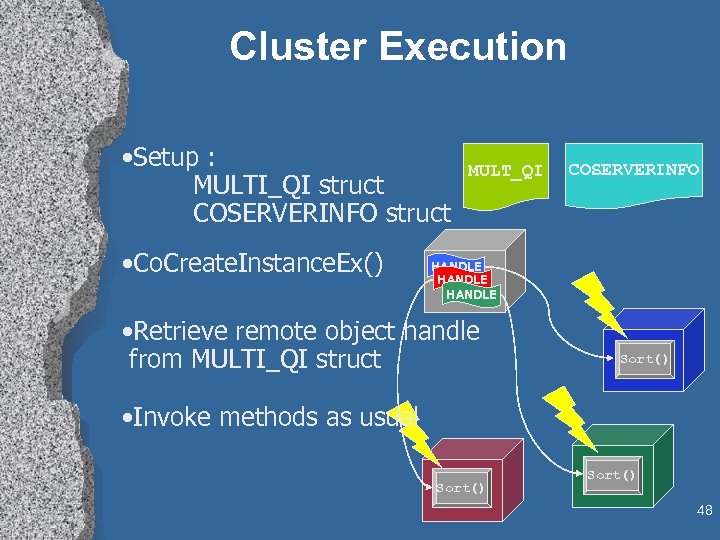
Cluster Execution • Setup : MULTI_QI struct COSERVERINFO struct • Co. Create. Instance. Ex() MULT_QI COSERVERINFO HANDLE • Retrieve remote object handle from MULTI_QI struct Sort() • Invoke methods as usual Sort() 48
467595fede319461317d93dae42b7ed4.ppt