ac0fcb8f9172fbc9353019c4facd565e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Scalable Software Hardware Architecture Platform for Embedded Systems SHAPES at DATE 2007 Pier Stanislao PAOLUCCI chief technical officer – ATMEL Roma & (part-time) permanent staff researcher – INFN Roma for the SHAPES Consortium

Project Motivation and Final Objective n SHAPES Acronym: Scalable Software Hardware Architecture Platform for Embedded Systems n Objective: Develop a prototype of Tiled Scalable HW & SW architecture for embedded applications characterized by inherent parallelism Experiment: “Small” Tiles (<10 MGate) connected by “short wires” weaving a packet switching on-chip and off-chip network The HW architecture should scale on next deep-submicron technologies n n Challenges: how to program a tiled architecture n Benchmarks ¨ multi-loudspeaker multi-source wave field synthesis, ¨ Multi-microphone voice extraction from noise on multi-microphone ¨ Ultrasound scanners ¨ Physical modelling of quantum chromo dynamics January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES 2 2
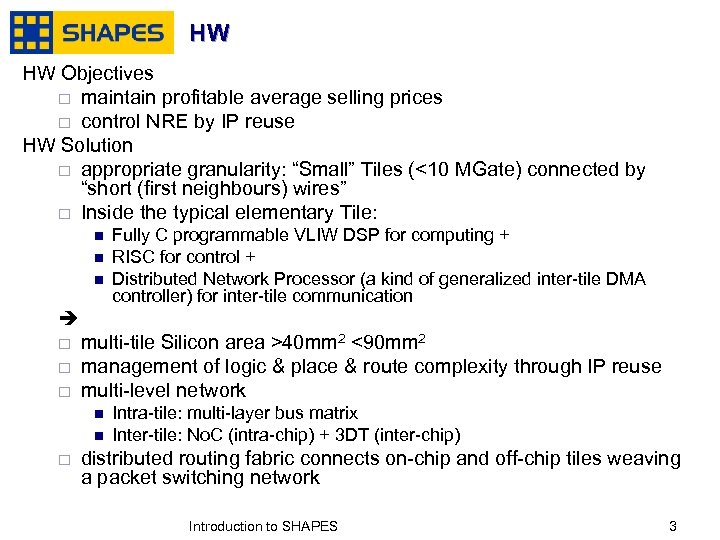
HW HW Objectives ¨ maintain profitable average selling prices ¨ control NRE by IP reuse HW Solution ¨ appropriate granularity: “Small” Tiles (<10 MGate) connected by “short (first neighbours) wires” ¨ Inside the typical elementary Tile: n n n Fully C programmable VLIW DSP for computing + RISC for control + Distributed Network Processor (a kind of generalized inter-tile DMA controller) for inter-tile communication ¨ ¨ ¨ multi-tile Silicon area >40 mm 2 <90 mm 2 management of logic & place & route complexity through IP reuse multi-level network n n ¨ Intra-tile: multi-layer bus matrix Inter-tile: No. C (intra-chip) + 3 DT (inter-chip) distributed routing fabric connects on-chip and off-chip tiles weaving a packet switching network January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES 3 3

SW ¨ Communication centric, real-time aware programming environment n Application description: model based with explicit annotation of real-time constraints n Provide automated optimized binding of processes to computing resources and binding of inter-process communication on communication resources + scheduling of processes and their communication n Provide automated generation of hardware dependent software support n Retargetable compilation managing intra-tile and intertile parallelism, bandwidth and latencies n Fast simulation January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES 4 4

Consortium Composition and Roles of the Partners System SW ETH Zurich - Distributed Operation Layer: manages application parallelism TIMA Lab and THALES - Hardware dependent Software Layer and RTOS TARGET Compiler Tech. - Retargetable Compilers RWTH Aachen Univ. – Fast Simulation of Heterogeneous Multi Proc. Systems System HW ATMEL Roma - Tile: Evolution of (Diopsis®: m. Agic. V VLIW DSPTM + RISC) + INFN DNPTM INFN Roma - DNPTM Distributed Network Processor + 3 D Toroidal Eng. : Evolution of APE Massive Parallel Processors STMicrolectronics + Univ. of Cagliari and Pisa – Network on Chip: Evolution of Spidergon. TM Packet Switching Network on Chip Parallel Application benchmarking Fraunhofer IDMT – multi-loudspeaker Audio Wave Field Synthesis ESAOTE, Med. Com, Fraunhofer IGD - Ultrasound scanner INFN - Physical Modelling ATMEL – multi-microphone arrays for voice-extraction January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES 5 5
Deep Sub-micron Architectures… n n n ~160 MGate available on a 100 mm 2 chip (45 nm CMOS, 2008) Increasing GATES/CHIP Design Complexity Management: ¨ embedded processors use a few million gates only, IP reuse possible and needed; WIRING threatens Moore’s law: ¨ Wiring delay increases on new CMOS silicon generations ¨ The full chip cannot be reached in a single clock cycle ¨ Classic monolithic processor architectures do not scale ¨ Locally Synchronous, Globally Asynchronous needed ¨ Communication Centric SW and HW Architecture needed … PROPOSED SOLUTION: … TILED ARCHITECTURE…BY SIMPLE GEOMETRIC DEMONSTRATION… IF CONSTANT LOGIC COMPLEXITY INSIDE EACH TILE… THEN (LENGTH OF INTRA-TILE WIRES SCALES DOWN AS THE TILE ITSELF… AND SHORT ~ FIRST NEIGHBOURS ONCHIP AND OFF-CHIP INTER-TILE WIRES) QUEST OF BEST TILE, ON-CHIP AND OFF-CHIP INTERCONNECT. BUT HOW TO PROGRAM? EXPLICIT PARALLEL PROGRAMMING PARADIGM, and CULTURE NEEDED POWER DISSIPATION density approaching prohibitive values if higher clock speed used; much better Oper/Watt at moderate clock + parallelism (the human brain parallel architecture performs an excellent job at 50 HZ!. . . room for improvement) January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES 6 6
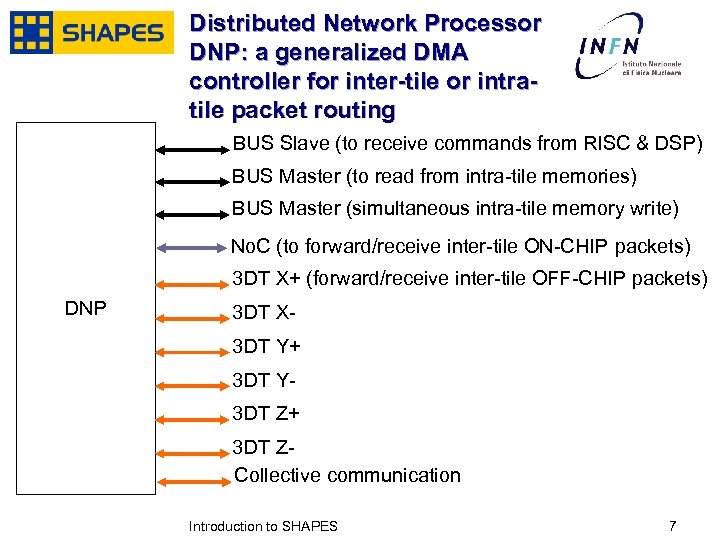
Distributed Network Processor DNP: a generalized DMA controller for inter-tile or intratile packet routing BUS Slave (to receive commands from RISC & DSP) BUS Master (to read from intra-tile memories) BUS Master (simultaneous intra-tile memory write) No. C (to forward/receive inter-tile ON-CHIP packets) 3 DT X+ (forward/receive inter-tile OFF-CHIP packets) DNP 3 DT X 3 DT Y+ 3 DT Y 3 DT Z+ 3 DT ZCollective communication January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES 7 7
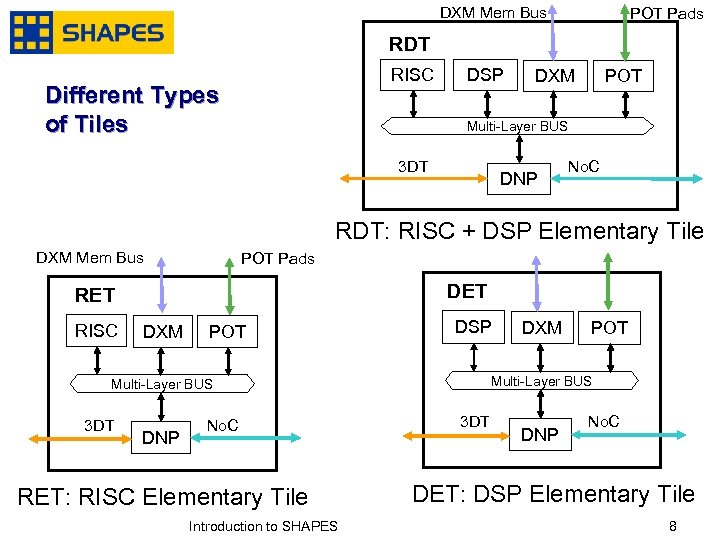
DXM Mem Bus POT Pads RDT RISC Different Types of Tiles DSP DXM POT Multi-Layer BUS 3 DT DNP No. C RDT: RISC + DSP Elementary Tile DXM Mem Bus POT Pads DET RISC DXM POT DSP DNP No. C RET: RISC Elementary Tile January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES POT Multi-Layer BUS 3 DT DXM 3 DT DNP No. C DET: DSP Elementary Tile 8 8
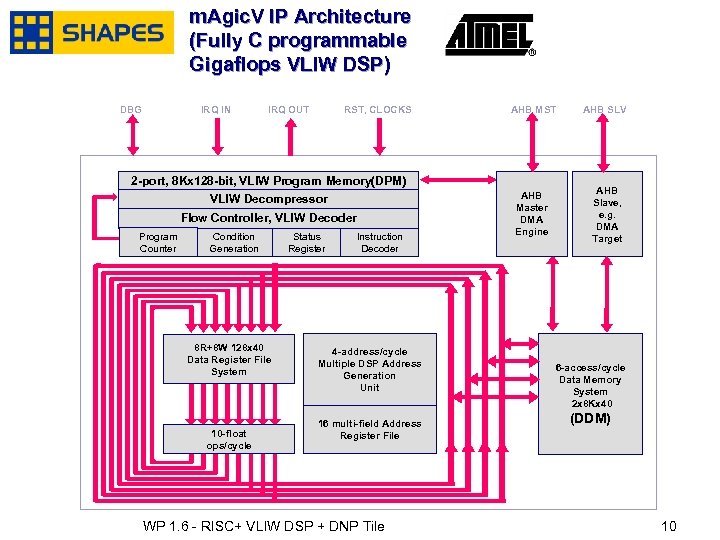
m. Agic. V IP Architecture (Fully C programmable Gigaflops VLIW DSP) DBG IRQ IN IRQ OUT RST, CLOCKS AHB MST AHB SLV AHB Master DMA Engine AHB Slave, e. g. DMA Target 2 -port, 8 Kx 128 -bit, VLIW Program Memory(DPM) VLIW Decompressor Flow Controller, VLIW Decoder Program Counter Condition Generation 8 R+8 W 128 x 40 Data Register File System 10 -float ops/cycle January, 2007 Status Register Instruction Decoder 4 -address/cycle Multiple DSP Address Generation Unit 16 multi-field Address Register File WP 1. 6 - RISC+ VLIW DSP + DNP Tile 6 -access/cycle Data Memory System 2 x 8 Kx 40 (DDM) 1010

Tile Complexity estimated through Synthesis & Place & Route trials n n n m. Agic. V DSP: ¨ 915 Kgates + 1 Mbit Prog Mem + 640 Kbit Data Mem ARM 926 & peripherals ¨ <2 equivalent Mgate (including 640 Kbit mem) Tile Complexity ¨ 4230 equivalent Kgate + DNP gate count n January, 2007 including on chip memories WP 1. 6 - RISC+ VLIW DSP + DNP Tile 1111
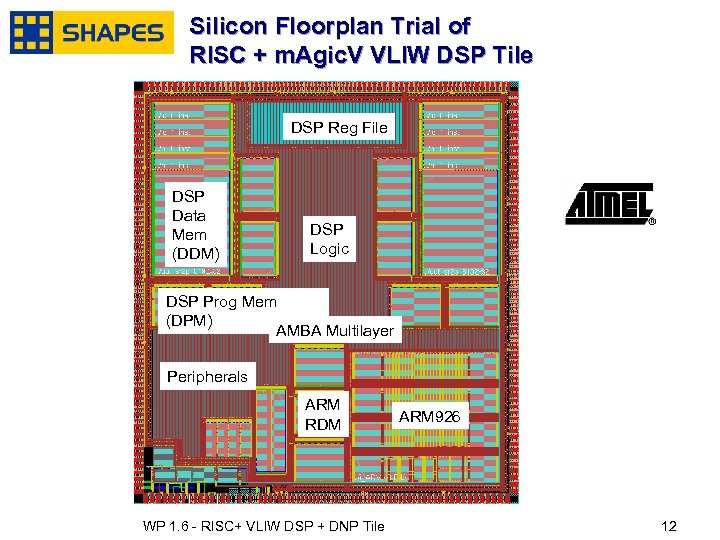
Silicon Floorplan Trial of RISC + m. Agic. V VLIW DSP Tile DSP Reg File DSP Data Mem (DDM) DSP Logic DSP Prog Mem (DPM) AMBA Multilayer Peripherals ARM RDM January, 2007 WP 1. 6 - RISC+ VLIW DSP + DNP Tile ARM 926 1212
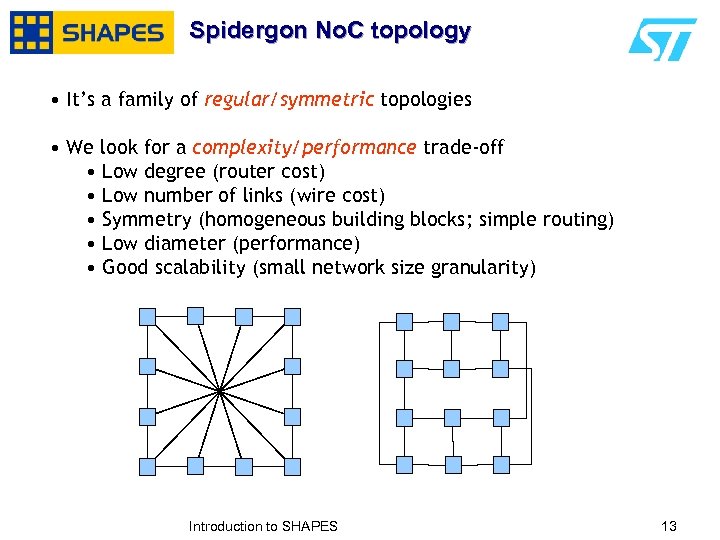
Spidergon No. C topology • It’s a family of regular/symmetric topologies • We look for a complexity/performance trade-off • Low degree (router cost) • Low number of links (wire cost) • Symmetry (homogeneous building blocks; simple routing) • Low diameter (performance) • Good scalability (small network size granularity) January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES 1313
Background: APENext (2005) 2048 processor system, VLIW processors designed by INFN, manufactured by ATMEL January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES 1616

SW challenges from Tiled Architectures n n n n Facilitate expression of parallelism: e. g. Network of Actors Express real time constraints in a formal manner, feature missing in classical languages. This is a key cultural point!!! Avoid destroying information about available algorithm parallelism Compilation chain must fully aware of key architectural parameters: bandwidth, computational power, pipeline and latencies Exploit memory locality – efficient management of Distributed Memories – get rid of classical caches Manage Long delays between distant tiles Reduce Hot Spots in communications Reduce Tiled RTOS overhead (time and memory footprint) Introduce Hardware dependent Software and Hardware Abstraction Layers Capture scalability in a library of characterized SW/HW components Support for (semi)-automation of iterative design over HW, SW, Appl Monitor quality and real-time constraints on real HW and Simulators Simulation speed of multi-tiled architectures January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES 1818
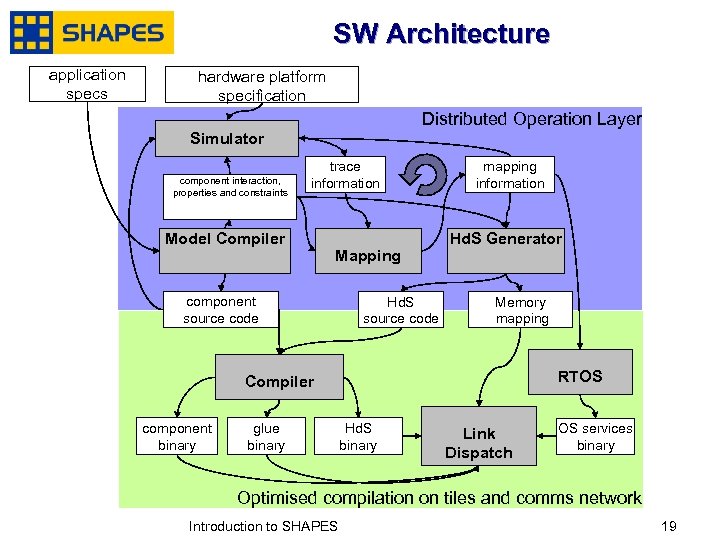
SW Architecture application specs hardware platform specification Distributed Operation Layer Simulator component interaction, properties and constraints trace information Model Compiler Mapping component source code Hd. S source code mapping information Hd. S Generator Memory mapping RTOS Compiler component binary glue binary Hd. S binary Link Dispatch OS services binary Optimised compilation on tiles and comms network January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES 1919
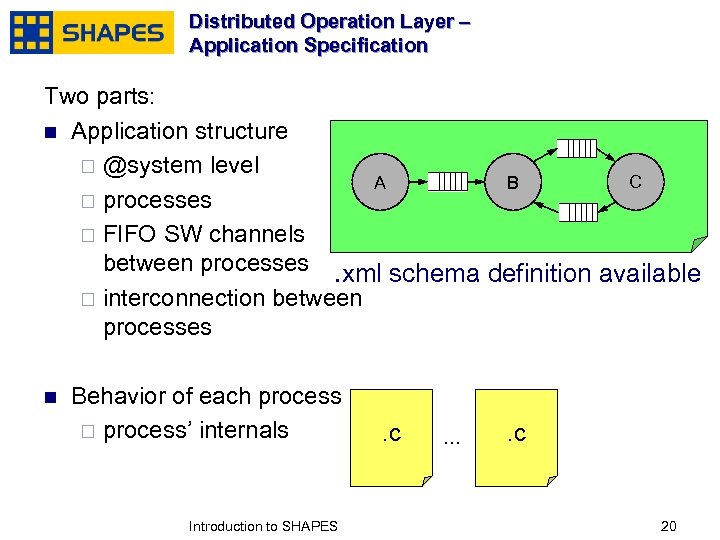
Distributed Operation Layer – Application Specification Two parts: n Application structure ¨ @system level C A B ¨ processes ¨ FIFO SW channels between processes. xml schema definition available ¨ interconnection between processes n Behavior of each process ¨ process’ internals January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES . c … . c 2020
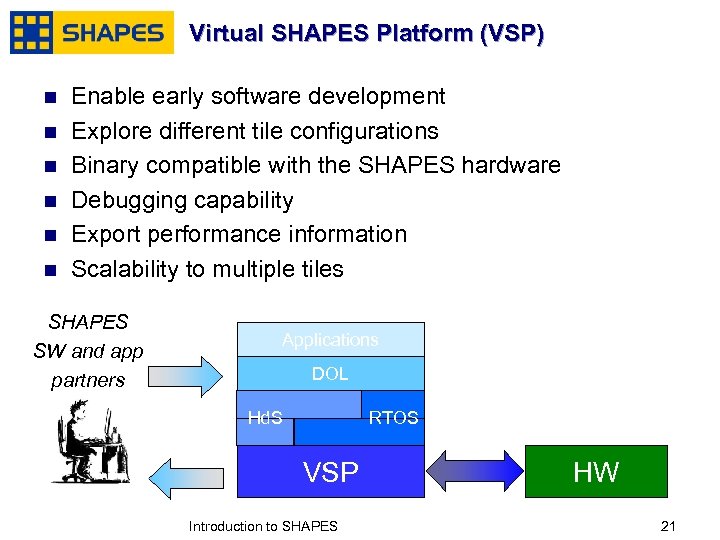
Virtual SHAPES Platform (VSP) n n n Enable early software development Explore different tile configurations Binary compatible with the SHAPES hardware Debugging capability Export performance information Scalability to multiple tiles SHAPES SW and app partners Applications DOL Hd. S RTOS VSP January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES HW 2121
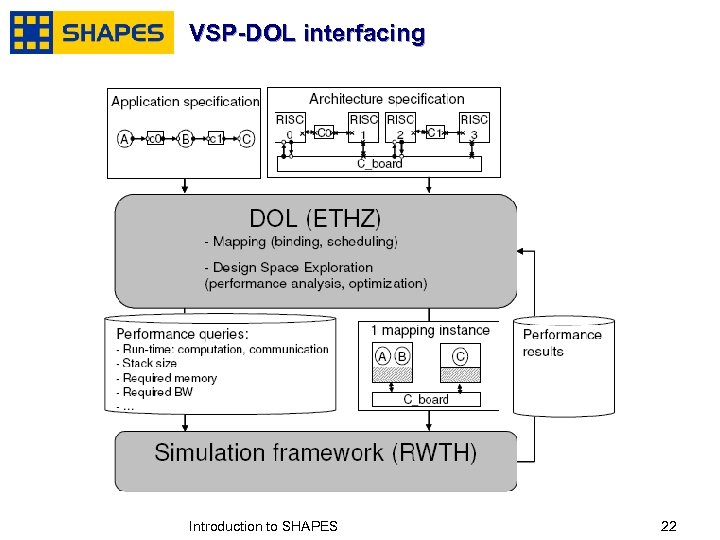
VSP-DOL interfacing January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES 2222
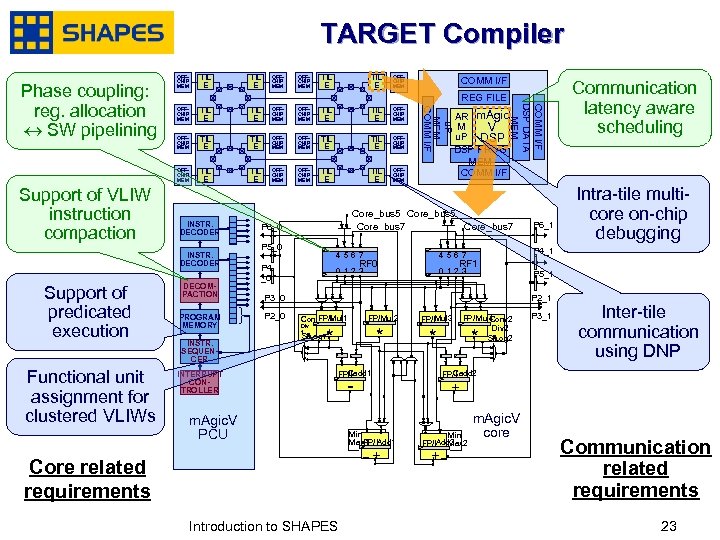
TARGET Compiler TIL E TIL E OFFCHIP MEM OFFCHIP MEM TIL E OFFCHIP MEM TIL E OFFCHIP MEM INSTR. DECODER Support of predicated execution Functional unit assignment for clustered VLIWs DECOMPACTION PROGRAM MEMORY INSTR. SEQUENCER INTERRUPT CONTROLLER Core_bus 5 Core_bus 7 P 6_0 P 5_0 4567 0123 P 4 _0 0123 P 5_1 P 2_1 Mul 2 FP/I Conv 1 Mul 1 Div 1 * * Sh /Log 1 Cadd 1 FP/I m. Agic. V PCU - FP/IMul 3 FP/IMul 4 Conv 2 Div 2 Sh /Log 2 * * P 3_1 Inter-tile communication using DNP Cadd 2 FP/I + Min FP/I Max 1 Add 1 -+ Introduction to SHAPES Intra-tile multicore on-chip debugging RF 1 P 3_0 P 2_0 P 6_1 Communication latency aware scheduling P 4_1 4567 RF 0 Core related requirements January, 2007 AR m. Agic M V u. P DSP PROG MEM COMM I/F DSP DATA MEM REG FILE OFFCHIP MEM Support of VLIW instruction compaction COMM I/F u. P MEM COMM I/F Phase coupling: reg. allocation SW pipelining OFFCHIP MEM Min FP/IAdd 2 Max 2 +- m. Agic. V core Communication related requirements 2323
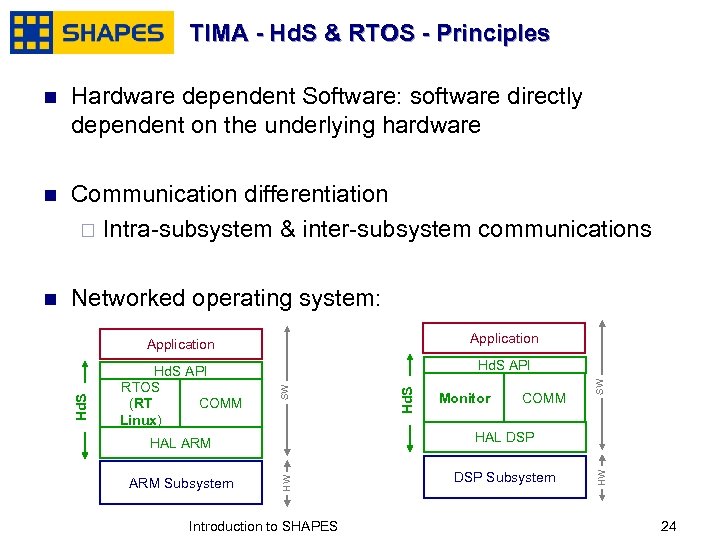
TIMA - Hd. S & RTOS - Principles n Hardware dependent Software: software directly dependent on the underlying hardware n Communication differentiation ¨ Intra-subsystem & inter-subsystem communications n Networked operating system: Hd. S API Monitor COMM DSP Subsystem Introduction to SHAPES HW ARM Subsystem January, 2007 HAL DSP HW HAL ARM SW Hd. S API RTOS (RT COMM Linux) Hd. S Application SW Hd. S Application 2424
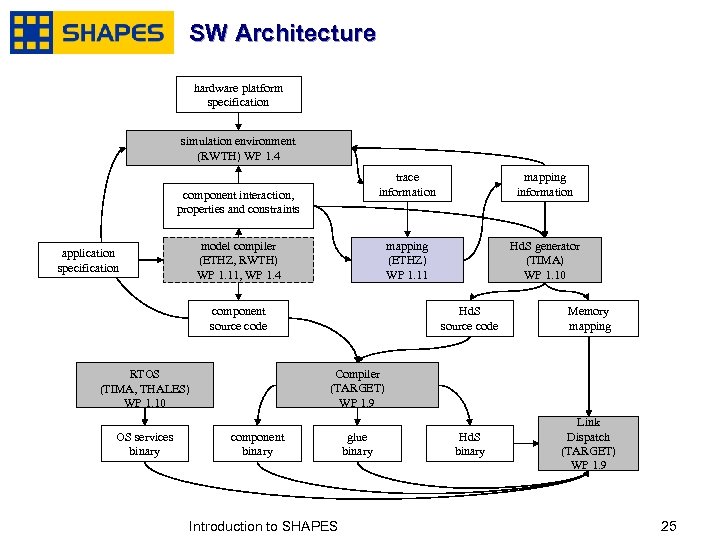
SW Architecture hardware platform specification simulation environment (RWTH) WP 1. 4 trace information mapping (ETHZ) WP 1. 11 component interaction, properties and constraints mapping information Hd. S generator (TIMA) WP 1. 10 model compiler (ETHZ, RWTH) WP 1. 11, WP 1. 4 application specification component source code January, 2007 Memory mapping Hd. S binary Link Dispatch (TARGET) WP 1. 9 Compiler (TARGET) WP 1. 9 RTOS (TIMA, THALES) WP 1. 10 OS services binary Hd. S source code component binary Introduction to SHAPES glue binary 2525
SHAPES SW Architecture: challenges n n n High-level exploration, mapping, and simulation: ¨ What is the degree of available parallelism? How can it be exposed to the mapping stage? What is suitable model-based specification formalism? What adaptations are necessary in order to expose the inherent parallelism? ¨ Define a common Profiling Trace Interface (PTI) over which information can be exchanged. Hardware-dependent software and operation system: ¨ To use the provided features of the Hd. S (i. e. platform abstraction) a generic interface API has to be defined. Compiler technology: ¨ Modeling low-latency communication interfaces in the C source code that is the input for the C compiler, for the computational tiles. ¨ Investigate how Hd. S can be modeled entirely in C source code, to be compiled by the C compiler for the computational tiles. January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES 2626
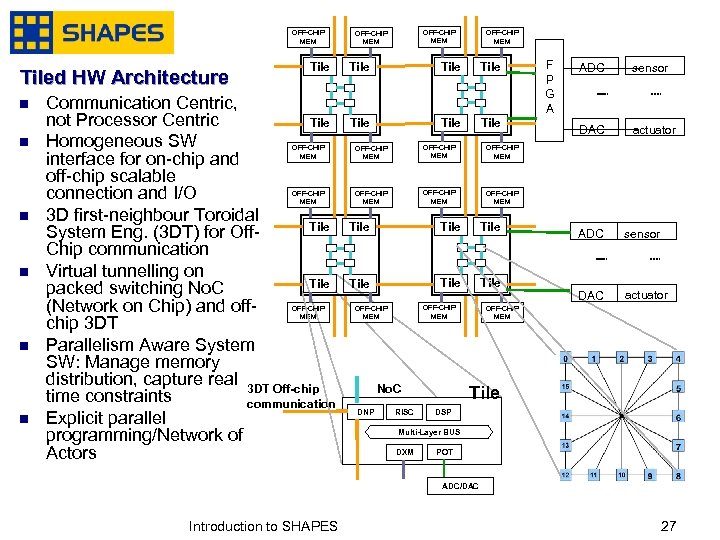
OFF-CHIP MEM Tiled HW Architecture n n Tile Communication Centric, not Processor Centric Tile Homogeneous SW interface for on-chip and off-chip scalable connection and I/O 3 D first-neighbour Toroidal Tile System Eng. (3 DT) for Off. Chip communication Virtual tunnelling on Tile packed switching No. C (Network on Chip) and offchip 3 DT Parallelism Aware System SW: Manage memory distribution, capture real 3 DT Off-chip time constraints communication Explicit parallel programming/Network of Actors OFF-CHIP MEM Tile Tile n OFF-CHIP MEM n sensor DAC actuator OFF-CHIP MEM n ADC OFF-CHIP MEM n OFF-CHIP MEM F P G A Tile Tile OFF-CHIP MEM No. C DNP RISC ADC sensor DAC actuator OFF-CHIP MEM Tile DSP Multi-Layer BUS DXM POT ADC/DAC January, 2007 Introduction to SHAPES 2727
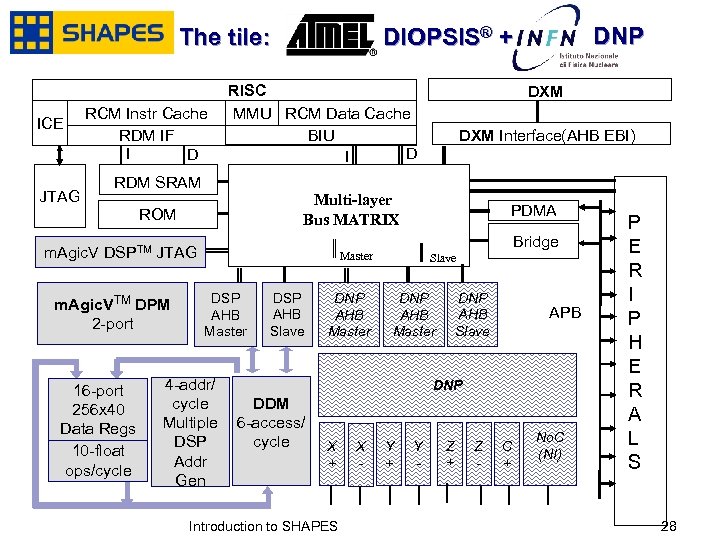
ICE RCM Instr Cache RDM IF I D JTAG RISC MMU RCM Data Cache BIU D I DXM Interface(AHB EBI) RDM SRAM Multi-layer Bus MATRIX ROM m. Agic. V DSPTM JTAG m. Agic. VTM DPM 2 -port 16 -port 256 x 40 Data Regs 10 -float ops/cycle January, 2007 DNP DIOPSIS® + The tile: PDMA Bridge Master DSP AHB Master 4 -addr/ cycle Multiple DSP Addr Gen DSP AHB Slave DNP AHB Master APB DNP DDM 6 -access/ cycle X + Introduction to SHAPES X - Y + Y - Z + Z - C + No. C (NI) P E R I P H E R A L S 2828
ac0fcb8f9172fbc9353019c4facd565e.ppt