2b3aad267a1f5480410259f0e01c4a0e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

SCADA - Communication Abhimanyu Gartia DY GENERAL Manager WESTERN REGIONAL LOAD DESPATCH CENTER MUMBAI

COMMUNICATION REQUIREMENTS FOR SCADA n Communication media should have: * High Reliability * High Availability * Rapid Response * Transparency * Economy * Flexibility * Maintainability
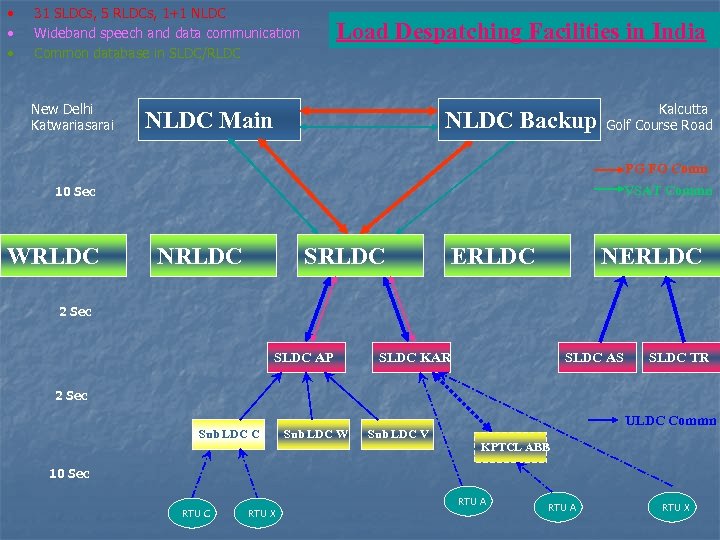
• • • 31 SLDCs, 5 RLDCs, 1+1 NLDC Wideband speech and data communication Common database in SLDC/RLDC New Delhi Katwariasarai Load Despatching Facilities in India NLDC Main NLDC Backup Kalcutta Golf Course Road PG FO Comn VSAT Commn 10 Sec WRLDC NRLDC SRLDC ERLDC NERLDC 2 Sec SLDC AP SLDC KAR SLDC AS SLDC TR 2 Sec Sub LDC C Sub LDC W Sub LDC V ULDC Commn KPTCL ABB 10 Sec RTU C RTU X RTU A RTU X
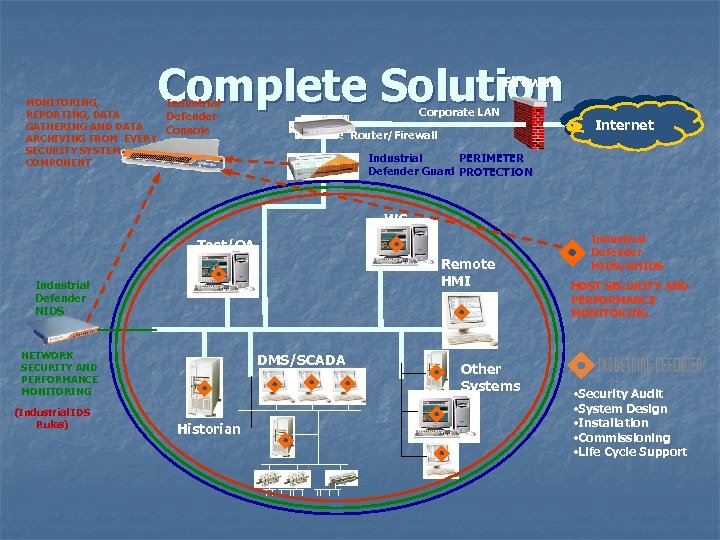
Complete Solution Firewall MONITORING, Industrial REPORTING, DATA Defender GATHERING AND DATA Console ARCHIVING FROM EVERY SECURITY SYSTEM COMPONENT Corporate LAN Router/Firewall Internet Industrial PERIMETER Defender Guard PROTECTION WS Test/QA Remote HMI Industrial Defender NIDS NETWORK SECURITY AND PERFORMANCE MONITORING (Industrial IDS Rules) DMS/SCADA Historian Other Systems Industrial Defender HIDS/RHIDS HOST SECURITY AND PERFORMANCE MONITORING • Security Audit • System Design • Installation • Commissioning • Life Cycle Support
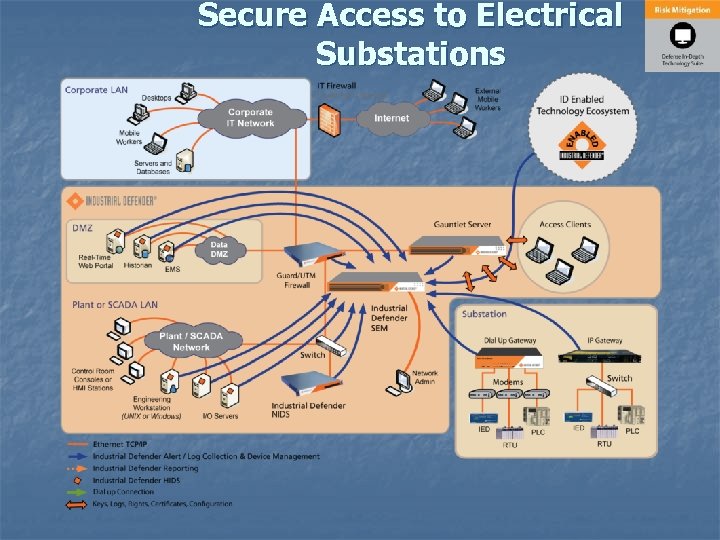
Secure Access to Electrical Substations

POSSIBLE COMMUNICATION n Data on different Protocol n n n IEC 60870 -5 -101 IEC 60870 -5 -104 IEC 61850 Modbus OPC server IT interface n n Scheduling Data wear housing Web interface PMU interface
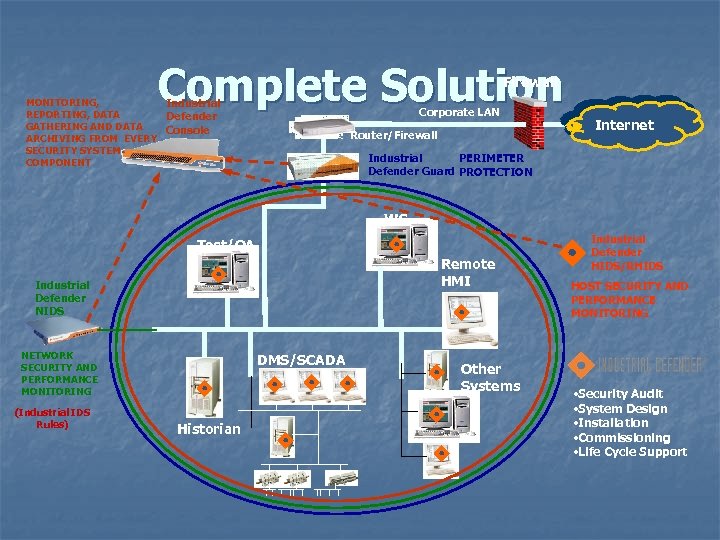
Complete Solution Firewall MONITORING, Industrial REPORTING, DATA Defender GATHERING AND DATA Console ARCHIVING FROM EVERY SECURITY SYSTEM COMPONENT Corporate LAN Router/Firewall Internet Industrial PERIMETER Defender Guard PROTECTION WS Test/QA Remote HMI Industrial Defender NIDS NETWORK SECURITY AND PERFORMANCE MONITORING (Industrial IDS Rules) DMS/SCADA Historian Other Systems Industrial Defender HIDS/RHIDS HOST SECURITY AND PERFORMANCE MONITORING • Security Audit • System Design • Installation • Commissioning • Life Cycle Support
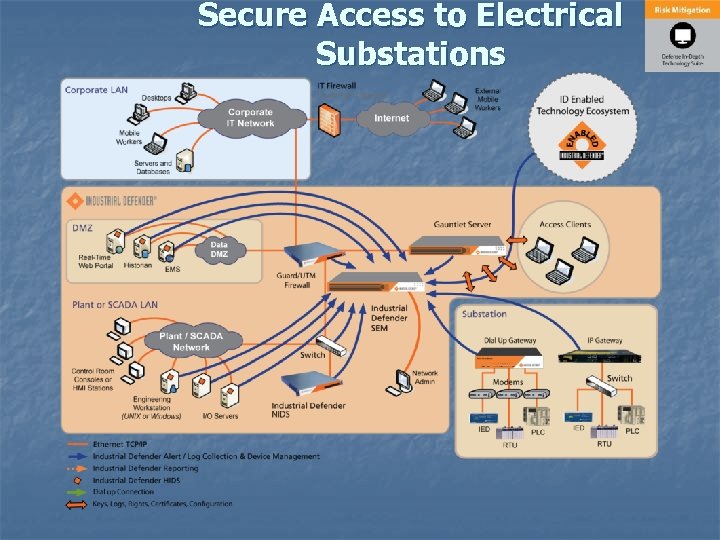
Secure Access to Electrical Substations

Scan Cycles n n n All the analog data are scanned every 10/12 seconds Status information are reported by exception All status information are scanned for integrity check every 10 minutes The SOE datas are time stamped at 1 ms resolution Time synchronisation is done every 10 minutes

Modes of Communication n n PLCC Leased Telephone circuits Microwave Communication Fibre Optics Communication Satellite Communication

PLCC n n n High voltage lines themselves are used as communication links. Carrier Frequency: 50 -300 KHz. 3 channels are used generally: Main-Channel -> speech channel – 300 Hz to 2000 Hz Telemetring- 2000 Hz to 3400 Hz Protection-Channel-I -> speech channel – 300 Hz to 2000 Hz Teleprotection- 2000 Hz to 3400 Hz Protection-Channel-II (Backup-Protection)-> speech channel – 300 Hz to 2000 Hz Teleprotection- 2000 Hz to 3400 Hz

Advantages: 1. 2. PLCC High reliability All channels are available for dedicated use by power-utility alone Disadvantages: 1. 2. 3. Cost of insulating communication equipment is high High noise level due to Corona High speed data-transfer not possible because of Bandwidth limitations.

Applications of PLCC n n Voice Communication Fascimile Transmission Tele-Protection Tele-Metering

Types of Couplings n 3 coupling schemes to couple voice, fax, tele-protection and tele-metering to the high-voltage transmission line: Phase-to-Ground Coupling Phase-to-Phase Coupling Inter-Line Coupling
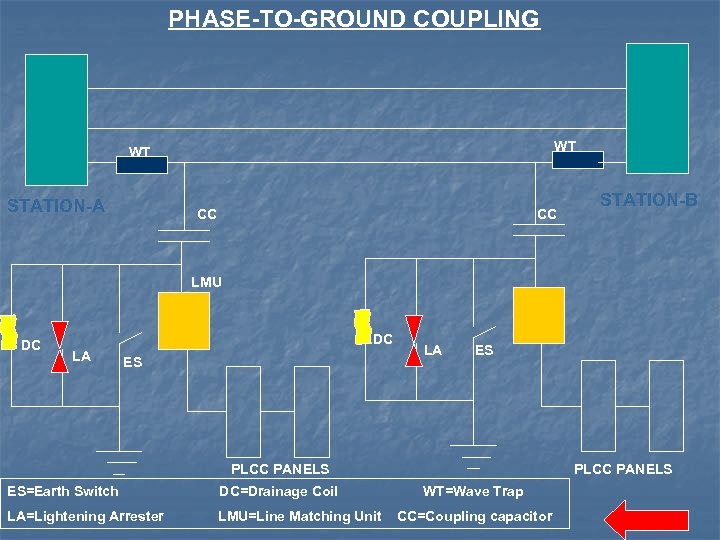
PHASE-TO-GROUND COUPLING WT WT STATION-A CC CC STATION-B LMU DC DC LA ES PLCC PANELS ES=Earth Switch DC=Drainage Coil LA=Lightening Arrester LMU=Line Matching Unit WT=Wave Trap CC=Coupling capacitor
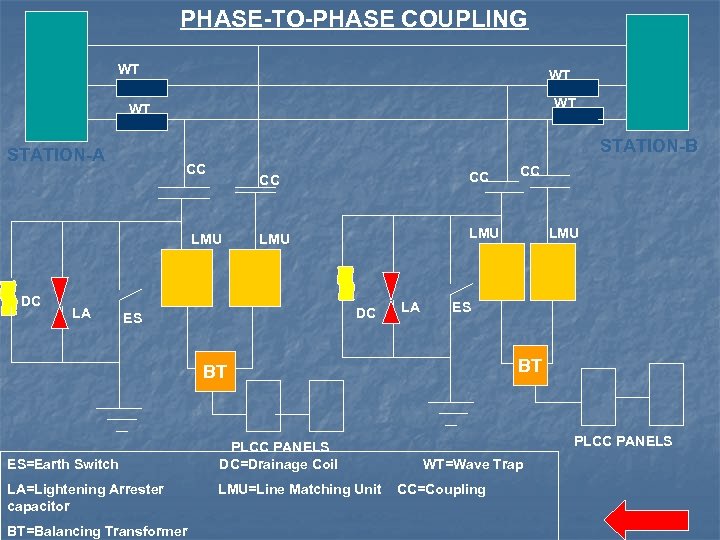
PHASE-TO-PHASE COUPLING WT WT STATION-B STATION-A CC CC LMU DC LA CC LMU DC ES LA LA=Lightening Arrester capacitor BT=Balancing Transformer PLCC PANELS DC=Drainage Coil LMU=Line Matching Unit LMU ES BT BT ES=Earth Switch CC PLCC PANELS WT=Wave Trap CC=Coupling
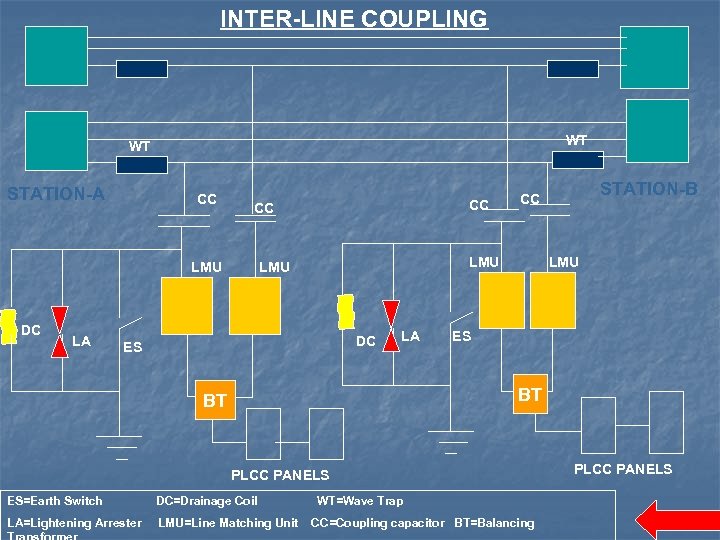
INTER-LINE COUPLING WT WT STATION-A CC LMU DC LA CC CC LMU DC ES LA STATION-B CC LMU ES BT BT PLCC PANELS ES=Earth Switch DC=Drainage Coil LA=Lightening Arrester LMU=Line Matching Unit WT=Wave Trap CC=Coupling capacitor BT=Balancing PLCC PANELS

Microwave Communication n n n Line-of-sight communication Requires repeaters at 50 -60 kms. Intervals Provides sufficient bandwidth to meet the needs of power utility Higher availability than PLCC, availablity not affected by maintenance or faults on the power lines Suffers from multipath-fading effect In India, WPC (wireless planning & co-ordination) wing has assigned 2. 3 -2. 5 GHz and 2. 8 -5 GHz bands to power sector usage.

Digital Microwave Systems

Leased Telephone Circuits • Simple solution, no need to develop own dedicated communication facility by power utility • Availability of this mode of communication at remotely located substations is the deciding factor
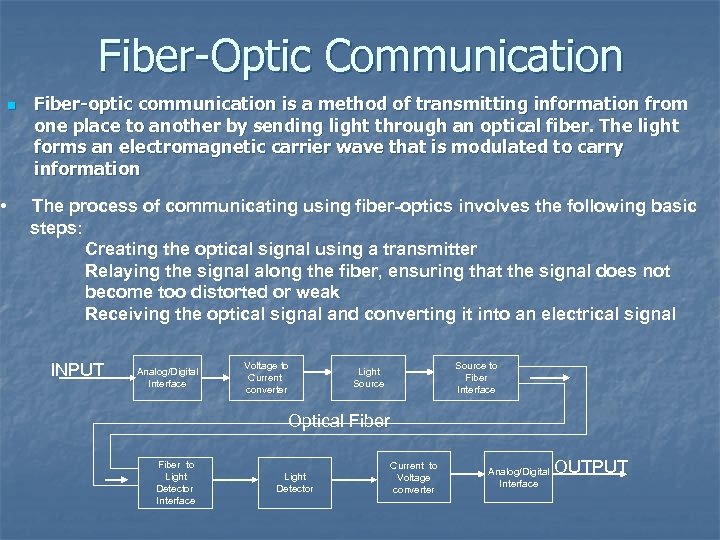
Fiber-Optic Communication n • Fiber-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information The process of communicating using fiber-optics involves the following basic steps: Creating the optical signal using a transmitter Relaying the signal along the fiber, ensuring that the signal does not become too distorted or weak Receiving the optical signal and converting it into an electrical signal INPUT Analog/Digital Interface Voltage to Current converter Source to Fiber Interface Light Source Optical Fiber to Light Detector Interface Light Detector Current to Voltage converter Analog/Digital Interface OUTPUT

Fiber Optic Communication n Advantages: The ability to carry much more information and deliver it with greater fidelity than either copper wire or coaxial cable. Fiber optic cable can support much higher data rates, and at greater distances n The fiber is totally immune to virtually all kinds of interference, including lightning, and will not conduct electricity. It can therefore come in direct contact with high voltage electrical equipment and power lines. POWERGRID uses overhead fiber optic communication: OPGW (optical ground wire cable) ADSS (all dielectric self supporting cable) WRAP AROUND

Fibre Optic Systems
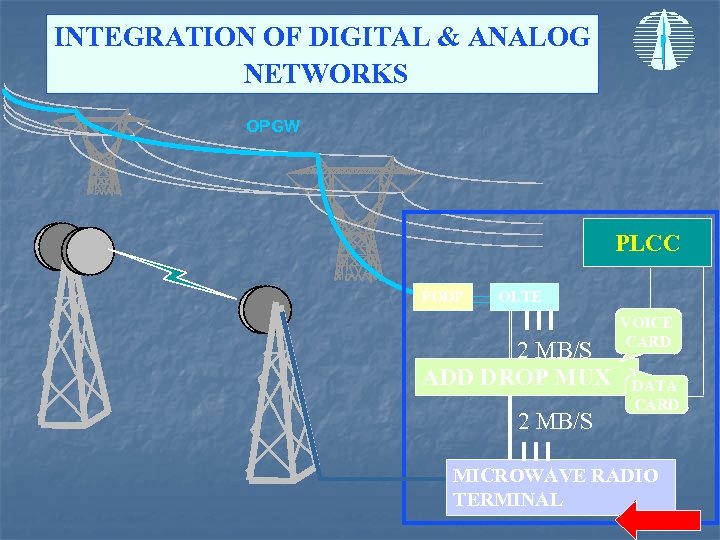
INTEGRATION OF DIGITAL & ANALOG NETWORKS OPGW PLCC FODP OLTE 2 MB/S ADD DROP MUX 2 MB/S VOICE CARD DATA CARD MICROWAVE RADIO TERMINAL

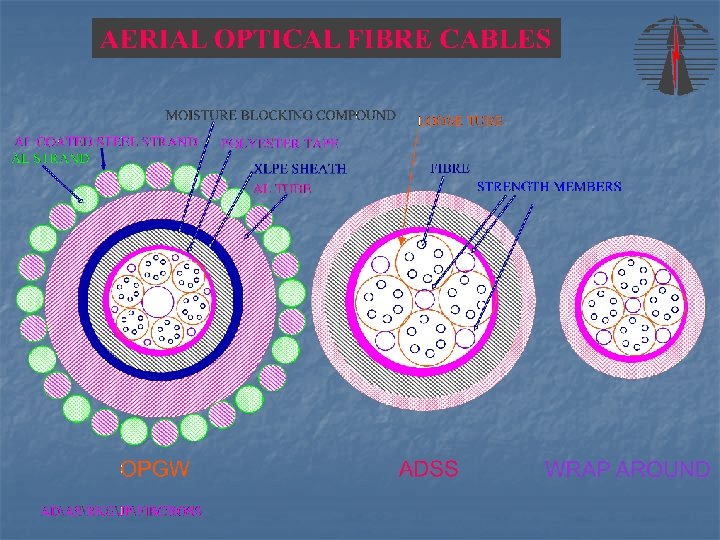
OPGW (optical ground wire) replaces shield wires • Provides lightning protection • Provides communication • Lightning short circuit damage • Installation requires long term outage • Expensive • Superior performance n

ADSS F. O n n n ADSS (all dielectric self supporting) which is mounted at various locations, typically 3 to 10 meters below the phase conductors. ADSS costs less than OPGW Higher fiber count than Wrap type. Can be installed on towers not designed for shield wires. Suitable for hot line installation

WRAP AROUND F. O n n n Wrap-type which is wound around shield wires and, in some instances, around energized conductors Hot-line installation is difficult Cost more than ADSS, but less than OPGW Need a shield wire No operation problem is observed
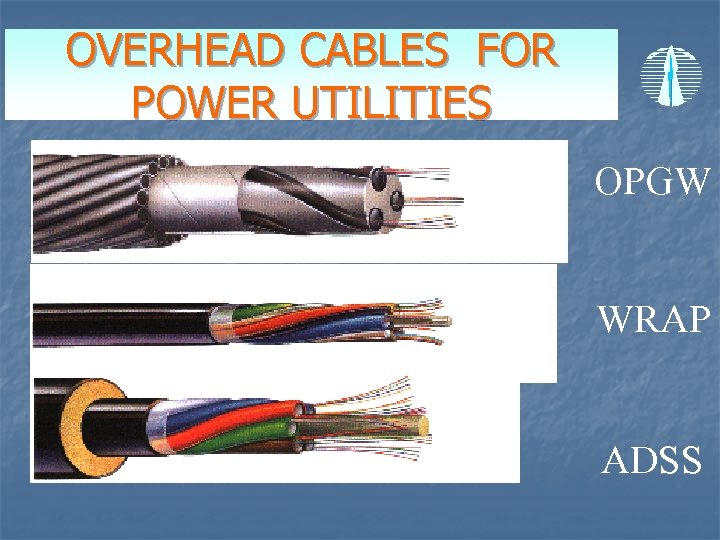
OVERHEAD CABLES FOR POWER UTILITIES OPGW WRAP ADSS
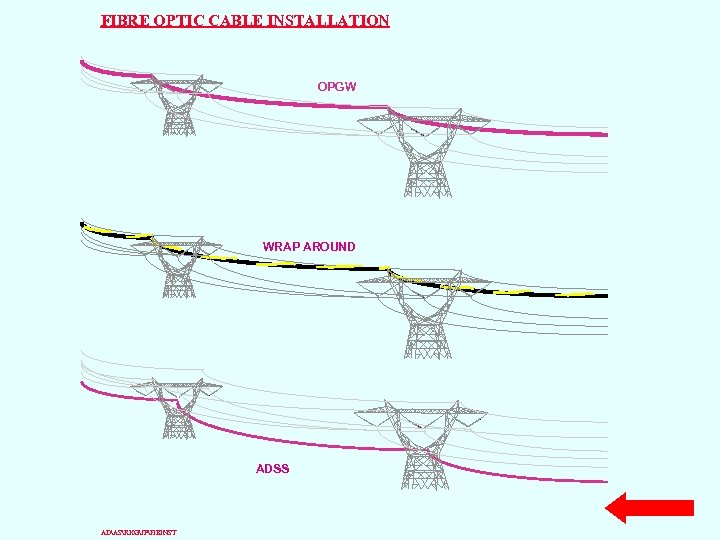
FIBRE OPTIC CABLE INSTALLATION OPGW WRAP AROUND ADSS ADASRKGJPFIBINST
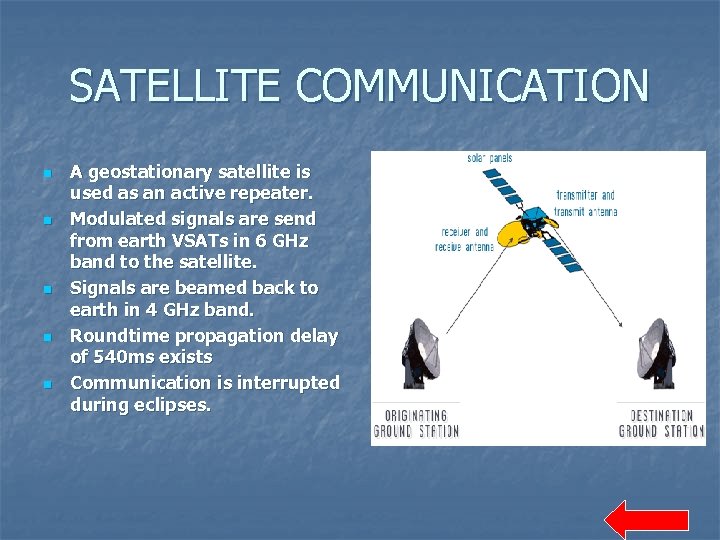
SATELLITE COMMUNICATION n n n A geostationary satellite is used as an active repeater. Modulated signals are send from earth VSATs in 6 GHz band to the satellite. Signals are beamed back to earth in 4 GHz band. Roundtime propagation delay of 540 ms exists Communication is interrupted during eclipses.
Lingasugur
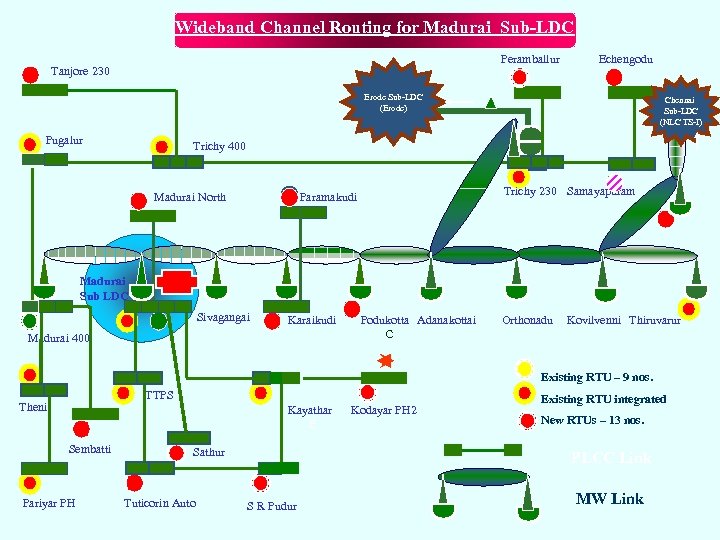
Wideband Channel Routing for Madurai Sub-LDC Peramballur Tanjore 230 Echengodu Erode Sub-LDC (Erode) Pugalur Chennai Sub-LDC (NLC TS-I) Trichy 400 Madurai North Trichy 230 Samayapuram Paramakudi Madurai Sub LDC Sivagangai Karaikudi Madurai 400 Podukotta Adanakottai C Orthonadu Kovilvenni Thiruvarur Existing RTU – 9 nos. TTPS Theni Kayathar E Sembatti Pariyar PH Sathur Tuticorin Auto Kodayar PH 2 Existing RTU integrated New RTUs – 13 nos. PLCC Link S R Pudur MW Link
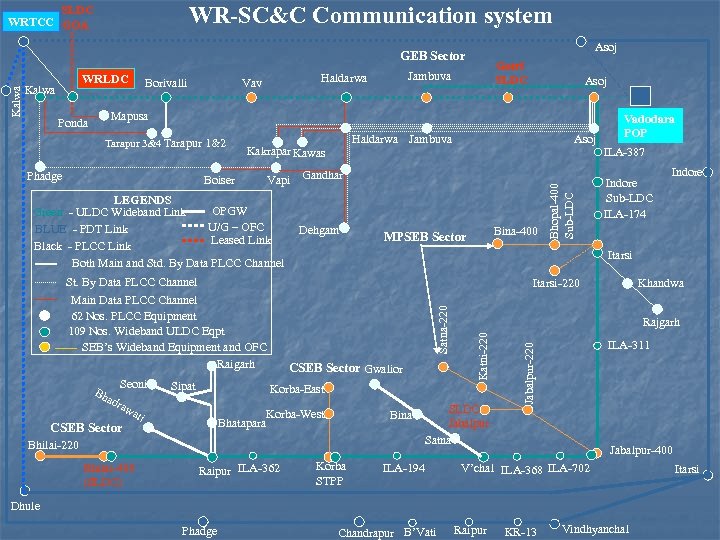
WR-SC&C Communication system SLDC WRTCC GOA Asoj WRLDC Vav Asoj Mapusa Tarapur 3&4 Tarapur 1&2 Phadge Boiser St. By Data PLCC Channel Main Data PLCC Channel 62 Nos. PLCC Equipment 109 Nos. Wideband ULDC Eqpt SEB’s Wideband Equipment and OFC Raigarh Seoni Sipat Dehgam ati Vadodara POP ILA-387 Indore Sub-LDC ILA-174 Satna-220 Itarsi-220 CSEB Sector Gwalior Korba-West Bhatapara Raipur ILA-362 Bina Korba STPP Rajgarh SLDCJabalpur Satna ILA-194 Khandwa ILA-311 Jabalpur-400 V’chal ILA-368 ILA-702 Dhule Phadge Indore Itarsi Bhilai-220 Bhilai-400 (SLDC) Bina-400 MPSEB Sector Korba-East raw CSEB Sector Asoj Vapi Gandhar LEGENDS OPGW Green - ULDC Wideband Link U/G – OFC BLUE - PDT Link Leased Link Black - PLCC Link Both Main and Std. By Data PLCC Channel Bh ad Haldarwa Jambuva Kakrapar Kawas Bhopal-400 Sub-LDC Ponda Borivalli Jabalpur-220 Kalwa Gotri SLDC Jambuva Haldarwa Katni-220 Kalwa GEB Sector Chandrapur B’Vati Raipur KR-13 Vindhyanchal Itarsi
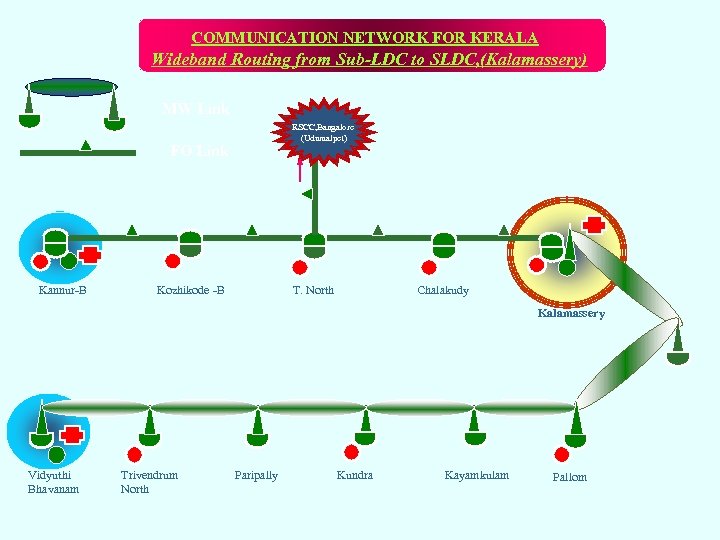
COMMUNICATION NETWORK FOR KERALA Wideband Routing from Sub-LDC to SLDC, (Kalamassery) MW Link RSCC, Bangalore (Udumalpet) FO Link Kannur-B Kozhikode -B T. North Chalakudy Kalamassery Vidyuthi Bhavanam Trivendrum North Paripally Kundra Kayamkulam Pallom
2b3aad267a1f5480410259f0e01c4a0e.ppt