212ead71a686e207647c0e5e099a4fd3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 Saving, Investment and the Financial System www. Assignment. Point. com
Saving, Investment and the Financial System www. Assignment. Point. com
 Overview u Financial Markets and Intermediaries u Saving and Investment u Market for Loan-able Funds u Government policies that affect the economy’s savings and investment www. Assignment. Point. com
Overview u Financial Markets and Intermediaries u Saving and Investment u Market for Loan-able Funds u Government policies that affect the economy’s savings and investment www. Assignment. Point. com
 Financial Markets. . . u. . . are the markets in the economy that help to match one person’s saving with another person’s investment. u. . . move the economy’s scarce resources from savers to borrowers. u. . . are opportunities for savers to channel unspent funds into the hands of borrowers. www. Assignment. Point. com
Financial Markets. . . u. . . are the markets in the economy that help to match one person’s saving with another person’s investment. u. . . move the economy’s scarce resources from savers to borrowers. u. . . are opportunities for savers to channel unspent funds into the hands of borrowers. www. Assignment. Point. com
 Financial Institutions in the Economy u Institutions that allow savers and borrowers to interact are called financial intermediaries. u Types of Financial Intermediaries: ◦ Banks ◦ Stock Market ◦ Other - Bond Market - Mutual Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
Financial Institutions in the Economy u Institutions that allow savers and borrowers to interact are called financial intermediaries. u Types of Financial Intermediaries: ◦ Banks ◦ Stock Market ◦ Other - Bond Market - Mutual Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
 Financial Intermediaries: Banks u Banks take in deposits from people who want to save and make loans to people who want to borrow. u Banks pay depositors interest and charge borrowers higher interest on their loans. u Banks help create a medium of exchange, by allowing people to write cheques against their deposits. www. Assignment. Point. com
Financial Intermediaries: Banks u Banks take in deposits from people who want to save and make loans to people who want to borrow. u Banks pay depositors interest and charge borrowers higher interest on their loans. u Banks help create a medium of exchange, by allowing people to write cheques against their deposits. www. Assignment. Point. com
 Financial Intermediaries: The Bond Market u. A bond is a certificate of indebtedness that specifies obligations of the borrower to the holder of the bond. u. Characteristics of a bond: ◦ Term: the length of time until maturity. ◦ Credit Risk: the probability that the borrower will fail to pay some of the interest or principle. ◦ Tax Treatment: The interest on most bonds is taxable income. www. Assignment. Point. com
Financial Intermediaries: The Bond Market u. A bond is a certificate of indebtedness that specifies obligations of the borrower to the holder of the bond. u. Characteristics of a bond: ◦ Term: the length of time until maturity. ◦ Credit Risk: the probability that the borrower will fail to pay some of the interest or principle. ◦ Tax Treatment: The interest on most bonds is taxable income. www. Assignment. Point. com
 Financial Intermediaries: The Stock Market u. Stock represents ownership in a firm, thus the owner has claim to the profits that the firm makes. u. Sale of stock infers “equity finance” but offers both higher risk and potentially higher return. u. Markets in which stock is traded: ◦ Toronto Stock Exchange ◦ New York Stock Exchange www. Assignment. Point. com
Financial Intermediaries: The Stock Market u. Stock represents ownership in a firm, thus the owner has claim to the profits that the firm makes. u. Sale of stock infers “equity finance” but offers both higher risk and potentially higher return. u. Markets in which stock is traded: ◦ Toronto Stock Exchange ◦ New York Stock Exchange www. Assignment. Point. com
 Financial Intermediaries: Mutual Funds u. A Mutual Fund is an institution that sells shares to the public and uses the proceeds to buy a selection, or portfolio, of various types of stocks, bonds, or both. u Allows people with small amounts of money to diversify. www. Assignment. Point. com
Financial Intermediaries: Mutual Funds u. A Mutual Fund is an institution that sells shares to the public and uses the proceeds to buy a selection, or portfolio, of various types of stocks, bonds, or both. u Allows people with small amounts of money to diversify. www. Assignment. Point. com
 Financial Intermediaries: Other u Other ◦ ◦ ◦ financial intermediaries include: Savings and Loans Associations Credit Unions Pension Funds Insurance Companies Loan Sharks www. Assignment. Point. com
Financial Intermediaries: Other u Other ◦ ◦ ◦ financial intermediaries include: Savings and Loans Associations Credit Unions Pension Funds Insurance Companies Loan Sharks www. Assignment. Point. com
 Quick Quiz! u What is a stock? u What is a bond? u How are they different? u How are they similar?
Quick Quiz! u What is a stock? u What is a bond? u How are they different? u How are they similar?
 Overview ü Financial Markets and Intermediaries u Saving and Investment u Market for Loanable Funds u Government policies that affect the economy’s savings and investment. www. Assignment. Point. com
Overview ü Financial Markets and Intermediaries u Saving and Investment u Market for Loanable Funds u Government policies that affect the economy’s savings and investment. www. Assignment. Point. com
 Saving and Investment in the National Income Accounts u. Recall: GDP is both total income in an economy and the total expenditure on the economy’s output of goods and services: u. Assume u. National Y = C + I + G + NX a closed economy: Y=C+I+G Saving or Saving is equal to: Y-C-G=I=S www. Assignment. Point. com
Saving and Investment in the National Income Accounts u. Recall: GDP is both total income in an economy and the total expenditure on the economy’s output of goods and services: u. Assume u. National Y = C + I + G + NX a closed economy: Y=C+I+G Saving or Saving is equal to: Y-C-G=I=S www. Assignment. Point. com
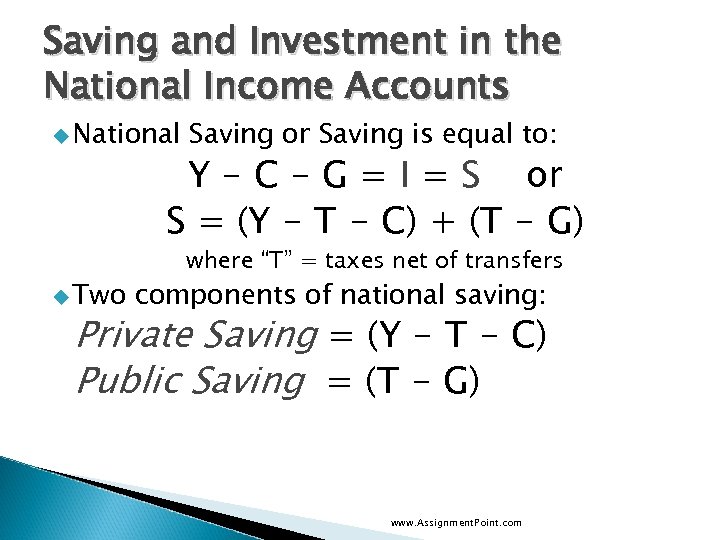 Saving and Investment in the National Income Accounts u National Saving or Saving is equal to: Y - C - G = I = S or S = (Y - T - C) + (T - G) u Two where “T” = taxes net of transfers components of national saving: Private Saving = (Y - T - C) Public Saving = (T - G) www. Assignment. Point. com
Saving and Investment in the National Income Accounts u National Saving or Saving is equal to: Y - C - G = I = S or S = (Y - T - C) + (T - G) u Two where “T” = taxes net of transfers components of national saving: Private Saving = (Y - T - C) Public Saving = (T - G) www. Assignment. Point. com
 Saving and Investment u Private Saving is the amount of income that households have left after paying their taxes and paying for their consumption. u Public Saving is the amount of tax revenue that the government has left after paying for its spending. u For the economy as a whole, saving must be equal to investment. www. Assignment. Point. com
Saving and Investment u Private Saving is the amount of income that households have left after paying their taxes and paying for their consumption. u Public Saving is the amount of tax revenue that the government has left after paying for its spending. u For the economy as a whole, saving must be equal to investment. www. Assignment. Point. com
 Quick Quiz! u Define private saving, public saving, national saving, and investment. u How are they related?
Quick Quiz! u Define private saving, public saving, national saving, and investment. u How are they related?
 Overview ü Financial Markets and Intermediaries ü Saving and Investment u Market for Loanable Funds u Government policies that affect the economy’s savings and investment. www. Assignment. Point. com
Overview ü Financial Markets and Intermediaries ü Saving and Investment u Market for Loanable Funds u Government policies that affect the economy’s savings and investment. www. Assignment. Point. com
 The Market For Loanable Funds u Financial markets co-ordinate the economy’s saving and investment in u The Loanable Funds Market Supply of Loanable Funds comes from people who have extra income that they want to loan out. u The Demand for Loanable Funds comes from those who wish to borrow to make investments. www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds u Financial markets co-ordinate the economy’s saving and investment in u The Loanable Funds Market Supply of Loanable Funds comes from people who have extra income that they want to loan out. u The Demand for Loanable Funds comes from those who wish to borrow to make investments. www. Assignment. Point. com
 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply Demand Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply Demand Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
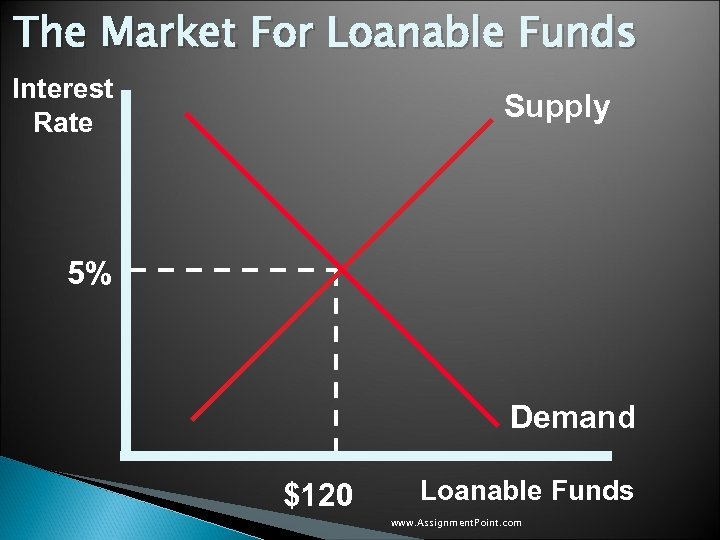 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
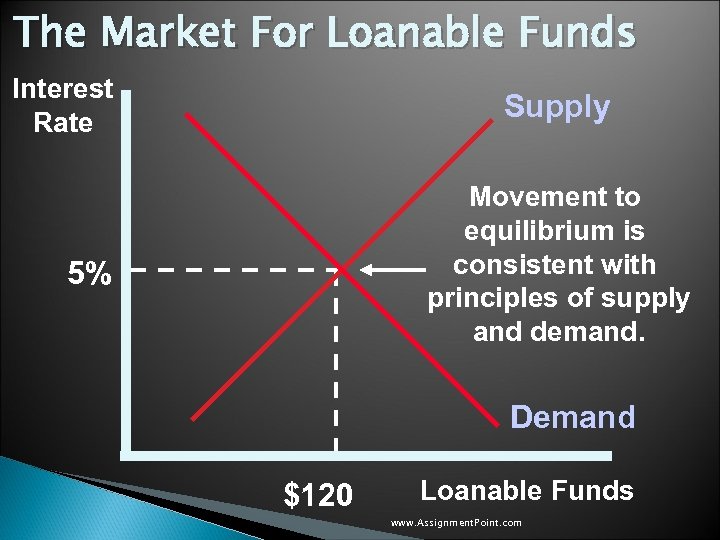 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply Movement to equilibrium is consistent with principles of supply and demand. 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply Movement to equilibrium is consistent with principles of supply and demand. 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
 www. Assignment. Point. com
www. Assignment. Point. com
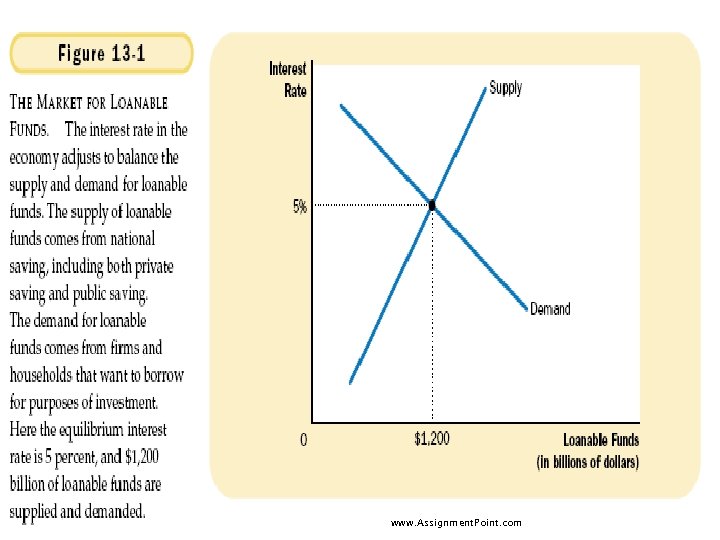
 The Market For Loanable Funds u The supply and demand for loanable funds depends on the real interest rate. Movement to equilibrium is the process of determining the real interest rate in the economy. u Saving represents the supply of loanable funds, while investment represents demand. www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds u The supply and demand for loanable funds depends on the real interest rate. Movement to equilibrium is the process of determining the real interest rate in the economy. u Saving represents the supply of loanable funds, while investment represents demand. www. Assignment. Point. com
 economists distinguish between the real interest rate and the nominal interest rate. The nominal interest rate is the interest rate as usually reported the monetary return to saving and cost of borrowing. The real interest rate is the nominal interest rate corrected for inflation www. Assignment. Point. com
economists distinguish between the real interest rate and the nominal interest rate. The nominal interest rate is the interest rate as usually reported the monetary return to saving and cost of borrowing. The real interest rate is the nominal interest rate corrected for inflation www. Assignment. Point. com
 The real interest equals the nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate. Because inflation erodes the value of money over time, the real interest rate more accurately reflects the real return to saving and cost of borrowing. the supply and demand for loanable funds depend on the real (rather than nominal) interest rate www. Assignment. Point. com
The real interest equals the nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate. Because inflation erodes the value of money over time, the real interest rate more accurately reflects the real return to saving and cost of borrowing. the supply and demand for loanable funds depend on the real (rather than nominal) interest rate www. Assignment. Point. com
 Overview ü Financial Markets and Intermediaries ü Saving and Investment ü Market for Loanable Funds u Government policies that affect the economy’s savings and investment. www. Assignment. Point. com
Overview ü Financial Markets and Intermediaries ü Saving and Investment ü Market for Loanable Funds u Government policies that affect the economy’s savings and investment. www. Assignment. Point. com
 Government Policy That Affects The Economy’s Saving and Investment u Policies that influence the loanable funds market: ◦ Taxes and Saving ◦ Taxes and Investment ◦ Government Budget Deficits/Surpluses u Observe how policy affects equilibrium, interest rates and funds. www. Assignment. Point. com
Government Policy That Affects The Economy’s Saving and Investment u Policies that influence the loanable funds market: ◦ Taxes and Saving ◦ Taxes and Investment ◦ Government Budget Deficits/Surpluses u Observe how policy affects equilibrium, interest rates and funds. www. Assignment. Point. com
 Government Policy That Affects The Economy’s Saving and Investment u Taxes on savings reduce the incentive to save. A tax decrease would alter the incentive for households to save at any given interest rate and would affect the supply of loanable funds resulting in the: ◦ Supply curve shifting to the right. ◦ Equilibrium interest rate would drop. ◦ Quantity demanded for funds would rise. www. Assignment. Point. com
Government Policy That Affects The Economy’s Saving and Investment u Taxes on savings reduce the incentive to save. A tax decrease would alter the incentive for households to save at any given interest rate and would affect the supply of loanable funds resulting in the: ◦ Supply curve shifting to the right. ◦ Equilibrium interest rate would drop. ◦ Quantity demanded for funds would rise. www. Assignment. Point. com
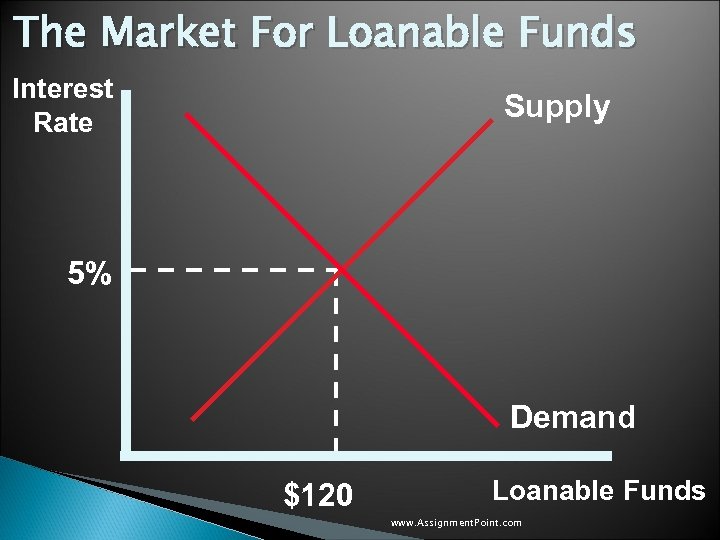 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
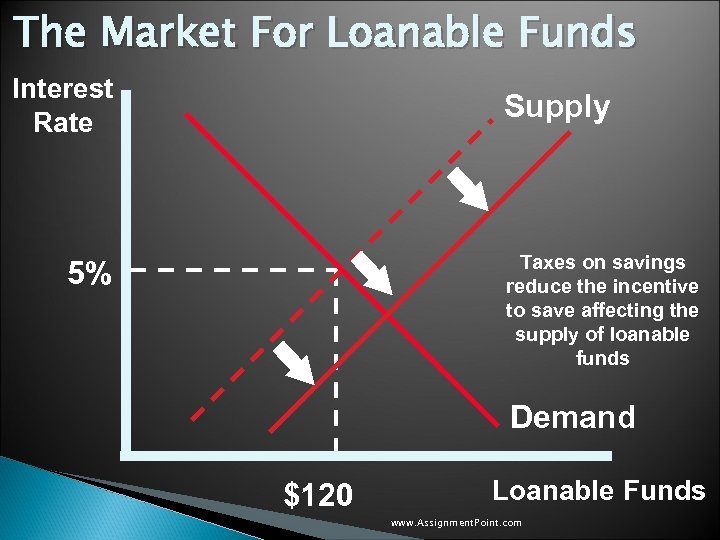 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply Taxes on savings reduce the incentive to save affecting the supply of loanable funds 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply Taxes on savings reduce the incentive to save affecting the supply of loanable funds 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
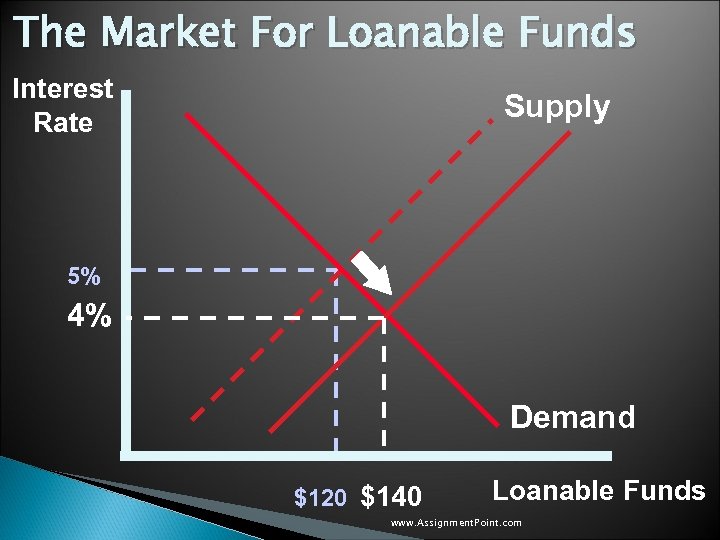 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 5% 4% Demand $120 $140 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 5% 4% Demand $120 $140 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
 Government Policy That Affects The Economy’s Saving and Investment u. A Tax Break on investment would increase the incentive to borrow if an investment tax credit were given. u An investment tax credit would: ◦ Alter the demand for loanable funds. ◦ Cause the demand curve to shift to the right. ◦ Result in a higher interest rate and greater saving. www. Assignment. Point. com
Government Policy That Affects The Economy’s Saving and Investment u. A Tax Break on investment would increase the incentive to borrow if an investment tax credit were given. u An investment tax credit would: ◦ Alter the demand for loanable funds. ◦ Cause the demand curve to shift to the right. ◦ Result in a higher interest rate and greater saving. www. Assignment. Point. com
 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
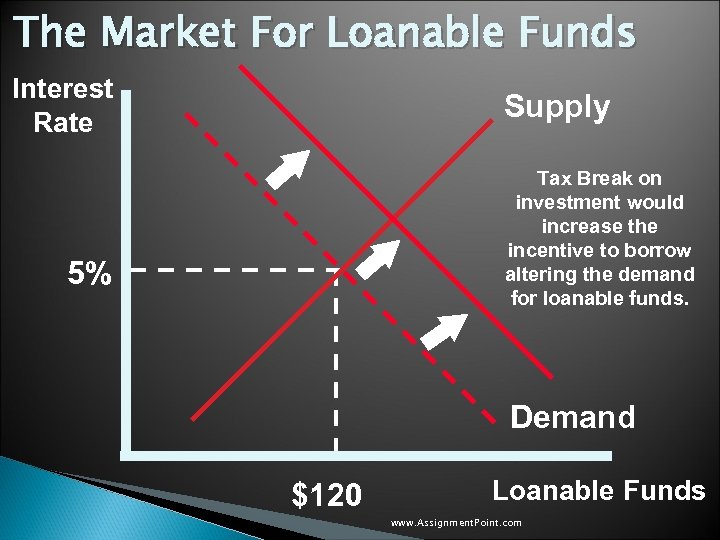 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply Tax Break on investment would increase the incentive to borrow altering the demand for loanable funds. 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply Tax Break on investment would increase the incentive to borrow altering the demand for loanable funds. 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
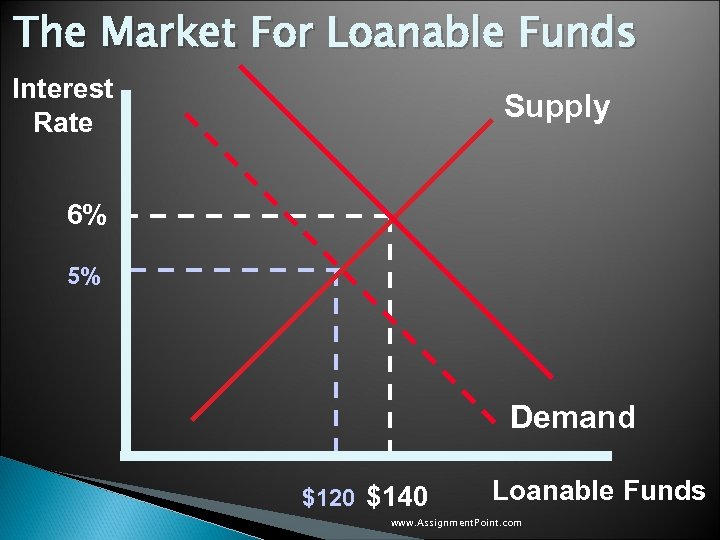 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 6% 5% Demand $120 $140 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 6% 5% Demand $120 $140 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
 Government Policy That Affects The Economy’s Saving and Investment u Government Budget Deficit: ◦ When the government spends more than it receives in tax revenues the accumulation of past budget deficits is called the government debt. u The budget deficit: ◦ Alters the supply curve, reducing supply. ◦ Causes the supply to shift to the left. ◦ Results in Crowding Out. www. Assignment. Point. com
Government Policy That Affects The Economy’s Saving and Investment u Government Budget Deficit: ◦ When the government spends more than it receives in tax revenues the accumulation of past budget deficits is called the government debt. u The budget deficit: ◦ Alters the supply curve, reducing supply. ◦ Causes the supply to shift to the left. ◦ Results in Crowding Out. www. Assignment. Point. com
 Government Policy That Affects The Economy’s Saving and Investment u When the government borrows to finance its budget deficit, it reduces the supply of loanable funds available to finance investment by households and firms. u This deficit borrowing “crowds out” the private borrowers who are trying to finance investments. www. Assignment. Point. com
Government Policy That Affects The Economy’s Saving and Investment u When the government borrows to finance its budget deficit, it reduces the supply of loanable funds available to finance investment by households and firms. u This deficit borrowing “crowds out” the private borrowers who are trying to finance investments. www. Assignment. Point. com
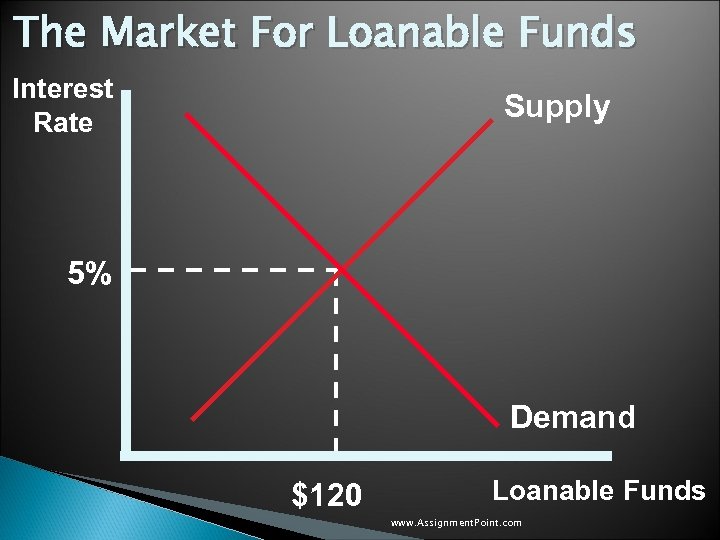 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
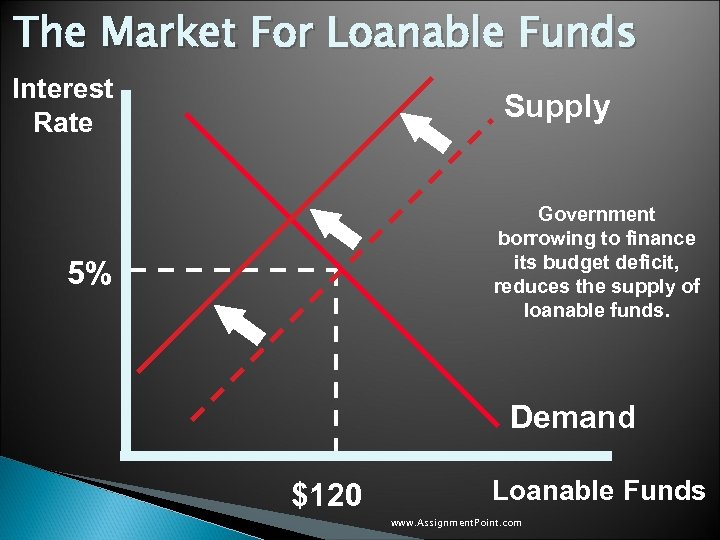 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply Government borrowing to finance its budget deficit, reduces the supply of loanable funds. 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply Government borrowing to finance its budget deficit, reduces the supply of loanable funds. 5% Demand $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
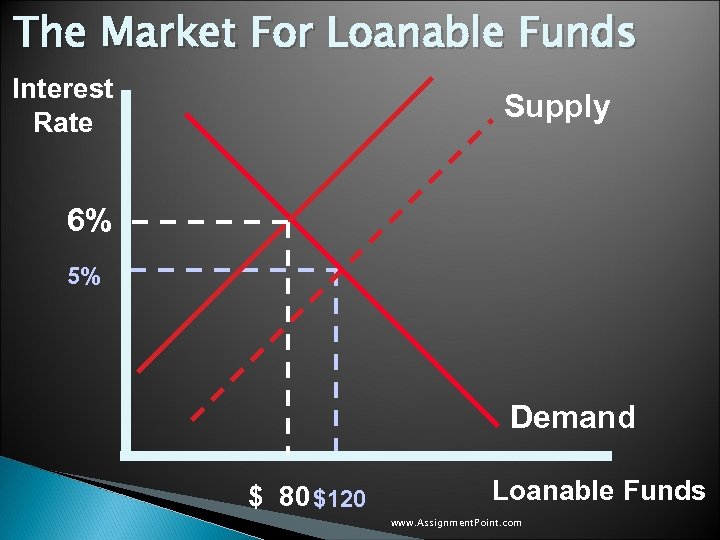 The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 6% 5% Demand $ 80 $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
The Market For Loanable Funds Interest Rate Supply 6% 5% Demand $ 80 $120 Loanable Funds www. Assignment. Point. com
 Government Policy That Affects The Economy’s Saving and Investment u. A budget surplus increases the supply of loanable funds, reduces the interest rate, and stimulates investment. www. Assignment. Point. com
Government Policy That Affects The Economy’s Saving and Investment u. A budget surplus increases the supply of loanable funds, reduces the interest rate, and stimulates investment. www. Assignment. Point. com
 Conclusion u Financial markets coordinate borrowing and lending and thereby help allocate the economy’s scarce resources efficiently. u Financial markets are like other markets in the economy. The price in the loanable funds market - interest rate - is governed by the forces of supply and demand. www. Assignment. Point. com
Conclusion u Financial markets coordinate borrowing and lending and thereby help allocate the economy’s scarce resources efficiently. u Financial markets are like other markets in the economy. The price in the loanable funds market - interest rate - is governed by the forces of supply and demand. www. Assignment. Point. com
 Overview ü Financial Markets and Intermediaries ü Saving and Investment ü Market for Loanable Funds ü Government policies that affect the economy’s savings and investment. www. Assignment. Point. com
Overview ü Financial Markets and Intermediaries ü Saving and Investment ü Market for Loanable Funds ü Government policies that affect the economy’s savings and investment. www. Assignment. Point. com


