dba4023ee4b86014c17f0ebf7cf960e7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 SARS
SARS
 What is SARS? • Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome • Respiratory illness • Asia, North America, and Europe • Previously unrecognized coronavirus
What is SARS? • Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome • Respiratory illness • Asia, North America, and Europe • Previously unrecognized coronavirus
 Symptoms • Fever of greater than 100. 4 o F • Cough or difficulty breathing • Headache • Body aches
Symptoms • Fever of greater than 100. 4 o F • Cough or difficulty breathing • Headache • Body aches
 Spread of SARS • Primary method appears to be close person-to-person contact • Potentially by fomites, or air-borne routes
Spread of SARS • Primary method appears to be close person-to-person contact • Potentially by fomites, or air-borne routes
 Incubation period for SARS • 2 - 7 days • May be as long as 10 days
Incubation period for SARS • 2 - 7 days • May be as long as 10 days
 Who is at risk? • Most US cases occur in travelers with history to areas with ongoing transmission • China, Hong Kong, Singapore, Hanoi • Household contacts of people with SARS • Healthcare workers exposed to SARS patients
Who is at risk? • Most US cases occur in travelers with history to areas with ongoing transmission • China, Hong Kong, Singapore, Hanoi • Household contacts of people with SARS • Healthcare workers exposed to SARS patients
 Case Definition • Clinical Criteria • Epidemiologic Criteria • Laboratory Criteria
Case Definition • Clinical Criteria • Epidemiologic Criteria • Laboratory Criteria
 Clinical Criteria • Asymptomatic or mild respiratory illness • Moderate respiratory illness • Severe respiratory illness • Radiographic evidence of pneumonia OR • Respiratory distress syndrome
Clinical Criteria • Asymptomatic or mild respiratory illness • Moderate respiratory illness • Severe respiratory illness • Radiographic evidence of pneumonia OR • Respiratory distress syndrome
 Epidemiologic Criteria • Travel (including transit in an airport) within 10 days of onset of symptoms to an area with current or recently documented or suspected community transmission of SARS • Close contacts within 10 days of onset of symptoms with a person known or suspected to have SARS infection
Epidemiologic Criteria • Travel (including transit in an airport) within 10 days of onset of symptoms to an area with current or recently documented or suspected community transmission of SARS • Close contacts within 10 days of onset of symptoms with a person known or suspected to have SARS infection
 Laboratory Criteria • Confirmed – Detection of SARS- Co. V antibody less than 21 days after the onset of illness or – Detection of SARS- Co. V RNA using RT-PCR then confirmed using a second PCR assay using separate specimens and primers – Isolation of SARS-Co. V • Negative – Absence of antibody in convalescent sera obtained more than 21 days after onset of symptoms. • Undetermined – laboratory testing not preformed or incomplete
Laboratory Criteria • Confirmed – Detection of SARS- Co. V antibody less than 21 days after the onset of illness or – Detection of SARS- Co. V RNA using RT-PCR then confirmed using a second PCR assay using separate specimens and primers – Isolation of SARS-Co. V • Negative – Absence of antibody in convalescent sera obtained more than 21 days after onset of symptoms. • Undetermined – laboratory testing not preformed or incomplete
 Case Classification • Probable Case: – meets the clinical criteria for severe respiratory illness of unknown etiology with onset since 2/13/03 and epidemiologic criteria and laboratory criteria confirmed, negative or undetermined. • Suspect Case: – meets the clinical criteria for moderate respiratory illness of unknown etiology with onset since 2/13/03 and epidemiologic criteria and laboratory criteria confirmed, negative, or undetermined.
Case Classification • Probable Case: – meets the clinical criteria for severe respiratory illness of unknown etiology with onset since 2/13/03 and epidemiologic criteria and laboratory criteria confirmed, negative or undetermined. • Suspect Case: – meets the clinical criteria for moderate respiratory illness of unknown etiology with onset since 2/13/03 and epidemiologic criteria and laboratory criteria confirmed, negative, or undetermined.
 Treatment of SARS • Should be similar to that used for patients affected with serious community acquired atypical pneumonia • Antivirals and steroids have not been tested in clinical trails and their effectiveness is unknown
Treatment of SARS • Should be similar to that used for patients affected with serious community acquired atypical pneumonia • Antivirals and steroids have not been tested in clinical trails and their effectiveness is unknown
 Mortality of SARS • As of 5/15/03 8% overall 0 to 50% depending on the age group – Overall 14 -15% Canada: 15 -19% China: 3 - 13% Hong Kong: 11 -17% Singapore: 13 -15% Vietnam: 8%
Mortality of SARS • As of 5/15/03 8% overall 0 to 50% depending on the age group – Overall 14 -15% Canada: 15 -19% China: 3 - 13% Hong Kong: 11 -17% Singapore: 13 -15% Vietnam: 8%
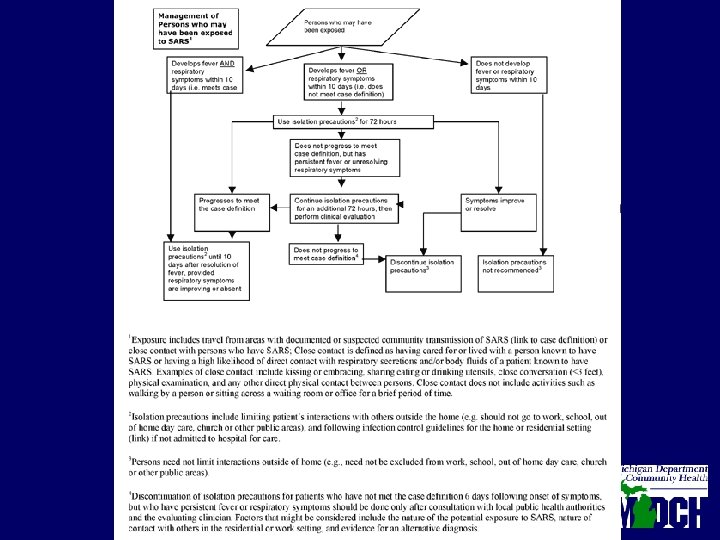
 Travel • Travel Alert- Informs travelers of a health concern in a particular area No recommendation against nonessential travel to the area. Singapore, Hanoi, Toronto (WHO removed Toronto as of 5/14, CDC still lists Toronto as area under Travel alert) • Travel Advisory- Potentially more serious situation There is a recommendation against nonessential travel to the area China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan
Travel • Travel Alert- Informs travelers of a health concern in a particular area No recommendation against nonessential travel to the area. Singapore, Hanoi, Toronto (WHO removed Toronto as of 5/14, CDC still lists Toronto as area under Travel alert) • Travel Advisory- Potentially more serious situation There is a recommendation against nonessential travel to the area China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan
 Quarantine • CDC quarantine officers are distributing health alert cards to all passengers returning from areas on travel alerts or advisories • Cards inform travelers about SARS, asked to monitor health for 10 days • Procedures for airlines and ships
Quarantine • CDC quarantine officers are distributing health alert cards to all passengers returning from areas on travel alerts or advisories • Cards inform travelers about SARS, asked to monitor health for 10 days • Procedures for airlines and ships
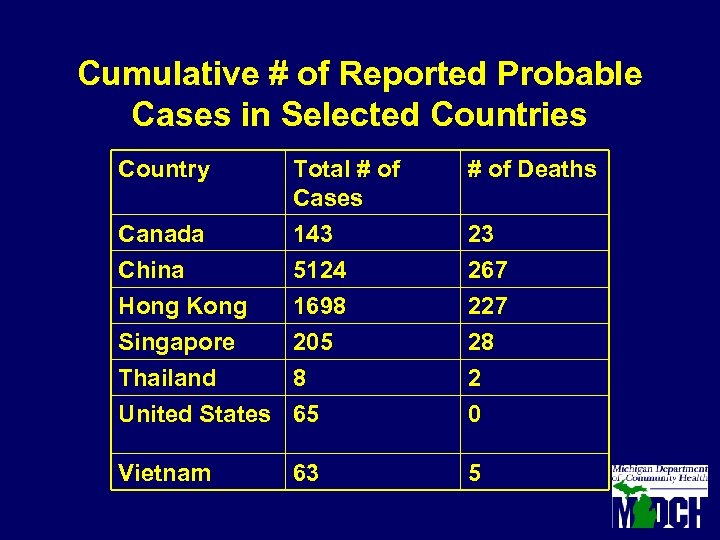 Cumulative # of Reported Probable Cases in Selected Countries Country Total # of Cases # of Deaths Canada China 143 5124 23 267 Hong Kong Singapore Thailand 1698 205 8 227 28 2 United States 65 0 Vietnam 5 63
Cumulative # of Reported Probable Cases in Selected Countries Country Total # of Cases # of Deaths Canada China 143 5124 23 267 Hong Kong Singapore Thailand 1698 205 8 227 28 2 United States 65 0 Vietnam 5 63
 Michigan cases • 3 suspect cases as of 5/15/03 • All with travel history to Asia • All have recovered
Michigan cases • 3 suspect cases as of 5/15/03 • All with travel history to Asia • All have recovered
 Misconceptions • No reason to believe related to terrorist activities • Does not appear to be caused by a paramyxovirus • No travel restrictions, instead travel advisories and alerts • No evidence of spreading disease within the USA
Misconceptions • No reason to believe related to terrorist activities • Does not appear to be caused by a paramyxovirus • No travel restrictions, instead travel advisories and alerts • No evidence of spreading disease within the USA
 References • www. cdc. gov • www. cdc. gov/mmwr/ • www. who. int/en/
References • www. cdc. gov • www. cdc. gov/mmwr/ • www. who. int/en/


