50bb2d4089ac7e15d37312aaa20d5ff1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 SAROPS Search and Rescue Optimal Planning System
SAROPS Search and Rescue Optimal Planning System
 SAROPS Technologies for Search, Assistance, and Rescue Seminar, Le Quartz, Brest, France, 18 – 20 October 2004 Malcolm L. Spaulding Applied Science Associates, Inc. (ASA), Narragansett, RI
SAROPS Technologies for Search, Assistance, and Rescue Seminar, Le Quartz, Brest, France, 18 – 20 October 2004 Malcolm L. Spaulding Applied Science Associates, Inc. (ASA), Narragansett, RI
 SAROPS Team n n United States Coast Guard Northrop Grumman Applied Science Associates (ASA) Metron
SAROPS Team n n United States Coast Guard Northrop Grumman Applied Science Associates (ASA) Metron
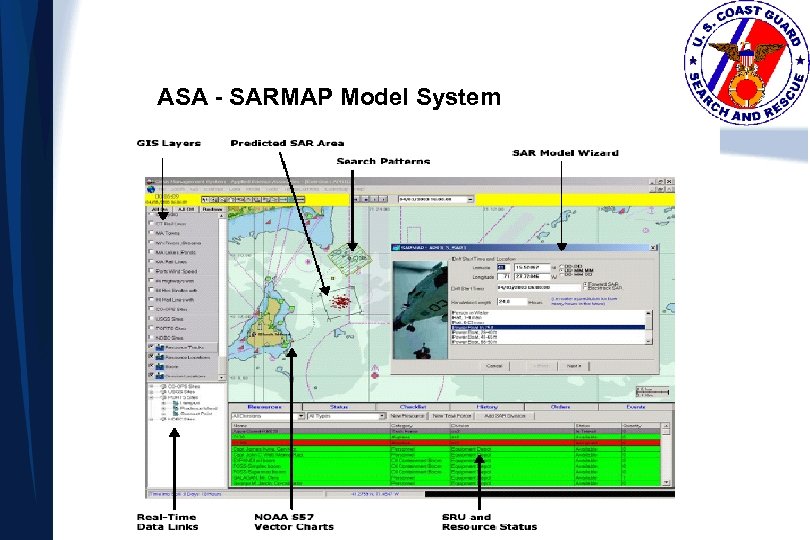 ASA - SARMAP Model System
ASA - SARMAP Model System
 Search & Rescue Problem n n n n n Create a SAR case when alerted Gather data, estimate uncertainties Use model to determine search area Estimate resource availability and capability Plan the next search Promulgate the search plan Perform the search plan Evaluate the completed search Repeat above until survivors are found and rescued
Search & Rescue Problem n n n n n Create a SAR case when alerted Gather data, estimate uncertainties Use model to determine search area Estimate resource availability and capability Plan the next search Promulgate the search plan Perform the search plan Evaluate the completed search Repeat above until survivors are found and rescued
 USCG Transition n n SARTools – Joint Automated Worksheet (JAWS) n Near-shore search planning n Based on 1950’s paper & pencil technology – Computer Assisted Search Planning (CASP) n Offshore search planning n Based on 1970’s technology SAROPS – Technologically current software tool – Near-shore and offshore search planning – Extensible to land-based search planning
USCG Transition n n SARTools – Joint Automated Worksheet (JAWS) n Near-shore search planning n Based on 1950’s paper & pencil technology – Computer Assisted Search Planning (CASP) n Offshore search planning n Based on 1970’s technology SAROPS – Technologically current software tool – Near-shore and offshore search planning – Extensible to land-based search planning
 SAROPS Goals n n n To provide fast, simple Search & Rescue predictions Minimize data entry and potential for error Automate data linkages – Environmental data inputs – Search Action Plan outputs n Simple visualization of results
SAROPS Goals n n n To provide fast, simple Search & Rescue predictions Minimize data entry and potential for error Automate data linkages – Environmental data inputs – Search Action Plan outputs n Simple visualization of results
 SAROPS Scenario Types – Voyage scenario where object can pass through or loiter in a number of locations (positions or areas) using any combination of great circle and rhumb line routes – Initial Position (with bivariate normal uncertainty) and time uncertainty for an event, plus an offset for initial location and time of distress – Positions obtained from COSPAS-SARSAT, other GMDSS – Lines of Bearing (from Radio Direction Finding, Flare Sightings, Loran, and others) – Areas defined by polygons – “Reverse Drift” scenarios – Scenarios may be “weighted” COSPAS-SARSAT – Satellite based emergency beacon locator for search and rescue, GMDSS – Global Marine Distress Safety System
SAROPS Scenario Types – Voyage scenario where object can pass through or loiter in a number of locations (positions or areas) using any combination of great circle and rhumb line routes – Initial Position (with bivariate normal uncertainty) and time uncertainty for an event, plus an offset for initial location and time of distress – Positions obtained from COSPAS-SARSAT, other GMDSS – Lines of Bearing (from Radio Direction Finding, Flare Sightings, Loran, and others) – Areas defined by polygons – “Reverse Drift” scenarios – Scenarios may be “weighted” COSPAS-SARSAT – Satellite based emergency beacon locator for search and rescue, GMDSS – Global Marine Distress Safety System
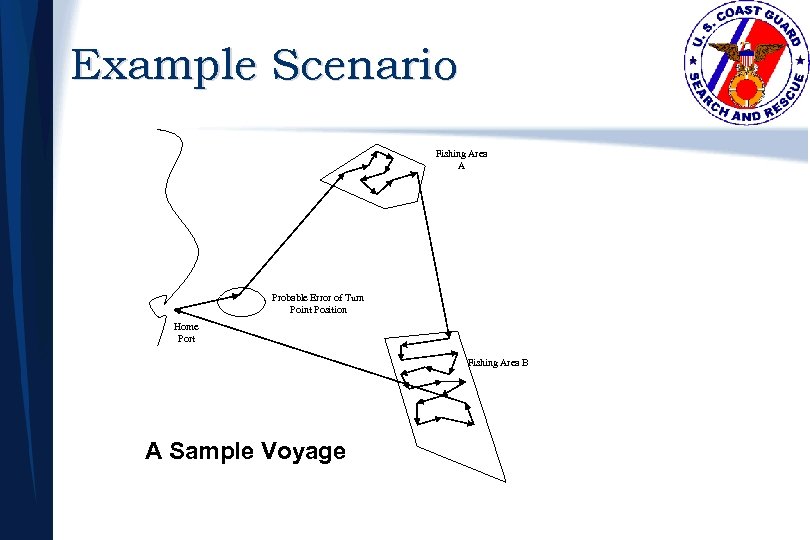 Example Scenario Fishing Area A Probable Error of Turn Point Position Home Port Fishing Area B A Sample Voyage
Example Scenario Fishing Area A Probable Error of Turn Point Position Home Port Fishing Area B A Sample Voyage
 SAROPS Components Graphical User Interface/ (GUI) n Environmental Data Server (EDS) n Simulator (SIM) n
SAROPS Components Graphical User Interface/ (GUI) n Environmental Data Server (EDS) n Simulator (SIM) n
 GUI Requirements n n n n n Deployable on ESRI® GIS mapping engine (C/JMTK) Wizard based interface Minimize keystrokes Chart support (vector/raster) Display environmental data Animated display capabilities Display recommended search plans/areas/patterns Display probability maps (by scenario, object type or combined) Reporting C/JMTK – Commercial/Joint Mapping Tool Kit
GUI Requirements n n n n n Deployable on ESRI® GIS mapping engine (C/JMTK) Wizard based interface Minimize keystrokes Chart support (vector/raster) Display environmental data Animated display capabilities Display recommended search plans/areas/patterns Display probability maps (by scenario, object type or combined) Reporting C/JMTK – Commercial/Joint Mapping Tool Kit
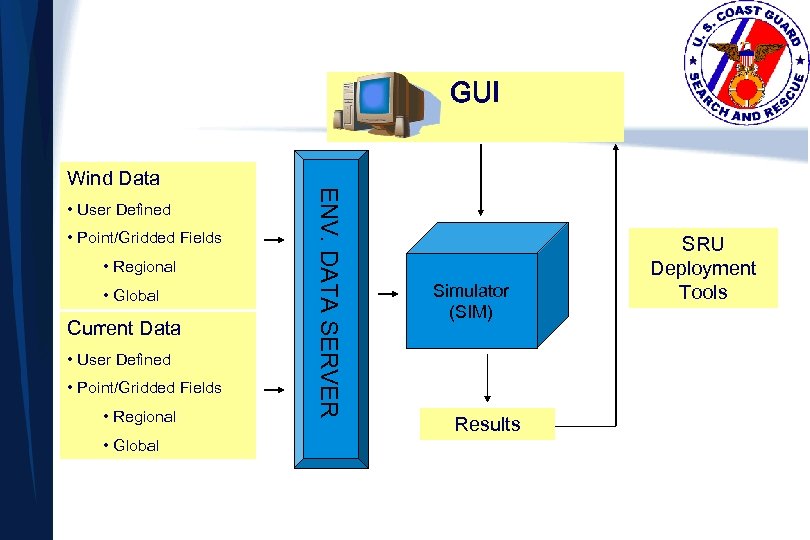 GUI • User Defined • Point/Gridded Fields • Regional • Global Current Data • User Defined • Point/Gridded Fields • Regional • Global ENV. DATA SERVER Wind Data Simulator (SIM) Results SRU Deployment Tools
GUI • User Defined • Point/Gridded Fields • Regional • Global Current Data • User Defined • Point/Gridded Fields • Regional • Global ENV. DATA SERVER Wind Data Simulator (SIM) Results SRU Deployment Tools
 SIM Requirements n “Monte Carlo” (particle) simulation (random walk/flight) – Simulate pre-distress motion & fixed hazards – Simulate distress incidents and outcomes – Simulate post-distress motion (drift) – Calculate near-optimal search plan (max POS) – Simulate simultaneous SRU and search object motion (use POD vs. range at CPA on each leg) – Compute cumulative POS – Account for effects of previous unsuccessful searching when recommending subsequent search plans. POD- probability of detection, POS- probability of success, SRU- search rescue unit, CPA –closest point of approach
SIM Requirements n “Monte Carlo” (particle) simulation (random walk/flight) – Simulate pre-distress motion & fixed hazards – Simulate distress incidents and outcomes – Simulate post-distress motion (drift) – Calculate near-optimal search plan (max POS) – Simulate simultaneous SRU and search object motion (use POD vs. range at CPA on each leg) – Compute cumulative POS – Account for effects of previous unsuccessful searching when recommending subsequent search plans. POD- probability of detection, POS- probability of success, SRU- search rescue unit, CPA –closest point of approach
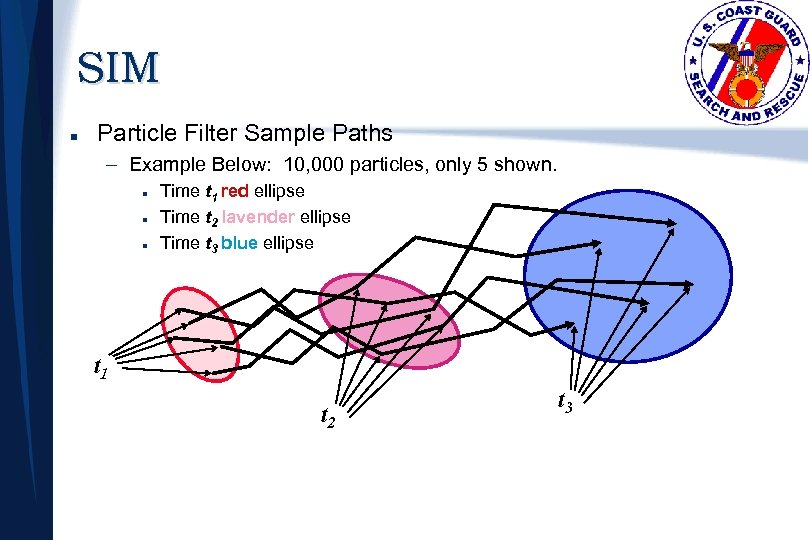 SIM n Particle Filter Sample Paths – Example Below: 10, 000 particles, only 5 shown. n n n Time t 1 red ellipse Time t 2 lavender ellipse Time t 3 blue ellipse t 1 t 2 t 3
SIM n Particle Filter Sample Paths – Example Below: 10, 000 particles, only 5 shown. n n n Time t 1 red ellipse Time t 2 lavender ellipse Time t 3 blue ellipse t 1 t 2 t 3
 EDS Requirements n n n n Surface current data Surface wind data Other (visibility, cloud cover, sea state, etc) Automatically accommodate variable spatial scales/resolution Select best data available Global land database Expansion of data products and uses
EDS Requirements n n n n Surface current data Surface wind data Other (visibility, cloud cover, sea state, etc) Automatically accommodate variable spatial scales/resolution Select best data available Global land database Expansion of data products and uses
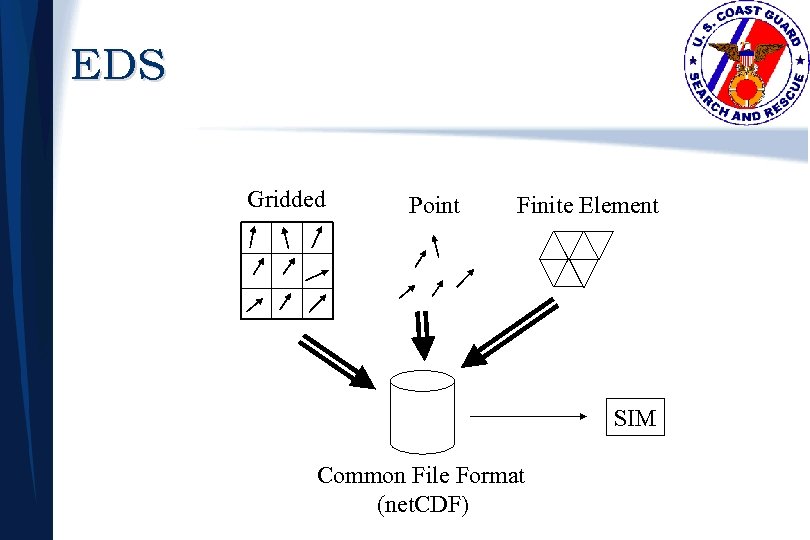 EDS Gridded Point Finite Element SIM Common File Format (net. CDF)
EDS Gridded Point Finite Element SIM Common File Format (net. CDF)
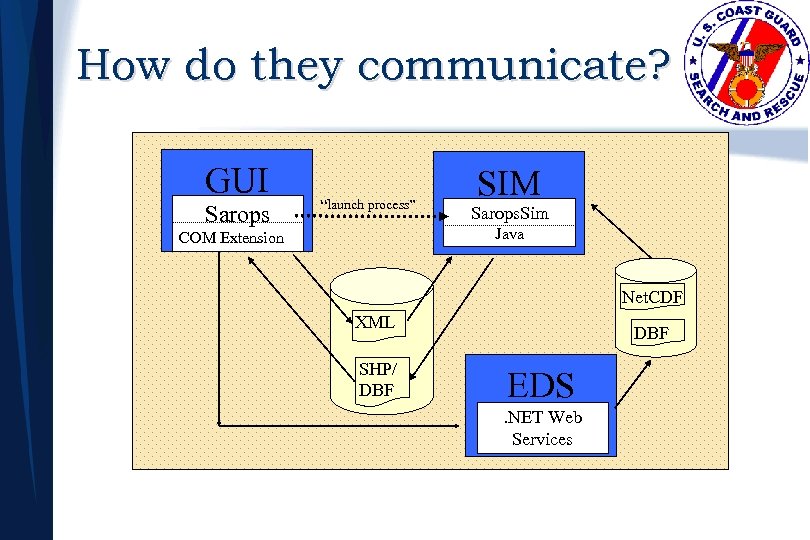 How do they communicate? GUI Sarops “launch process” SIM Sarops. Sim Java COM Extension Net. CDF XML SHP/ DBF EDS. NET Web Services
How do they communicate? GUI Sarops “launch process” SIM Sarops. Sim Java COM Extension Net. CDF XML SHP/ DBF EDS. NET Web Services
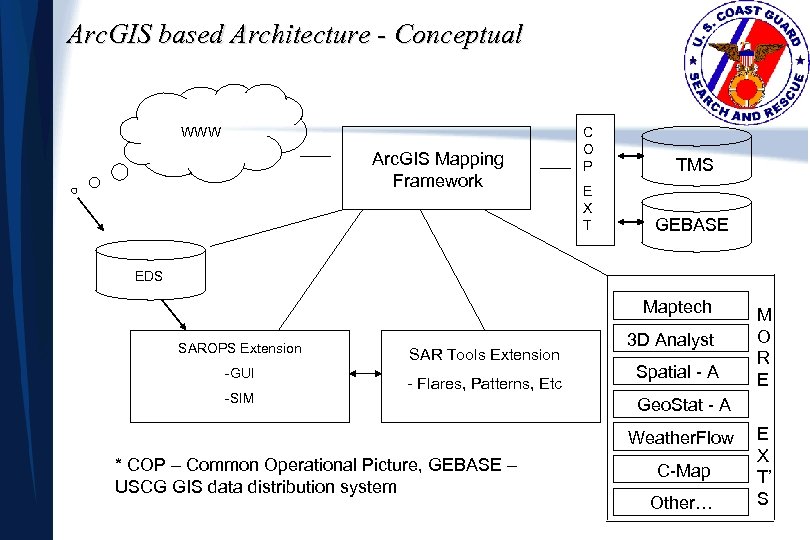 Arc. GIS based Architecture - Conceptual WWW Arc. GIS Mapping Framework C O P TMS E X T GEBASE EDS Maptech SAROPS Extension -GUI -SIM SAR Tools Extension - Flares, Patterns, Etc 3 D Analyst Spatial - A Geo. Stat - A Weather. Flow * COP – Common Operational Picture, GEBASE – USCG GIS data distribution system M O R E C-Map Other… E X T’ S
Arc. GIS based Architecture - Conceptual WWW Arc. GIS Mapping Framework C O P TMS E X T GEBASE EDS Maptech SAROPS Extension -GUI -SIM SAR Tools Extension - Flares, Patterns, Etc 3 D Analyst Spatial - A Geo. Stat - A Weather. Flow * COP – Common Operational Picture, GEBASE – USCG GIS data distribution system M O R E C-Map Other… E X T’ S
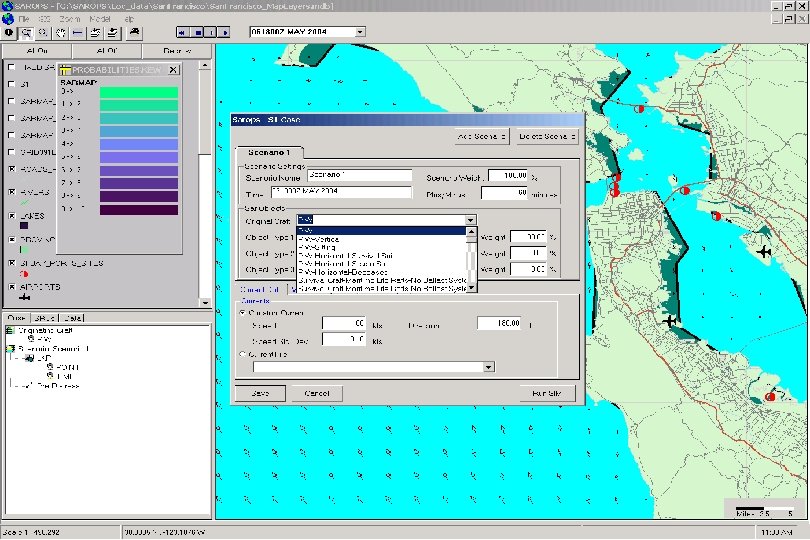
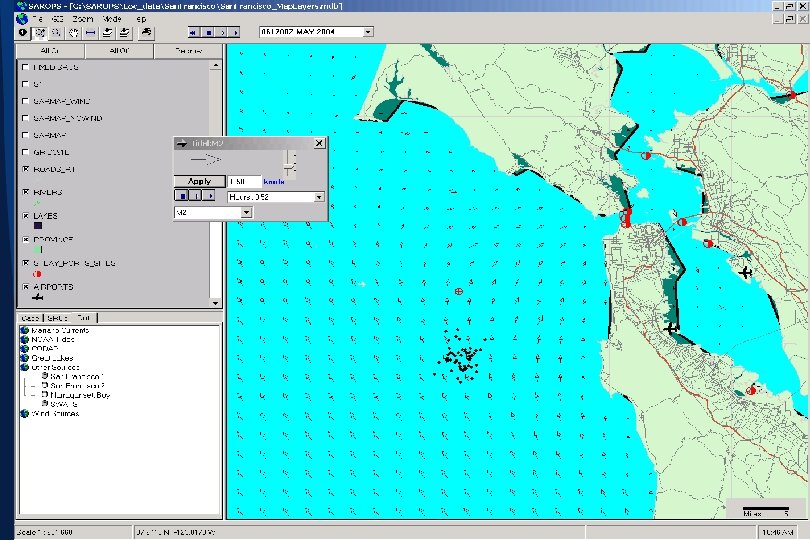
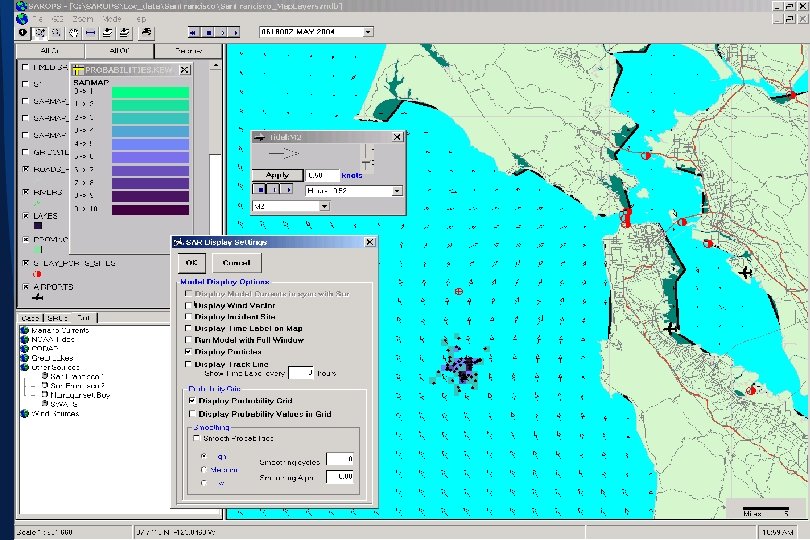
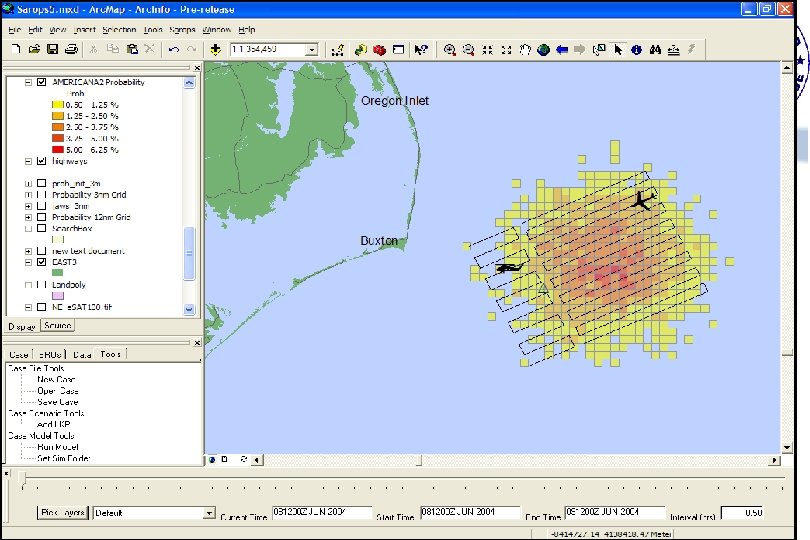
 SAROPS Screens (Initial Development)
SAROPS Screens (Initial Development)
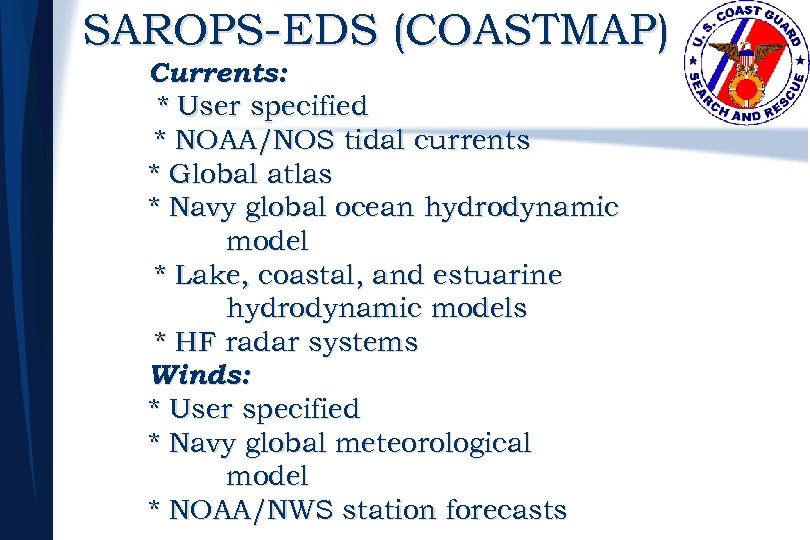 SAROPS-EDS (COASTMAP) Currents: * User specified * NOAA/NOS tidal currents * Global atlas * Navy global ocean hydrodynamic model * Lake, coastal, and estuarine hydrodynamic models * HF radar systems Winds: * User specified * Navy global meteorological model * NOAA/NWS station forecasts
SAROPS-EDS (COASTMAP) Currents: * User specified * NOAA/NOS tidal currents * Global atlas * Navy global ocean hydrodynamic model * Lake, coastal, and estuarine hydrodynamic models * HF radar systems Winds: * User specified * Navy global meteorological model * NOAA/NWS station forecasts
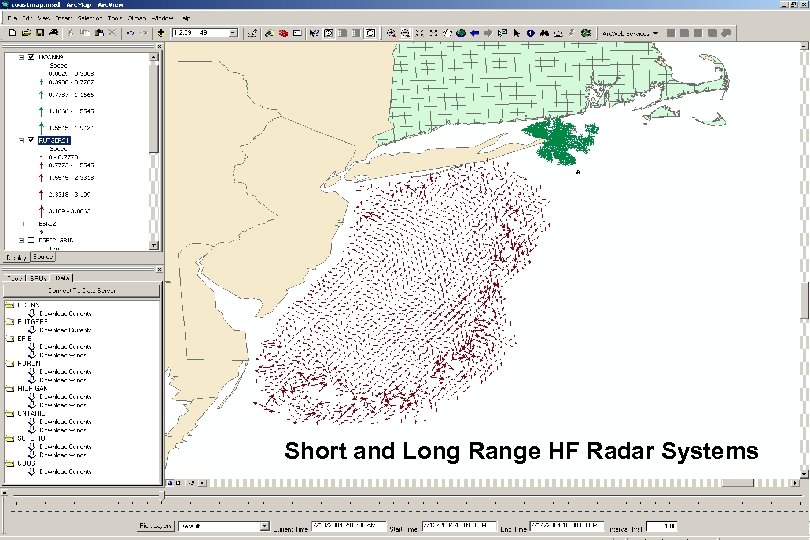 Short and Long Range HF Radar Systems
Short and Long Range HF Radar Systems
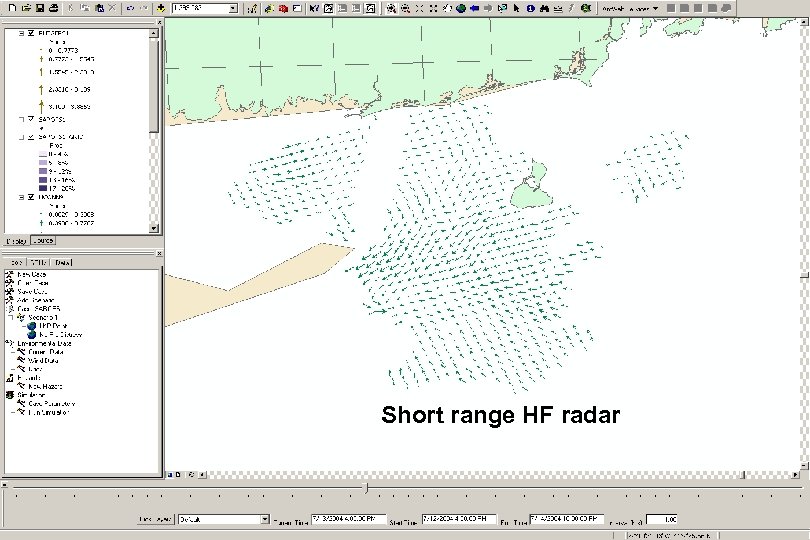 Short range HF radar
Short range HF radar
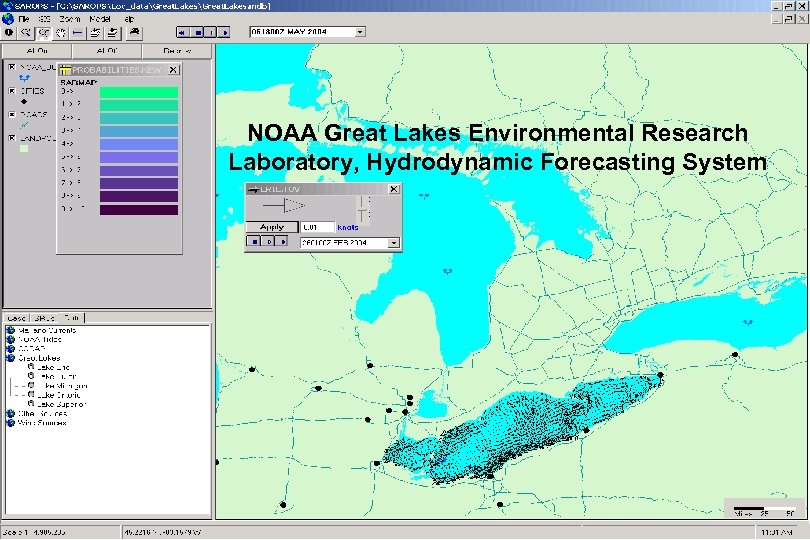 NOAA Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory, Hydrodynamic Forecasting System
NOAA Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory, Hydrodynamic Forecasting System
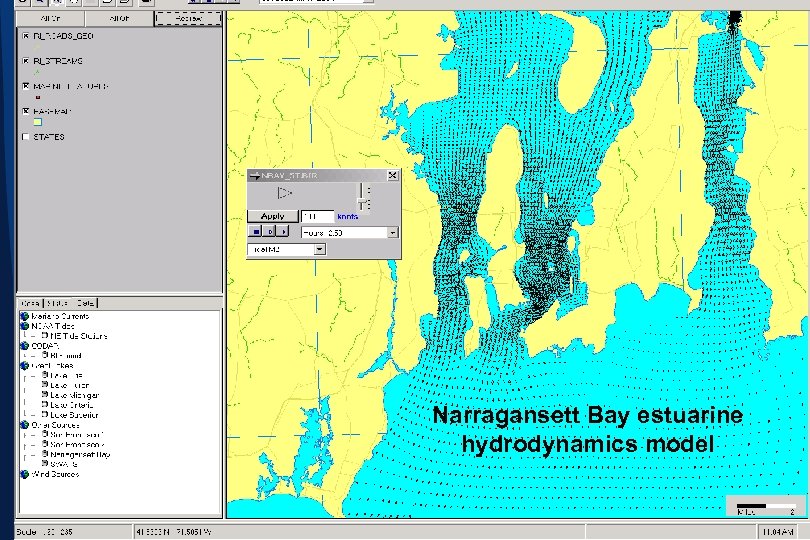 Narragansett Bay estuarine hydrodynamics model
Narragansett Bay estuarine hydrodynamics model
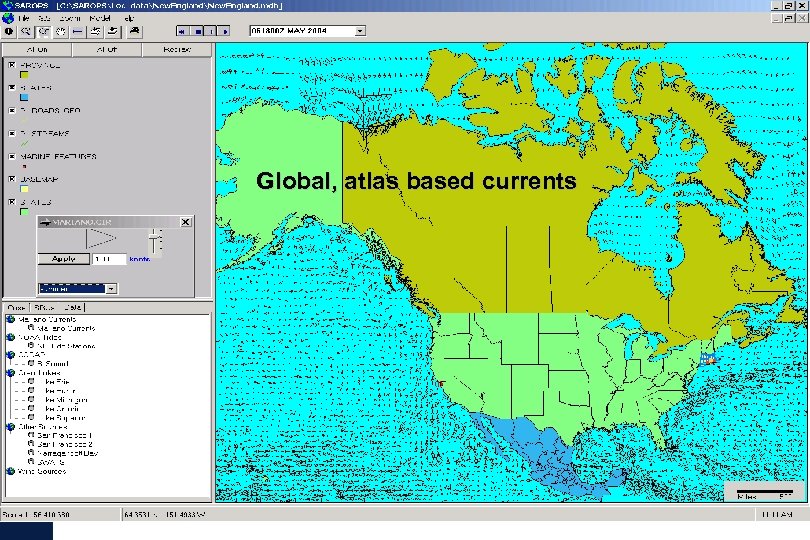 Global, atlas based currents
Global, atlas based currents

 Related Development Demonstration of linkage of SAROPS/ SARMAP to high frequency radar surface current data Sponsor: US Coast Guard, Research and Development Center Project Team: Anteon, ASA, University of RI and CT, and Rutgers University
Related Development Demonstration of linkage of SAROPS/ SARMAP to high frequency radar surface current data Sponsor: US Coast Guard, Research and Development Center Project Team: Anteon, ASA, University of RI and CT, and Rutgers University
 Major Study Components • Link HF radar (Block Island Sound(BIS) and Mid Atlantic Bight (MAB)) to SARMAP/SAROPS • Extend development of short term forecasting system to include wind forcing • Compare random walk and random flight model predictions, using HF radar as input, to observed trajectories of 7 drifting buoys deployed in BIS and MAB • Demonstration of integrated system in operational setting for USCG
Major Study Components • Link HF radar (Block Island Sound(BIS) and Mid Atlantic Bight (MAB)) to SARMAP/SAROPS • Extend development of short term forecasting system to include wind forcing • Compare random walk and random flight model predictions, using HF radar as input, to observed trajectories of 7 drifting buoys deployed in BIS and MAB • Demonstration of integrated system in operational setting for USCG


