31b6d2903f1bc56f847e77a08a157326.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 73
 Sarcoma Research Center UT MDACC Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNST): clinical, pathologic and molecular predictors of survival Kerrington Smith, M. D. CTOS Nov 14, 2008
Sarcoma Research Center UT MDACC Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNST): clinical, pathologic and molecular predictors of survival Kerrington Smith, M. D. CTOS Nov 14, 2008
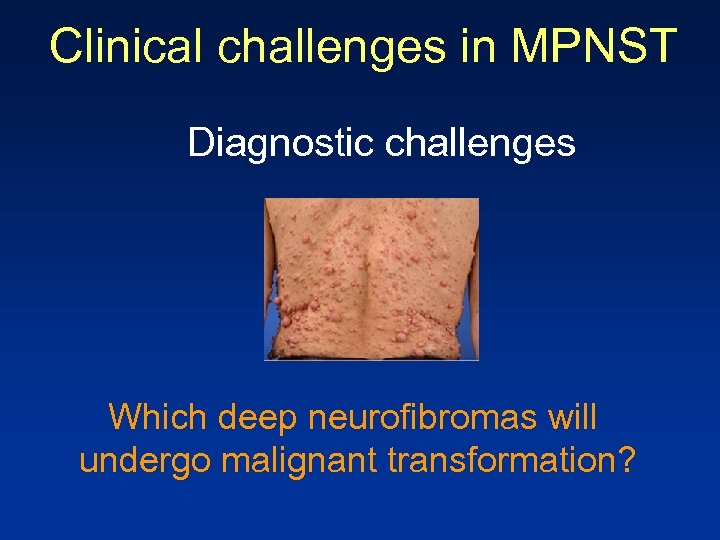 Clinical challenges in MPNST Diagnostic challenges Which deep neurofibromas will undergo malignant transformation?
Clinical challenges in MPNST Diagnostic challenges Which deep neurofibromas will undergo malignant transformation?
 Clinical challenges in MPNST Prognostic challenges After resection which patients will recur? What is the pattern of recurrence? NF 1 -MPNST vs. sporadic MPNST?
Clinical challenges in MPNST Prognostic challenges After resection which patients will recur? What is the pattern of recurrence? NF 1 -MPNST vs. sporadic MPNST?
 Clinical challenges in MPNST Therapeutic challenges Effective systemic therapy?
Clinical challenges in MPNST Therapeutic challenges Effective systemic therapy?
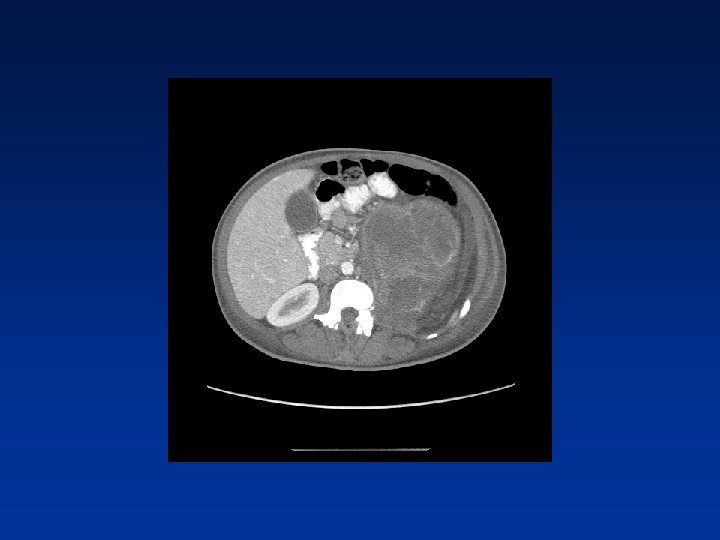
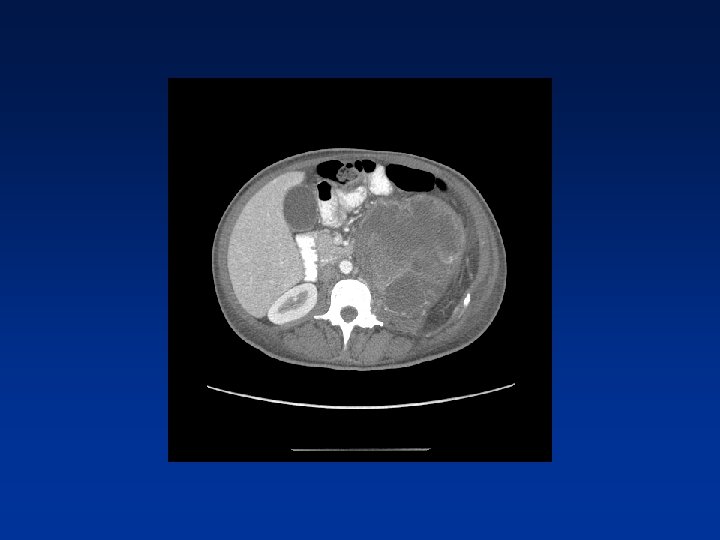
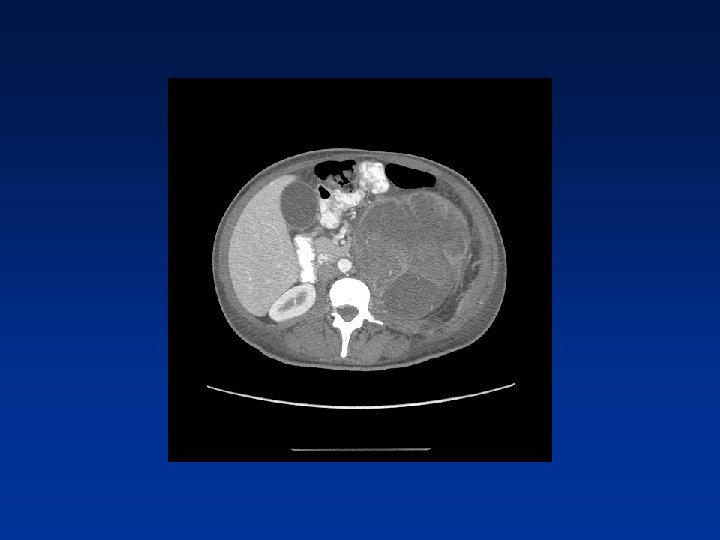
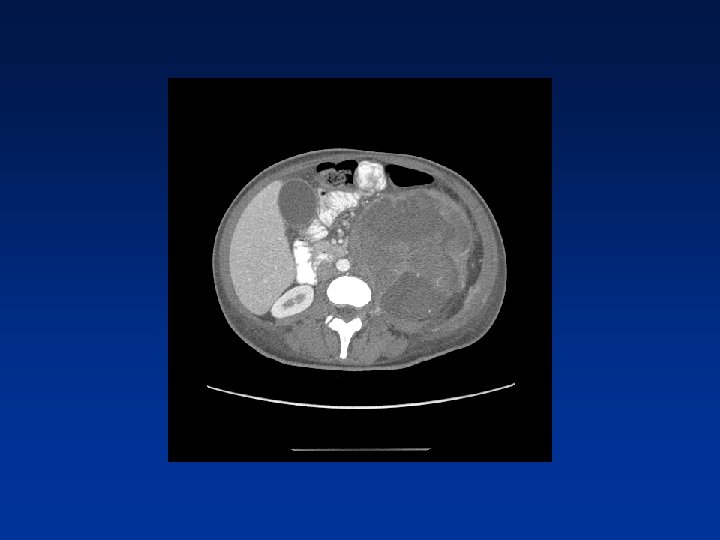
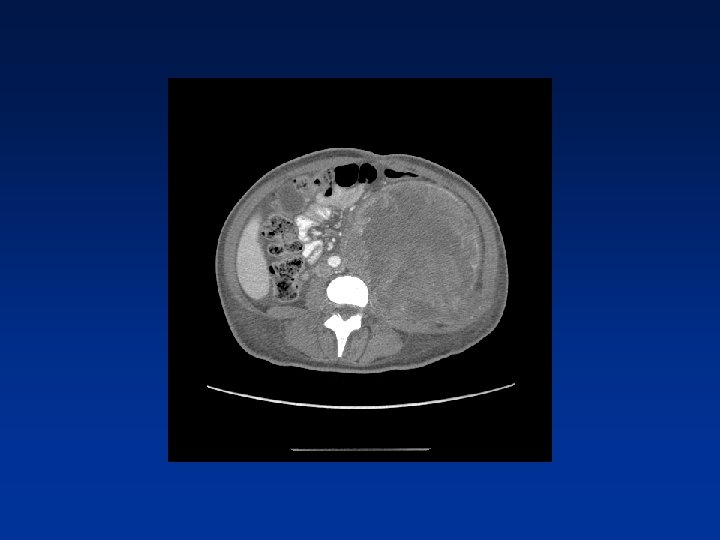
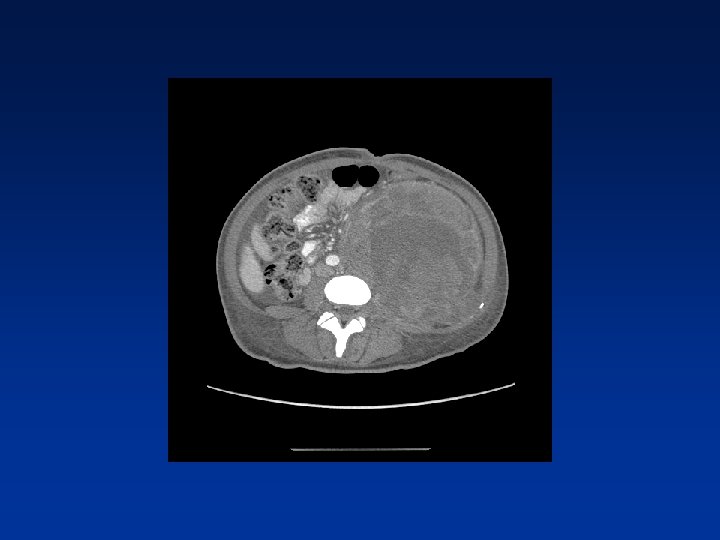
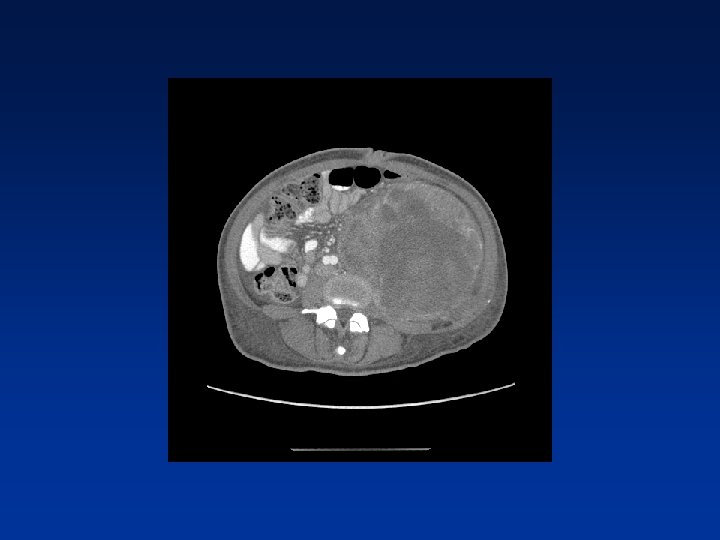
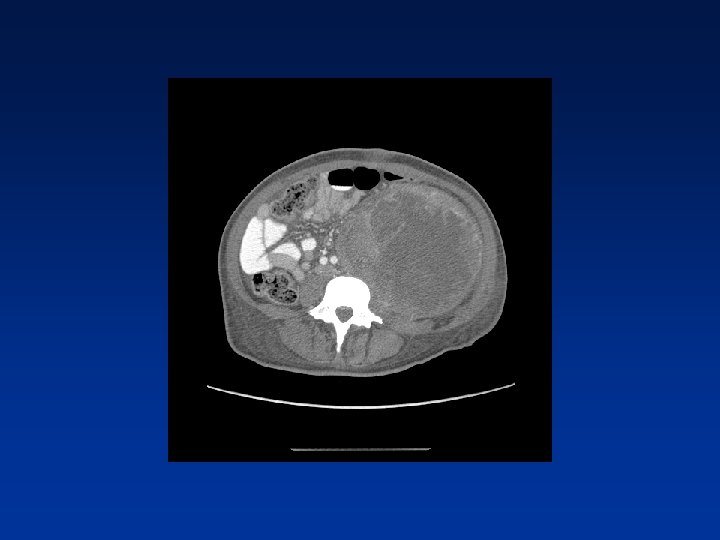
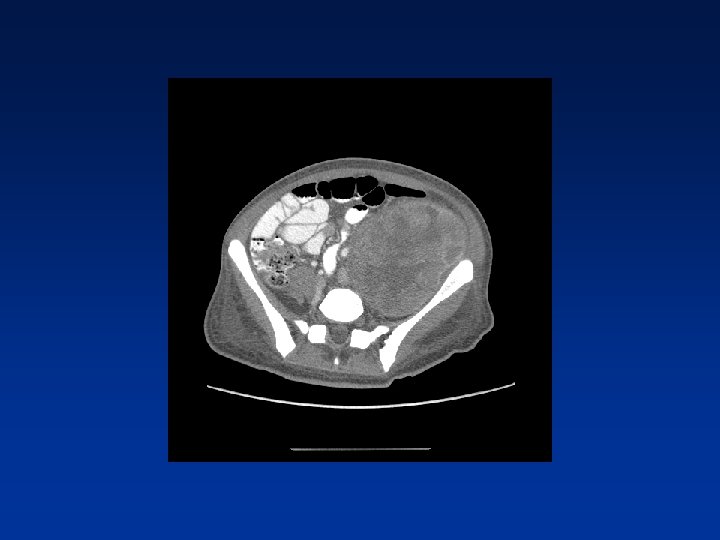
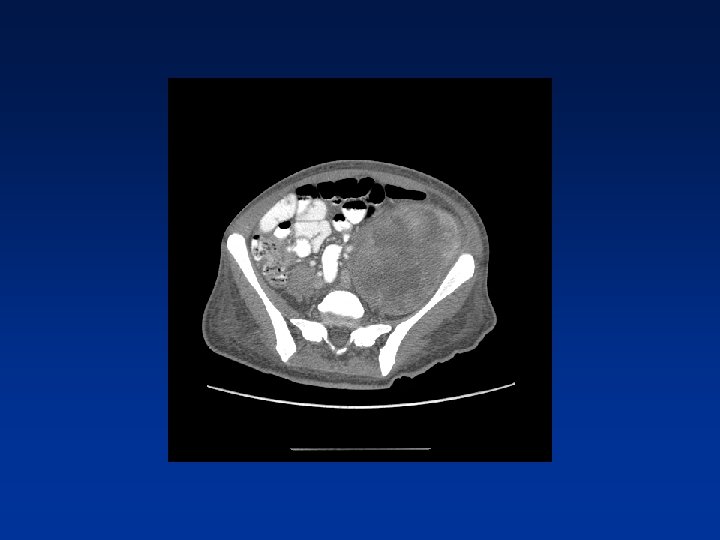
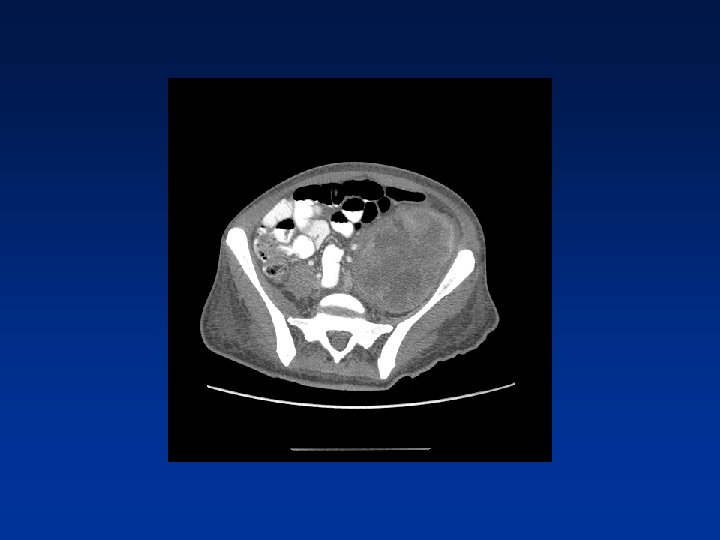
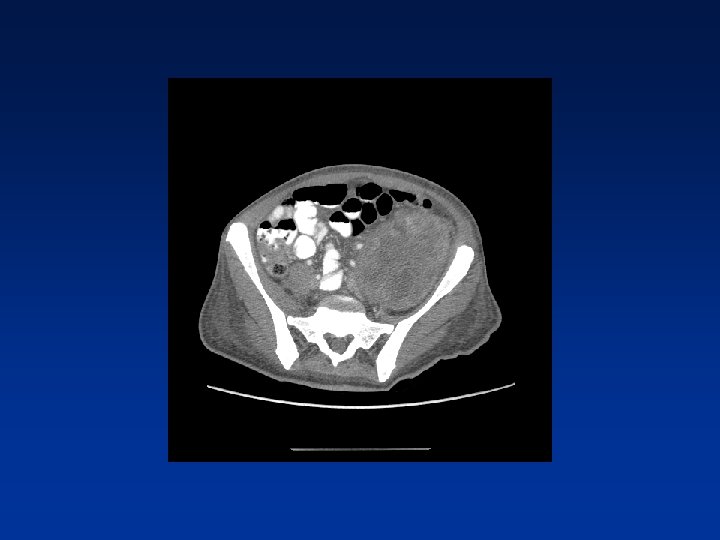
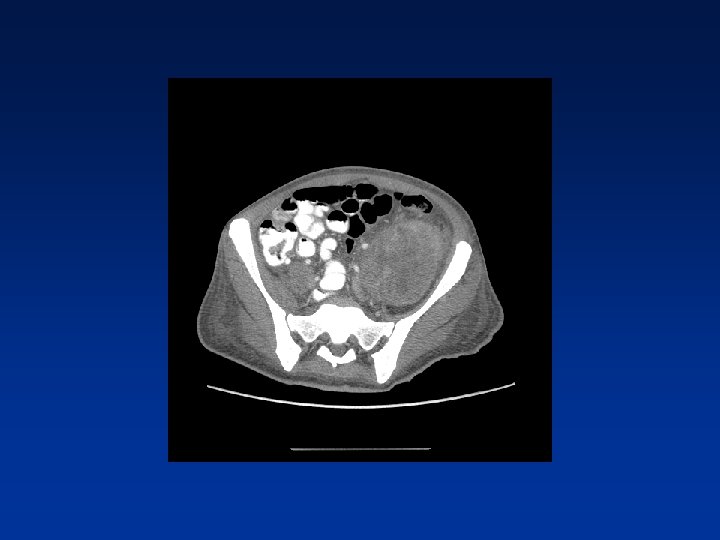
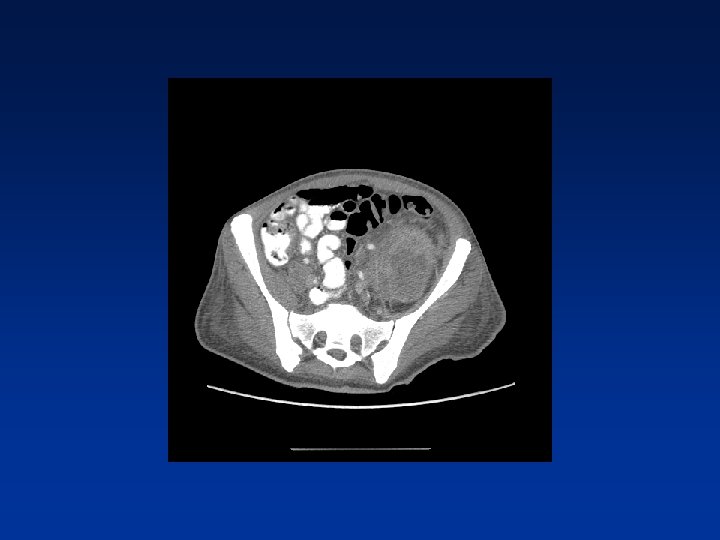
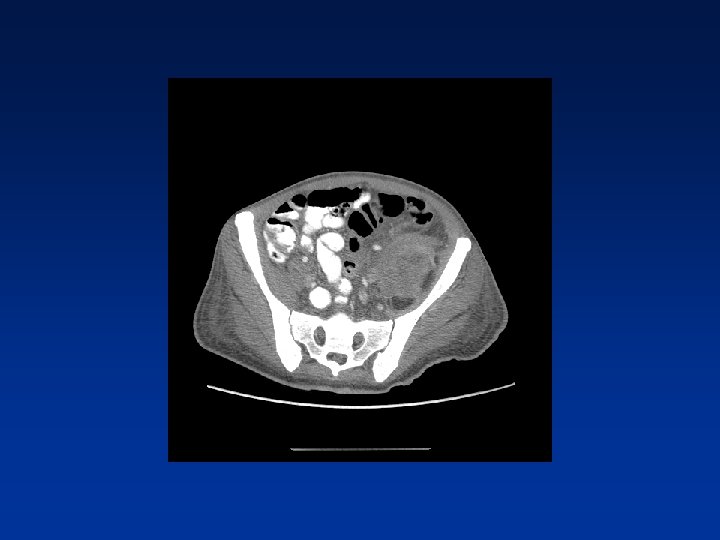
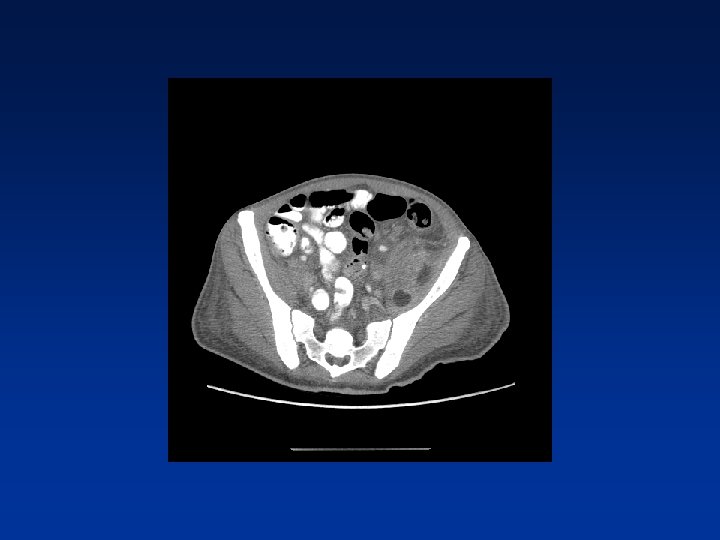
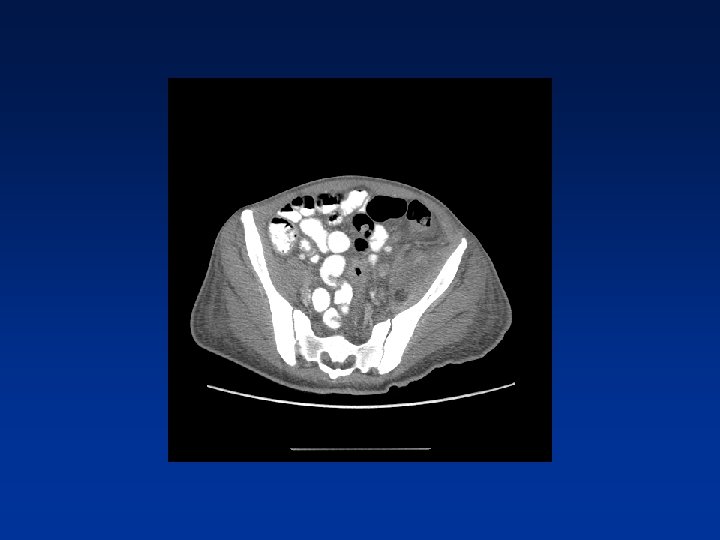
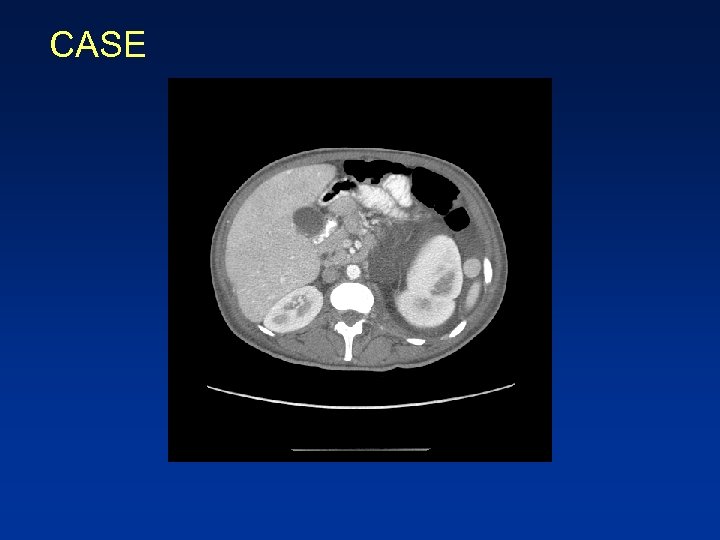 CASE
CASE
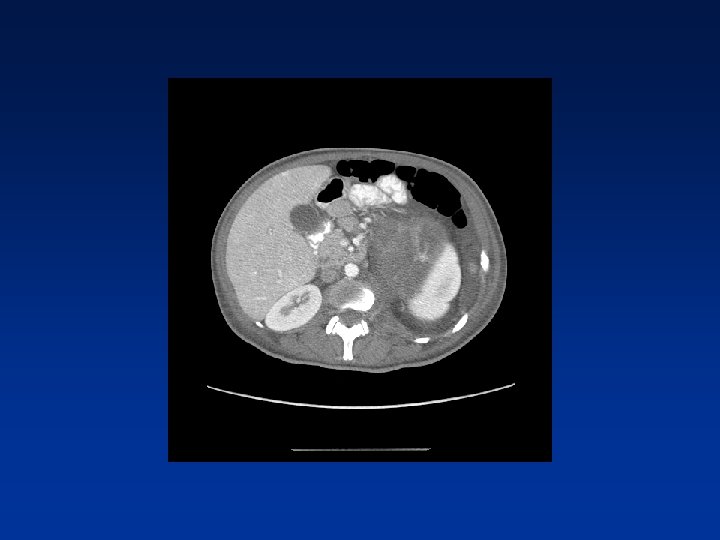
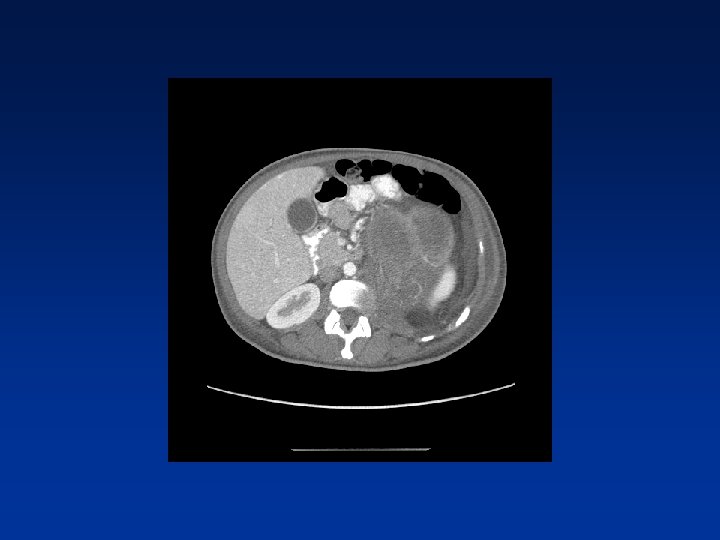
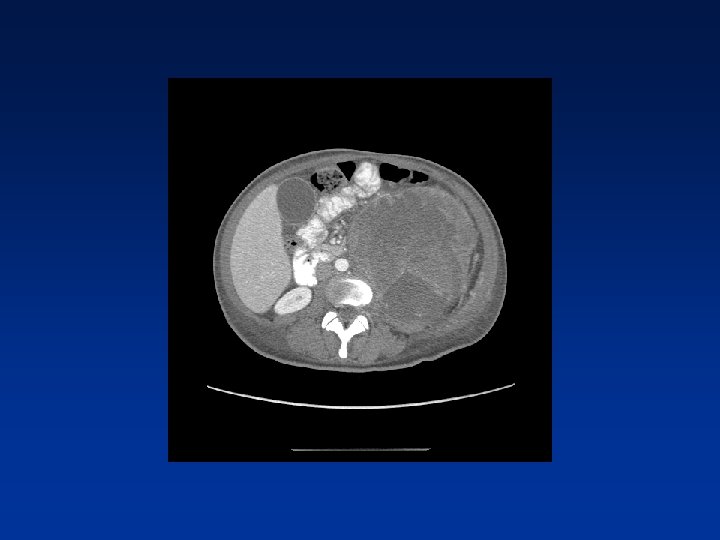
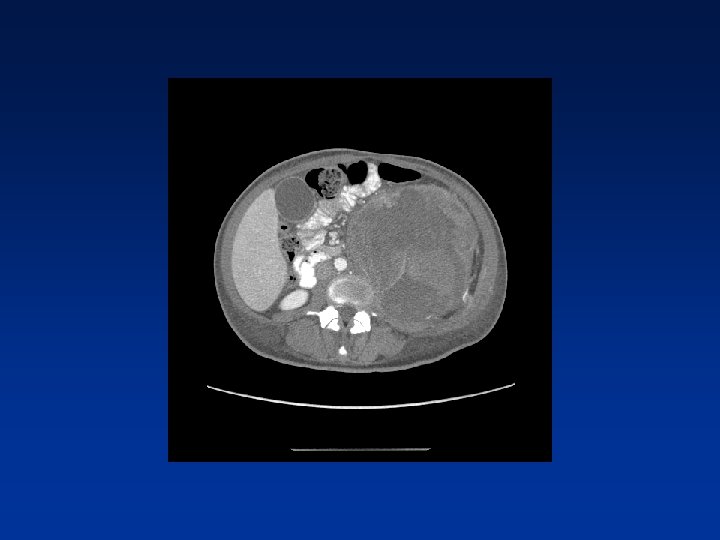
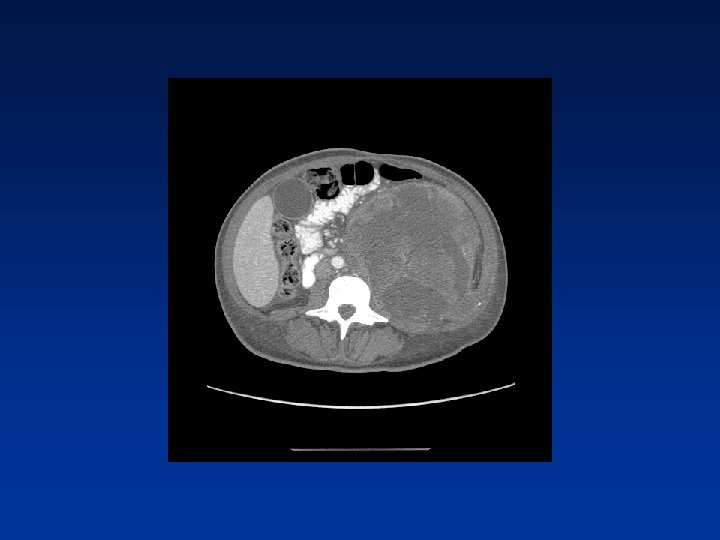
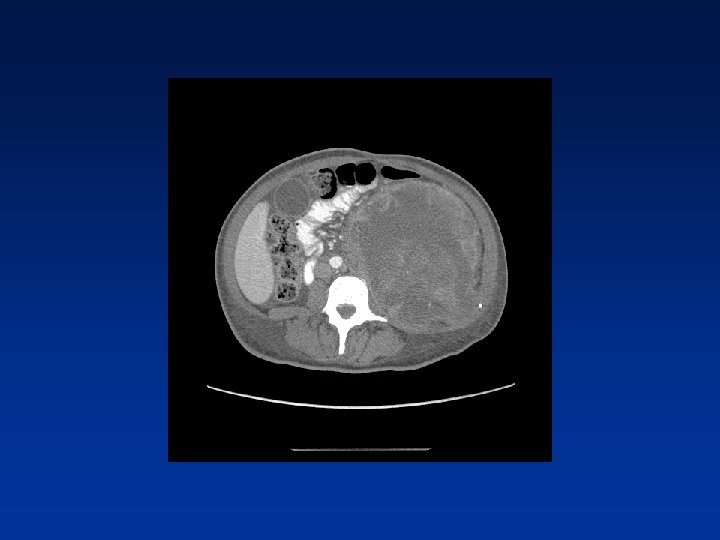
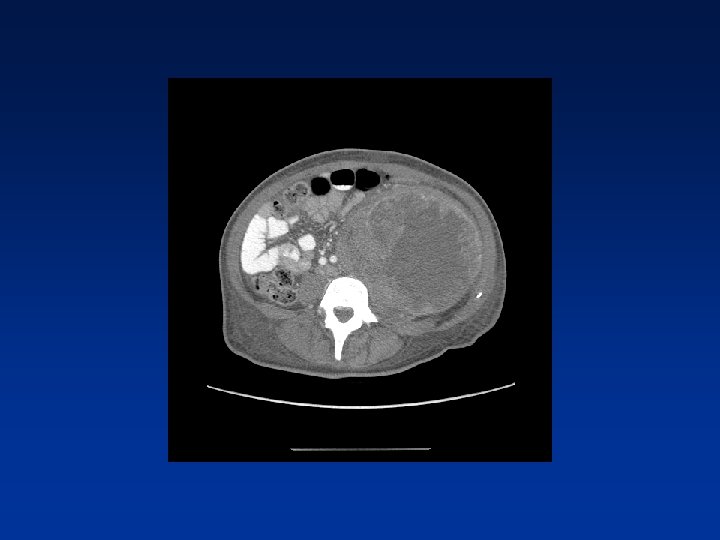
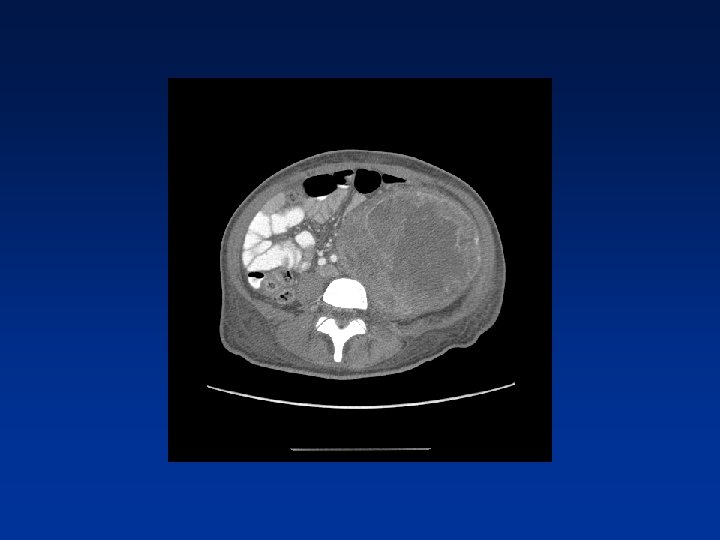
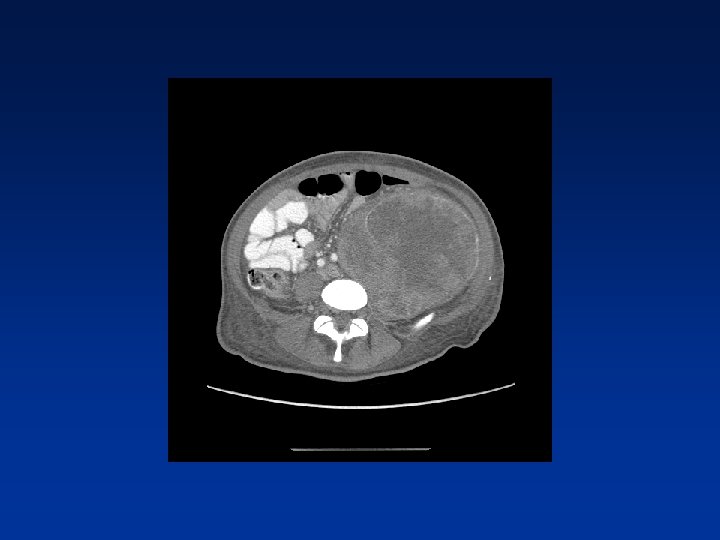
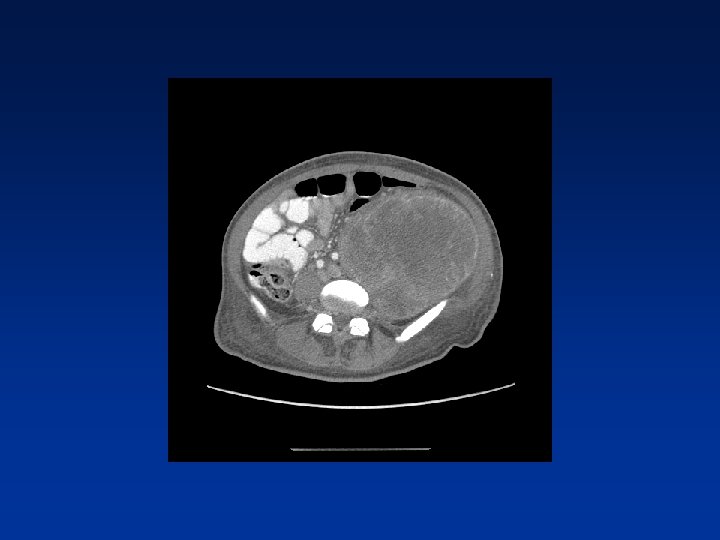
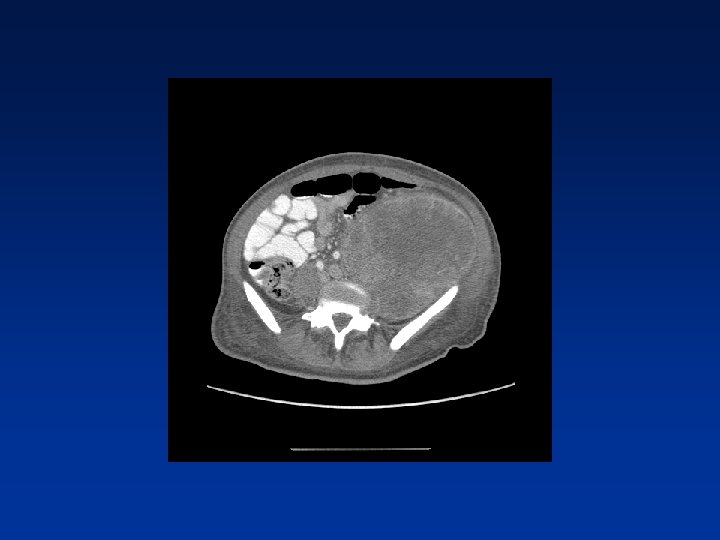
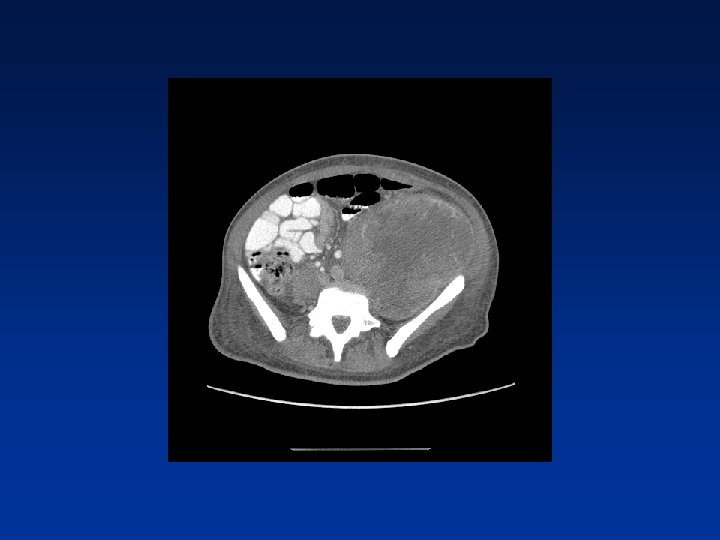
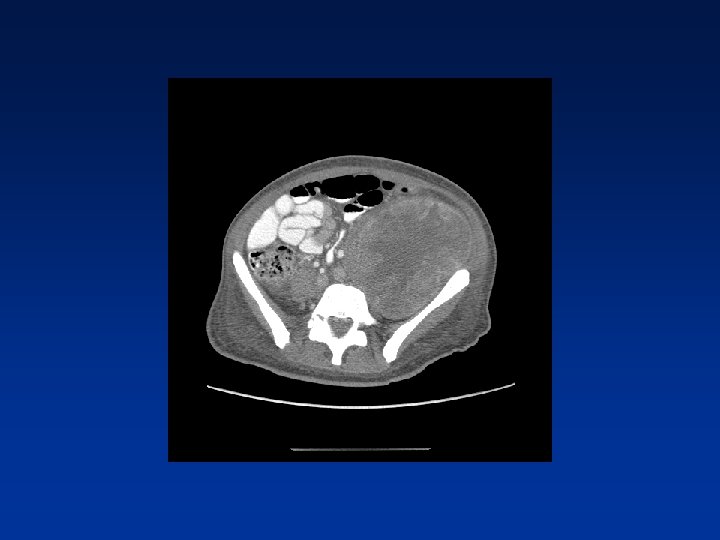
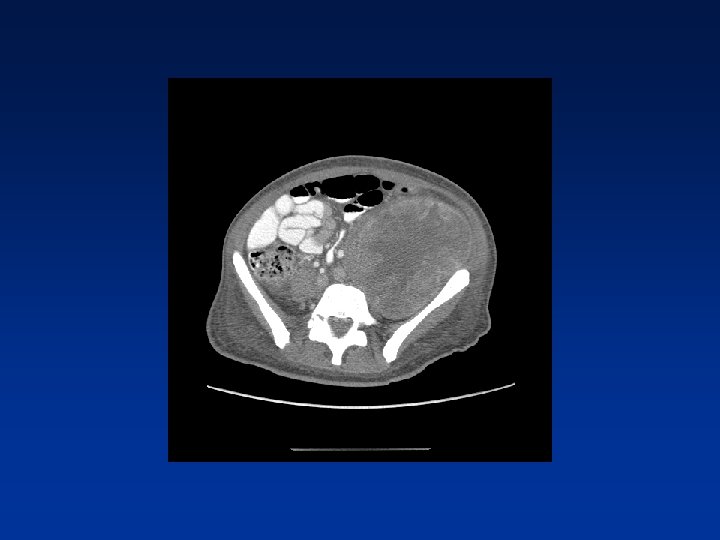
 Which factors alter clinical outcome? Patient factors…. NF-1 status? Tumor factors? Treatment related factors?
Which factors alter clinical outcome? Patient factors…. NF-1 status? Tumor factors? Treatment related factors?
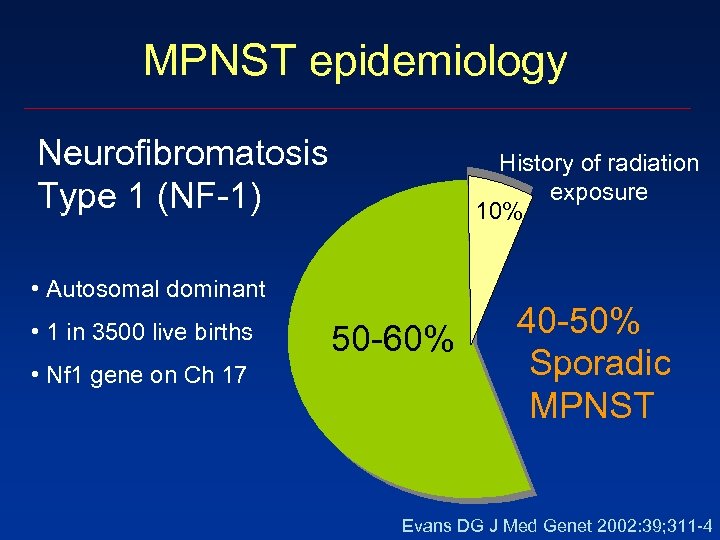 MPNST epidemiology Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF-1) History of radiation exposure 10% • Autosomal dominant • 1 in 3500 live births • Nf 1 gene on Ch 17 50 -60% 40 -50% Sporadic MPNST Evans DG J Med Genet 2002: 39; 311 -4
MPNST epidemiology Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF-1) History of radiation exposure 10% • Autosomal dominant • 1 in 3500 live births • Nf 1 gene on Ch 17 50 -60% 40 -50% Sporadic MPNST Evans DG J Med Genet 2002: 39; 311 -4
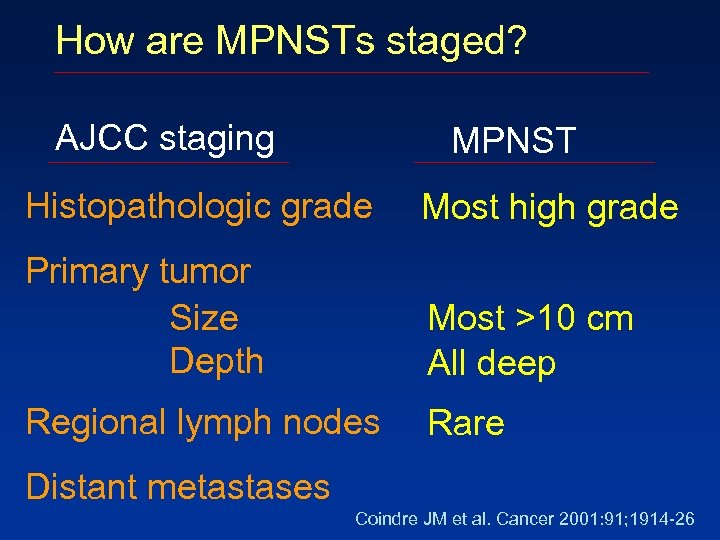 How are MPNSTs staged? AJCC staging MPNST Histopathologic grade Most high grade Primary tumor Size Depth Most >10 cm All deep Regional lymph nodes Rare Distant metastases Coindre JM et al. Cancer 2001: 91; 1914 -26
How are MPNSTs staged? AJCC staging MPNST Histopathologic grade Most high grade Primary tumor Size Depth Most >10 cm All deep Regional lymph nodes Rare Distant metastases Coindre JM et al. Cancer 2001: 91; 1914 -26
 There is a need to subclassify stage III MPNST
There is a need to subclassify stage III MPNST
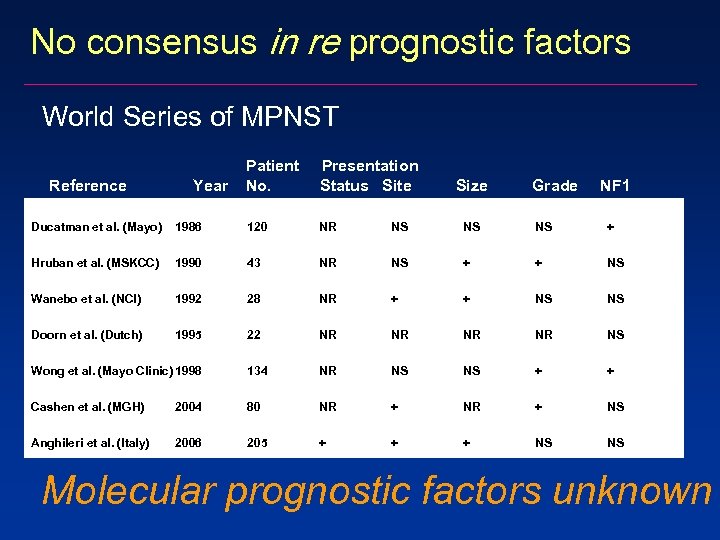 No consensus in re prognostic factors World Series of MPNST Reference Year Patient No. Presentation Status Site Size Grade NF 1 Ducatman et al. (Mayo) 1986 120 NR NS NS NS + Hruban et al. (MSKCC) 1990 43 NR NS + + NS Wanebo et al. (NCI) 1992 28 NR + + NS NS Doorn et al. (Dutch) 1995 22 NR NR NS Wong et al. (Mayo Clinic) 1998 134 NR NS NS + + Cashen et al. (MGH) 2004 80 NR + NS Anghileri et al. (Italy) 2006 205 + + + NS NS Molecular prognostic factors unknown
No consensus in re prognostic factors World Series of MPNST Reference Year Patient No. Presentation Status Site Size Grade NF 1 Ducatman et al. (Mayo) 1986 120 NR NS NS NS + Hruban et al. (MSKCC) 1990 43 NR NS + + NS Wanebo et al. (NCI) 1992 28 NR + + NS NS Doorn et al. (Dutch) 1995 22 NR NR NS Wong et al. (Mayo Clinic) 1998 134 NR NS NS + + Cashen et al. (MGH) 2004 80 NR + NS Anghileri et al. (Italy) 2006 205 + + + NS NS Molecular prognostic factors unknown
 Purpose To identify and validate tumor, pathologic and molecular factors prognostic of MPNST clinical behavior
Purpose To identify and validate tumor, pathologic and molecular factors prognostic of MPNST clinical behavior
 Methods • MDACC clinical database • Univariate and multivariate statistical analyses • MPNST tissue microarray
Methods • MDACC clinical database • Univariate and multivariate statistical analyses • MPNST tissue microarray
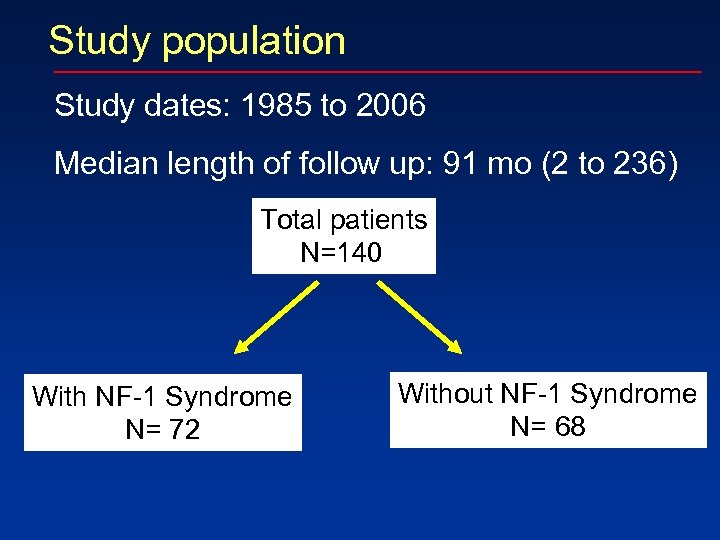 Study population Study dates: 1985 to 2006 Median length of follow up: 91 mo (2 to 236) Total patients N=140 With NF-1 Syndrome N= 72 Without NF-1 Syndrome N= 68
Study population Study dates: 1985 to 2006 Median length of follow up: 91 mo (2 to 236) Total patients N=140 With NF-1 Syndrome N= 72 Without NF-1 Syndrome N= 68
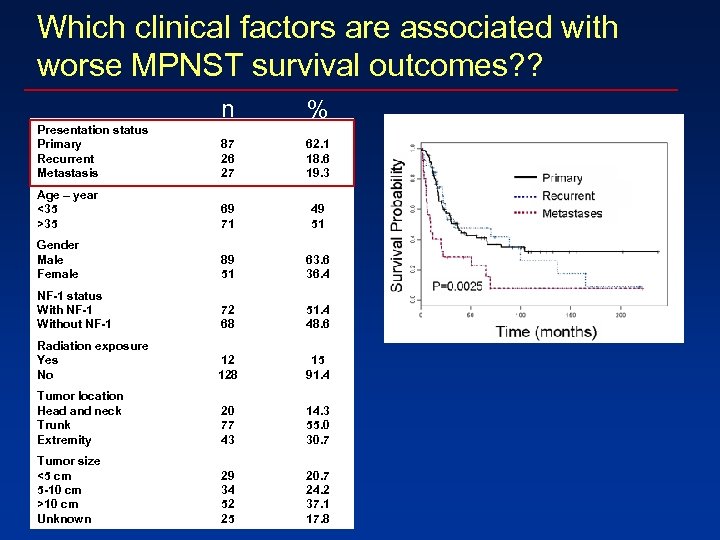 Which clinical factors are associated with worse MPNST survival outcomes? ? n % Presentation status Primary Recurrent Metastasis 87 26 27 62. 1 18. 6 19. 3 Age – year <35 >35 69 71 49 51 Gender Male Female 89 51 63. 6 36. 4 NF-1 status With NF-1 Without NF-1 72 68 51. 4 48. 6 Radiation exposure Yes No 12 128 15 91. 4 Tumor location Head and neck Trunk Extremity 20 77 43 14. 3 55. 0 30. 7 Tumor size <5 cm 5 -10 cm >10 cm Unknown 29 34 52 25 20. 7 24. 2 37. 1 17. 8
Which clinical factors are associated with worse MPNST survival outcomes? ? n % Presentation status Primary Recurrent Metastasis 87 26 27 62. 1 18. 6 19. 3 Age – year <35 >35 69 71 49 51 Gender Male Female 89 51 63. 6 36. 4 NF-1 status With NF-1 Without NF-1 72 68 51. 4 48. 6 Radiation exposure Yes No 12 128 15 91. 4 Tumor location Head and neck Trunk Extremity 20 77 43 14. 3 55. 0 30. 7 Tumor size <5 cm 5 -10 cm >10 cm Unknown 29 34 52 25 20. 7 24. 2 37. 1 17. 8
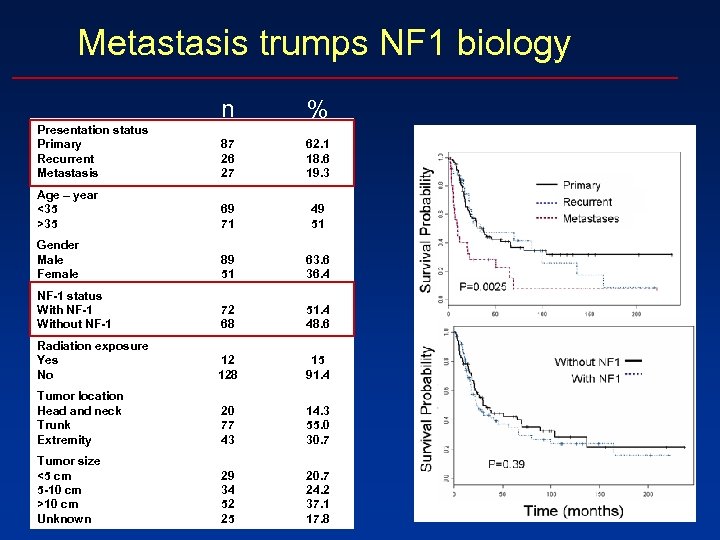 Metastasis trumps NF 1 biology n % Presentation status Primary Recurrent Metastasis 87 26 27 62. 1 18. 6 19. 3 Age – year <35 >35 69 71 49 51 Gender Male Female 89 51 63. 6 36. 4 NF-1 status With NF-1 Without NF-1 72 68 51. 4 48. 6 Radiation exposure Yes No 12 128 15 91. 4 Tumor location Head and neck Trunk Extremity 20 77 43 14. 3 55. 0 30. 7 Tumor size <5 cm 5 -10 cm >10 cm Unknown 29 34 52 25 20. 7 24. 2 37. 1 17. 8
Metastasis trumps NF 1 biology n % Presentation status Primary Recurrent Metastasis 87 26 27 62. 1 18. 6 19. 3 Age – year <35 >35 69 71 49 51 Gender Male Female 89 51 63. 6 36. 4 NF-1 status With NF-1 Without NF-1 72 68 51. 4 48. 6 Radiation exposure Yes No 12 128 15 91. 4 Tumor location Head and neck Trunk Extremity 20 77 43 14. 3 55. 0 30. 7 Tumor size <5 cm 5 -10 cm >10 cm Unknown 29 34 52 25 20. 7 24. 2 37. 1 17. 8
 What drives metastasis in patients with localized MPNST? ?
What drives metastasis in patients with localized MPNST? ?
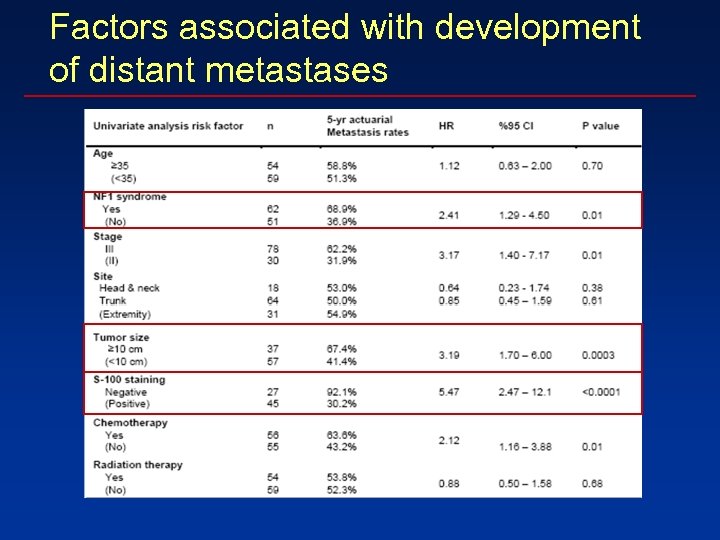 Factors associated with development of distant metastases
Factors associated with development of distant metastases
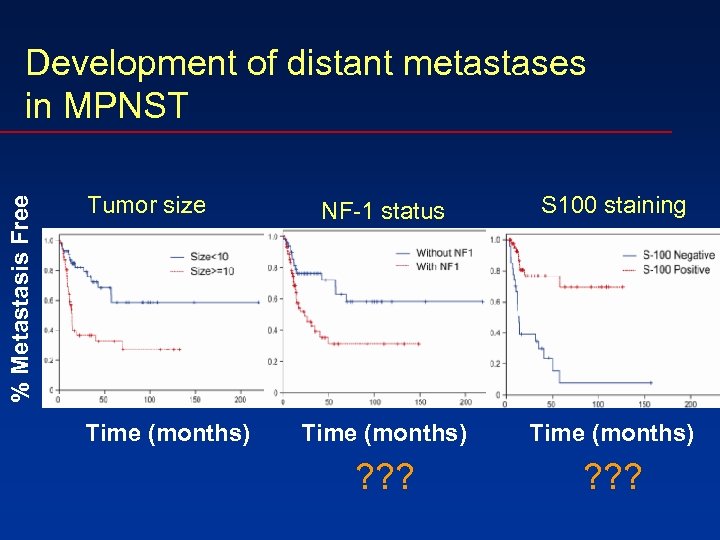 % Metastasis Free Development of distant metastases in MPNST Tumor size Time (months) NF-1 status S 100 staining Time (months) ? ? ?
% Metastasis Free Development of distant metastases in MPNST Tumor size Time (months) NF-1 status S 100 staining Time (months) ? ? ?
 What drives survival in localized MPNST?
What drives survival in localized MPNST?
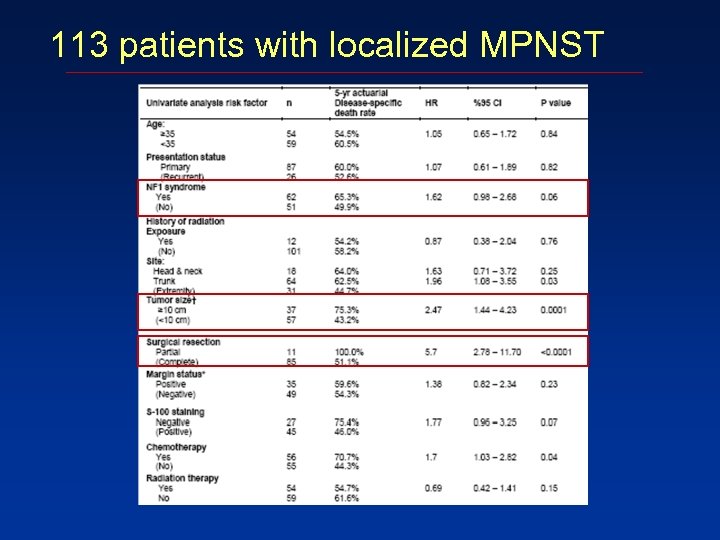 113 patients with localized MPNST
113 patients with localized MPNST
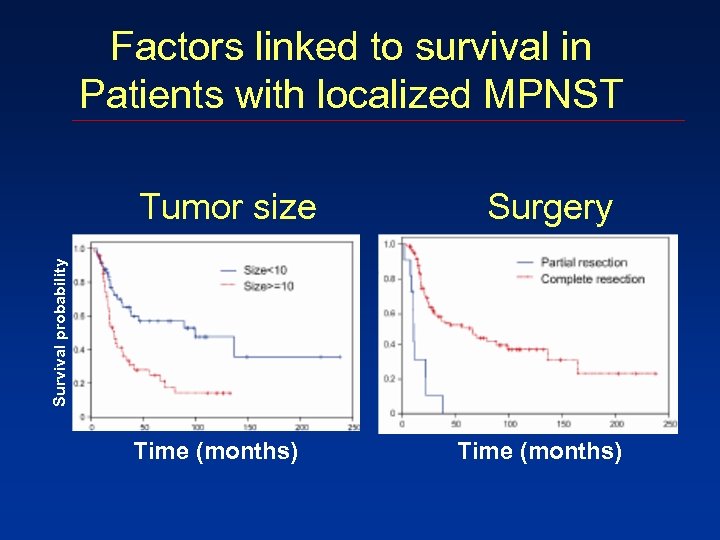 Factors linked to survival in Patients with localized MPNST Surgery Survival probability Tumor size Time (months)
Factors linked to survival in Patients with localized MPNST Surgery Survival probability Tumor size Time (months)
 What drives survival after complete surgical resection?
What drives survival after complete surgical resection?
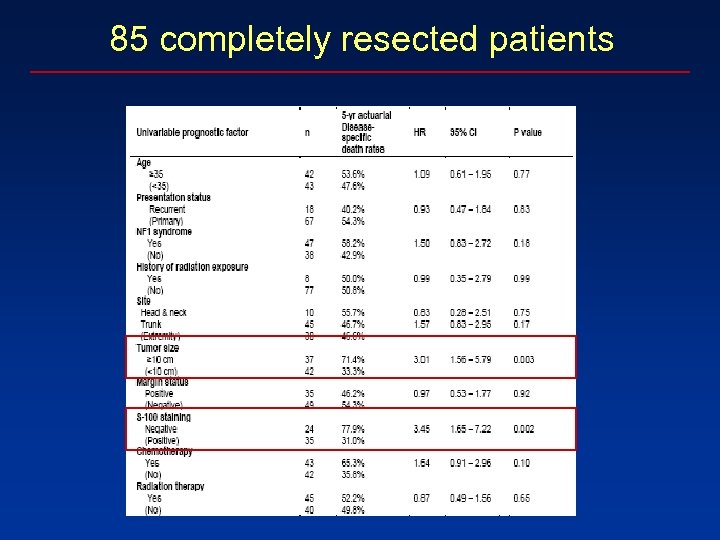 85 completely resected patients
85 completely resected patients
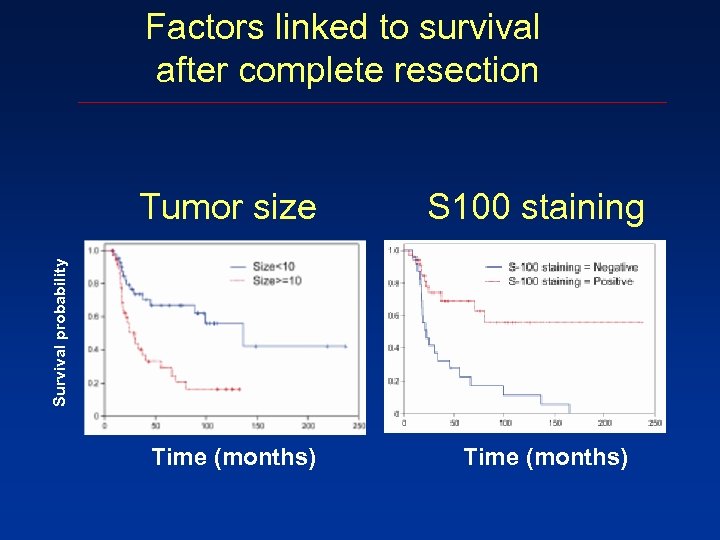 Factors linked to survival after complete resection S 100 staining Survival probability Tumor size Time (months)
Factors linked to survival after complete resection S 100 staining Survival probability Tumor size Time (months)
 Can molecular factors predict survival outcomes in MPNST? ?
Can molecular factors predict survival outcomes in MPNST? ?
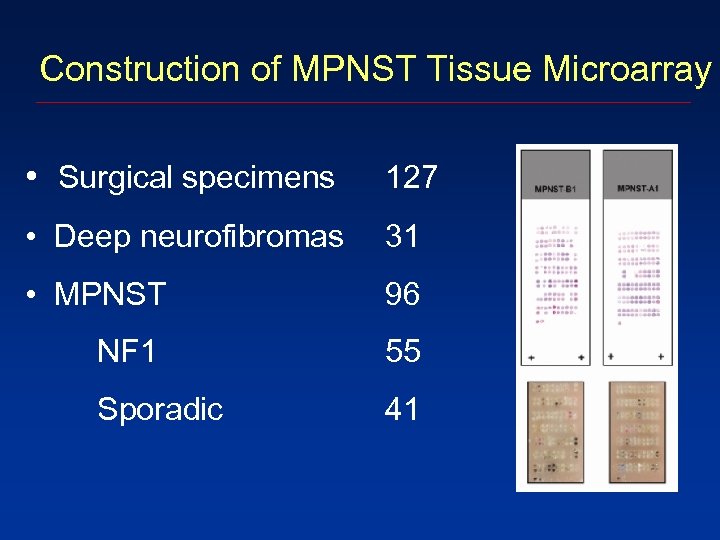 Construction of MPNST Tissue Microarray • Surgical specimens 127 • Deep neurofibromas 31 • MPNST 96 NF 1 55 Sporadic 41
Construction of MPNST Tissue Microarray • Surgical specimens 127 • Deep neurofibromas 31 • MPNST 96 NF 1 55 Sporadic 41
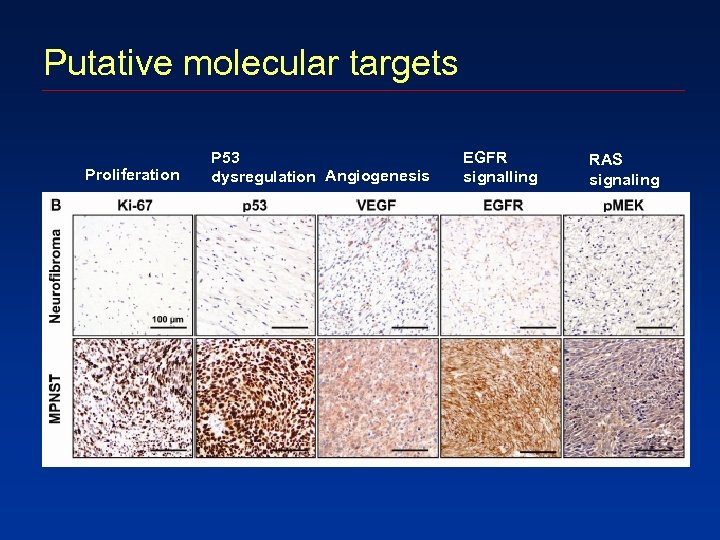 Putative molecular targets Proliferation P 53 dysregulation Angiogenesis EGFR signalling RAS signaling
Putative molecular targets Proliferation P 53 dysregulation Angiogenesis EGFR signalling RAS signaling
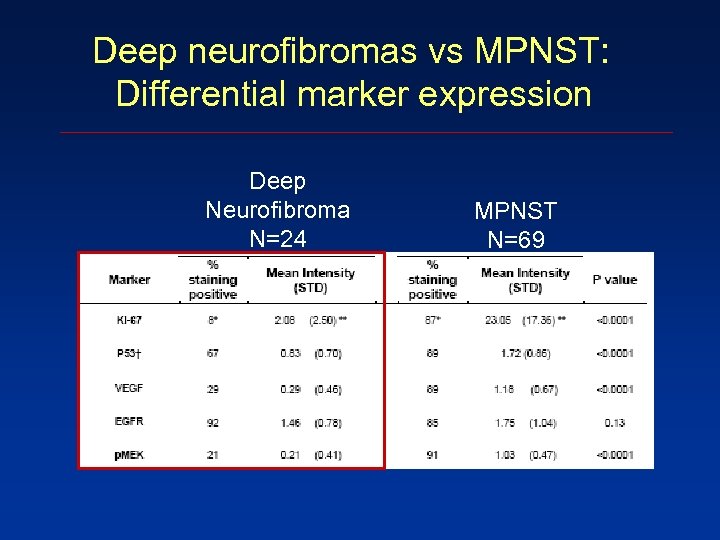 Deep neurofibromas vs MPNST: Differential marker expression Deep Neurofibroma N=24 MPNST N=69
Deep neurofibromas vs MPNST: Differential marker expression Deep Neurofibroma N=24 MPNST N=69
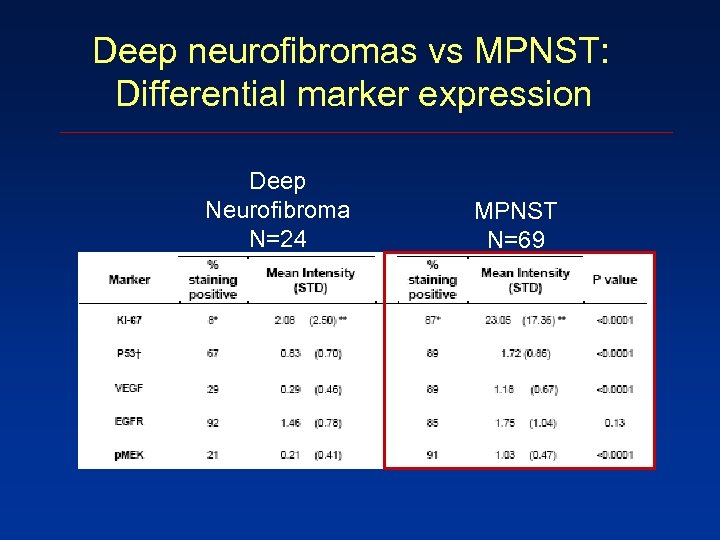 Deep neurofibromas vs MPNST: Differential marker expression Deep Neurofibroma N=24 MPNST N=69
Deep neurofibromas vs MPNST: Differential marker expression Deep Neurofibroma N=24 MPNST N=69
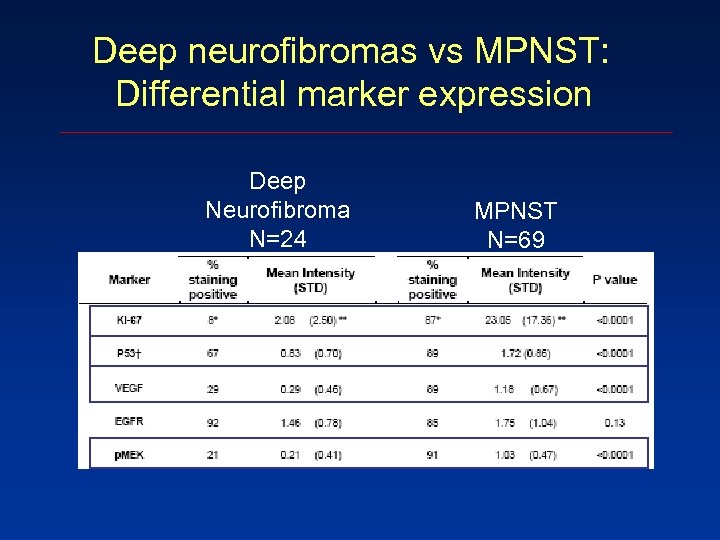 Deep neurofibromas vs MPNST: Differential marker expression Deep Neurofibroma N=24 MPNST N=69
Deep neurofibromas vs MPNST: Differential marker expression Deep Neurofibroma N=24 MPNST N=69
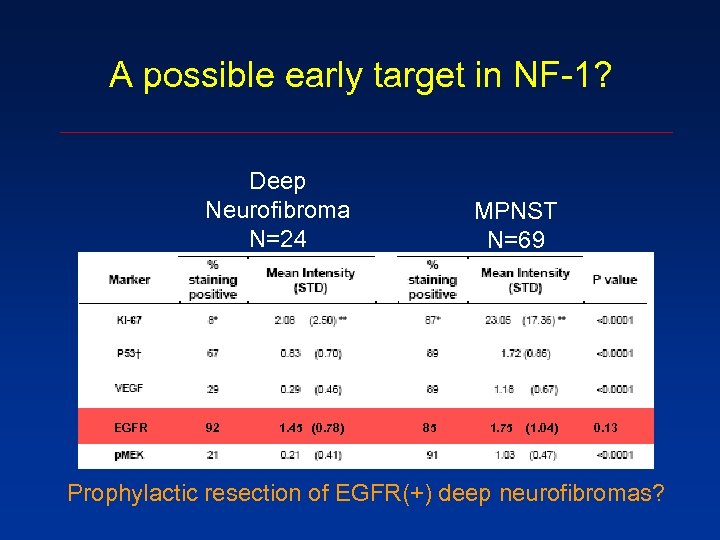 A possible early target in NF-1? Deep Neurofibroma N=24 EGFR 92 1. 45 (0. 78) MPNST N=69 85 1. 75 (1. 04) 0. 13 Prophylactic resection of EGFR(+) deep neurofibromas?
A possible early target in NF-1? Deep Neurofibroma N=24 EGFR 92 1. 45 (0. 78) MPNST N=69 85 1. 75 (1. 04) 0. 13 Prophylactic resection of EGFR(+) deep neurofibromas?
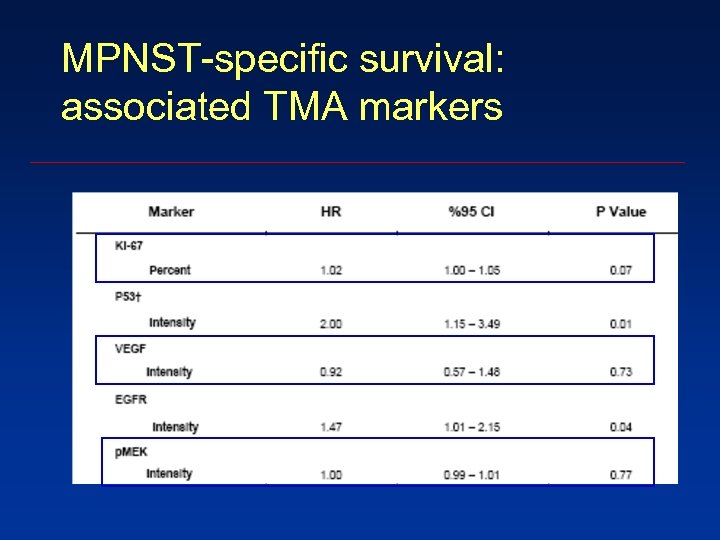 MPNST-specific survival: associated TMA markers
MPNST-specific survival: associated TMA markers
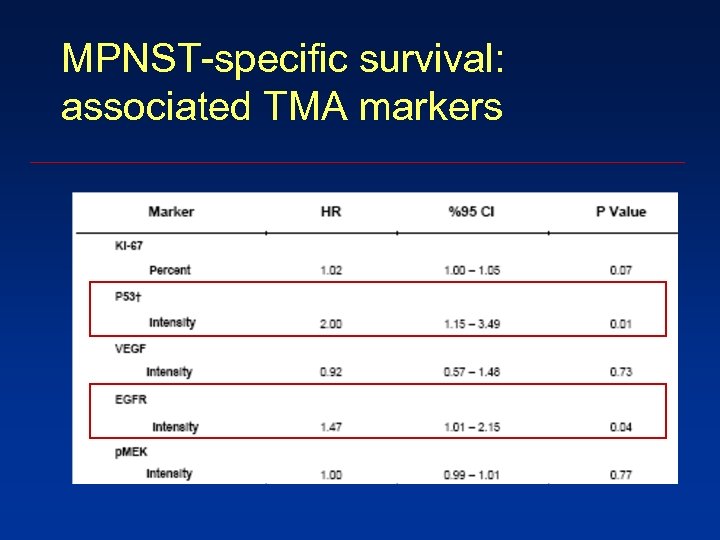 MPNST-specific survival: associated TMA markers
MPNST-specific survival: associated TMA markers
 Conclusions 1. MPNST patients presenting with metastasis 2. have significantly worse outcomes
Conclusions 1. MPNST patients presenting with metastasis 2. have significantly worse outcomes
 Conclusions 2. Tumor size, NF-1 status and loss of S 100 3. are linked to development of metastasis
Conclusions 2. Tumor size, NF-1 status and loss of S 100 3. are linked to development of metastasis
 Conclusions 3. Complete surgical resection is the dominant factor affecting survival of patients with localized MPNST
Conclusions 3. Complete surgical resection is the dominant factor affecting survival of patients with localized MPNST
 Conclusions 4. After a complete resection: Large tumor size Loss of S 100 staining Worse MPNST-specific survival
Conclusions 4. After a complete resection: Large tumor size Loss of S 100 staining Worse MPNST-specific survival
 Conclusions 5. EGFR and nuclear P 53 expression A worse MPNST-specific survival
Conclusions 5. EGFR and nuclear P 53 expression A worse MPNST-specific survival
 Acknowledgments Dina Lev Raphael Pollock Alexander Lazar Chang-Ye Zou Guy Lahat The UT MDACC Sarcoma Research Center
Acknowledgments Dina Lev Raphael Pollock Alexander Lazar Chang-Ye Zou Guy Lahat The UT MDACC Sarcoma Research Center
 Thank you for your attention Sunset over Houston, Texas
Thank you for your attention Sunset over Houston, Texas

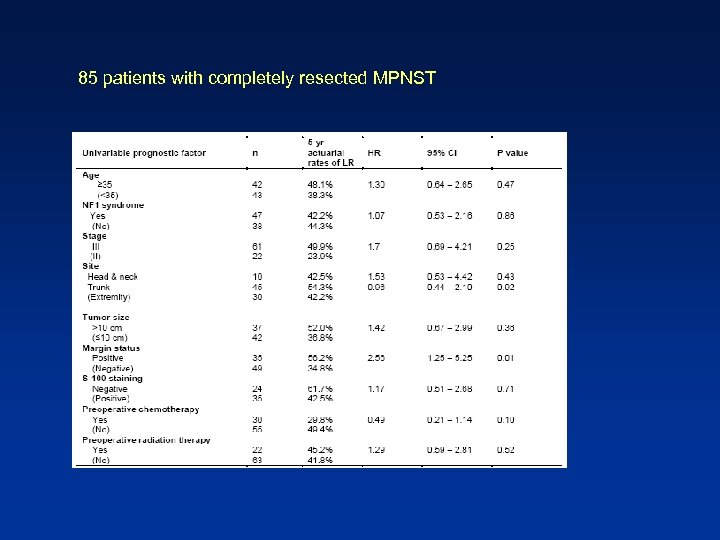 85 patients with completely resected MPNST
85 patients with completely resected MPNST


