232f3cba2ab3a86130164a74557fac45.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
 SAP IM vs. WM: How to Choose, Use, and Optimize Gavin Klaus Catalyst International, Inc.
SAP IM vs. WM: How to Choose, Use, and Optimize Gavin Klaus Catalyst International, Inc.
 What We’ll Cover … > Understanding the difference between WM and IM > Choosing between WM and IM > Optimizing and overcoming limitations with IM and WM
What We’ll Cover … > Understanding the difference between WM and IM > Choosing between WM and IM > Optimizing and overcoming limitations with IM and WM
 Inventory Management (IM) > Key features/strengths • Inventory management by quantity – Visibility of on-hand quantity by storage location – Management of special stocks • Entry and documentation of all material movements – Real-time updates of inventory – Documentation of all receipts, issues and transfers • Physical inventory – Carry out physical inventory at the material level – Perform inventory adjustments
Inventory Management (IM) > Key features/strengths • Inventory management by quantity – Visibility of on-hand quantity by storage location – Management of special stocks • Entry and documentation of all material movements – Real-time updates of inventory – Documentation of all receipts, issues and transfers • Physical inventory – Carry out physical inventory at the material level – Perform inventory adjustments
 R/3 Inventory Management (IM) (cont. ) > Key features/strengths (cont. ): • Inventory management by value – Postings update account assignments for cost accounting – Updates G/L account for financial accounting • Key integration points – Integrates directly with MRP, purchasing and invoice verification – Provides information for MRP, updates PO; used to check conformity during invoice verification • Real-time updates – When transactions are entered, the results the stock updates real time to reflect actual changes
R/3 Inventory Management (IM) (cont. ) > Key features/strengths (cont. ): • Inventory management by value – Postings update account assignments for cost accounting – Updates G/L account for financial accounting • Key integration points – Integrates directly with MRP, purchasing and invoice verification – Provides information for MRP, updates PO; used to check conformity during invoice verification • Real-time updates – When transactions are entered, the results the stock updates real time to reflect actual changes
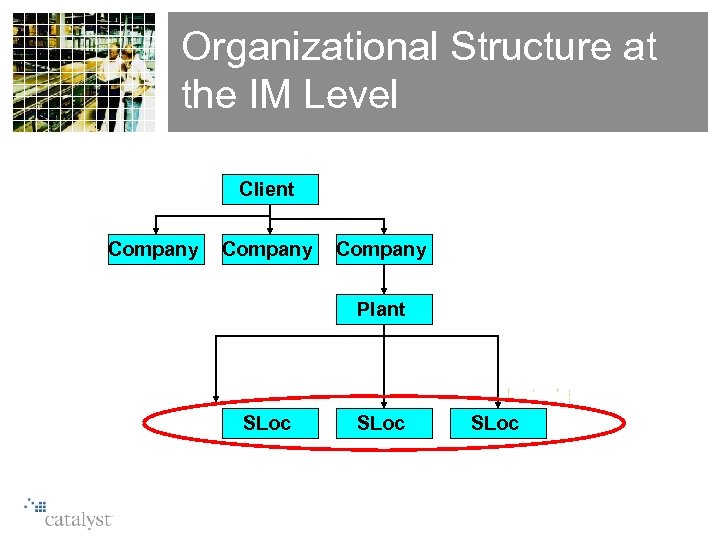 Organizational Structure at the IM Level SAP Organizational Structure Client Company Plant SLoc
Organizational Structure at the IM Level SAP Organizational Structure Client Company Plant SLoc
 Challenges with Inventory Management > Lack of detailed visibility to material flow • e. g. When the delivery pick list is generated, the delivery’s “actual pick quantity” is updated prior to actual picking • Requires manual updates when quantities differ > Inability to assign incoming materials to outbound demand to avoid multiple material handling continued. . .
Challenges with Inventory Management > Lack of detailed visibility to material flow • e. g. When the delivery pick list is generated, the delivery’s “actual pick quantity” is updated prior to actual picking • Requires manual updates when quantities differ > Inability to assign incoming materials to outbound demand to avoid multiple material handling continued. . .
 Challenges with Inventory Management (cont. ) > Immediate update of inventory receipts and issues • System inventory and status NOT representative of the physical process > Limited visibility to locations of materials • Only possible to assign a single fixed bin location per storage location • Bin location is “text” only; no strategies are available
Challenges with Inventory Management (cont. ) > Immediate update of inventory receipts and issues • System inventory and status NOT representative of the physical process > Limited visibility to locations of materials • Only possible to assign a single fixed bin location per storage location • Bin location is “text” only; no strategies are available
 Solution: R/3 Warehouse Management > Initially released with R/2 as an Extension of IM • IM-WM integration is real-time and automatic > Enables granular traceability and control • Ability to synchronize the system and material flow • Simple-to-complex placement and removal strategies • Assignment of inbound orders to outbound deliveries • Allocation of storage bins > Processing of all stock movements valid for WM • Receipts, issues, transfers • Utilizes stock placement and removal strategies – e. g. Next empty bin, addition to stock, FIFO, LG/SM qtys.
Solution: R/3 Warehouse Management > Initially released with R/2 as an Extension of IM • IM-WM integration is real-time and automatic > Enables granular traceability and control • Ability to synchronize the system and material flow • Simple-to-complex placement and removal strategies • Assignment of inbound orders to outbound deliveries • Allocation of storage bins > Processing of all stock movements valid for WM • Receipts, issues, transfers • Utilizes stock placement and removal strategies – e. g. Next empty bin, addition to stock, FIFO, LG/SM qtys.
 Solution: R/3 Warehouse Management (cont. ) > Infancy to maturity • Functionality considerably expanded with 4. 6 x and higher – Two-step picking, two-step confirmation, managing multiple storage locations with a single warehouse • Extension set 2. 0 for Enterprise to include Cross Docking, Yard Management, Value Added Services
Solution: R/3 Warehouse Management (cont. ) > Infancy to maturity • Functionality considerably expanded with 4. 6 x and higher – Two-step picking, two-step confirmation, managing multiple storage locations with a single warehouse • Extension set 2. 0 for Enterprise to include Cross Docking, Yard Management, Value Added Services
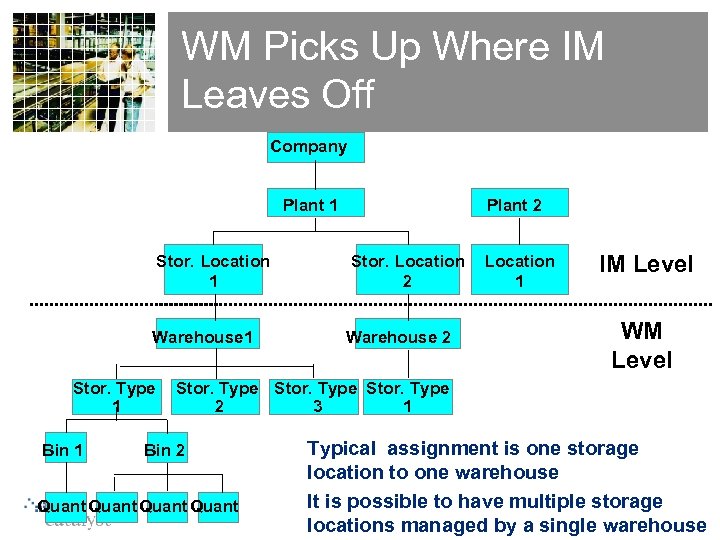 WM Picks Up Where IM Leaves Off Company Plant 1 Stor. Location 1 Warehouse 1 Stor. Type 1 Bin 1 Plant 2 Stor. Location 2 Warehouse 2 Location 1 IM Level WM Level Stor. Type 2 3 1 Bin 2 Quant Typical assignment is one storage location to one warehouse It is possible to have multiple storage locations managed by a single warehouse
WM Picks Up Where IM Leaves Off Company Plant 1 Stor. Location 1 Warehouse 1 Stor. Type 1 Bin 1 Plant 2 Stor. Location 2 Warehouse 2 Location 1 IM Level WM Level Stor. Type 2 3 1 Bin 2 Quant Typical assignment is one storage location to one warehouse It is possible to have multiple storage locations managed by a single warehouse
 Key WM Features > Management of materials • Provides bin-level tracking • Inventory management functions • Various placement and removal strategies > Value-added services • e. g. Special handling requirements (labeling, packaging) > Powerful picking control • Two-step picking, wave picking • FIFO, LIFO, large/small quantity picking strategies
Key WM Features > Management of materials • Provides bin-level tracking • Inventory management functions • Various placement and removal strategies > Value-added services • e. g. Special handling requirements (labeling, packaging) > Powerful picking control • Two-step picking, wave picking • FIFO, LIFO, large/small quantity picking strategies
 Key WM Features (cont. ) > Warehouse activity monitors • WAM, RF Monitor, outbound delivery monitor, wave picking monitor, TRM Monitor, Yard Management Cockpit, Cross. Docking Monitor > Cross-docking • Management of inbound and outbound movements > Yard Management • Appointment scheduling, check in and check out, assignment of dock doors, loading/unloading activities > Task Resource Management • Enhances WM by breaking work down into distinct task
Key WM Features (cont. ) > Warehouse activity monitors • WAM, RF Monitor, outbound delivery monitor, wave picking monitor, TRM Monitor, Yard Management Cockpit, Cross. Docking Monitor > Cross-docking • Management of inbound and outbound movements > Yard Management • Appointment scheduling, check in and check out, assignment of dock doors, loading/unloading activities > Task Resource Management • Enhances WM by breaking work down into distinct task
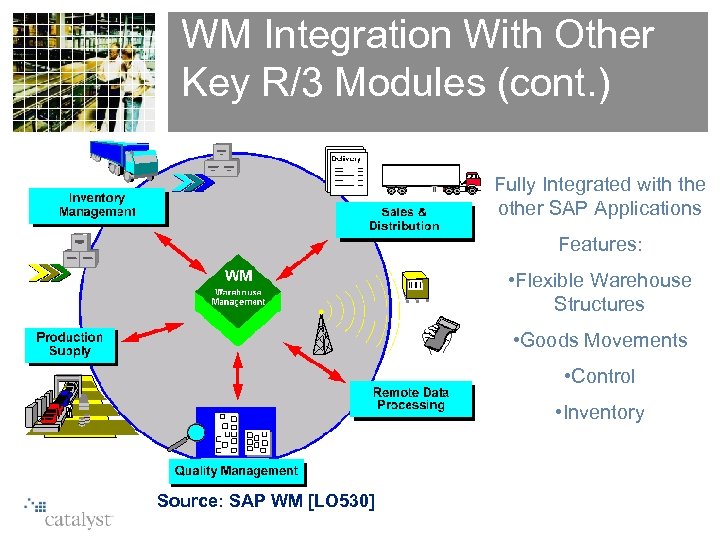 WM Integration With Other Key R/3 Modules (cont. ) Fully Integrated with the other SAP Applications Features: • Flexible Warehouse Structures • Goods Movements • Control • Inventory Source: SAP WM [LO 530]
WM Integration With Other Key R/3 Modules (cont. ) Fully Integrated with the other SAP Applications Features: • Flexible Warehouse Structures • Goods Movements • Control • Inventory Source: SAP WM [LO 530]
 WM Integration With Other Key R/3 Modules (cont. ) > IM-WM • Processing of all material movements • Automated communication with configurable processing > SD-WM • Two-step picking with SD-WM integration • Wave picking opportunities • Processing individual deliveries > PP-WM • Production support with PP-WM integration • Supplying materials to the shop floor • Internal and external automated replenishment options
WM Integration With Other Key R/3 Modules (cont. ) > IM-WM • Processing of all material movements • Automated communication with configurable processing > SD-WM • Two-step picking with SD-WM integration • Wave picking opportunities • Processing individual deliveries > PP-WM • Production support with PP-WM integration • Supplying materials to the shop floor • Internal and external automated replenishment options
 WM Integration With Other Key R/3 Modules (cont. ) QM-WM • Handling of inventory samples • Inspection lot is maintained with the material data Hand-held terminals-WM • Processing of transfer requirements • Processing of transfer orders • Bin and material inquiries
WM Integration With Other Key R/3 Modules (cont. ) QM-WM • Handling of inventory samples • Inspection lot is maintained with the material data Hand-held terminals-WM • Processing of transfer requirements • Processing of transfer orders • Bin and material inquiries
 Benefits of WM > Benefits • Better control of inventory – More accurate inventory – Able to maintain lower inventory levels • Better control of information – Visibility to picking and put away status • Reduced cycle time – Gartner: 16 -25% Picking Productivity Improvement • Better manage work and workforce to gain efficiencies – Tools to balance and optimize resources • Increased picking / shipping accuracy – 11 -25% Reduction in Customer Returns
Benefits of WM > Benefits • Better control of inventory – More accurate inventory – Able to maintain lower inventory levels • Better control of information – Visibility to picking and put away status • Reduced cycle time – Gartner: 16 -25% Picking Productivity Improvement • Better manage work and workforce to gain efficiencies – Tools to balance and optimize resources • Increased picking / shipping accuracy – 11 -25% Reduction in Customer Returns
 Benefits of WM (cont. ) > Measurable benefits • 16 -25% Picking Productivity Improvement • 11 -25% Reduction in Customer Returns • 10 -25% Savings in Material Handling Labor • 10 -40% Space Utilization Improvement • 13 -30% Reduction in Scrap • 8 -15% Reduction in Carrying Costs Source: Gartner Report
Benefits of WM (cont. ) > Measurable benefits • 16 -25% Picking Productivity Improvement • 11 -25% Reduction in Customer Returns • 10 -25% Savings in Material Handling Labor • 10 -40% Space Utilization Improvement • 13 -30% Reduction in Scrap • 8 -15% Reduction in Carrying Costs Source: Gartner Report
 What We’ll Cover … > Understanding the difference between WM and IM > Choosing between WM and IM > Optimizing and overcoming limitations with IM and WM
What We’ll Cover … > Understanding the difference between WM and IM > Choosing between WM and IM > Optimizing and overcoming limitations with IM and WM
 When Is Inventory Management the Answer? > IM is great when. . . • Small facility • Lower levels of inventory on hand • Simplistic material handling processes • Lower volume of activity • Outsourced warehouse operations – Only need storage location or bucket of inventory visibility
When Is Inventory Management the Answer? > IM is great when. . . • Small facility • Lower levels of inventory on hand • Simplistic material handling processes • Lower volume of activity • Outsourced warehouse operations – Only need storage location or bucket of inventory visibility
 Key Elements With IM > Required data for IM • Plant, valuation and storage location data > Relevant data for IM • Work scheduling, accounting, materials planning, purchasing, classification, storage and quality management > IM menu • Goods movements • Material documents • Reservations • Environment – Focused on reporting, lists and LIS
Key Elements With IM > Required data for IM • Plant, valuation and storage location data > Relevant data for IM • Work scheduling, accounting, materials planning, purchasing, classification, storage and quality management > IM menu • Goods movements • Material documents • Reservations • Environment – Focused on reporting, lists and LIS
 When is Warehouse Management the Answer? > WM is great when • Larger facilities • Large number of materials on hand • Higher volume or flow through • Traceability and visibility is critical – Track material flow, status, inventory levels • Complex processes – Automated systems, wide spread site
When is Warehouse Management the Answer? > WM is great when • Larger facilities • Large number of materials on hand • Higher volume or flow through • Traceability and visibility is critical – Track material flow, status, inventory levels • Complex processes – Automated systems, wide spread site
 Key Elements With WM > Extend material master • Warehouse management view • No required data > Define warehouse structure • Minimize the number of storage types – Define based on similar and different rules for storing materials – Mixed stock, Storage or Handling Unit Management > Define the WM Processes • Automatic, semi-automatic and manual processing – Transfer order creation, confirmation, posting changes
Key Elements With WM > Extend material master • Warehouse management view • No required data > Define warehouse structure • Minimize the number of storage types – Define based on similar and different rules for storing materials – Mixed stock, Storage or Handling Unit Management > Define the WM Processes • Automatic, semi-automatic and manual processing – Transfer order creation, confirmation, posting changes
 Evaluating IM vs. WM > 1 – Define business processes > 2 – Evaluate ROI of a WMS solution > 3 – Consider RF functionality > 4 – Training resources and schedule > 5 – Focus on optimization opportunities
Evaluating IM vs. WM > 1 – Define business processes > 2 – Evaluate ROI of a WMS solution > 3 – Consider RF functionality > 4 – Training resources and schedule > 5 – Focus on optimization opportunities
 Step 1 - Define Business Processes > Start with receiving, inventory and pick/ship first • Create and evaluate process flow charts • Look at process improvement opportunities • Score the level of complexity > Target areas for improvement • Reduce travel time • Inventory accuracy • Reduce material handling > Map improvements to IM and WM functionality
Step 1 - Define Business Processes > Start with receiving, inventory and pick/ship first • Create and evaluate process flow charts • Look at process improvement opportunities • Score the level of complexity > Target areas for improvement • Reduce travel time • Inventory accuracy • Reduce material handling > Map improvements to IM and WM functionality
 1 - Define Business Processes (cont. ) > “The level of functionality that customers need in a WMS is completely dependent upon their environment. Customers have to define their needs before they can realistically look for a WMS. ” Source: Integrated Solutions
1 - Define Business Processes (cont. ) > “The level of functionality that customers need in a WMS is completely dependent upon their environment. Customers have to define their needs before they can realistically look for a WMS. ” Source: Integrated Solutions
 Step 2 - Evaluate ROI of a WMS Solution > Measure productivity and accuracy before and after the WMS installation > Review and analyze picking operations • Key area of improvement > Review and analyze inventory accuracy • When supported with RF, accuracy can reach >98%
Step 2 - Evaluate ROI of a WMS Solution > Measure productivity and accuracy before and after the WMS installation > Review and analyze picking operations • Key area of improvement > Review and analyze inventory accuracy • When supported with RF, accuracy can reach >98%
 2 - Evaluate ROI of a WMS Solution (cont. ) > “There is no ‘right’ time for paying back a WMS, but typical paybacks are within six to 18 months, depending on the inefficiencies of the current operation and how much safety stock was needed to cover daily operations. ” Source: Total Supply Chain
2 - Evaluate ROI of a WMS Solution (cont. ) > “There is no ‘right’ time for paying back a WMS, but typical paybacks are within six to 18 months, depending on the inefficiencies of the current operation and how much safety stock was needed to cover daily operations. ” Source: Total Supply Chain
 Step 3 - Consider RF Functionality > RF supports improves warehouse bin accuracy • Bin accuracy >98% is possible > Reduces order fill process cycle time > RF projects often have a 1 year or less payback period Source: Intermec Compare current receipt process to the time saved when the task is aided by automatic data collection (ADC)
Step 3 - Consider RF Functionality > RF supports improves warehouse bin accuracy • Bin accuracy >98% is possible > Reduces order fill process cycle time > RF projects often have a 1 year or less payback period Source: Intermec Compare current receipt process to the time saved when the task is aided by automatic data collection (ADC)
 3 - Consider RF Functionality: Example > As-is • 1, 000 pallets at five minutes / pallet = 5, 000 minutes > With two minutes saved per pallet • 2 minutes * 1, 000 pallets = 2, 000 minutes • 2, 000 / 480 minutes worked by each receiver per day = 4. 16 receivers saved from the pallet receiving process
3 - Consider RF Functionality: Example > As-is • 1, 000 pallets at five minutes / pallet = 5, 000 minutes > With two minutes saved per pallet • 2 minutes * 1, 000 pallets = 2, 000 minutes • 2, 000 / 480 minutes worked by each receiver per day = 4. 16 receivers saved from the pallet receiving process
 Step 4 - Training Resources and Schedule > Resources to evaluate, guide and support a WM solution • A full-time, dedicated WM resource is critical • This may or may not be the same IM resource > Training schedule • A WM solution will require a certain level of IM training • WM training will vary based on the degree of functionality > Support resources • Consider a single resource for IM and WM if possible
Step 4 - Training Resources and Schedule > Resources to evaluate, guide and support a WM solution • A full-time, dedicated WM resource is critical • This may or may not be the same IM resource > Training schedule • A WM solution will require a certain level of IM training • WM training will vary based on the degree of functionality > Support resources • Consider a single resource for IM and WM if possible
 5 - Optimization Opportunities > Picking operations and inventory accuracy • What are your baseline requirements • What is the volume of activity • Evaluate picking paths and demand • Look at your accuracy numbers over a period of time – Perhaps monthly, quarterly, annually > Material handling labor costs > Space utilization improvements > Packing tasks • Can you benefit from packing while picking
5 - Optimization Opportunities > Picking operations and inventory accuracy • What are your baseline requirements • What is the volume of activity • Evaluate picking paths and demand • Look at your accuracy numbers over a period of time – Perhaps monthly, quarterly, annually > Material handling labor costs > Space utilization improvements > Packing tasks • Can you benefit from packing while picking
 What is the BEST Stock Management Solution? > 1 - Inventory Management > 2 - Lean Warehouse Management > 3 - Full Warehouse Management > 4 - Decentralized Warehouse Management
What is the BEST Stock Management Solution? > 1 - Inventory Management > 2 - Lean Warehouse Management > 3 - Full Warehouse Management > 4 - Decentralized Warehouse Management
 Option #1 - Inventory Management > Pro’s • Simplistic – Key receipt, issue or transfer in a single step transaction – Immediate update of inventory • Requires less training commitment – Fewer transactions to document and present • Trace-ability of all material postings into SAP R/3 – Date, user, material, quantity, storage location • Real-time update of accounting information
Option #1 - Inventory Management > Pro’s • Simplistic – Key receipt, issue or transfer in a single step transaction – Immediate update of inventory • Requires less training commitment – Fewer transactions to document and present • Trace-ability of all material postings into SAP R/3 – Date, user, material, quantity, storage location • Real-time update of accounting information
 1 - Inventory Management (cont. ) > Con’s • Does not handle complex warehouses operations well – Unable to monitor activities – Lacks tools to manage resources and tasks – Lacks functionality to optimize key processes (picking) • Inaccurate system inventory – Inventory updated before the physical movement – Requires additional work if there are discrepancies • Limited trace-ability – Only visibility is when the system posting took place – No visibility to the follow on physical activities
1 - Inventory Management (cont. ) > Con’s • Does not handle complex warehouses operations well – Unable to monitor activities – Lacks tools to manage resources and tasks – Lacks functionality to optimize key processes (picking) • Inaccurate system inventory – Inventory updated before the physical movement – Requires additional work if there are discrepancies • Limited trace-ability – Only visibility is when the system posting took place – No visibility to the follow on physical activities
 Option #2 - “Lean” Warehouse Management > Use of very small portion of WM capabilities • You do not process goods receipts or issues as a subsequent process in WM, • No storage bins are managed in the WM application > Evolved from SD pick list > Put-away and pick from 1 or more fixed bins > Bin is hard assigned on material master > TO’s are created for picks and put away, and pick list is created from TO’s
Option #2 - “Lean” Warehouse Management > Use of very small portion of WM capabilities • You do not process goods receipts or issues as a subsequent process in WM, • No storage bins are managed in the WM application > Evolved from SD pick list > Put-away and pick from 1 or more fixed bins > Bin is hard assigned on material master > TO’s are created for picks and put away, and pick list is created from TO’s
 2 - “Lean” Warehouse Management (cont. ) > Pro’s • Requires less configuration than full WM • Reduced number of steps in the process – Use of transfer orders as pick lists – Confirmation is not required • Additional processing options – Confirm put-away, picking, over-deliveries, shortages, batches – Print transfer orders – Integration to HR • Additional picking functionality – Wave picking is possible with Lean WM
2 - “Lean” Warehouse Management (cont. ) > Pro’s • Requires less configuration than full WM • Reduced number of steps in the process – Use of transfer orders as pick lists – Confirmation is not required • Additional processing options – Confirm put-away, picking, over-deliveries, shortages, batches – Print transfer orders – Integration to HR • Additional picking functionality – Wave picking is possible with Lean WM
 2 - “Lean” Warehouse Management (cont. ) > Con’s • Must have a fixed bin assigned for all materials – Random storage is not possible • Inventory is still under IM functionality only – Inventory options are at the storage location – Stock differences can only be processed in MM-IM • Lacks additional optimization opportunities – Picking, packing, bin accuracy • No strategies are used – Lack of picking and put away strategies
2 - “Lean” Warehouse Management (cont. ) > Con’s • Must have a fixed bin assigned for all materials – Random storage is not possible • Inventory is still under IM functionality only – Inventory options are at the storage location – Stock differences can only be processed in MM-IM • Lacks additional optimization opportunities – Picking, packing, bin accuracy • No strategies are used – Lack of picking and put away strategies
 Option #3 - Full Warehouse Management > Pro’s • Optimization opportunities – Picking - Two step picking – Packing - Pick and pack in a single step – Cross-docking - Inbound, outbound, prod. materials • Monitoring and real time visibility to process status – Visual queues at the detailed steps – Open tasks, completed tasks • Additional inventory methods (annual, zero stock) • The module is FREE with the purchase of SAP
Option #3 - Full Warehouse Management > Pro’s • Optimization opportunities – Picking - Two step picking – Packing - Pick and pack in a single step – Cross-docking - Inbound, outbound, prod. materials • Monitoring and real time visibility to process status – Visual queues at the detailed steps – Open tasks, completed tasks • Additional inventory methods (annual, zero stock) • The module is FREE with the purchase of SAP
 3 - Full Warehouse Management (cont. ) > Con’s • Inventory counting interferes with operations without RF – Prior to 4. 7 extension set 2. 0 • Initial overhead to set up depending on design – Master data – Capacity checking, control cycles – Configuration requirements – Designing the warehouse layout and set up • Potential for additional steps to support processing – Confirmations – Clearing differences – Processing posting changes
3 - Full Warehouse Management (cont. ) > Con’s • Inventory counting interferes with operations without RF – Prior to 4. 7 extension set 2. 0 • Initial overhead to set up depending on design – Master data – Capacity checking, control cycles – Configuration requirements – Designing the warehouse layout and set up • Potential for additional steps to support processing – Confirmations – Clearing differences – Processing posting changes
 Option #4 - Decentralized Warehouse Management > Use of SAP as a standalone WMS • With SAP or other ERP/host as the core system • Core system and decentralized WM run on separate machines > Communication is through BAPI’s for transactions and IDOC’s for master data > Goods movements done through delivery notes to the stand-alone SAP WM system
Option #4 - Decentralized Warehouse Management > Use of SAP as a standalone WMS • With SAP or other ERP/host as the core system • Core system and decentralized WM run on separate machines > Communication is through BAPI’s for transactions and IDOC’s for master data > Goods movements done through delivery notes to the stand-alone SAP WM system
 4 - Decentralized Warehouse Management (cont. ) > Pro’s • On a separate machine – Decreases criticality of down time – 24 x 7 operation • Can leverage newer SAP R/3 releases – Even if core system is on an older release • Can additional warehouses without impact to the core system • Can communicate to multiple core ERP systems
4 - Decentralized Warehouse Management (cont. ) > Pro’s • On a separate machine – Decreases criticality of down time – 24 x 7 operation • Can leverage newer SAP R/3 releases – Even if core system is on an older release • Can additional warehouses without impact to the core system • Can communicate to multiple core ERP systems
 4 - Decentralized Warehouse Management (cont. ) > Con’s • Core system is not 24 x 7 operation – IDOC and/or BAPI errors • IDOC failures – Human intervention is required to work the error queue • IDOC overhead – IDOC’s do not offer all of the available field options that a user may or may not use with the PC transaction – Must modify the IDOC • SAPConsole has to be set up in the decentralized system and in the core system
4 - Decentralized Warehouse Management (cont. ) > Con’s • Core system is not 24 x 7 operation – IDOC and/or BAPI errors • IDOC failures – Human intervention is required to work the error queue • IDOC overhead – IDOC’s do not offer all of the available field options that a user may or may not use with the PC transaction – Must modify the IDOC • SAPConsole has to be set up in the decentralized system and in the core system
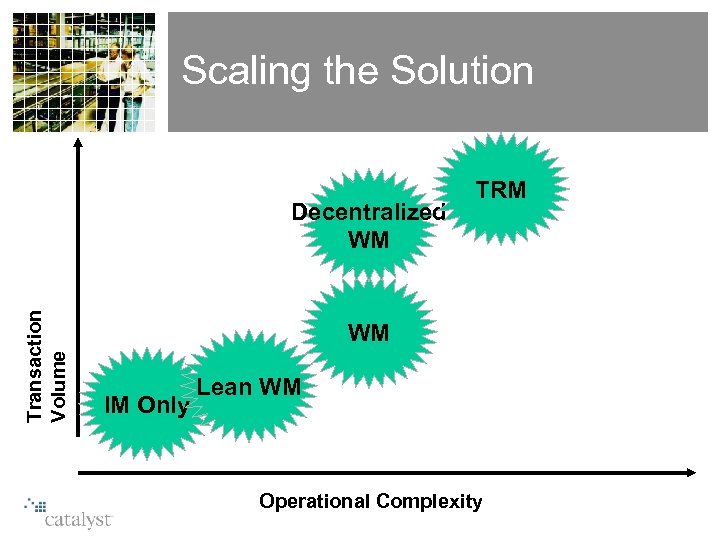 Scaling the Solution Transaction Volume Decentralized WM TRM WM IM Only Lean WM Operational Complexity
Scaling the Solution Transaction Volume Decentralized WM TRM WM IM Only Lean WM Operational Complexity
 What We’ll Cover … > Understanding the difference between WM and IM > Choosing between WM and IM > Optimizing and overcoming limitations with IM and WM
What We’ll Cover … > Understanding the difference between WM and IM > Choosing between WM and IM > Optimizing and overcoming limitations with IM and WM
 Optimizing and Overcoming Limitations With IM and WM > 1 - Physical Inventory tips > 2 - Enhance visibility of material flow and locations > 3 - Automate picking and put-away > 4 - Automatically replenish fixed bins > 5 - Consolidate your picking activities > 6 - Overcome bottlenecks with RF
Optimizing and Overcoming Limitations With IM and WM > 1 - Physical Inventory tips > 2 - Enhance visibility of material flow and locations > 3 - Automate picking and put-away > 4 - Automatically replenish fixed bins > 5 - Consolidate your picking activities > 6 - Overcome bottlenecks with RF
 1 - Physical Inventory Tips (IM) > Only possible if the storage location data has been maintained • Solution: Activate automatic storage location for movement types that receive material into the plant – Avoids the need to create storage data manually > For materials with multiple storage location reqmts. • Use the mass creation option for entering all valid storage locations at one time into a single entry screen – Transaction code = MMSC
1 - Physical Inventory Tips (IM) > Only possible if the storage location data has been maintained • Solution: Activate automatic storage location for movement types that receive material into the plant – Avoids the need to create storage data manually > For materials with multiple storage location reqmts. • Use the mass creation option for entering all valid storage locations at one time into a single entry screen – Transaction code = MMSC
 2 - Enhance Visibility of Material Flow and Locations (IM) > Use fixed bin assignment to gain additional visibility • Material master storage location view > Two-step transfers vs. one-step movements • Storage location-to-storage location (movements 313, 315) • Plant-to-plant (movements 303, 305, 351, 352) > Outbound delivery monitor • Use to view outbound deliveries, shipments and loading activities
2 - Enhance Visibility of Material Flow and Locations (IM) > Use fixed bin assignment to gain additional visibility • Material master storage location view > Two-step transfers vs. one-step movements • Storage location-to-storage location (movements 313, 315) • Plant-to-plant (movements 303, 305, 351, 352) > Outbound delivery monitor • Use to view outbound deliveries, shipments and loading activities
 3 - Automate Picking and Put -away (WM) > Define a picking strategy per storage type • A - Partial quantity management – If picking results in partial quantities, pick from here first to avoid breaking new pallets • M - Large/small quantities included – Use to facilitate larger quantity picks from bulk areas and smaller quantity picks from rack areas • P - Fixed bin from material master – For fast moving items, assign a dedication location toward the front of the warehouse – Use replenishment to enough maintain stock for demand
3 - Automate Picking and Put -away (WM) > Define a picking strategy per storage type • A - Partial quantity management – If picking results in partial quantities, pick from here first to avoid breaking new pallets • M - Large/small quantities included – Use to facilitate larger quantity picks from bulk areas and smaller quantity picks from rack areas • P - Fixed bin from material master – For fast moving items, assign a dedication location toward the front of the warehouse – Use replenishment to enough maintain stock for demand
 3 - Automate Picking and Put -away (WM) (cont. ) > Define a put away strategy per storage type • AVOID manual put away practices • C - Open storage – Use for large items that don’t require a specific bin assignment • I - Addition to existing stock – Useful for consolidating receipts of the same material upon put-away – Caution: Since only one quant resides in a bin, all materials in the bin adopt the same receipt date (unless batch or storage unit managed)
3 - Automate Picking and Put -away (WM) (cont. ) > Define a put away strategy per storage type • AVOID manual put away practices • C - Open storage – Use for large items that don’t require a specific bin assignment • I - Addition to existing stock – Useful for consolidating receipts of the same material upon put-away – Caution: Since only one quant resides in a bin, all materials in the bin adopt the same receipt date (unless batch or storage unit managed)
 3 - Automate Picking and Put -away (WM) (cont. ) > Define a picking strategy per storage type (cont. ) • L - Next empty bin – Great fit for high rack storage; whereby a standard rack section can hold 2 -3 units of storage – Useful for storing pallets of material; one pallet per bin location
3 - Automate Picking and Put -away (WM) (cont. ) > Define a picking strategy per storage type (cont. ) • L - Next empty bin – Great fit for high rack storage; whereby a standard rack section can hold 2 -3 units of storage – Useful for storing pallets of material; one pallet per bin location
 4 - Automatically Replenish Fwd. Picking Locations (WM) > Batch program • A scheduled job to read fixed bin data and generate replenishment transfer orders • 2 required programs – RLLNACH 1 – RLAUTA 10 > “Upon transfer order confirmation” option • Creates an automatic replenishment TO when a pick confirmation drives the fixed bin location below the min. stock level
4 - Automatically Replenish Fwd. Picking Locations (WM) > Batch program • A scheduled job to read fixed bin data and generate replenishment transfer orders • 2 required programs – RLLNACH 1 – RLAUTA 10 > “Upon transfer order confirmation” option • Creates an automatic replenishment TO when a pick confirmation drives the fixed bin location below the min. stock level
 5 - Consolidate Your Picking Activities (WM) > Two-step picking • Based on selection criteria, relevant deliveries are read and like material requests are collected • This collection results in a single aggregated picking order and task for each like material (first step) – TO splitting can be leveraged to distribute large picks • The second step is the re-allocation procedure – This is the process of “re-assigning” the specific materials and quantities back to the original requirement • Reduces duplicate picking efforts • Cuts order fulfillment cycles
5 - Consolidate Your Picking Activities (WM) > Two-step picking • Based on selection criteria, relevant deliveries are read and like material requests are collected • This collection results in a single aggregated picking order and task for each like material (first step) – TO splitting can be leveraged to distribute large picks • The second step is the re-allocation procedure – This is the process of “re-assigning” the specific materials and quantities back to the original requirement • Reduces duplicate picking efforts • Cuts order fulfillment cycles
 6 - Overcoming WM Performance Bottlenecks with RF > Potential bottlenecks and solutions • More detailed operations require more transactional steps – Leverage RF to reduce the data entry requirements – Leverage RF to consolidate/combine transactions • Physical inventory blocking – Leverage RF to reduce the time a bin is blocked – In R/3 Enterprise, inventory can be processed if an open transfer order exists • Pick and pack in a single step with RF – Incorporate RF to pick into a handling unit to avoid the need to perform packing as a separate task
6 - Overcoming WM Performance Bottlenecks with RF > Potential bottlenecks and solutions • More detailed operations require more transactional steps – Leverage RF to reduce the data entry requirements – Leverage RF to consolidate/combine transactions • Physical inventory blocking – Leverage RF to reduce the time a bin is blocked – In R/3 Enterprise, inventory can be processed if an open transfer order exists • Pick and pack in a single step with RF – Incorporate RF to pick into a handling unit to avoid the need to perform packing as a separate task
 Resources > “How to Select a WMS” • By Christopher Trunk, Total. Supply. Chain. com, > “Warehouse Management Systems, Defining Your Business Needs” • by Doug Campbell, Integrated Solutions, January 2000 > Gartner Report TU-09 -0762 > Supply Chain Forum White Paper • By John Hill, ESYNC, Logistics Execution System Perspective
Resources > “How to Select a WMS” • By Christopher Trunk, Total. Supply. Chain. com, > “Warehouse Management Systems, Defining Your Business Needs” • by Doug Campbell, Integrated Solutions, January 2000 > Gartner Report TU-09 -0762 > Supply Chain Forum White Paper • By John Hill, ESYNC, Logistics Execution System Perspective
 7 Key Points to Take Home > Evaluate your business processes to determine the BEST inventory management tool > Inventory management strengths focuses on managing stock at the quantity and value levels > Inventory management offers a single bin assignment per material per storage location; no strategies > Lean WM offers transfer order functionality to support receiving/put away and picking for deliveries continued…
7 Key Points to Take Home > Evaluate your business processes to determine the BEST inventory management tool > Inventory management strengths focuses on managing stock at the quantity and value levels > Inventory management offers a single bin assignment per material per storage location; no strategies > Lean WM offers transfer order functionality to support receiving/put away and picking for deliveries continued…
 7 Key Points to Take Home (cont. ) > Warehouse management offers additional areas of functionality not available with IM • Cross docking, Inventory methods and more! > Decentralized WM offers functionality that will work with SAP and other ERP solutions > Implement RF to increase accuracy, speed, real time inventory and status updates with any solution
7 Key Points to Take Home (cont. ) > Warehouse management offers additional areas of functionality not available with IM • Cross docking, Inventory methods and more! > Decentralized WM offers functionality that will work with SAP and other ERP solutions > Implement RF to increase accuracy, speed, real time inventory and status updates with any solution


