 Sang Wook Kim (Pusan N. Univ) Optimal condition of Q-SZE Busan (2015. 11. 28)
Sang Wook Kim (Pusan N. Univ) Optimal condition of Q-SZE Busan (2015. 11. 28)
 Collaborators Simone de Liberato (Univ. of Southampton) Hee Jun Jeon (PNU) Takahiro Sagawa (Univ. of Tokyo) Masahito Ueda (Univ. of Tokyo) Jung Jun Park (Singapore Natl. U. ) Kang-Hwan Kim (KAIST)
Collaborators Simone de Liberato (Univ. of Southampton) Hee Jun Jeon (PNU) Takahiro Sagawa (Univ. of Tokyo) Masahito Ueda (Univ. of Tokyo) Jung Jun Park (Singapore Natl. U. ) Kang-Hwan Kim (KAIST)
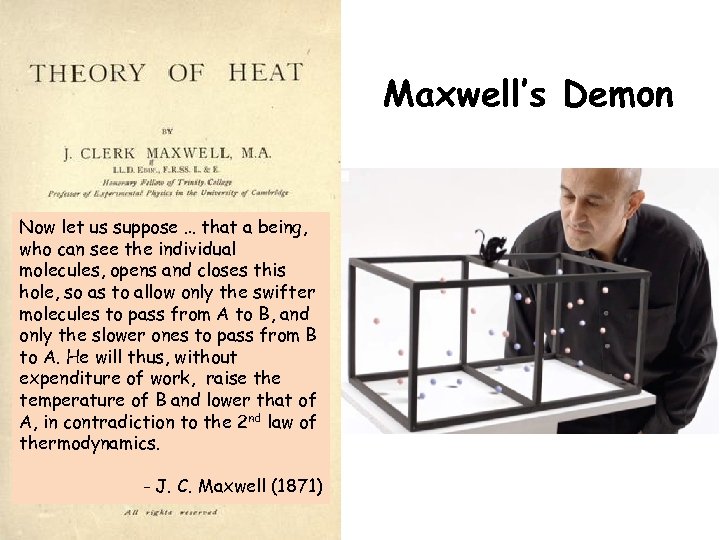 Maxwell’s Demon Now let us suppose … that a being, who can see the individual molecules, opens and closes this hole, so as to allow only the swifter molecules to pass from A to B, and only the slower ones to pass from B to A. He will thus, without expenditure of work, raise the temperature of B and lower that of A, in contradiction to the 2 nd law of thermodynamics. - J. C. Maxwell (1871)
Maxwell’s Demon Now let us suppose … that a being, who can see the individual molecules, opens and closes this hole, so as to allow only the swifter molecules to pass from A to B, and only the slower ones to pass from B to A. He will thus, without expenditure of work, raise the temperature of B and lower that of A, in contradiction to the 2 nd law of thermodynamics. - J. C. Maxwell (1871)
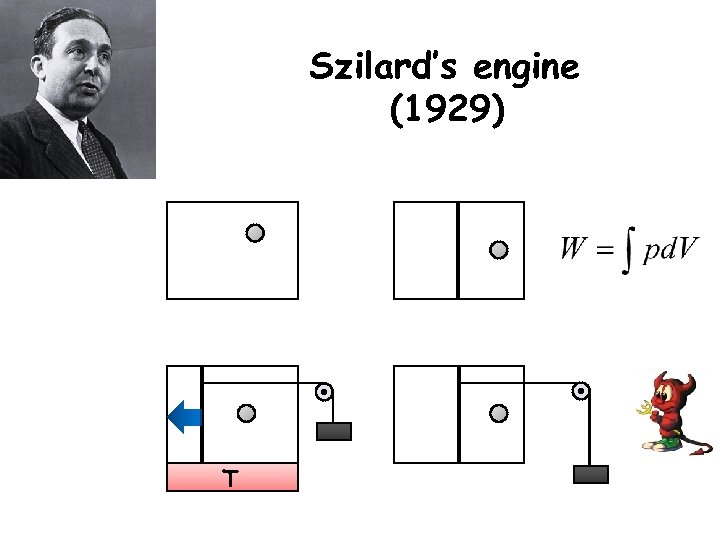 Szilard’s engine (1929) T
Szilard’s engine (1929) T
 Quantum Maxwell’s demon?
Quantum Maxwell’s demon?
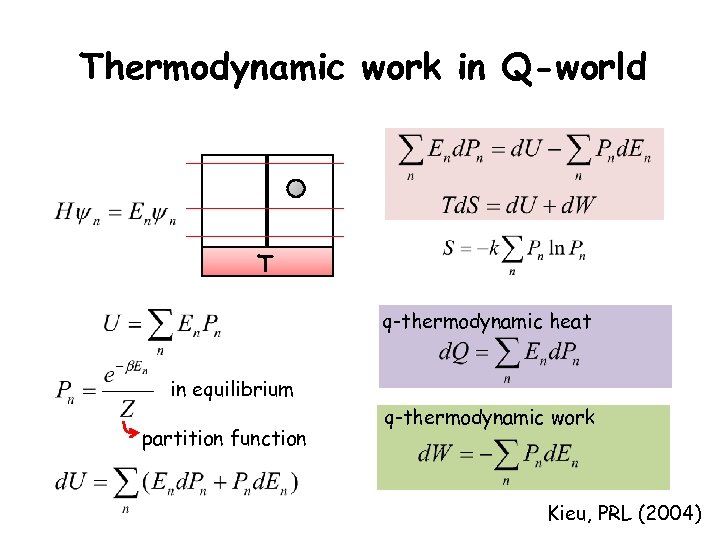 Thermodynamic work in Q-world T q-thermodynamic heat in equilibrium partition function q-thermodynamic work Kieu, PRL (2004)
Thermodynamic work in Q-world T q-thermodynamic heat in equilibrium partition function q-thermodynamic work Kieu, PRL (2004)
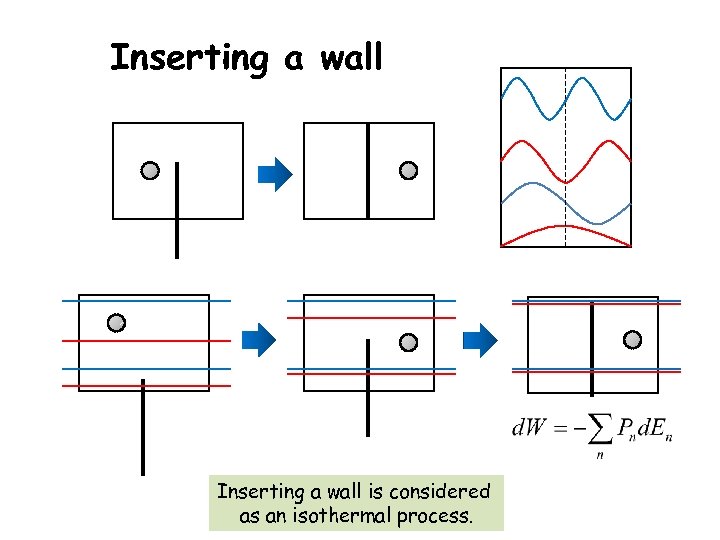 Inserting a wall is considered as an isothermal process.
Inserting a wall is considered as an isothermal process.
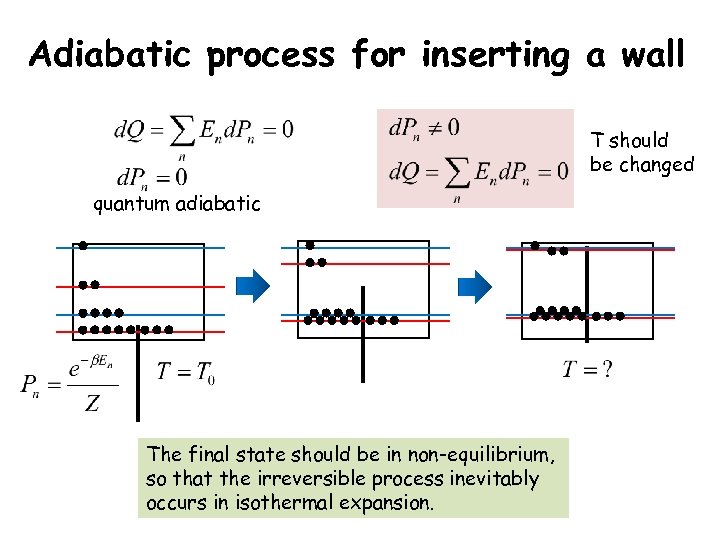 Adiabatic process for inserting a wall T should be changed quantum adiabatic The final state should be in non-equilibrium, so that the irreversible process inevitably occurs in isothermal expansion.
Adiabatic process for inserting a wall T should be changed quantum adiabatic The final state should be in non-equilibrium, so that the irreversible process inevitably occurs in isothermal expansion.
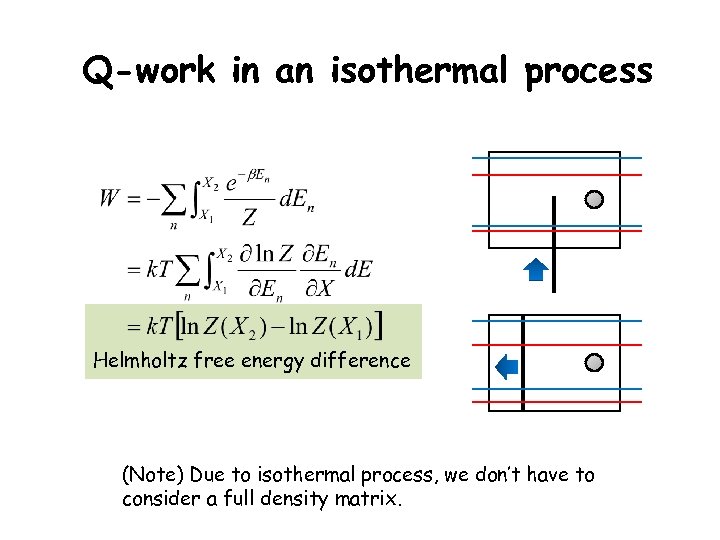 Q-work in an isothermal process Helmholtz free energy difference (Note) Due to isothermal process, we don’t have to consider a full density matrix.
Q-work in an isothermal process Helmholtz free energy difference (Note) Due to isothermal process, we don’t have to consider a full density matrix.
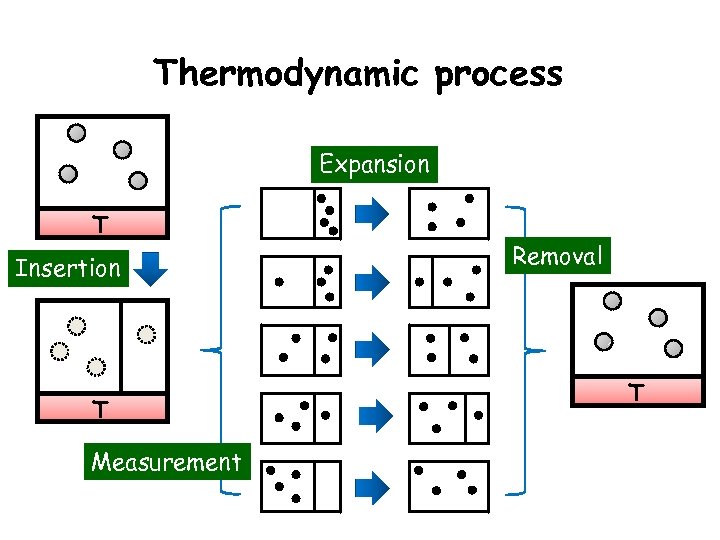 Thermodynamic process Expansion T Insertion T Measurement Removal T
Thermodynamic process Expansion T Insertion T Measurement Removal T
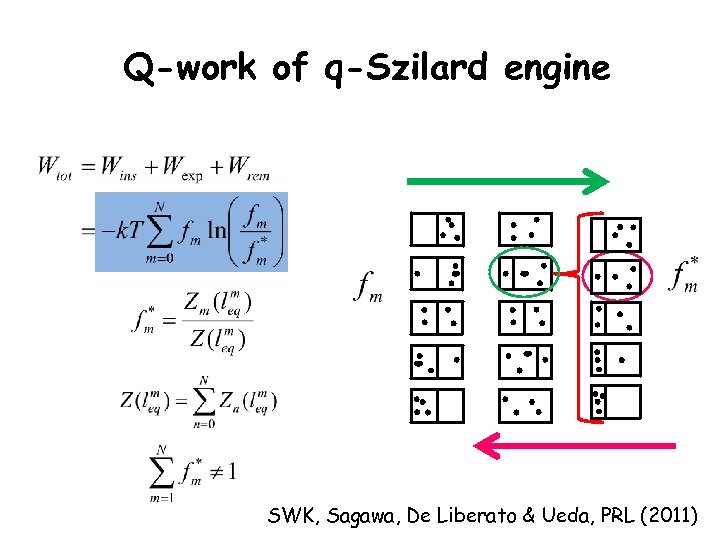 Q-work of q-Szilard engine SWK, Sagawa, De Liberato & Ueda, PRL (2011)
Q-work of q-Szilard engine SWK, Sagawa, De Liberato & Ueda, PRL (2011)
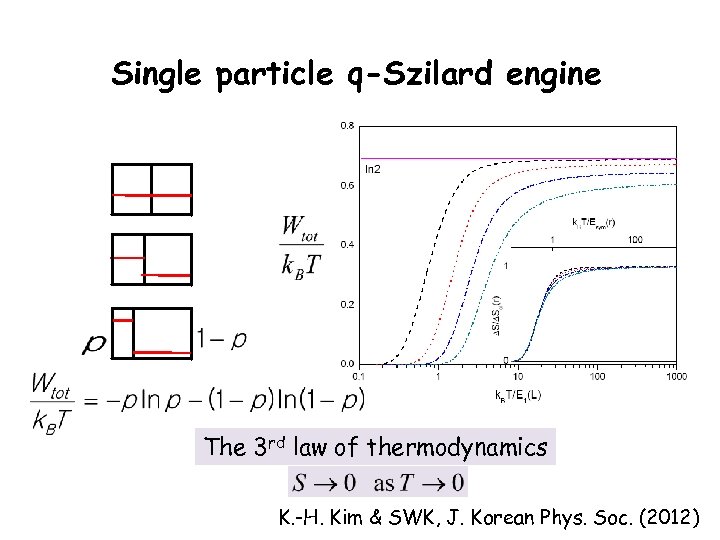 Single particle q-Szilard engine The 3 rd law of thermodynamics K. -H. Kim & SWK, J. Korean Phys. Soc. (2012)
Single particle q-Szilard engine The 3 rd law of thermodynamics K. -H. Kim & SWK, J. Korean Phys. Soc. (2012)
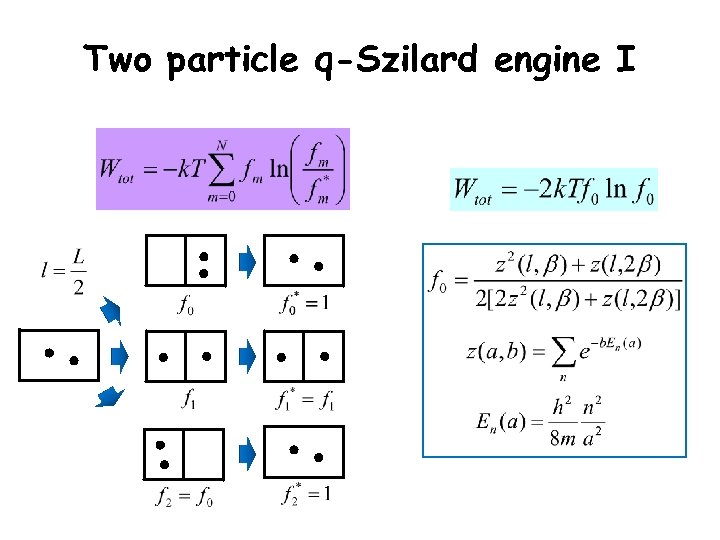 Two particle q-Szilard engine I
Two particle q-Szilard engine I
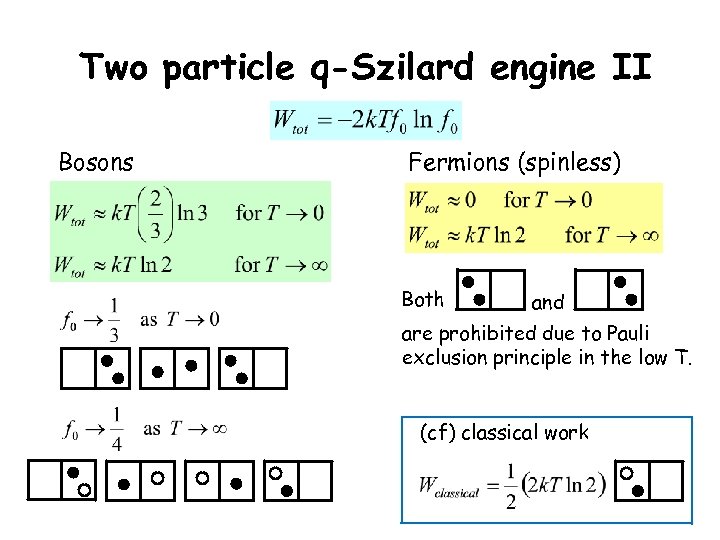 Two particle q-Szilard engine II Bosons Fermions (spinless) Both and are prohibited due to Pauli exclusion principle in the low T. (cf) classical work
Two particle q-Szilard engine II Bosons Fermions (spinless) Both and are prohibited due to Pauli exclusion principle in the low T. (cf) classical work
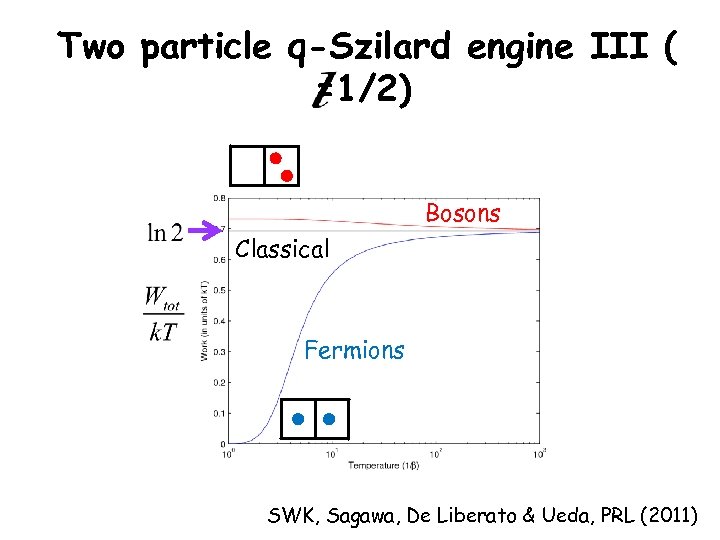 Two particle q-Szilard engine III ( =1/2) Bosons Classical Fermions SWK, Sagawa, De Liberato & Ueda, PRL (2011)
Two particle q-Szilard engine III ( =1/2) Bosons Classical Fermions SWK, Sagawa, De Liberato & Ueda, PRL (2011)
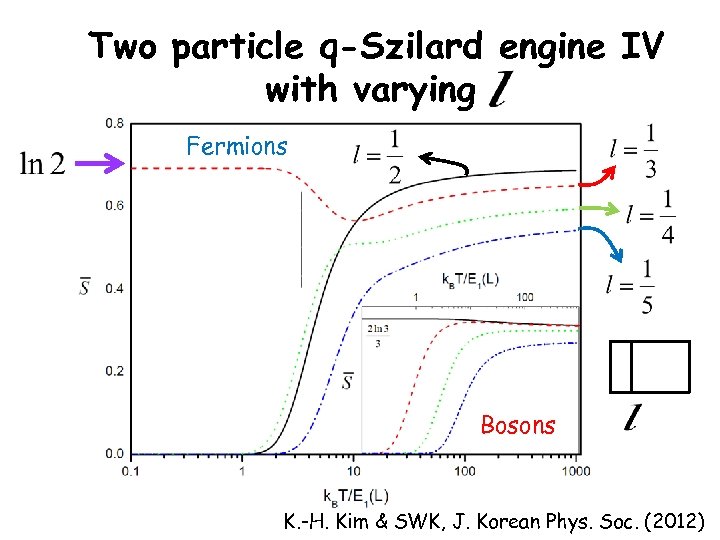 Two particle q-Szilard engine IV with varying Fermions Bosons K. -H. Kim & SWK, J. Korean Phys. Soc. (2012)
Two particle q-Szilard engine IV with varying Fermions Bosons K. -H. Kim & SWK, J. Korean Phys. Soc. (2012)
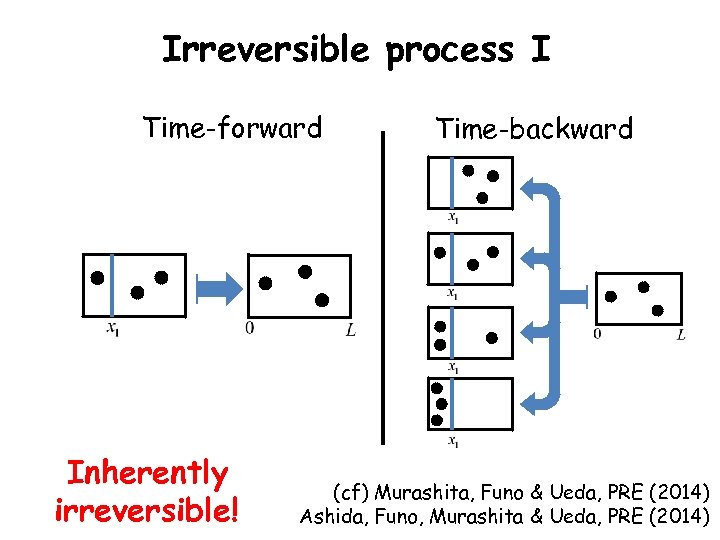 Irreversible process I Time-forward Inherently irreversible! Time-backward (cf) Murashita, Funo & Ueda, PRE (2014) Ashida, Funo, Murashita & Ueda, PRE (2014)
Irreversible process I Time-forward Inherently irreversible! Time-backward (cf) Murashita, Funo & Ueda, PRE (2014) Ashida, Funo, Murashita & Ueda, PRE (2014)
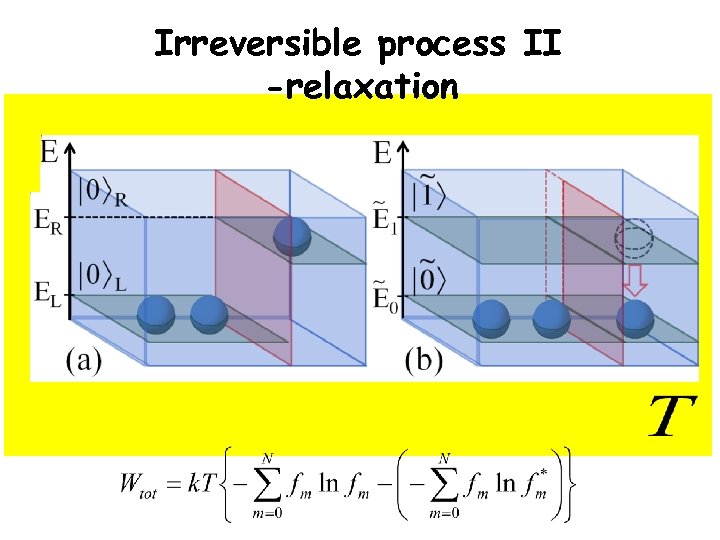 Irreversible process II -relaxation
Irreversible process II -relaxation
 “A reversible heat engine has the maximum efficiency. ” - Carnot
“A reversible heat engine has the maximum efficiency. ” - Carnot
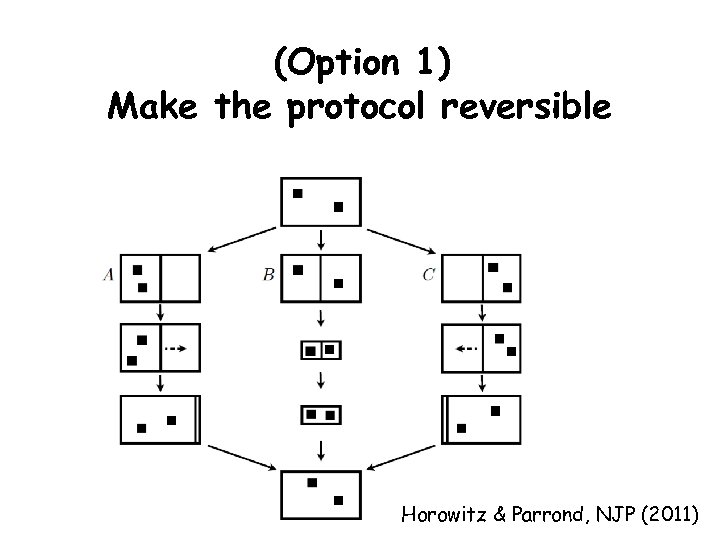 (Option 1) Make the protocol reversible Horowitz & Parrond, NJP (2011)
(Option 1) Make the protocol reversible Horowitz & Parrond, NJP (2011)
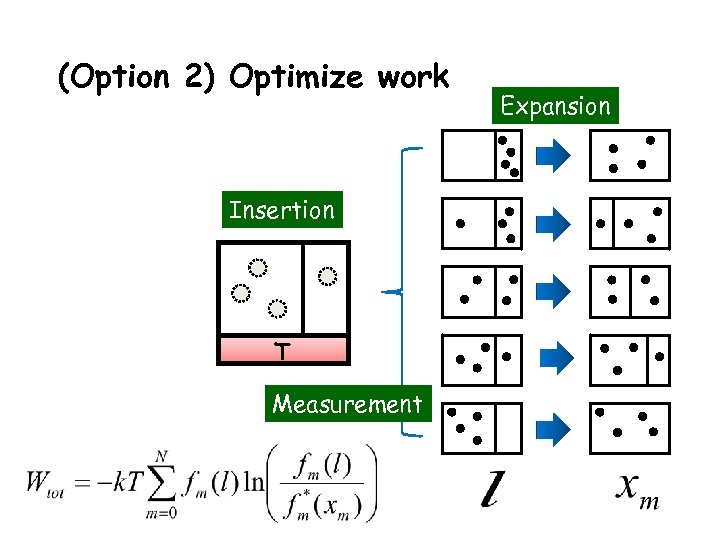 (Option 2) Optimize work Insertion T Measurement Expansion
(Option 2) Optimize work Insertion T Measurement Expansion
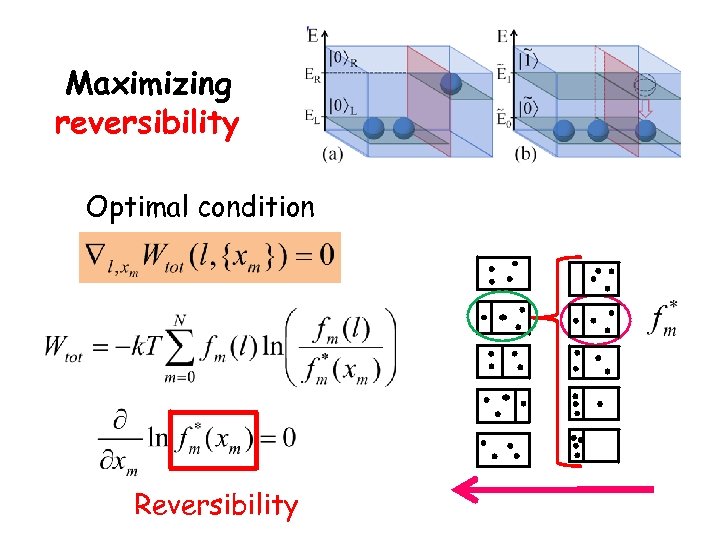 Maximizing reversibility Optimal condition Reversibility
Maximizing reversibility Optimal condition Reversibility
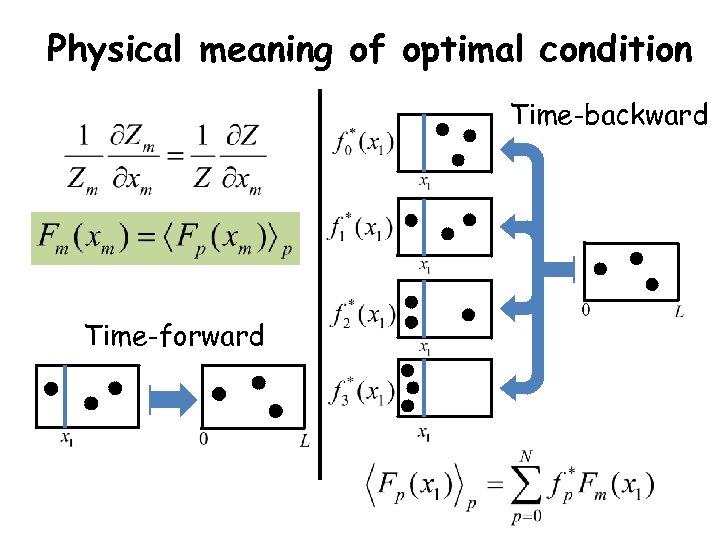 Physical meaning of optimal condition Time-backward Time-forward
Physical meaning of optimal condition Time-backward Time-forward
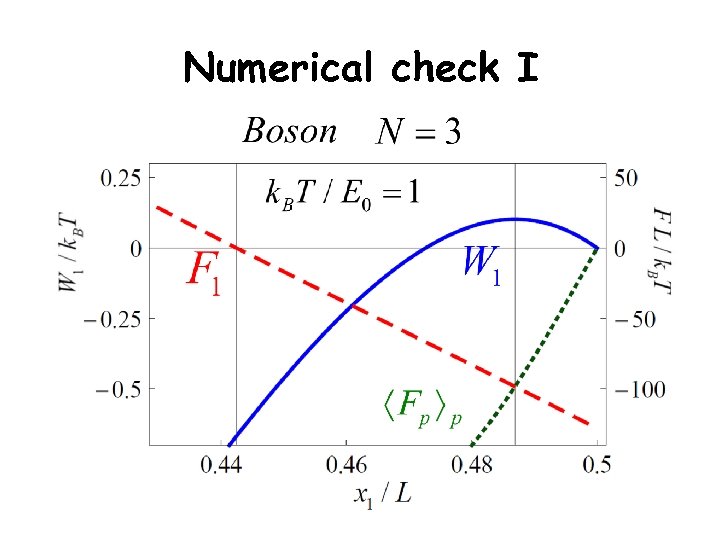 Numerical check I
Numerical check I
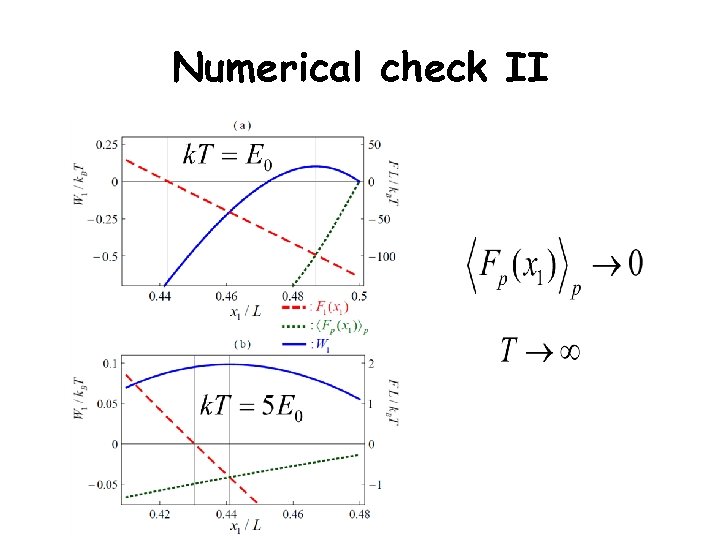 Numerical check II
Numerical check II
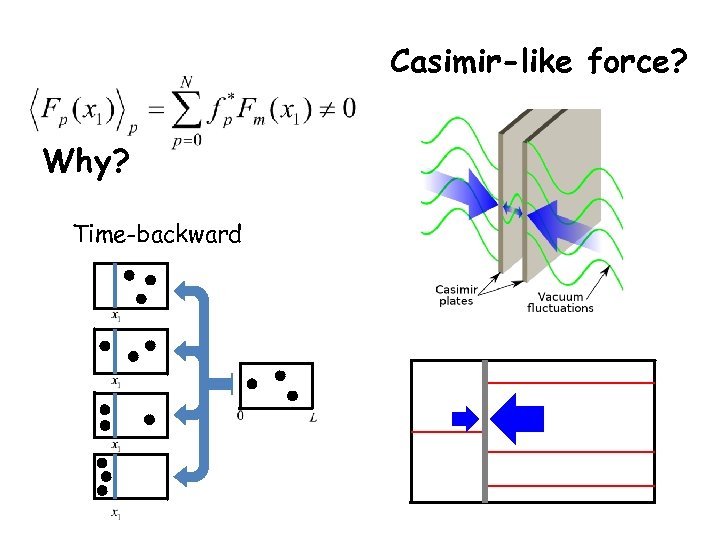 Casimir-like force? Why? Time-backward
Casimir-like force? Why? Time-backward
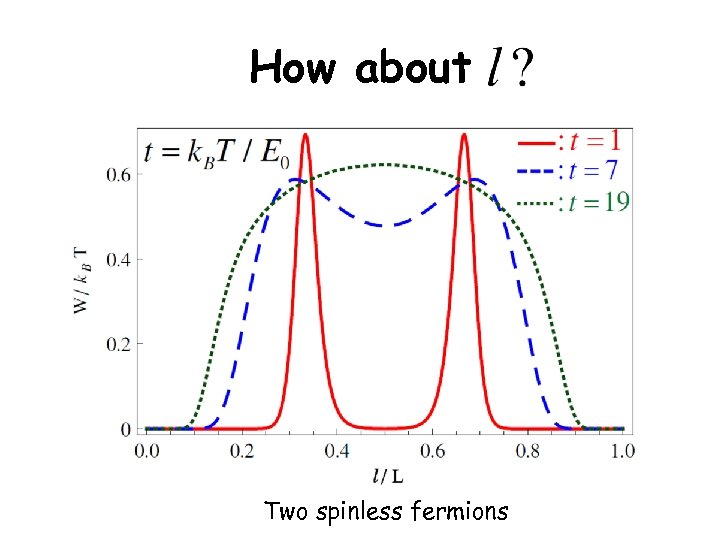 How about Two spinless fermions
How about Two spinless fermions
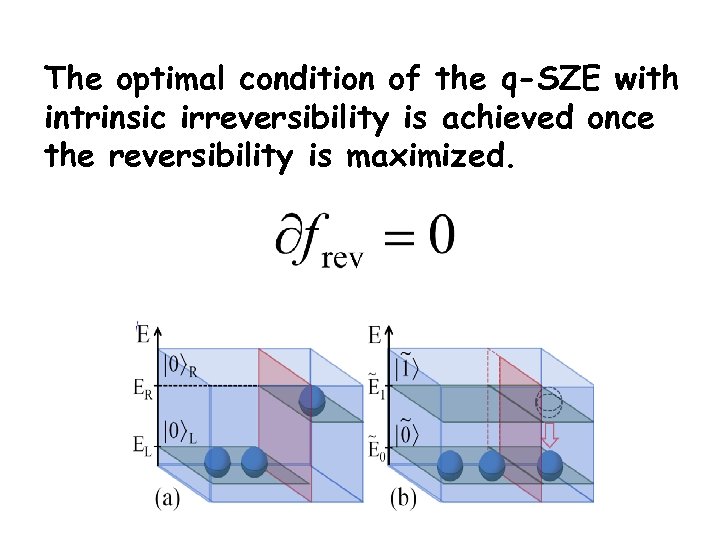 The optimal condition of the q-SZE with intrinsic irreversibility is achieved once the reversibility is maximized.
The optimal condition of the q-SZE with intrinsic irreversibility is achieved once the reversibility is maximized.
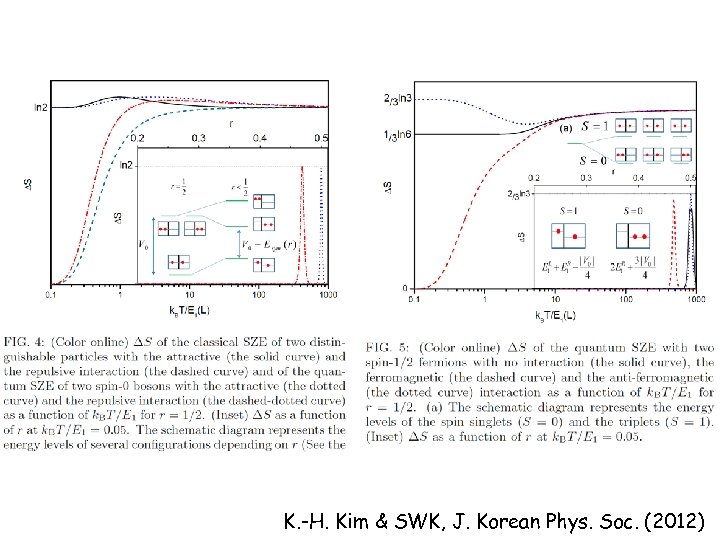 K. -H. Kim & SWK, J. Korean Phys. Soc. (2012)
K. -H. Kim & SWK, J. Korean Phys. Soc. (2012)