8792fc1cc086e8e125ec10607206e6cf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS Seoul, Korea Japan / Korea Trip 2001 Fabio Armani Julian Carey Jennifer Goodwin
SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS Seoul, Korea Japan / Korea Trip 2001 Fabio Armani Julian Carey Jennifer Goodwin
 Agenda • Samsung Group – History & Structure • Samsung Electronics – – – History Company Focus Financial Overview Strategy Organizational Structure Challenges
Agenda • Samsung Group – History & Structure • Samsung Electronics – – – History Company Focus Financial Overview Strategy Organizational Structure Challenges
 Samsung Group • Founded in 1938 – exporter of dried fish, vegetables, and fruits – flour mill and confectionery machines • 1950’s Economic Stabilization – Korean War - Samsung lost all assets – aimed to help rebuild Korean economy; entered the manufacturing industry (sugar, fabrics) – became a leader in modern business practices (recruiting from outside) • 1960’s Expansion of Key Industries – entered electronics and chemical industries – 1969 established Samsung Electronics Co.
Samsung Group • Founded in 1938 – exporter of dried fish, vegetables, and fruits – flour mill and confectionery machines • 1950’s Economic Stabilization – Korean War - Samsung lost all assets – aimed to help rebuild Korean economy; entered the manufacturing industry (sugar, fabrics) – became a leader in modern business practices (recruiting from outside) • 1960’s Expansion of Key Industries – entered electronics and chemical industries – 1969 established Samsung Electronics Co.
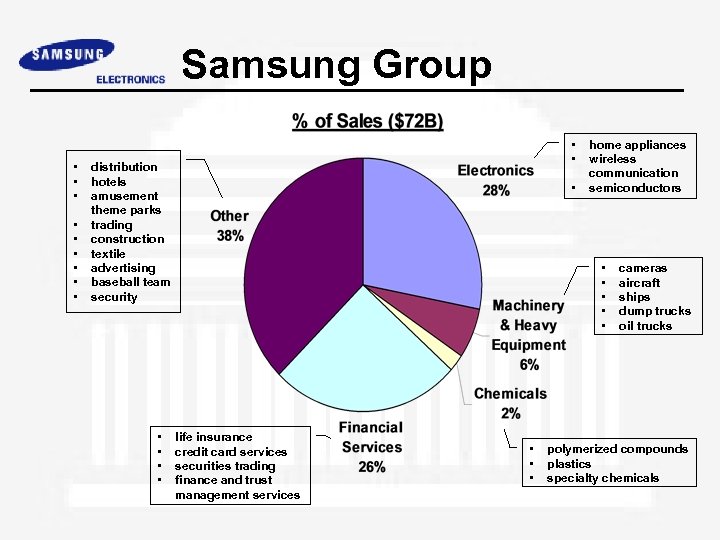 Samsung Group • • • distribution hotels amusement theme parks trading construction textile advertising baseball team security • • • home appliances wireless communication semiconductors • • • life insurance credit card services securities trading finance and trust management services • • • cameras aircraft ships dump trucks oil trucks polymerized compounds plastics specialty chemicals
Samsung Group • • • distribution hotels amusement theme parks trading construction textile advertising baseball team security • • • home appliances wireless communication semiconductors • • • life insurance credit card services securities trading finance and trust management services • • • cameras aircraft ships dump trucks oil trucks polymerized compounds plastics specialty chemicals
 Samsung Electronics • Established in January, 1969 • 1970’s: Bet the future on electronics – laid the groundwork for electronics in Korea – helped the domestic economy grow – paved the way for exports • 1980’s: A more comprehensive electronics company – established plants in Portugal and US – established Semiconductor and Communication corporation – began memory chip business • Early 90’s: Integration and Globalization • Mid-Late 90’s: Implementing new management strategies • New Millenium: Digital Vision
Samsung Electronics • Established in January, 1969 • 1970’s: Bet the future on electronics – laid the groundwork for electronics in Korea – helped the domestic economy grow – paved the way for exports • 1980’s: A more comprehensive electronics company – established plants in Portugal and US – established Semiconductor and Communication corporation – began memory chip business • Early 90’s: Integration and Globalization • Mid-Late 90’s: Implementing new management strategies • New Millenium: Digital Vision
 Focus: 4 Core Markets Home Multimedia Mobile Multimedia Personal Multimedia Core Components
Focus: 4 Core Markets Home Multimedia Mobile Multimedia Personal Multimedia Core Components
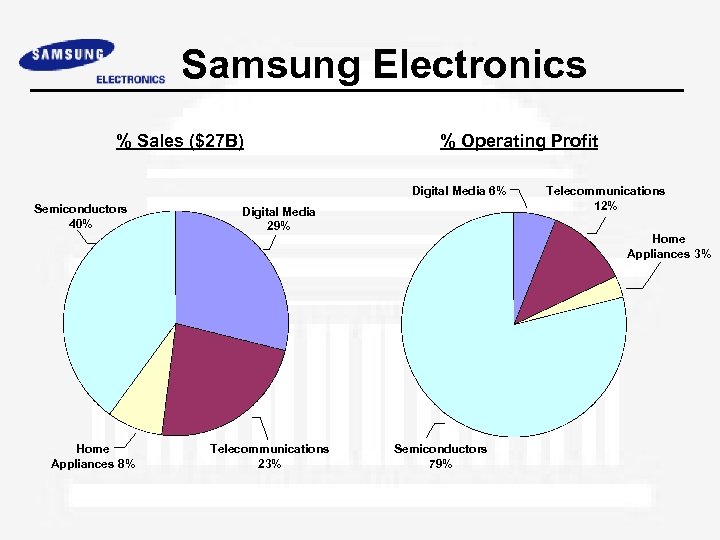 Samsung Electronics % Sales ($27 B) % Operating Profit Digital Media 6% Semiconductors 40% Home Appliances 8% Digital Media 29% Telecommunications 23% Telecommunications 12% Home Appliances 3% Semiconductors 79%
Samsung Electronics % Sales ($27 B) % Operating Profit Digital Media 6% Semiconductors 40% Home Appliances 8% Digital Media 29% Telecommunications 23% Telecommunications 12% Home Appliances 3% Semiconductors 79%
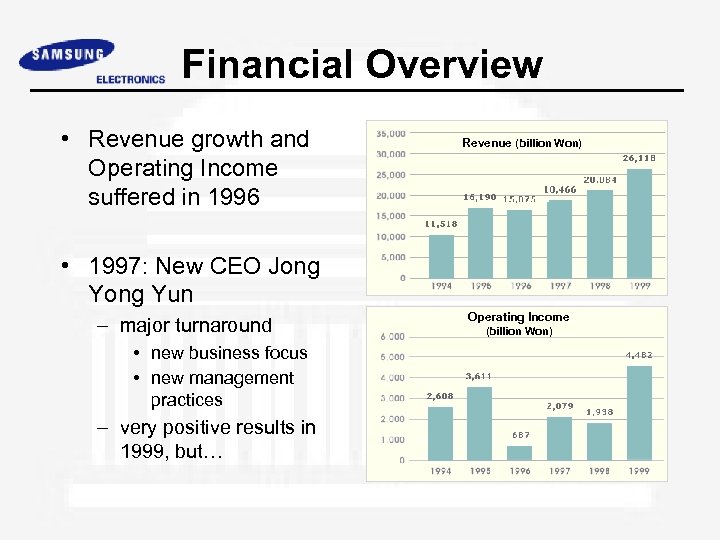 Financial Overview • Revenue growth and Operating Income suffered in 1996 Revenue (billion Won) • 1997: New CEO Jong Yun – major turnaround • new business focus • new management practices – very positive results in 1999, but… Operating Income (billion Won)
Financial Overview • Revenue growth and Operating Income suffered in 1996 Revenue (billion Won) • 1997: New CEO Jong Yun – major turnaround • new business focus • new management practices – very positive results in 1999, but… Operating Income (billion Won)
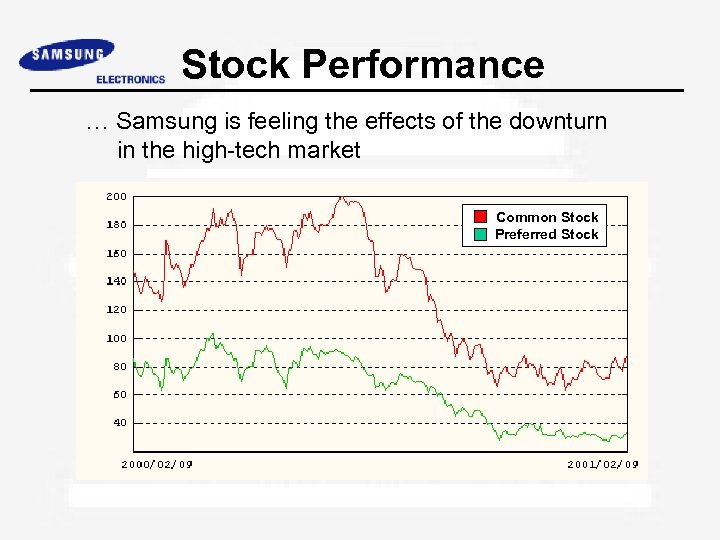 Stock Performance … Samsung is feeling the effects of the downturn in the high-tech market Common Stock Preferred Stock
Stock Performance … Samsung is feeling the effects of the downturn in the high-tech market Common Stock Preferred Stock
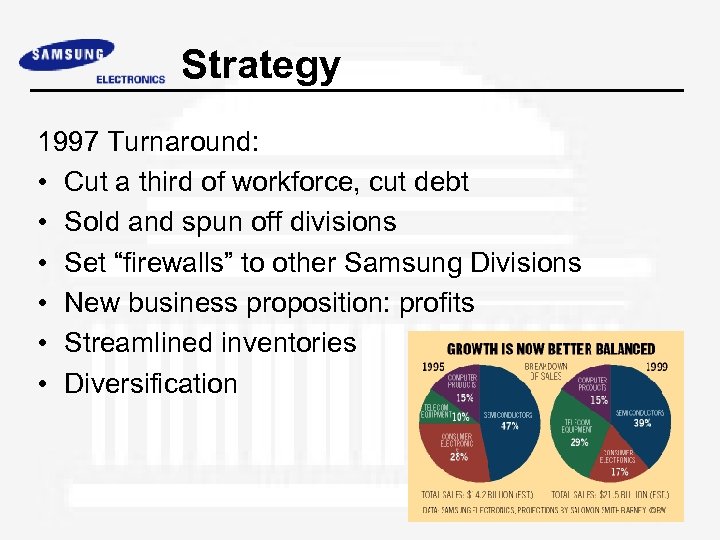 Strategy 1997 Turnaround: • Cut a third of workforce, cut debt • Sold and spun off divisions • Set “firewalls” to other Samsung Divisions • New business proposition: profits • Streamlined inventories • Diversification
Strategy 1997 Turnaround: • Cut a third of workforce, cut debt • Sold and spun off divisions • Set “firewalls” to other Samsung Divisions • New business proposition: profits • Streamlined inventories • Diversification
 Strategy New Economy: • Exodus of engineers and managers to startups • Top 4 conglomerates: $1. 2 B in startups (Samsung: $520 M) – Stakes of up to 29. 9% in 80+ startups • Startups benefit from links to global networks and financial expertise “You simply can’t survive without adapting to the fast-changing Internet era, and one solution is linking up with startups”
Strategy New Economy: • Exodus of engineers and managers to startups • Top 4 conglomerates: $1. 2 B in startups (Samsung: $520 M) – Stakes of up to 29. 9% in 80+ startups • Startups benefit from links to global networks and financial expertise “You simply can’t survive without adapting to the fast-changing Internet era, and one solution is linking up with startups”
 Strategy Digital Vision: “A Company that leads the digital convergence revolution” • Brand power, logistics, IP: – High-margin products – Create value chain that integrates competencies of all areas – Customer and market oriented • Global network by function • Performance evaluation and compensation system
Strategy Digital Vision: “A Company that leads the digital convergence revolution” • Brand power, logistics, IP: – High-margin products – Create value chain that integrates competencies of all areas – Customer and market oriented • Global network by function • Performance evaluation and compensation system
 Strategy Digital Vision: • Innovation, meeting challenges and creativity • Target debt-to-equity ratio: 50% • R&D: 7% of total revenues • Overseas partners: – Joint R&D projects – Technology transfer arrangements – Joint investments
Strategy Digital Vision: • Innovation, meeting challenges and creativity • Target debt-to-equity ratio: 50% • R&D: 7% of total revenues • Overseas partners: – Joint R&D projects – Technology transfer arrangements – Joint investments
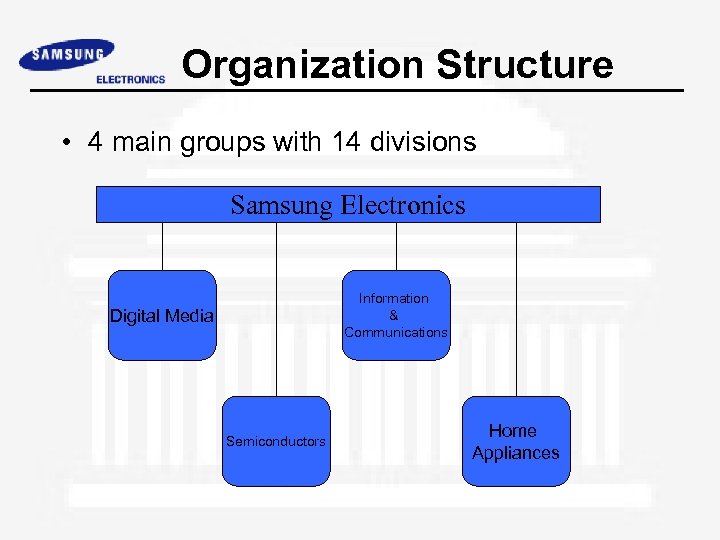 Organization Structure • 4 main groups with 14 divisions Samsung Electronics Information & Communications Digital Media Semiconductors Home Appliances
Organization Structure • 4 main groups with 14 divisions Samsung Electronics Information & Communications Digital Media Semiconductors Home Appliances
 Management & Employees • 59, 000 employees • Development of employees strategic to success • “Making rounds” encouraged as a key management practice
Management & Employees • 59, 000 employees • Development of employees strategic to success • “Making rounds” encouraged as a key management practice
 Recruiting and Training • Heavy investment • Focus on creating agents of change • Expertise in technology and marketing
Recruiting and Training • Heavy investment • Focus on creating agents of change • Expertise in technology and marketing
 Culture • • Entrepreneurial Profit focused Decisive Different from other firms in Korea and within chaebol
Culture • • Entrepreneurial Profit focused Decisive Different from other firms in Korea and within chaebol
 Current Challenges Internal: “You must maintain a sense of crisis to stay competitive” • Profits vs. Growth – Financial discipline • Foster creativity • Executives jumping ship for startups
Current Challenges Internal: “You must maintain a sense of crisis to stay competitive” • Profits vs. Growth – Financial discipline • Foster creativity • Executives jumping ship for startups
 Current Challenges External: • Abandon dependence on cheap commodity products • Emphasis on goods developed in-house – Rivals are outsourcing production and design • Guide the company into the global electronics elite
Current Challenges External: • Abandon dependence on cheap commodity products • Emphasis on goods developed in-house – Rivals are outsourcing production and design • Guide the company into the global electronics elite
 Current Challenges Corporate Governance: • Cross-shareholding among affiliates – Shifth funds among subsidiaries – Manipulate debt-to-equity ratios • Outside directors appointed by family • Lack of accountability to outside shareholders
Current Challenges Corporate Governance: • Cross-shareholding among affiliates – Shifth funds among subsidiaries – Manipulate debt-to-equity ratios • Outside directors appointed by family • Lack of accountability to outside shareholders


