71a80c659c7b7c104e43a53381f377bd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
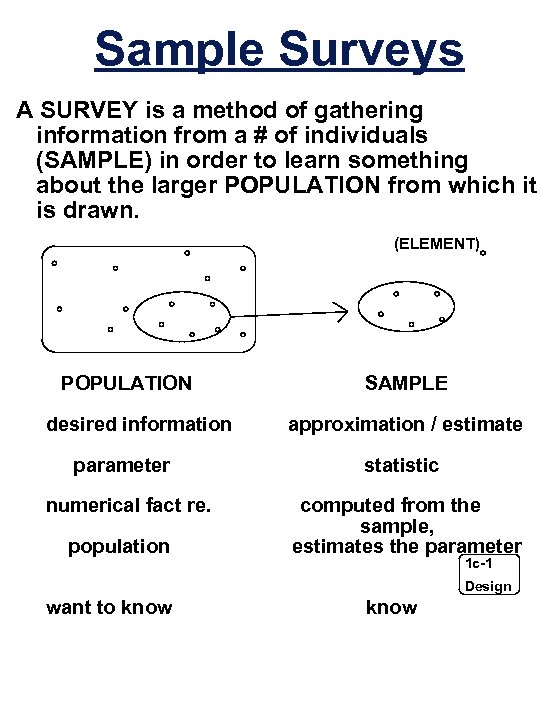 Sample Surveys A SURVEY is a method of gathering information from a # of individuals (SAMPLE) in order to learn something about the larger POPULATION from which it is drawn. (ELEMENT) POPULATION desired information parameter numerical fact re. population SAMPLE approximation / estimate statistic computed from the sample, estimates the parameter 1 c-1 Design want to know
Sample Surveys A SURVEY is a method of gathering information from a # of individuals (SAMPLE) in order to learn something about the larger POPULATION from which it is drawn. (ELEMENT) POPULATION desired information parameter numerical fact re. population SAMPLE approximation / estimate statistic computed from the sample, estimates the parameter 1 c-1 Design want to know
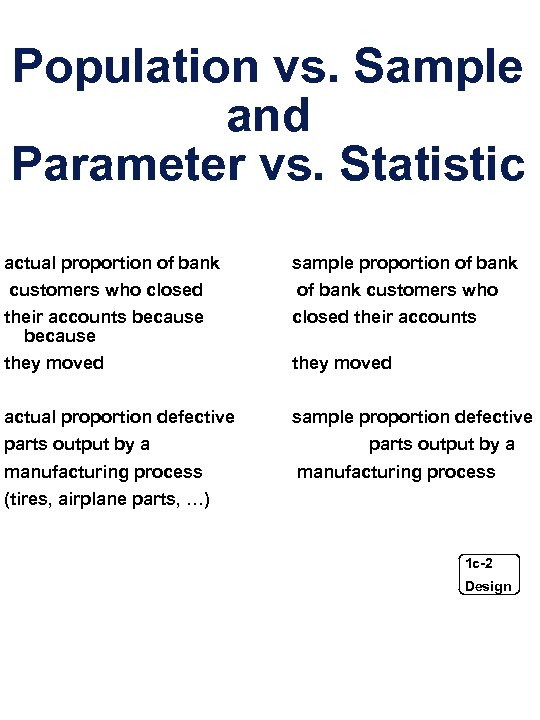 Population vs. Sample and Parameter vs. Statistic actual proportion of bank sample proportion of bank customers who closed of bank customers who their accounts because closed their accounts they moved actual proportion defective sample proportion defective parts output by a manufacturing process (tires, airplane parts, …) 1 c-2 Design
Population vs. Sample and Parameter vs. Statistic actual proportion of bank sample proportion of bank customers who closed of bank customers who their accounts because closed their accounts they moved actual proportion defective sample proportion defective parts output by a manufacturing process (tires, airplane parts, …) 1 c-2 Design
 Sample Surveys Marketing surveys Customer Satisfaction surveys Public Opinion polls Needle Exchange Program survey Child Immunization survey Alaska Airlines survey Customer Churn survey : : Other surveys 1 c-3 Design
Sample Surveys Marketing surveys Customer Satisfaction surveys Public Opinion polls Needle Exchange Program survey Child Immunization survey Alaska Airlines survey Customer Churn survey : : Other surveys 1 c-3 Design
 Some Sampling Definitions ELEMENT: entity upon which a measurement is made SAMPLING UNIT: collection of one or more elements. Each element should belong to exactly one sampling unit. SAMPLING FRAME: (should be) list of all sampling units in the population SELECTION BIAS: the systematic tendency on the part of the sampling procedure to exclude one kind of subject (sampling unit) or another from the sample NON-RESPONSE BIAS: bias due to nonresponders being characteristically different from responders A LARGE SAMPLE DOES NOT PROTECT AGAINST SELECTION BIAS !! !! !! 1 c-4 Design
Some Sampling Definitions ELEMENT: entity upon which a measurement is made SAMPLING UNIT: collection of one or more elements. Each element should belong to exactly one sampling unit. SAMPLING FRAME: (should be) list of all sampling units in the population SELECTION BIAS: the systematic tendency on the part of the sampling procedure to exclude one kind of subject (sampling unit) or another from the sample NON-RESPONSE BIAS: bias due to nonresponders being characteristically different from responders A LARGE SAMPLE DOES NOT PROTECT AGAINST SELECTION BIAS !! !! !! 1 c-4 Design
 Newspaper Examples 1 c-5 Design
Newspaper Examples 1 c-5 Design
 1 c-6 Design
1 c-6 Design
 Model for Estimation from a Sample Survey sample value = parameter value + error (estimate) = (desired information) + (error) bias error = chance error + causes for bias: - selection bias - non-response 1 c-7 - many other causes Design
Model for Estimation from a Sample Survey sample value = parameter value + error (estimate) = (desired information) + (error) bias error = chance error + causes for bias: - selection bias - non-response 1 c-7 - many other causes Design
 Types of Surveys mail: telephone: face-to-face interview: fax: 1 c-8 e-mail: Design
Types of Surveys mail: telephone: face-to-face interview: fax: 1 c-8 e-mail: Design
 Types of Sampling Procedures Probability versus Non-Probability Sampling: • subjects are selected randomly and according to pre-assigned selection probabilities Simple Random Sampling: • each subject (& group of subjects) is equally likely to be selected Stratified Sampling: • partition the population into subgroups (strata) 1 c-9 • sample separately within each stratum Design • appropriately combine the information across strata
Types of Sampling Procedures Probability versus Non-Probability Sampling: • subjects are selected randomly and according to pre-assigned selection probabilities Simple Random Sampling: • each subject (& group of subjects) is equally likely to be selected Stratified Sampling: • partition the population into subgroups (strata) 1 c-9 • sample separately within each stratum Design • appropriately combine the information across strata
 Some More Types of Sampling Procedures Stratified Random Sampling: • stratify • take srs within each stratum Systematic Sampling: • sample every kth individual • example Quota Sampling: • fill pre-specified quotas • example Convenience Sample: 1 c-10 Cluster Sampling: Design • select clusters of individuals • example: Current Population Survey
Some More Types of Sampling Procedures Stratified Random Sampling: • stratify • take srs within each stratum Systematic Sampling: • sample every kth individual • example Quota Sampling: • fill pre-specified quotas • example Convenience Sample: 1 c-10 Cluster Sampling: Design • select clusters of individuals • example: Current Population Survey
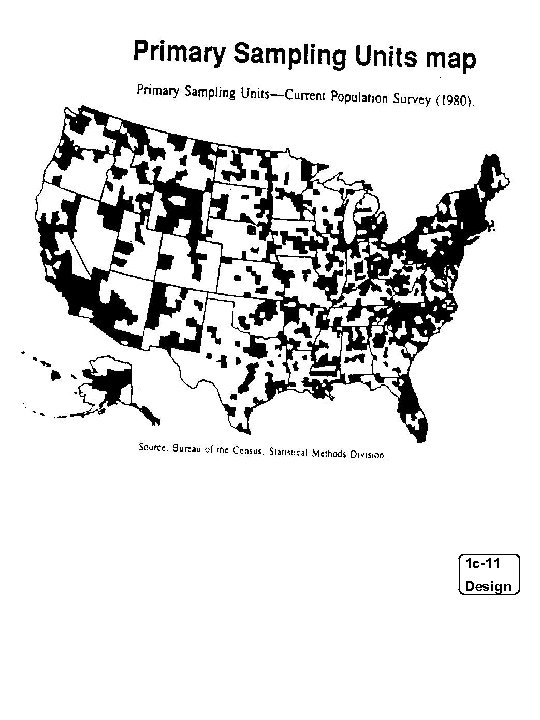 Primary Sampling Units map 1 c-11 Design
Primary Sampling Units map 1 c-11 Design
 Random #'s exercise 1 c-12 Design
Random #'s exercise 1 c-12 Design
 Table of Random Numbers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 51449 16144 48145 83780 95329 39284 56830 48280 48351 84829 85527 67507 99481 85422 35103 67168 97275 13050 42978 91706 91284 25982 81818 26088 36834 19954 69294 25282 17869 05878 91166 32841 66466 94245 04514 70918 20861 24461 26622 30588 85957 83114 97021 48318 19239 19492 12531 21072 73850 7072 6 7 8 9 10 11179 94631 64275 72125 16463 69004 52413 10294 19232 42028 34273 31524 35027 10782 27927 36062 02316 25604 30615 48403 26234 27661 65695 42005 88963 58601 15888 36014 90419 79615 47159 13525 17988 32447 41218 82248 43809 02734 53688 43290 95968 40014 31732 36125 53618 99722 30667 29911 28456 68082 1 c-13 Design
Table of Random Numbers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 51449 16144 48145 83780 95329 39284 56830 48280 48351 84829 85527 67507 99481 85422 35103 67168 97275 13050 42978 91706 91284 25982 81818 26088 36834 19954 69294 25282 17869 05878 91166 32841 66466 94245 04514 70918 20861 24461 26622 30588 85957 83114 97021 48318 19239 19492 12531 21072 73850 7072 6 7 8 9 10 11179 94631 64275 72125 16463 69004 52413 10294 19232 42028 34273 31524 35027 10782 27927 36062 02316 25604 30615 48403 26234 27661 65695 42005 88963 58601 15888 36014 90419 79615 47159 13525 17988 32447 41218 82248 43809 02734 53688 43290 95968 40014 31732 36125 53618 99722 30667 29911 28456 68082 1 c-13 Design
 Steps in Conducting a Survey (1) Identify the problem; Set out the objectives (2) Select the sampling design & method (3) Design the questionnaire (4) Select the sample (5) Collect the data (6) Analyze the data 1 c-14 Design
Steps in Conducting a Survey (1) Identify the problem; Set out the objectives (2) Select the sampling design & method (3) Design the questionnaire (4) Select the sample (5) Collect the data (6) Analyze the data 1 c-14 Design
 example cover letter CBS COLLEGE PUBLISHING CBS Educational and Professional. Publishing A Division of CBS Inc 383 Madison Avenue New York 10017 (212)872 -2000 October 10, 1986 Dear Professor: We are conducting a major market research study in the area Of Business Statistics. This study is being conducted nationwide Amoung a selected sample of all Business Statistics professors. For the results of this study to represent the opinions of all Business Statistics professors, it is vital that each questionnaire be completed and returned. Your ideas and opinions will help us develop texts designed to meet your course needs. Please take a few minutes to complete this brief survey. Thank you for your time. Sincerely, Eva M. Bronstein-Greenwald Manager of Market Research P. S. As a token of appreciation for your completed survey, we will send you a customized digital clock/bookmark if your completed survey is returned on or before November 21. Please fill in the enclosed mailing label and include it with your completed questionnaire. 1 c-15 Design Holt, Rinehart and Winston Dryden Press, Saunders Coillege Publishing
example cover letter CBS COLLEGE PUBLISHING CBS Educational and Professional. Publishing A Division of CBS Inc 383 Madison Avenue New York 10017 (212)872 -2000 October 10, 1986 Dear Professor: We are conducting a major market research study in the area Of Business Statistics. This study is being conducted nationwide Amoung a selected sample of all Business Statistics professors. For the results of this study to represent the opinions of all Business Statistics professors, it is vital that each questionnaire be completed and returned. Your ideas and opinions will help us develop texts designed to meet your course needs. Please take a few minutes to complete this brief survey. Thank you for your time. Sincerely, Eva M. Bronstein-Greenwald Manager of Market Research P. S. As a token of appreciation for your completed survey, we will send you a customized digital clock/bookmark if your completed survey is returned on or before November 21. Please fill in the enclosed mailing label and include it with your completed questionnaire. 1 c-15 Design Holt, Rinehart and Winston Dryden Press, Saunders Coillege Publishing
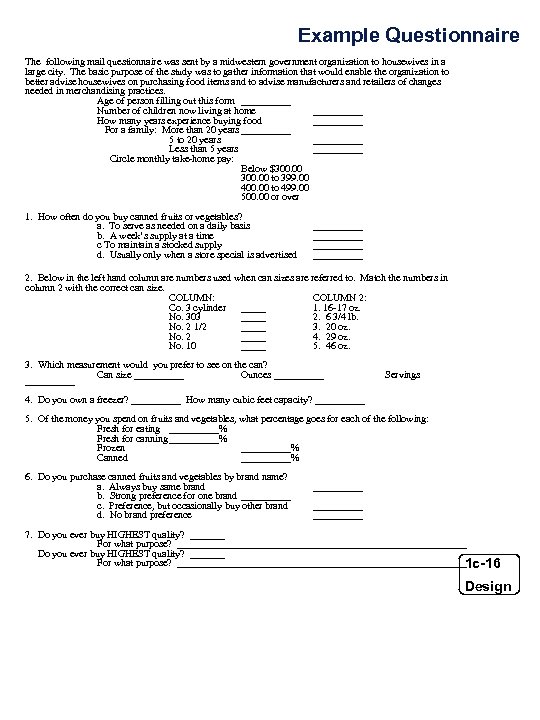 Example Questionnaire The following mail questionnaire was sent by a midwestern government organization to housewives in a large city. The basic purpose of the study was to gather information that would enable the organization to better advise housewives on purchasing food items and to advise manufacturers and retailers of changes needed in merchandising practices. Age of person filling out this form _____ Number of children now living at home _____ How many years experience buying food _____ For a family: More than 20 years _____ 5 to 20 years _____ Less than 5 years _____ Circle monthly take-home pay: Below $300. 00 to 399. 00 400. 00 to 499. 00 500. 00 or over 1. How often do you buy canned fruits or vegetables? a. To serve as needed on a daily basis b. A week’s supply at a time c To maintain a stocked supply d. Usually only when a store special is advertised __________ 2. Below in the left hand column are numbers used when can sizes are referred to. Match the numbers in column 2 with the correct can size. COLUMN: COLUMN 2: Co. 3 cylinder _____ 1. 16 -17 oz. No. 303 _____ 2. 6 3/4 lb. No. 2 1/2 _____ 3. 20 oz. No. 2 _____ 4. 29 oz. No. 10 _____ 5. 46 oz. 3. Which measurement would you prefer to see on the can? Can size _____ Ounces __________ Servings 4. Do you own a freezer? _____ How many cubic feet capacity? _____ 5. Of the money you spend on fruits and vegetables, what percentage goes for each of the following: Fresh for eating _____% Fresh for canning _____% Frozen _____% Canned _____% 6. Do you purchase canned fruits and vegetables by brand name? a. Always buy same brand b. Strong preference for one brand _____ c. Preference, but occasionally buy other brand d. No brand preference __________ 7. Do you ever buy HIGHEST quality? _______ For what purpose? __________________________________________________________ 1 c-16 Design
Example Questionnaire The following mail questionnaire was sent by a midwestern government organization to housewives in a large city. The basic purpose of the study was to gather information that would enable the organization to better advise housewives on purchasing food items and to advise manufacturers and retailers of changes needed in merchandising practices. Age of person filling out this form _____ Number of children now living at home _____ How many years experience buying food _____ For a family: More than 20 years _____ 5 to 20 years _____ Less than 5 years _____ Circle monthly take-home pay: Below $300. 00 to 399. 00 400. 00 to 499. 00 500. 00 or over 1. How often do you buy canned fruits or vegetables? a. To serve as needed on a daily basis b. A week’s supply at a time c To maintain a stocked supply d. Usually only when a store special is advertised __________ 2. Below in the left hand column are numbers used when can sizes are referred to. Match the numbers in column 2 with the correct can size. COLUMN: COLUMN 2: Co. 3 cylinder _____ 1. 16 -17 oz. No. 303 _____ 2. 6 3/4 lb. No. 2 1/2 _____ 3. 20 oz. No. 2 _____ 4. 29 oz. No. 10 _____ 5. 46 oz. 3. Which measurement would you prefer to see on the can? Can size _____ Ounces __________ Servings 4. Do you own a freezer? _____ How many cubic feet capacity? _____ 5. Of the money you spend on fruits and vegetables, what percentage goes for each of the following: Fresh for eating _____% Fresh for canning _____% Frozen _____% Canned _____% 6. Do you purchase canned fruits and vegetables by brand name? a. Always buy same brand b. Strong preference for one brand _____ c. Preference, but occasionally buy other brand d. No brand preference __________ 7. Do you ever buy HIGHEST quality? _______ For what purpose? __________________________________________________________ 1 c-16 Design
 8. What would be your advice to the young housewife starting out in homemaking concerning buying canned fruits and vegetables? How can she be sure the is buying a good quality product? 9. Where do you frequently buy canned fruits and vegetables? A and P _____ IGA _____ KROGER-KRAMBO _____ NATIONAL SENTRY _____ LOCAL STORE _____ INDEPENDENT _____ KOHL _____ HALAN’S 10. Rate the following names for quality. (1. Top quality, 2. Good, 3. Poor) _____Garden Fresh _____Avondale _____Sultana _____Ann Page _____ Old Time _____ Iona _____Serve U Rite _____ Kroger _____ Del Monte _____Natco _____Roundy’s _____ Ligbby’s 11. When you are buying canned foods, peaches for example, how important are each of the following to you? (Place X in column. ) VERY NOT TOO IMPORTANT DESIRABLE IMPORTANT Firmness _____ Flavor _____ Color _____ Low percentage of _____ syrup or juice Odor _____ Food value _____ Uniform size _____ 12. What do the government grades A, B, C mean to you? __________________ 13. Would you like such letter grades on all canned fruits and vegetables? Yes _____ No _____ 14. When can labels show suggestions for serving canned fruits or vegetables do you make use of them? Yes _____ No _____ 15. Rather than the serving suggestion, would you prefer to see recipes on the labels of canned fruits and vegetables? Yes _____ No _____ 16. Some foods are sold with an official grade on the package. Do you happen to recall how each of the following foods is sold? (Place X in column. ) PACKAGE ALWAYS SHOWS GRADE Butter _____ Cheese _____ Canned Tuna _____ Hamburger _____ Frozen Fish _____ Canned Peas _____ Fresh Apples _____ Pork Loin Roast _____ Canned Beets _____ Eggs _____ SOMETIMES SHOWS GRADE _____ _____ _____ NEVER SHOWS GRADE _____ _____ _____ DON’T RECALL _____ _____ _____ PLEASE RETURN THIS FORM IN THE STAMPED ADDRESSED ENVELOPE BY MAY 26. THANK YOU 1 c-17 Design
8. What would be your advice to the young housewife starting out in homemaking concerning buying canned fruits and vegetables? How can she be sure the is buying a good quality product? 9. Where do you frequently buy canned fruits and vegetables? A and P _____ IGA _____ KROGER-KRAMBO _____ NATIONAL SENTRY _____ LOCAL STORE _____ INDEPENDENT _____ KOHL _____ HALAN’S 10. Rate the following names for quality. (1. Top quality, 2. Good, 3. Poor) _____Garden Fresh _____Avondale _____Sultana _____Ann Page _____ Old Time _____ Iona _____Serve U Rite _____ Kroger _____ Del Monte _____Natco _____Roundy’s _____ Ligbby’s 11. When you are buying canned foods, peaches for example, how important are each of the following to you? (Place X in column. ) VERY NOT TOO IMPORTANT DESIRABLE IMPORTANT Firmness _____ Flavor _____ Color _____ Low percentage of _____ syrup or juice Odor _____ Food value _____ Uniform size _____ 12. What do the government grades A, B, C mean to you? __________________ 13. Would you like such letter grades on all canned fruits and vegetables? Yes _____ No _____ 14. When can labels show suggestions for serving canned fruits or vegetables do you make use of them? Yes _____ No _____ 15. Rather than the serving suggestion, would you prefer to see recipes on the labels of canned fruits and vegetables? Yes _____ No _____ 16. Some foods are sold with an official grade on the package. Do you happen to recall how each of the following foods is sold? (Place X in column. ) PACKAGE ALWAYS SHOWS GRADE Butter _____ Cheese _____ Canned Tuna _____ Hamburger _____ Frozen Fish _____ Canned Peas _____ Fresh Apples _____ Pork Loin Roast _____ Canned Beets _____ Eggs _____ SOMETIMES SHOWS GRADE _____ _____ _____ NEVER SHOWS GRADE _____ _____ _____ DON’T RECALL _____ _____ _____ PLEASE RETURN THIS FORM IN THE STAMPED ADDRESSED ENVELOPE BY MAY 26. THANK YOU 1 c-17 Design
 In considering a survey report: • What is the PURPOSE OF THE STUDY ? • How was the STUDY DESIGNED (& implemented) ? • How were the DATA ANALYZED ? • Are the CONCLUSIONS backed by the data? . . . of appropriate generality? 1 c-18 Design
In considering a survey report: • What is the PURPOSE OF THE STUDY ? • How was the STUDY DESIGNED (& implemented) ? • How were the DATA ANALYZED ? • Are the CONCLUSIONS backed by the data? . . . of appropriate generality? 1 c-18 Design
 Margin of Error Newspaper Examples 1 c-19 Design
Margin of Error Newspaper Examples 1 c-19 Design
 Designed Experiment versus Observational Study In a DESIGNED EXPERIMENT the investigator assigns experimental units to treatments. versus In an OBSERVATIONAL STUDY the investigator does not assign experimental units to treatments, but merely observes the treatments and the response on a set of experimental units. 1 c-20 Design
Designed Experiment versus Observational Study In a DESIGNED EXPERIMENT the investigator assigns experimental units to treatments. versus In an OBSERVATIONAL STUDY the investigator does not assign experimental units to treatments, but merely observes the treatments and the response on a set of experimental units. 1 c-20 Design


