c97a8a2f8c99917792666e48153a1e68.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Salmonella typhimurium Casey County, KY Jasie L. Jackson, MPH Regional Epidemiologist Epidemiology Rapid Response Team Fall Conference Sept. 15 -16 2004
Salmonella typhimurium Casey County, KY Jasie L. Jackson, MPH Regional Epidemiologist Epidemiology Rapid Response Team Fall Conference Sept. 15 -16 2004
 Clinical Description • Infection of variable severity commonly manifested by diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, fever, and sometimes vomiting. Asymptomatic infections may occur and the organism may cause extraintestinal infections. ~ Kentucky Reportable Disease Desk Reference
Clinical Description • Infection of variable severity commonly manifested by diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, fever, and sometimes vomiting. Asymptomatic infections may occur and the organism may cause extraintestinal infections. ~ Kentucky Reportable Disease Desk Reference
 Salmonellosis • > 2000 known serotypes • 200 serotypes are detected each year in the United States • Two most common (in most countries) – Salmonella Typhimurium – Salmonella Enteritidis
Salmonellosis • > 2000 known serotypes • 200 serotypes are detected each year in the United States • Two most common (in most countries) – Salmonella Typhimurium – Salmonella Enteritidis
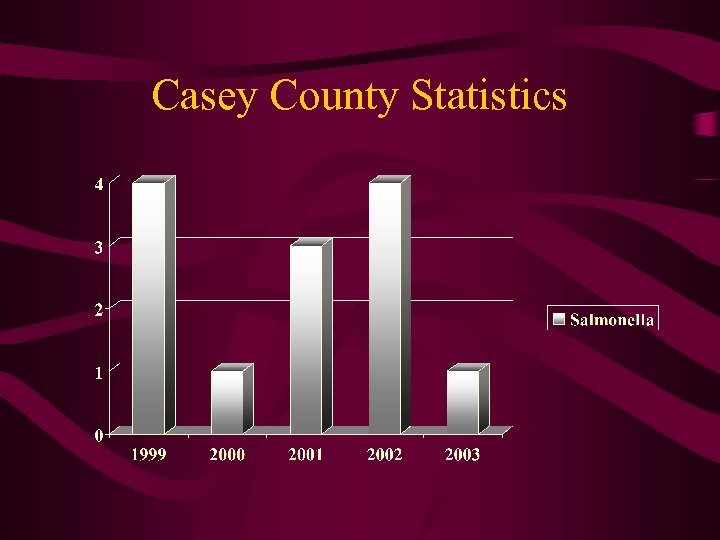 Casey County Statistics
Casey County Statistics
 Positive Case • March 4, 2004 • Case reported • Galilean Home for Children – Angel House • Infant – 4 months old (Baby 1) • Sx – diarrhea and vomiting • 3 more cases developed subsequently
Positive Case • March 4, 2004 • Case reported • Galilean Home for Children – Angel House • Infant – 4 months old (Baby 1) • Sx – diarrhea and vomiting • 3 more cases developed subsequently
 Galilean Children’s Home • A home for children that are either castaways or come from homes whose parents are unable to care for them. Also a few are placed by loving families who need assistance in caring for their severely disabled children.
Galilean Children’s Home • A home for children that are either castaways or come from homes whose parents are unable to care for them. Also a few are placed by loving families who need assistance in caring for their severely disabled children.
 The Angel House • Home to infants from birth • Separate structure from home where other children reside. • Most of the babies’ mothers are in prison • • • 15 workers 9 babies 3 babies per room Each has own bed Common room for play-time
The Angel House • Home to infants from birth • Separate structure from home where other children reside. • Most of the babies’ mothers are in prison • • • 15 workers 9 babies 3 babies per room Each has own bed Common room for play-time
 Investigation Initiated • Objectives – Confirm other cases – Determine mode of transmission – Determine source – Culture all workers/childcare personnel – Culture all infants – Education on proper hygiene – Institute prevention/protection measures
Investigation Initiated • Objectives – Confirm other cases – Determine mode of transmission – Determine source – Culture all workers/childcare personnel – Culture all infants – Education on proper hygiene – Institute prevention/protection measures
 Site Visit • Site visit conducted by: – Nursing Supervisor – Environmentalist – Regional Epidemiologist • Interviews conducted with: – Director of Angel House – Employees
Site Visit • Site visit conducted by: – Nursing Supervisor – Environmentalist – Regional Epidemiologist • Interviews conducted with: – Director of Angel House – Employees
 Investigation • Standard Case definition used • All workers and infants in “Angel House” cultured • Stool specimens collected and sent to State Lab • All workers negative • 5 of 9 infants negative • 4 infants with symptoms – 3 initially cultured positive for S. typhimurium – Baby 4 cultured positive one week later after re-culture due to prolonged illness
Investigation • Standard Case definition used • All workers and infants in “Angel House” cultured • Stool specimens collected and sent to State Lab • All workers negative • 5 of 9 infants negative • 4 infants with symptoms – 3 initially cultured positive for S. typhimurium – Baby 4 cultured positive one week later after re-culture due to prolonged illness
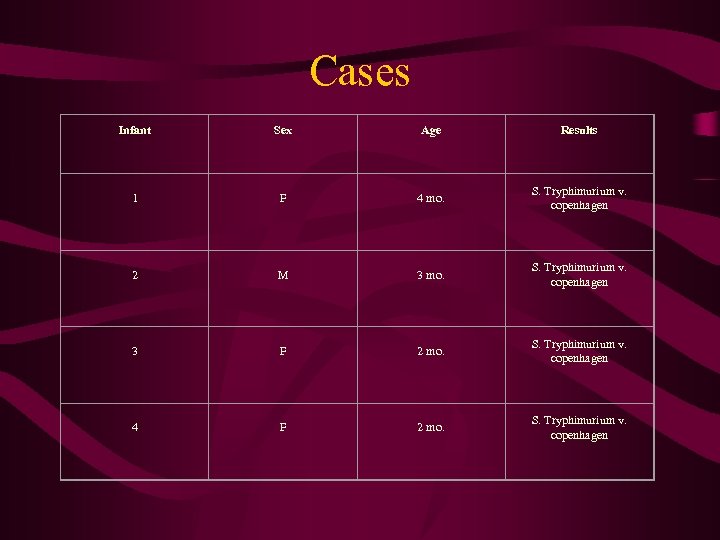 Cases Infant Sex Age Results 1 F 4 mo. S. Tryphimurium v. copenhagen 2 M 3 mo. S. Tryphimurium v. copenhagen 3 F 2 mo. S. Tryphimurium v. copenhagen 4 F 2 mo. S. Tryphimurium v. copenhagen
Cases Infant Sex Age Results 1 F 4 mo. S. Tryphimurium v. copenhagen 2 M 3 mo. S. Tryphimurium v. copenhagen 3 F 2 mo. S. Tryphimurium v. copenhagen 4 F 2 mo. S. Tryphimurium v. copenhagen
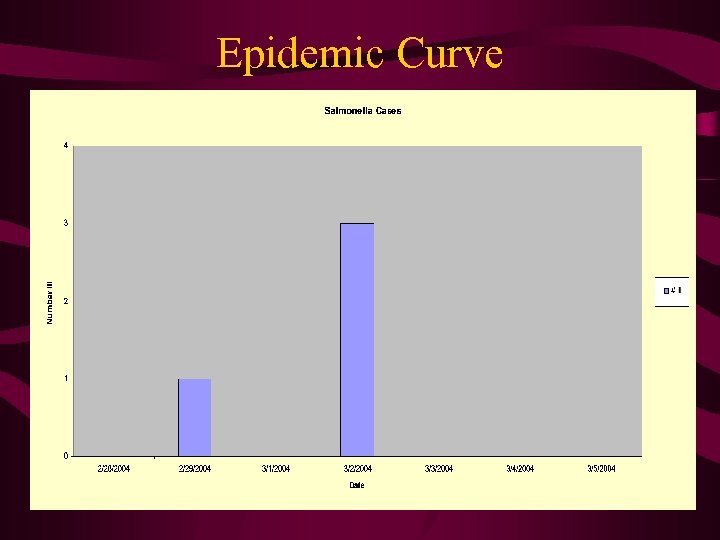 Epidemic Curve
Epidemic Curve
 Investigation Findings • All infants use same formula • All positive cultures were S. typhimurium • Common Source? ? – Couldn’t be identified • Infants do not have assigned caretaker • Kitchen and sleeping areas inspected • Sanitary practices discussed – Use bleach as sanitizing solution
Investigation Findings • All infants use same formula • All positive cultures were S. typhimurium • Common Source? ? – Couldn’t be identified • Infants do not have assigned caretaker • Kitchen and sleeping areas inspected • Sanitary practices discussed – Use bleach as sanitizing solution
 Investigation Findings (continued) • 3 of 4 infants slept in same bedroom • 2 caretakers sick prior to infant illness – Continued to work • Baby 1 visited mother in prison week prior to onset
Investigation Findings (continued) • 3 of 4 infants slept in same bedroom • 2 caretakers sick prior to infant illness – Continued to work • Baby 1 visited mother in prison week prior to onset
 Recommendations • Good hygiene • Stress handwashing • Stress sanitization of changing areas • Exclude sick caretakers • Exclude sick infants • Only one caretaker per infant • Do not wash hands in the same sink as dishes are washed • DO NOT drink unpasteurized milk or juices • Caution on handling and contact with reptiles, chicks, ducklings, amphibians, etc • Clean and disinfect bathrooms • Clean and disinfect toys at least daily and when soiled • Thoroughly cook all foods • Store uncooked meats on a shelf lower than other foods
Recommendations • Good hygiene • Stress handwashing • Stress sanitization of changing areas • Exclude sick caretakers • Exclude sick infants • Only one caretaker per infant • Do not wash hands in the same sink as dishes are washed • DO NOT drink unpasteurized milk or juices • Caution on handling and contact with reptiles, chicks, ducklings, amphibians, etc • Clean and disinfect bathrooms • Clean and disinfect toys at least daily and when soiled • Thoroughly cook all foods • Store uncooked meats on a shelf lower than other foods
 Further Developments • Initially the outbreak was contained to 4 infants in the Angel House • 2 months later another infant (Baby 5) associated with the Angel House develops symptoms and cultures positive for S. typhimurium
Further Developments • Initially the outbreak was contained to 4 infants in the Angel House • 2 months later another infant (Baby 5) associated with the Angel House develops symptoms and cultures positive for S. typhimurium
 More Cultures • Mother of Baby 5 works at Galilean Home for Children • Baby 5 stays at “Angel House” while mother works • Baby 5 re-cultured • Family of Baby 5 cultured • Original 4 infants repeat cultures • Mother and sister of Baby 5 negative • Father positive • Baby 1 still positive – Returned home with mother week prior to culture results
More Cultures • Mother of Baby 5 works at Galilean Home for Children • Baby 5 stays at “Angel House” while mother works • Baby 5 re-cultured • Family of Baby 5 cultured • Original 4 infants repeat cultures • Mother and sister of Baby 5 negative • Father positive • Baby 1 still positive – Returned home with mother week prior to culture results
 Culture, Culture • Father cultured 6 times – S. typhimurium • Father works in restaurant operated by Galilean Home – Advised – can’t work till 2 negative cultures • 2 negative cultures – 7 -20 -04 – 7 -27 -04
Culture, Culture • Father cultured 6 times – S. typhimurium • Father works in restaurant operated by Galilean Home – Advised – can’t work till 2 negative cultures • 2 negative cultures – 7 -20 -04 – 7 -27 -04
 Conclusions • • • Common Source of infection Source could not be identified 2 possible scenarios 1. Father of Baby 5 is carrier and passed via Baby 5 to other infants 2. Baby 1 is carrier and passed to all other infants. Baby 5 passed infection to Father during day-to-day care.
Conclusions • • • Common Source of infection Source could not be identified 2 possible scenarios 1. Father of Baby 5 is carrier and passed via Baby 5 to other infants 2. Baby 1 is carrier and passed to all other infants. Baby 5 passed infection to Father during day-to-day care.
 References • Chin, James, MD ed. Control of Communicable Diseases Manual. 17 th ed. Baltimore: United, 2000. • Hooker, Carol, Mary Beth Grimm, and Claudia Miller, eds. Infectious Diseases in Childcare Settings and Schools: Information for Directors, Caregivers, Parents or Guardians and School Health Staff. 5 th ed. Hopkins, MN: Hennipen County Community Health Department, 2003. • Kentucky Reportable Disease Desk Reference. Div. Of Epidemiology and Health Planning. 2003. • Reportable Diseases in Kentucky: 2002 Summary. Division of Epidemiology and Health Planning.
References • Chin, James, MD ed. Control of Communicable Diseases Manual. 17 th ed. Baltimore: United, 2000. • Hooker, Carol, Mary Beth Grimm, and Claudia Miller, eds. Infectious Diseases in Childcare Settings and Schools: Information for Directors, Caregivers, Parents or Guardians and School Health Staff. 5 th ed. Hopkins, MN: Hennipen County Community Health Department, 2003. • Kentucky Reportable Disease Desk Reference. Div. Of Epidemiology and Health Planning. 2003. • Reportable Diseases in Kentucky: 2002 Summary. Division of Epidemiology and Health Planning.


