0ec095a5551bb8501c386017d5649168.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Salmonella Laboratorio de Microbiología Aplicada Dra. Esther Z. Vega Bermúdez
Salmonella sp.
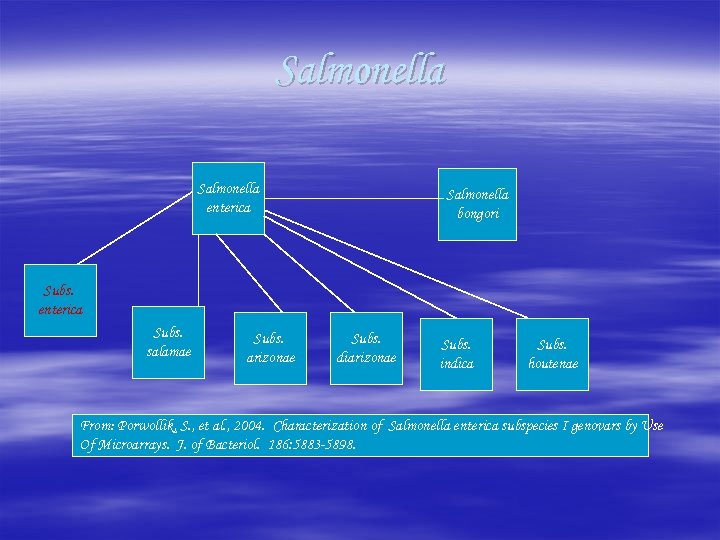
Salmonella enterica Salmonella bongori Subs. enterica Subs. salamae Subs. arizonae Subs. diarizonae Subs. indica Subs. houtenae From: Porwollik, S. , et al. , 2004. Characterization of Salmonella enterica subspecies I genovars by Use Of Microarrays. J. of Bacteriol. 186: 5883 -5898.
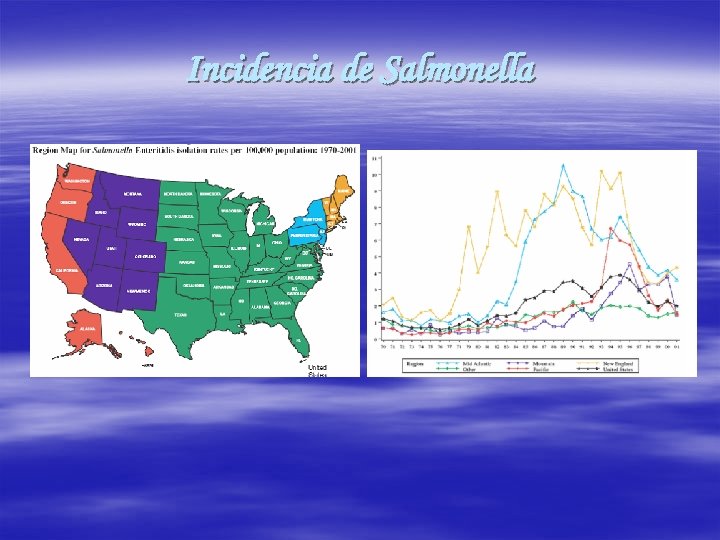
Incidencia de Salmonella

Características v Enterobacterias v Bacilos Gram (-) v Mótiles con flagelación perítrica v No esporulan v No fermentan lactosa v 2, 300 especies v Crece entre 40 -140 o. C

Variantes Genéticas § Mediada por Plasmidios – Utilización de lactosa y sucrosa § Microorganismos atípicos pueden “escapar”a la detección en situaciones clínicas § Las especies de Salmonella no son un grupo homogéneo de organismos

Reservorios / Alimentos Relacionados v Carnes crudas v Aves v Huevos v Leche y productos lácteos v Pescado v Camarones v Salsas v Mezclas para bizcocho v Postres de crema v otros

Patogénesis v Dosis infecciosa tan bajo como 15 -20 células (depediendo de hospedero) v Antígenos estructurales (pared celular o antígeno O, H- flagelar y el IV-antígeno capsular termolábil -poder frente a los ácidos) v Sustancias tóxicas v Endotoxinas v Exotoxinas (efecto irritante y citotóxico para el tracto intestinal) v Ruta oral-fecal

Sintomatología y Enfermedades v Período de incubación de 648 hrs v Diarreas v Dolor abdominal v Fiebre entre 8 -72 hrs v Dolor de cabeza y en el cuerpo v Escalofríos v Naúseas v Vómitos v Septicemias v Bacteremias v Cistitis, endocarditis y osteomilitis v Síndrome de Reiters que puede terminar en artritis crónica v Fiebre tifoidea ó paratifoidea

Diagnóstico y Tratamiento v Pruebas de serología y de heces fecales v Aislar el paciente v Tratamiento para todos en el hogar v Antibíoticos

Muestreo en Alimentos v. Métodos convencionales de aislación que requieren de cinco días para confirmar resultados. v. Cultivo 37 -420 C o en nevera.

Salmonella

Metodología § Pre-Enriquecimiento – Caldo de lactosa § Permite la recuperación de células “heridas” § Aumenta la razón Salmonella: Non-Salmonella – Agua de dilución peptonada Productos Animales § Dilución 1: 10 – I. e. . 25 g muesra a 225 ml de caldo § 24 horas a 35 o. C

Enriquecimiento Selectivo § 1 ml de caldo de Lactosa – 10 ml Selenite Cystine – 10 ml tetrathionate broth § Permite el crecimiento de Salmonella § No hay resultados despúes de este paso § 24 horas a 35 o. C

Placas Selectivas § Tres tipos de medio selectivo – Bismuth Sulfite § Marrón, gris, negro con “metallic sheen” – Hektoen Enteric Agar § Azul-verdoso con o sin centro negro o “glossy black” – Xylose Lysine Desoxycholate § Rosado con o sin centro negro § Estriado de “Selective Enrichments” § Incubación de 18 -24 h a 35 o. C § Resultados – PRESUMPTIVE POSITIVE

Medio Diferencial – Discernimiento bioquímico § Triple Sugar Iron Agar – – Streak Slant and Stab Butt 1% Lactosa 0. 1% Glucosa Sulfato Ferroso § Indicador de H 2 S – Tiosulfato § Producción de H 2 S – Rojo fenol § Alkalina – Rojo, Acido – Amarillo – Incubación a 35 o. C por 24 horas

Triple Sugar Iron Agar § Reacción de Salmonella – Red Slant (Alkalino) – Acid Butt (Amarillo) – Precipitado Negro

Lysine Iron Agar- Discernimiento bioquímico § Stab Butt and Streak Slant – Se quiere condiciones anaeróbicas en el fondo para que ocurra la decarboxilación § Decarboxilación a partir de L-Lysina § Sulfato Ferroso § Bromo Cresol Purple – Violeta – Alkalino, Amarillo - Acido § Glucosa § Tiosulfato

Lysine Iron Agar § Reacción de Salmonella – Alkaline Butt – Purple – Precipitado Negro § Sólo es negativo si hay condiciones ácidicas, pueden obtenerse otras reacciones no típicas

Confirmación Bioquímica § Aglutinación de antígenos superficiales con anticuerpos específicos para Salmonella § Antígenos de Salmonella – O – Somático – Lipopolisacárido – H – Flagellar – Proteína – K – Capsular - Polisacáridos

Aglutinación § Mezcle anticuerpos con un poco de cultivo § Aglutinación es un resultado positivo

Aislamiento vs. Enumeración § Usualmente sólo se aisla § Se enumera para propósitos de investigación – Método MPN – Método de filtración por membranas § No “Accurate”
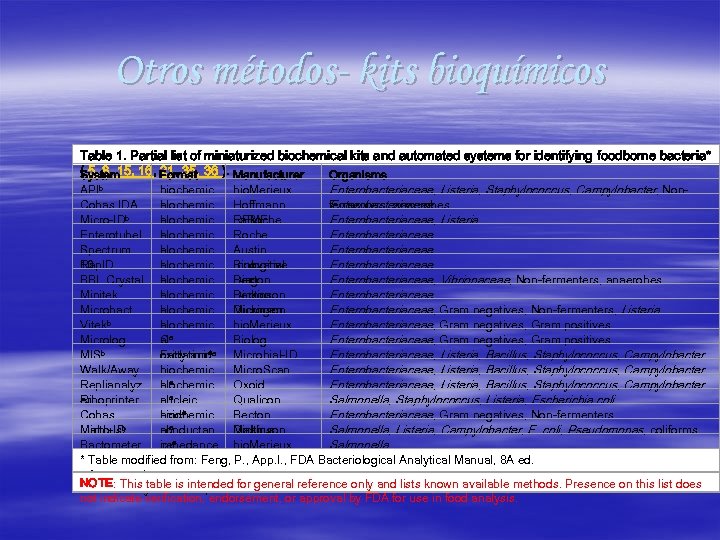
Otros métodos- kits bioquímicos Table 1. Partial list of miniaturized biochemical kits and automated systems for identifying foodborne bacteria* ( 5, 8, 15, 16, Format 36 ). Manufacturer 21, 35, System Organisms b API biochemic bio. Merieux Enterobacteriaceae, Listeria, Staphylococcus, Campylobacter, Nonal fermenters, anaerobes Cobas IDA biochemic Hoffmann Enterobacteriaceae b al La. Roche Micro-ID biochemic REMEL Enterobacteriaceae, Listeria Enterotube. I al biochemic Roche Enterobacteriaceae I al Spectrum biochemic Austin Enterobacteriaceae 10 al Biological Rap. ID biochemic Innovative Enterobacteriaceae al Diag. BBL Crystal biochemic Becton Enterobacteriaceae, Vibrionaceae, Non-fermenters, anaerobes al Dickinson Minitek biochemic Becton Enterobacteriaceae al Dickinson Microbact biochemic Microgen Enterobacteriaceae, Gram negatives, Non-fermenters, Listeria b al Vitek biochemic bio. Merieux Enterobacteriaceae, Gram negatives, Gram positives ala Microlog C Biolog Enterobacteriaceae, Gram negatives, Gram positives oxidationaa Microbial-ID MISb Fatty acid Enterobacteriaceae, Listeria, Bacillus, Staphylococcus, Campylobacter Walk/Away biochemic Micro. Scan Enterobacteriaceae, Listeria, Bacillus, Staphylococcus, Campylobacter a Replianalyz al biochemic Oxoid Enterobacteriaceae, Listeria, Bacillus, Staphylococcus, Campylobacter er ala Riboprinter nucleic Qualicon Salmonella, Staphylococcus, Listeria, Escherichia coli acida Cobas biochemic Becton Enterobacteriaceae, Gram negatives, Non-fermenters a b Micro-ID al Dickinson Malthus conductan Malthus Salmonella, Listeria, Campylobacter, E. coli, Pseudomonas, coliforms a ce Bactometer impedance bio. Merieux Salmonella a * Table modified from: Feng, P. , App. I. , FDA Bacteriological Analytical Manual, 8 A ed. a Automated systems NOTE: This table is adopted AOAC Official First or Final and lists known available methods. Presence on this list does b Selected systems intended for general reference only Action. not indicate verification, endorsement, or approval by FDA for use in food analysis.

Identificación basada DNA-DNA Table 2. Partial list of commercially-available, nucleic acid-based assays used in the detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens* (2, 5, 8, 12, 14, 22, 25, 36, 37). Organism Trade Name Format Manufacturer Salmonella GENE-TRAKc probe GENE-TRAK BAX PCR Qualicon BINDb phage Bio. Control Probelia PCR Bio. Control * Table modified from: Feng, P. , App. I, FDA Bacteriological Analytical Manual, 8 A ed. a Polymerase chain reaction b Bacterial Ice Nucleation Diagnostics c Adopted AOAC Official First or Final Action NOTE: This table is intended for general reference only and lists known available methods. Presence on this list does not indicate verification, endorsement, or approval by FDA for use in food analysis.
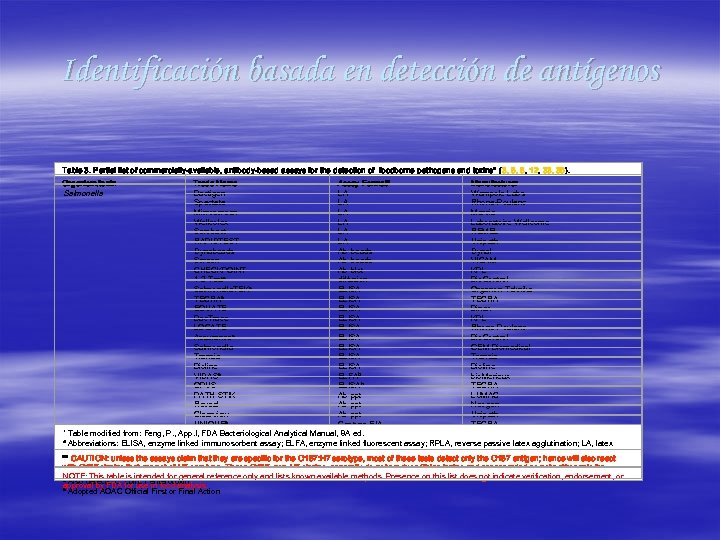
Identificación basada en detección de antígenos Table 3. Partial list of commercially-available, antibody-based assays for the detection of foodborne pathogens and toxins* (3, 5, 8, 12, 33, 36). Organism/toxin Trade Name Assay Formata Manufacturer Bactigen LA Wampole Labs Spectate LA Rhone-Poulenc Microscreen LA Mercia Wellcolex LA Laboratoire Wellcome Serobact LA REMEL RAPIDTEST LA Unipath Dynabeads Ab-beads Dynal Screen Ab-beads VICAM CHECKPOINT Ab-blot KPL 1 -2 Teste diffusion Bio. Control Salmonella. TEK e ELISA Organon Teknika TECRAe ELISA TECRA EQUATE ELISA Binax Bac. Trace ELISA KPL LOCATE ELISA Rhone-Poulenc Assurancee ELISA Bio. Control Salmonella ELISA GEM Biomedical Transia ELISA Transia Bioline ELISA Bioline VIDASe ELFAb bio. Merieux OPUS ELISAb TECRA PATH-STIK Ab-ppt LUMAC Reveal Ab-ppt Neogen Clearview Ab-ppt Unipath UNIQUEe Capture-EIA TECRA * Table modified from: Feng, P. , App. I, FDA Bacteriological Analytical Manual, 8 A ed. a Abbreviations: ELISA, enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; ELFA, enzyme linked fluorescent assay; RPLA, reverse passive latex agglutination; LA, latex agglutination; Ab-ppt, immunoprecipitation. ** CAUTION: unless b Automated ELISA the assays claim that they are specific for the O 157: H 7 serotype, most of these tests detect only the O 157 antigen; hence will also react with O 157 strains that are not E. coli; serotype. enterotoxigenic E. coli strains, generally do not produce Shiga toxins and are regarded as not pathogenic for c EHEC - Enterohemorrhagic of H 7 ETEC - These O 157, non-H 7 NOTE: This table is intended antibodies to O 157 can also cross react with Citrobacter, E. hermanii and other list does not indicate verification, endorsement, or humans. Furthermore, some for general reference only and lists known available methods. Presence on this enteric organisms. d Also detects E. coli LT enterotoxin approval by FDA for use in food analysis. e Adopted AOAC Official First or Final Action Salmonella

Identificación basada en la utilización de sustratos Table 4. Partial list of other commercially available rapid methods and specialty substrate media for detection of foodborne bacteria* (4, 8, 13, 20, 27, 36). Organism Trade Name Formata Assay Manufacturer Salmonella Isogridb HGMF QA Labs OSRT Medium/ motility Unipath (Oxoid) Rambach Medium CHROMagar MUCAP C 8 esterase Biolife XLT-4 Medium Difco MSRVb Medium * Table modified from: Feng, P. , App. I, FDA Bacteriological Analytical Manual, 8 A ed. a Abbreviations: APC, aerobic plate count; HGMF, hydrophobic grid membrane filter; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; MUG, 4 -methylumbelliferyl-ß-D-glucuronide; ONPG, O-nitrophenyl ß-D-galactoside; MPN, most probable number. b Adopted AOAC Official First or Final Action. NOTE: This c Applicationtable is intended for general reference only and lists known available methods. Presence on this for water analysis list does not indicate verification, endorsement, or approval by FDA for use in food analysis. d EHEC - enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli
0ec095a5551bb8501c386017d5649168.ppt