2010 - IMM X.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 43
 Salient Features of India’s Foreign Trade Policy 2009 -14 and Procedure & Documentation Chapter X
Salient Features of India’s Foreign Trade Policy 2009 -14 and Procedure & Documentation Chapter X
 I. Foreign Trade Policy 2009 -14 Backdrop -- 2009 was a challenging year in global history due to severe recession. -- Most of economic indicators, viz. industrial production, trade, capital flow, unemployment and consumption were badly affected all over world. -- WTO estimated 9% decline in volume of global trade. -- India was not so affected but India’s exports were badly hit due to contraction in its traditional export markets. -- Despite the situation being as serious since 2004, * India’s share of global merchandise trade grew to 1. 45% in 2008 from 0. 83% in 2003. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 2
I. Foreign Trade Policy 2009 -14 Backdrop -- 2009 was a challenging year in global history due to severe recession. -- Most of economic indicators, viz. industrial production, trade, capital flow, unemployment and consumption were badly affected all over world. -- WTO estimated 9% decline in volume of global trade. -- India was not so affected but India’s exports were badly hit due to contraction in its traditional export markets. -- Despite the situation being as serious since 2004, * India’s share of global merchandise trade grew to 1. 45% in 2008 from 0. 83% in 2003. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 2
 * India’s share of commercial service export grew to 2. 8% from 1. 4% 2003. * India’s total exports rose by 64% during the period in keeping with objectives of previous policy. * In this process about 14 million jobs were created. Objectives of Foreign Trade Policy 2009 -14 Short Term Objectives : -- To arrest and reverse declining trend of exports -- To provide additional support to sectors affected adversely in developed nations -- To achieve annual export growth of 15% and value of exports $ 200 bill. by March 2011. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 3
* India’s share of commercial service export grew to 2. 8% from 1. 4% 2003. * India’s total exports rose by 64% during the period in keeping with objectives of previous policy. * In this process about 14 million jobs were created. Objectives of Foreign Trade Policy 2009 -14 Short Term Objectives : -- To arrest and reverse declining trend of exports -- To provide additional support to sectors affected adversely in developed nations -- To achieve annual export growth of 15% and value of exports $ 200 bill. by March 2011. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 3
 Long Term Objectives * To return to high export growth path of 25% p. a. * To double India’s export of goods and services. * Long term objective is to double India’s share of global trade by 2020. Elements to achieve the Objectives : 1. Fiscal incentives 2. Institutional changes and simplification of process 3. Enhanced market access into South Korea and ASEAN 4. Infrastructural improvement 5. Reduction in transaction costs and full refund of indirect taxes and levies 6. Building confidence of exporters to face stressful situation [contd. ] 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 4
Long Term Objectives * To return to high export growth path of 25% p. a. * To double India’s export of goods and services. * Long term objective is to double India’s share of global trade by 2020. Elements to achieve the Objectives : 1. Fiscal incentives 2. Institutional changes and simplification of process 3. Enhanced market access into South Korea and ASEAN 4. Infrastructural improvement 5. Reduction in transaction costs and full refund of indirect taxes and levies 6. Building confidence of exporters to face stressful situation [contd. ] 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 4
 7. Extension of DEPB Scheme till December 2010 8. Extension of Income Tax benefits up to March 2011 9. Promoting “Brand India” through ‘Made in India’ shows 10. Upgradation of technology through duty-free import of capital goods under EPCG scheme. 11. “Export Status holders” to be permitted duty-free import of capital goods up to 1% of their FOB value of exports 12. To provide incentives to Towns of Export Excellence units 13. e-trade projects are to be implemented in time-bound manner to reduce costs 14. More ports to be brought under EDI to facilitate exports. 15. Trade related disputes to be sorted out under ‘Single Window Mechanism’ 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 5
7. Extension of DEPB Scheme till December 2010 8. Extension of Income Tax benefits up to March 2011 9. Promoting “Brand India” through ‘Made in India’ shows 10. Upgradation of technology through duty-free import of capital goods under EPCG scheme. 11. “Export Status holders” to be permitted duty-free import of capital goods up to 1% of their FOB value of exports 12. To provide incentives to Towns of Export Excellence units 13. e-trade projects are to be implemented in time-bound manner to reduce costs 14. More ports to be brought under EDI to facilitate exports. 15. Trade related disputes to be sorted out under ‘Single Window Mechanism’ 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 5
 II. Export Transaction Steps Formalities to be completed before initiating exports 1. Opening of Bank Account -- Company has to open a bank account in any commercial bank dealing in foreign exchange. 2. Importer - Exporter Code No. [IEC No. ] -- No person or company is allowed to export or import goods without obtaining IEC No. issued by DGFT or Regional Authority of DGFT. -- Application for IEC No. is to be made in prescribed format, attaching copies of photograph and PAN card along with requisite fees. To facilitate collection of documents from DGFT offices up to three sets of Identity cards are issued 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 6
II. Export Transaction Steps Formalities to be completed before initiating exports 1. Opening of Bank Account -- Company has to open a bank account in any commercial bank dealing in foreign exchange. 2. Importer - Exporter Code No. [IEC No. ] -- No person or company is allowed to export or import goods without obtaining IEC No. issued by DGFT or Regional Authority of DGFT. -- Application for IEC No. is to be made in prescribed format, attaching copies of photograph and PAN card along with requisite fees. To facilitate collection of documents from DGFT offices up to three sets of Identity cards are issued 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 6
![3. Registration cum Membership Certificate [RCMC] GOI have created Export Promotion Councils to promote 3. Registration cum Membership Certificate [RCMC] GOI have created Export Promotion Councils to promote](https://present5.com/presentation/226377210_238045213/image-7.jpg) 3. Registration cum Membership Certificate [RCMC] GOI have created Export Promotion Councils to promote and develop exports from India. There are 24 EPCs and 10 Commodity Boards each responsible for promotion of a particular group of products, projects or service. Major Functions of Export Promotion Councils : i) To provide commercially useful information and assistance to member exporters. ii) To provide professional advice to members on technologyupgradation, quality, standards, design improvement etc. iii) To organise visit of foreign delegations to India and Indian delgations abroad for buyer-seller meets. iv) To organise participation of member exporters in Tradefairs, exhibitions etc. abroad 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 7
3. Registration cum Membership Certificate [RCMC] GOI have created Export Promotion Councils to promote and develop exports from India. There are 24 EPCs and 10 Commodity Boards each responsible for promotion of a particular group of products, projects or service. Major Functions of Export Promotion Councils : i) To provide commercially useful information and assistance to member exporters. ii) To provide professional advice to members on technologyupgradation, quality, standards, design improvement etc. iii) To organise visit of foreign delegations to India and Indian delgations abroad for buyer-seller meets. iv) To organise participation of member exporters in Tradefairs, exhibitions etc. abroad 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 7
 -- An exporter should be registered with concerned EPC, CB or ‘Federation of Indian Exporters’ Organisation (FIEO)’ to avail of foreign trade benefits including licences and permission to import. -- For securing ‘Registration Cum Membership Certificate’ (RCMC) the exporter shall apply to concerned EPC or FIEO in prescribed form with registration fees. -- Once a RCMC No. is granted to an exporter, it remains valid for 5 years unless deregistered for any violation. -- As membership obligation, all RCMC holders are to provide quarterly return of export values to EPC. -- For exporters of those items for which there exists no EPC, registration is to be done at FIEO. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 8
-- An exporter should be registered with concerned EPC, CB or ‘Federation of Indian Exporters’ Organisation (FIEO)’ to avail of foreign trade benefits including licences and permission to import. -- For securing ‘Registration Cum Membership Certificate’ (RCMC) the exporter shall apply to concerned EPC or FIEO in prescribed form with registration fees. -- Once a RCMC No. is granted to an exporter, it remains valid for 5 years unless deregistered for any violation. -- As membership obligation, all RCMC holders are to provide quarterly return of export values to EPC. -- For exporters of those items for which there exists no EPC, registration is to be done at FIEO. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 8
 Registration with Sales Tax Authorities -- Export items are exempted from payment of State and Central Sales Tax. To avail of this benefit, exporters are to register themselves with local Sales Tax authorities. Procedure of Registration at State Sales Tax Authorities -- Application in prescribed form is to be made to the State Sales Tax official under whose jurisdiction exporter is situated. -- The Sales Tax Authorities may verify account books, house rent / tax receipts and partnership deeds. On being satisfied, Sales Tax authorities ask exporter to provide a security bond from another party holding said registration. Procedure of Registration for Central Sales Tax Exemption -- Separate application is to be made for CST registration, within 30 days of first interstate purchase after state registration. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 9
Registration with Sales Tax Authorities -- Export items are exempted from payment of State and Central Sales Tax. To avail of this benefit, exporters are to register themselves with local Sales Tax authorities. Procedure of Registration at State Sales Tax Authorities -- Application in prescribed form is to be made to the State Sales Tax official under whose jurisdiction exporter is situated. -- The Sales Tax Authorities may verify account books, house rent / tax receipts and partnership deeds. On being satisfied, Sales Tax authorities ask exporter to provide a security bond from another party holding said registration. Procedure of Registration for Central Sales Tax Exemption -- Separate application is to be made for CST registration, within 30 days of first interstate purchase after state registration. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 9
 III. Export Promotion Schemes & Incentives -- Because of increased economic uncertainty in developed nations, India’s export growth has been retarded. So to diversify exports from India Special Focus Initiatives are being allowed. i) For Market Diversification -- Focus is on diversification of exports to newer markets, following initiatives are being allowed : * 26 new markets have been chosen for Focus Market Scheme. * Under Focus Market Scheme incentives have been increased from existing 2. 5 to 3%. * In “Market linked Focus Product Scheme” more products have been included, particularly for Africa and South American nations. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 10
III. Export Promotion Schemes & Incentives -- Because of increased economic uncertainty in developed nations, India’s export growth has been retarded. So to diversify exports from India Special Focus Initiatives are being allowed. i) For Market Diversification -- Focus is on diversification of exports to newer markets, following initiatives are being allowed : * 26 new markets have been chosen for Focus Market Scheme. * Under Focus Market Scheme incentives have been increased from existing 2. 5 to 3%. * In “Market linked Focus Product Scheme” more products have been included, particularly for Africa and South American nations. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 10
 ii) For Technological Upgradation * Zero Duty EPCG Scheme to improve quality of export products is allowed. * Existing 3% EPCG Scheme has been made more customer-friendly. * To encourage export of value-added products, ‘ 15% value addition’ scheme on imported inputs has been introduced. * Automobiles and other engineering products have been introduced in “ Focus Product” and “Market Linked Focus Products” schemes. iii) to xiii) In addition, support to status holders, industries like Agriculture & Village Products, Handlooms, Handicrafts, Gems and Jewellery, Leather and Footwear, Marine items, Electronics, IT Hardware, Sports goods, Toys, Green products etc. is permitted. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 11
ii) For Technological Upgradation * Zero Duty EPCG Scheme to improve quality of export products is allowed. * Existing 3% EPCG Scheme has been made more customer-friendly. * To encourage export of value-added products, ‘ 15% value addition’ scheme on imported inputs has been introduced. * Automobiles and other engineering products have been introduced in “ Focus Product” and “Market Linked Focus Products” schemes. iii) to xiii) In addition, support to status holders, industries like Agriculture & Village Products, Handlooms, Handicrafts, Gems and Jewellery, Leather and Footwear, Marine items, Electronics, IT Hardware, Sports goods, Toys, Green products etc. is permitted. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 11
![xiv) Assistance to States for Developing Export Infrastructure & Allied Activities [ ASIDE ] xiv) Assistance to States for Developing Export Infrastructure & Allied Activities [ ASIDE ]](https://present5.com/presentation/226377210_238045213/image-12.jpg) xiv) Assistance to States for Developing Export Infrastructure & Allied Activities [ ASIDE ] xv) Market access Initiative (MAI) -- Providing financial assistance for export promotion on Focus Country & Focus Products basis. xvi) Market Development Assistance (MDA ) -- Financial assistance is provided under MDA for participation in trade fairs, buyer– seller meets, export promotion seminars, export travel grants etc. xvii) Towns of Export Excellence (TEE) -- Recognised units in TEE towns are provided export promotion incentives. xviii) Vishesh Krishi & Gram Udyog Yojana (VKGUY) -VKGUY promotes export of agricultural products, minor forest produce, village industries and other notified products. xix) & xx) Focus Product & Focus Market Schemes 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 12
xiv) Assistance to States for Developing Export Infrastructure & Allied Activities [ ASIDE ] xv) Market access Initiative (MAI) -- Providing financial assistance for export promotion on Focus Country & Focus Products basis. xvi) Market Development Assistance (MDA ) -- Financial assistance is provided under MDA for participation in trade fairs, buyer– seller meets, export promotion seminars, export travel grants etc. xvii) Towns of Export Excellence (TEE) -- Recognised units in TEE towns are provided export promotion incentives. xviii) Vishesh Krishi & Gram Udyog Yojana (VKGUY) -VKGUY promotes export of agricultural products, minor forest produce, village industries and other notified products. xix) & xx) Focus Product & Focus Market Schemes 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 12
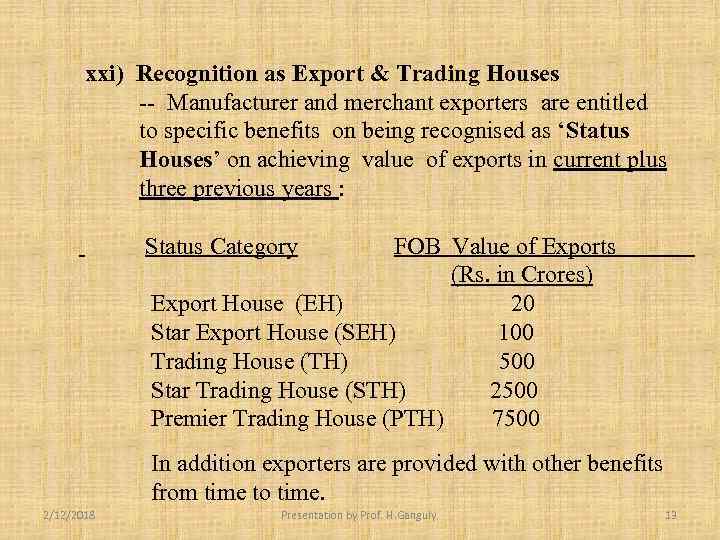 xxi) Recognition as Export & Trading Houses -- Manufacturer and merchant exporters are entitled to specific benefits on being recognised as ‘Status Houses’ on achieving value of exports in current plus three previous years : Status Category FOB Value of Exports (Rs. in Crores) Export House (EH) 20 Star Export House (SEH) 100 Trading House (TH) 500 Star Trading House (STH) 2500 Premier Trading House (PTH) 7500 In addition exporters are provided with other benefits from time to time. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 13
xxi) Recognition as Export & Trading Houses -- Manufacturer and merchant exporters are entitled to specific benefits on being recognised as ‘Status Houses’ on achieving value of exports in current plus three previous years : Status Category FOB Value of Exports (Rs. in Crores) Export House (EH) 20 Star Export House (SEH) 100 Trading House (TH) 500 Star Trading House (STH) 2500 Premier Trading House (PTH) 7500 In addition exporters are provided with other benefits from time to time. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 13
 IV. Shipping Credits A. Pre-shipment Credit Schemes -- In order to make exports competitive in international markets, exporters are provided with credit at attractive rate of interest called Pre-shipment credit or Packing credit. -- Pre-shipment credit or advance is granted by banks to purchase raw, packaging and other material, their processing /manufacture, packing and transportation. -- Bank does not ask for margin money for this credit. It is granted, if necessary, over and above Maximum Permissible Bank Finance [MPBF]. Types of Pre-shipment Credit -- Pre-shipment finance can be classified into 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 14
IV. Shipping Credits A. Pre-shipment Credit Schemes -- In order to make exports competitive in international markets, exporters are provided with credit at attractive rate of interest called Pre-shipment credit or Packing credit. -- Pre-shipment credit or advance is granted by banks to purchase raw, packaging and other material, their processing /manufacture, packing and transportation. -- Bank does not ask for margin money for this credit. It is granted, if necessary, over and above Maximum Permissible Bank Finance [MPBF]. Types of Pre-shipment Credit -- Pre-shipment finance can be classified into 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 14
 I. Pre-shipment Credit in Indian Currency -- Application is to be made by exporter to their bank along with following documents : * Confirmed export order / contract or original Letter of Credit * Copies of Income Tax / Wealth Tax assessment orders * Copy of RCMC * ECGC policy or guarantee * Undertaking that advance shall be used for export production / purchase only. -- Need for documents are waived when Packing Credit is required against Red-clause L/C issued by importer’s bank. -- In cases of indirect export, Packing Credit is allowed to manufacturers on a letter from merchant exporter. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 15
I. Pre-shipment Credit in Indian Currency -- Application is to be made by exporter to their bank along with following documents : * Confirmed export order / contract or original Letter of Credit * Copies of Income Tax / Wealth Tax assessment orders * Copy of RCMC * ECGC policy or guarantee * Undertaking that advance shall be used for export production / purchase only. -- Need for documents are waived when Packing Credit is required against Red-clause L/C issued by importer’s bank. -- In cases of indirect export, Packing Credit is allowed to manufacturers on a letter from merchant exporter. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 15
 * Period of Packing Credit -- It is granted for maximum period of 180 days, extendable to 270 days , in exceptional cases to 360 days. -- The Pre-shipment credit is to be liquidated from proceeds of export consignment for which credit is granted. * Rate of Interest on Packing Credit i) for first 180 days -- Bank rate less 2. 5% ii) between 180 to 360 days -- Bank is free to decide rate. II. Packing Credit in Foreign Currency (PCFC) -- Packing credit is also available in any freely convertible foreign currency. -- Rate of interest for first 180 days is [LIBOR plus 1. 5%] -- For next 90 days, another 2% is added to above rate. -- Other terms and conditions remain the same. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 16
* Period of Packing Credit -- It is granted for maximum period of 180 days, extendable to 270 days , in exceptional cases to 360 days. -- The Pre-shipment credit is to be liquidated from proceeds of export consignment for which credit is granted. * Rate of Interest on Packing Credit i) for first 180 days -- Bank rate less 2. 5% ii) between 180 to 360 days -- Bank is free to decide rate. II. Packing Credit in Foreign Currency (PCFC) -- Packing credit is also available in any freely convertible foreign currency. -- Rate of interest for first 180 days is [LIBOR plus 1. 5%] -- For next 90 days, another 2% is added to above rate. -- Other terms and conditions remain the same. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 16
 III. Pre-Shipment Credit Against Export Incentives -- Exporters are entitled to draw advance from their bank against export incentives for 90 days. -- Exporters are to apply to their bank for this advance enclosing ECGC’s guarantee. -- Banks charge interest at same rate as Packing Credit. IV. Pre-Shipment Credit for Import L/C -- Exporters’ banks establish ‘Letter of Credit’ at concessional rate to import raw and packaging material against Advance Licence for export production. V. Running Account Facility to Exporters -- Banks have been authorised to extend Pre-shipment credit on running basis without insisting on export order or Letter of credit to exporters having good track record. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 17
III. Pre-Shipment Credit Against Export Incentives -- Exporters are entitled to draw advance from their bank against export incentives for 90 days. -- Exporters are to apply to their bank for this advance enclosing ECGC’s guarantee. -- Banks charge interest at same rate as Packing Credit. IV. Pre-Shipment Credit for Import L/C -- Exporters’ banks establish ‘Letter of Credit’ at concessional rate to import raw and packaging material against Advance Licence for export production. V. Running Account Facility to Exporters -- Banks have been authorised to extend Pre-shipment credit on running basis without insisting on export order or Letter of credit to exporters having good track record. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 17
 VI. EXIM Bank’s Foreign Currency Pre-Shipment Credit -- EXIM Bank provides Packing credit in foreign currency through authorised F. E. dealers i. e. banks called Foreign Currency Packing Credit [FCPC]. -- Followings are entitled to the scheme : * Export Status Houses exceeding Rs. 10 cr. turnover * Manufacturing units exporting 25% or more of their produce * Exporters having satisfactory track record. -- EXIM Bank charges interest @ 2% more than rate at which they raise the funds. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 18
VI. EXIM Bank’s Foreign Currency Pre-Shipment Credit -- EXIM Bank provides Packing credit in foreign currency through authorised F. E. dealers i. e. banks called Foreign Currency Packing Credit [FCPC]. -- Followings are entitled to the scheme : * Export Status Houses exceeding Rs. 10 cr. turnover * Manufacturing units exporting 25% or more of their produce * Exporters having satisfactory track record. -- EXIM Bank charges interest @ 2% more than rate at which they raise the funds. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 18
 B. Post-Shipment Credit -- In order to enable exporters extend credit to buyers abroad, following credit or advance is allowed to them by their banks at concessional rate of interest: 1. Export Document negotiation under L/C -- When the exports and documents are as per L/C, negotiating bank may make payment to exporter immediately and negotiate documents to receive payment. 2. Purchase of Export Bill drawn under Confirmed Credit -- Under confirmed export order (in absence of L/C) banks purchase or discount Export Bills. -- Banks insist on ECGC policy or guarantee on foreign buyer before purchasing bills. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 19
B. Post-Shipment Credit -- In order to enable exporters extend credit to buyers abroad, following credit or advance is allowed to them by their banks at concessional rate of interest: 1. Export Document negotiation under L/C -- When the exports and documents are as per L/C, negotiating bank may make payment to exporter immediately and negotiate documents to receive payment. 2. Purchase of Export Bill drawn under Confirmed Credit -- Under confirmed export order (in absence of L/C) banks purchase or discount Export Bills. -- Banks insist on ECGC policy or guarantee on foreign buyer before purchasing bills. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 19
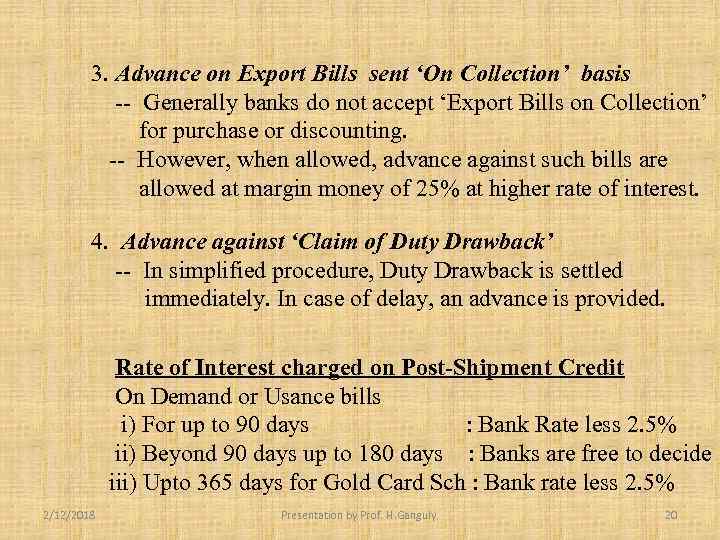 3. Advance on Export Bills sent ‘On Collection’ basis -- Generally banks do not accept ‘Export Bills on Collection’ for purchase or discounting. -- However, when allowed, advance against such bills are allowed at margin money of 25% at higher rate of interest. 4. Advance against ‘Claim of Duty Drawback’ -- In simplified procedure, Duty Drawback is settled immediately. In case of delay, an advance is provided. Rate of Interest charged on Post-Shipment Credit On Demand or Usance bills i) For up to 90 days : Bank Rate less 2. 5% ii) Beyond 90 days up to 180 days : Banks are free to decide iii) Upto 365 days for Gold Card Sch : Bank rate less 2. 5% 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 20
3. Advance on Export Bills sent ‘On Collection’ basis -- Generally banks do not accept ‘Export Bills on Collection’ for purchase or discounting. -- However, when allowed, advance against such bills are allowed at margin money of 25% at higher rate of interest. 4. Advance against ‘Claim of Duty Drawback’ -- In simplified procedure, Duty Drawback is settled immediately. In case of delay, an advance is provided. Rate of Interest charged on Post-Shipment Credit On Demand or Usance bills i) For up to 90 days : Bank Rate less 2. 5% ii) Beyond 90 days up to 180 days : Banks are free to decide iii) Upto 365 days for Gold Card Sch : Bank rate less 2. 5% 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 20
 V. Factoring -- It is a process of Short-term financing of export operations. -- In Factoring an institution purchases export receivables at a discounted price ( 2 -4%) of final value. -- The extent of discount depends up on type of product, terms of contract etc. -- Factoring may include with recourse to seller term i. e. in absence of payment by buyer, exporter shall be obliged to refund payment. 2/12/2018 Benefits of Factoring * Facilitates immediate payment – reinforces working capital. * In case of buyers’ default, factoring institution has to pay. * Factoring is a good substitute of bank credit particularly when interest rates are high. * It increases purchasing power of exporters without Presentation by Prof. 21 depending on bank finance. H. Ganguly.
V. Factoring -- It is a process of Short-term financing of export operations. -- In Factoring an institution purchases export receivables at a discounted price ( 2 -4%) of final value. -- The extent of discount depends up on type of product, terms of contract etc. -- Factoring may include with recourse to seller term i. e. in absence of payment by buyer, exporter shall be obliged to refund payment. 2/12/2018 Benefits of Factoring * Facilitates immediate payment – reinforces working capital. * In case of buyers’ default, factoring institution has to pay. * Factoring is a good substitute of bank credit particularly when interest rates are high. * It increases purchasing power of exporters without Presentation by Prof. 21 depending on bank finance. H. Ganguly.
 Factoring Process -- Exporter and importer enter into open sales contract with relevant terms of sale. -- Exporter ships goods directly to importer. -- Exporter submits invoice to his ‘Factoring Service Provider’. -- Exporter’s FSP immediately makes payment to Exporter. Interest for gap period and commission is to be paid by exporter. -- Exporter’s FSP transfers invoice to importer’s FSP who assumes credit risk and effects collection of receivables. -- Importer’s FSP presents invoice on due date to importer. -- Importer’s FSP collects payment from importer -- Importer’s FSP sends payment after deducting their commission to Exporter’s FSP. -- Generally factoring is an ongoing process between exporter and importer with FSPs in between based on long-term contract. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 22
Factoring Process -- Exporter and importer enter into open sales contract with relevant terms of sale. -- Exporter ships goods directly to importer. -- Exporter submits invoice to his ‘Factoring Service Provider’. -- Exporter’s FSP immediately makes payment to Exporter. Interest for gap period and commission is to be paid by exporter. -- Exporter’s FSP transfers invoice to importer’s FSP who assumes credit risk and effects collection of receivables. -- Importer’s FSP presents invoice on due date to importer. -- Importer’s FSP collects payment from importer -- Importer’s FSP sends payment after deducting their commission to Exporter’s FSP. -- Generally factoring is an ongoing process between exporter and importer with FSPs in between based on long-term contract. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 22
 B. Forfaiting -- Forfaiting is a French word meaning ‘to relinquish’. -- It is a medium-term credit sale of 1 – 3 years in which the exporter issues a bill of exchange which is accepted by buyer and their bank. -- Forfaitng is a financing technique that suits cash-short dealers. -- In forfaiting , exporter surrenders without recourse, right to claim payment of goods exported against cash payment. -- Forfaiting is useful for nations like India where postshipment credit is limited by banks to 180 days at reduced rates. -- It does away with fear of cross-border political and commercial risks. -- Exporter also saves credit insurance premium in this process. -- It also hedges exporters against interest and exchange rate fluctuation risks in deferred payments. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 23
B. Forfaiting -- Forfaiting is a French word meaning ‘to relinquish’. -- It is a medium-term credit sale of 1 – 3 years in which the exporter issues a bill of exchange which is accepted by buyer and their bank. -- Forfaitng is a financing technique that suits cash-short dealers. -- In forfaiting , exporter surrenders without recourse, right to claim payment of goods exported against cash payment. -- Forfaiting is useful for nations like India where postshipment credit is limited by banks to 180 days at reduced rates. -- It does away with fear of cross-border political and commercial risks. -- Exporter also saves credit insurance premium in this process. -- It also hedges exporters against interest and exchange rate fluctuation risks in deferred payments. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 23
 Forfaiting Procedure 1. Before entering into a contract with buyer abroad, exporter takes a ‘forfaitng quote’ from their bank ( who in turn get it from a Forfaitng agency like EXIM Bank) indicating their willingness and forfaiting charges (includes discounting , commitment and documentation fees). 2. Exporter then signs ‘Commercial contract’ with foreign buyer with term that buyer shall furnish ‘co-accepted bill of exchange’ along with their bank. 3. The exporter then enters into “Forfaitng contract” with forfaitng agency for the transaction. Now actual export operation may be undertaken. 4. Exporter ships consignment as per order and hands over documents including bill of Lading, bill of Exchange for 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 24 total amount to their bank.
Forfaiting Procedure 1. Before entering into a contract with buyer abroad, exporter takes a ‘forfaitng quote’ from their bank ( who in turn get it from a Forfaitng agency like EXIM Bank) indicating their willingness and forfaiting charges (includes discounting , commitment and documentation fees). 2. Exporter then signs ‘Commercial contract’ with foreign buyer with term that buyer shall furnish ‘co-accepted bill of exchange’ along with their bank. 3. The exporter then enters into “Forfaitng contract” with forfaitng agency for the transaction. Now actual export operation may be undertaken. 4. Exporter ships consignment as per order and hands over documents including bill of Lading, bill of Exchange for 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 24 total amount to their bank.
 5. Exporter’s bank sends these documents to foreign buyer or their bank to accept or co-accept the ‘Bill of Exchange’ with buyer ‘without recourse to forfaitng agency’ and send it back to exporter’s bank. 6. Exporter’s bank in turn forwards the co-accepted ‘Bill of exchange’ to forfaiting agency, who checks the papers and deposits forfaite proceeds to exporter’s bank. 7. Exporter’s bank deposits procceds in exporter’s account and issues Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC) alongwith GR form. That is how, one-time contract of forfaiting is completed. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 25
5. Exporter’s bank sends these documents to foreign buyer or their bank to accept or co-accept the ‘Bill of Exchange’ with buyer ‘without recourse to forfaitng agency’ and send it back to exporter’s bank. 6. Exporter’s bank in turn forwards the co-accepted ‘Bill of exchange’ to forfaiting agency, who checks the papers and deposits forfaite proceeds to exporter’s bank. 7. Exporter’s bank deposits procceds in exporter’s account and issues Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC) alongwith GR form. That is how, one-time contract of forfaiting is completed. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 25
 C. Finance to Foreign Buyers -- Line of Credit -- Commercial banks extend credit to local exporters, generally at concessional rate in the form of export promotion. -- In addition, sometimes Indian banks extend credit to foreign buyers to facilitate import of goods and services from India. These are carried out in two forms : I. Line of Credit -- When an Indian bank extend credit to an overseas bank, institution or govt. to enable them to import selected goods from India, it is called Line of Credit. -- On behalf of India, Line of Credit is generally extended by Export Import Bank of India [EXIM Bank] -- A number of importers in foreign country may draw from the same ‘Line of credit’ Prof. H. Ganguly. from India. 2/12/2018 Presentation by for import 26
C. Finance to Foreign Buyers -- Line of Credit -- Commercial banks extend credit to local exporters, generally at concessional rate in the form of export promotion. -- In addition, sometimes Indian banks extend credit to foreign buyers to facilitate import of goods and services from India. These are carried out in two forms : I. Line of Credit -- When an Indian bank extend credit to an overseas bank, institution or govt. to enable them to import selected goods from India, it is called Line of Credit. -- On behalf of India, Line of Credit is generally extended by Export Import Bank of India [EXIM Bank] -- A number of importers in foreign country may draw from the same ‘Line of credit’ Prof. H. Ganguly. from India. 2/12/2018 Presentation by for import 26
 II. Buyer’s Credit -- When credit is extended by an Indian bank to an overseas buyer to enable them to pay for specified type of imports from India, it is called Buyer’s Credit. -- Buyer’s credit may be established by EXIM Bank; but it is done projectwise to facilitate export of specific machineries and equipments approved by Govt. of India. -- Both of these two modes of credit ( viz. ‘Line of Credit’ and ‘Buyer’s Credit’ are operated against guarantee furnished by relevant country govt. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 27
II. Buyer’s Credit -- When credit is extended by an Indian bank to an overseas buyer to enable them to pay for specified type of imports from India, it is called Buyer’s Credit. -- Buyer’s credit may be established by EXIM Bank; but it is done projectwise to facilitate export of specific machineries and equipments approved by Govt. of India. -- Both of these two modes of credit ( viz. ‘Line of Credit’ and ‘Buyer’s Credit’ are operated against guarantee furnished by relevant country govt. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 27
 VI. Cargo & Credit Insurance -- There are different type of risks in international transactions like * Commercial Risks -- Exporter and importer are located in different nations having different legal and political systems, it may give rise to risks due to change in host Govt. rules, security threats, IPR problems etc. * Economic Risks -- Changes in BOP position of nations give rise to exchange rate fluctuation and other risks. • Transit Risks -- There are different type of loss in transit of cargo from exporter to importer. • Credit Risk -- In exports on credit, there are political and commercial risks in receipt of payments. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 28
VI. Cargo & Credit Insurance -- There are different type of risks in international transactions like * Commercial Risks -- Exporter and importer are located in different nations having different legal and political systems, it may give rise to risks due to change in host Govt. rules, security threats, IPR problems etc. * Economic Risks -- Changes in BOP position of nations give rise to exchange rate fluctuation and other risks. • Transit Risks -- There are different type of loss in transit of cargo from exporter to importer. • Credit Risk -- In exports on credit, there are political and commercial risks in receipt of payments. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 28
 A. Transit Risks Type of risks in transit are * Maritime risks i. e. damage or loss in transit due to natural calamity or manmade events of negligence. * Extraneous risks i. e. due to faulty loading, unloading, handling, theft, pilferage, hook damage etc. * War perils – damage or loss due to wars, revolution etc. * Strike perils -- labour disturbance, riot, civil commotion etc 2/12/2018 -- International cargo may be covered for total or partial loss through suitable marine cargo insurance policy by General Insurance Companies on payment of stipulated premium. -- In cif payment terms, insurance premium is to be borne by exporters and realised from buyer in price of 29 consignment. Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly.
A. Transit Risks Type of risks in transit are * Maritime risks i. e. damage or loss in transit due to natural calamity or manmade events of negligence. * Extraneous risks i. e. due to faulty loading, unloading, handling, theft, pilferage, hook damage etc. * War perils – damage or loss due to wars, revolution etc. * Strike perils -- labour disturbance, riot, civil commotion etc 2/12/2018 -- International cargo may be covered for total or partial loss through suitable marine cargo insurance policy by General Insurance Companies on payment of stipulated premium. -- In cif payment terms, insurance premium is to be borne by exporters and realised from buyer in price of 29 consignment. Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly.
 B. Credit Risks -- Exporters selling their goods on credit terms are exposed to foreign buyer’s becoming bankrupt, loosing capacity or willingness to pay. -- This risk is being covered through export credit risk insurance. -- In India, export credit risk insurance is provided by Export Credit Guarantee Corporation [ECGC] -- a Govt. of India Undertaking. * ECGC provides wide range of insurance covers for exporters against loss of credit for exported goods and services. * ECGC offers guarantees to banks and financial institutions in favour of exporters’ getting facilities from them. * ECGC provides ‘overseas investment insurance’ to Indian companies going into joint venture companies abroad. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 30
B. Credit Risks -- Exporters selling their goods on credit terms are exposed to foreign buyer’s becoming bankrupt, loosing capacity or willingness to pay. -- This risk is being covered through export credit risk insurance. -- In India, export credit risk insurance is provided by Export Credit Guarantee Corporation [ECGC] -- a Govt. of India Undertaking. * ECGC provides wide range of insurance covers for exporters against loss of credit for exported goods and services. * ECGC offers guarantees to banks and financial institutions in favour of exporters’ getting facilities from them. * ECGC provides ‘overseas investment insurance’ to Indian companies going into joint venture companies abroad. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 30
 * ECGC offers insurance to exporters against payment risks. * ECGC provides information on credit worthiness of overseas buyers and also helps exporters in recovering bad debts. Principal Credit Insurance Policies of ECGC 1. Standard Policy -- It is also known as Shipment (comprehensive risks) Policy. -- This policy covers goods in respect of short term credit not exceeding 180 days both for commercial and political risks -- It covers both political and commercial risks for exporters whose export turnover is more than Rs. 50 lakhs. -- A standard policy covers all shipments during next 24 months from date of issue. -- Normally ECGC pays 90% of loss, balance 10% is to be borne by exporter. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 31
* ECGC offers insurance to exporters against payment risks. * ECGC provides information on credit worthiness of overseas buyers and also helps exporters in recovering bad debts. Principal Credit Insurance Policies of ECGC 1. Standard Policy -- It is also known as Shipment (comprehensive risks) Policy. -- This policy covers goods in respect of short term credit not exceeding 180 days both for commercial and political risks -- It covers both political and commercial risks for exporters whose export turnover is more than Rs. 50 lakhs. -- A standard policy covers all shipments during next 24 months from date of issue. -- Normally ECGC pays 90% of loss, balance 10% is to be borne by exporter. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 31
 2. Small Exporters’ Policy -- Small Exporters’ Policy is issued where export turnover does not exceed Rs. 50 lakhs in 12 months. -- Minimum premium for this policy is Rs. 2000/-, it remains valid for 12 months. -- ECGC pays claims not exceeding 95% of commercial loss and 100% of political loss. 3. Specific Shipment Policy--Short Term -- This policy can be taken by Indian exporters for one or a few shipments for commercial and political risks for not exceeding 180 days. -- Specific Shipment Policies of ECGC are * Specific shipments (commercial and political risks) Policy * Specific shipments (political risks) Policy and * Specific shipments (insolvency and default of L/C opening bank & political. Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. risks) Policy. 2/12/2018 32
2. Small Exporters’ Policy -- Small Exporters’ Policy is issued where export turnover does not exceed Rs. 50 lakhs in 12 months. -- Minimum premium for this policy is Rs. 2000/-, it remains valid for 12 months. -- ECGC pays claims not exceeding 95% of commercial loss and 100% of political loss. 3. Specific Shipment Policy--Short Term -- This policy can be taken by Indian exporters for one or a few shipments for commercial and political risks for not exceeding 180 days. -- Specific Shipment Policies of ECGC are * Specific shipments (commercial and political risks) Policy * Specific shipments (political risks) Policy and * Specific shipments (insolvency and default of L/C opening bank & political. Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. risks) Policy. 2/12/2018 32
 VII. Export Transaction Steps -- When an exporter fulfills pre-requisites of export by procuring IEC no. , RCMC and other registrations; it goes for orders from abroad. The orders are to be scrutinised as under : Step I : Scrutiny of Order The export order (and L/C) is scrutinised for terms, conditions, product specifications, documents needed , delivery schedule, type of packaging etc. , the foreign exchange & import control rules in importers’ country is checked. If found satisfactory, acceptance of order is confirmed to buyer. The salient aspects of order like price, payment terms, delivery, shipping marks etc. are confirmed by mentioning again. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 33
VII. Export Transaction Steps -- When an exporter fulfills pre-requisites of export by procuring IEC no. , RCMC and other registrations; it goes for orders from abroad. The orders are to be scrutinised as under : Step I : Scrutiny of Order The export order (and L/C) is scrutinised for terms, conditions, product specifications, documents needed , delivery schedule, type of packaging etc. , the foreign exchange & import control rules in importers’ country is checked. If found satisfactory, acceptance of order is confirmed to buyer. The salient aspects of order like price, payment terms, delivery, shipping marks etc. are confirmed by mentioning again. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 33
 Step II. Production of Export Consignment Manufacture of export products is initiated in exporters’ unit or procured from market. Exemption from payment of sales tax on export material is availed through form 14/14 A. Step III. Booking of Space in Ship In some routes where ships are not frequent, space is to be booked in advance so that cargo can reach importer within delivery schedule. Of course, it is done mostly by C. & F. Agent. Step IV. Packing Credit Pre-shipment loan is availed from banks for export production. Step V. Export Inspection Export cargo is submitted for pre-shipment quality inspection. It is done by Export Inspection Council or other authorities indicated by buyer or self – certification by exporters 2/12/2018 34 in appropriate cases. Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly.
Step II. Production of Export Consignment Manufacture of export products is initiated in exporters’ unit or procured from market. Exemption from payment of sales tax on export material is availed through form 14/14 A. Step III. Booking of Space in Ship In some routes where ships are not frequent, space is to be booked in advance so that cargo can reach importer within delivery schedule. Of course, it is done mostly by C. & F. Agent. Step IV. Packing Credit Pre-shipment loan is availed from banks for export production. Step V. Export Inspection Export cargo is submitted for pre-shipment quality inspection. It is done by Export Inspection Council or other authorities indicated by buyer or self – certification by exporters 2/12/2018 34 in appropriate cases. Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly.
 Step VI. Certificate of Origin It is a commercial document generally needed by customs authorities in importers’ nation. As per importer’s needs exporter has to procure Certificate of Origin from a) Local Chamber of Commerce of which exporter is a member b) Consulate of importing country c) Export Inspection Council or DGFT or Commodity Boards for Generalised System of Preference (GSP). d) High Commission of importing nation for Commonwealth preference. Step VII. Marine Insurance Policy It is an agreement whereby insurer indemnifies the assured against losses to stated extent incidental upon journey by sea, air, land, rail, road transport or registered post. Insurer charges a premium for this service from exporter. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 35
Step VI. Certificate of Origin It is a commercial document generally needed by customs authorities in importers’ nation. As per importer’s needs exporter has to procure Certificate of Origin from a) Local Chamber of Commerce of which exporter is a member b) Consulate of importing country c) Export Inspection Council or DGFT or Commodity Boards for Generalised System of Preference (GSP). d) High Commission of importing nation for Commonwealth preference. Step VII. Marine Insurance Policy It is an agreement whereby insurer indemnifies the assured against losses to stated extent incidental upon journey by sea, air, land, rail, road transport or registered post. Insurer charges a premium for this service from exporter. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 35
 Types of Transit Risks or Covers Exporters choose the transit policies or covers depending on risks covered by them. 1. Institute Cargo Clause (C) This policy covers total loss or damage to goods insured by fire or explosion, sinking or grounding of vessels, overturning or derailment of land - conveyance, collision, discharge of cargo at port of distress, general average sacrifice, jettison etc. 2. Institute Cargo Clause (B) This policy covers all risks of earlier policy, in addition loss or damage due to earthquake, volcanic eruption or lightning, washing overboard, entry of sea, lake or river water or loss due to dropping while loading or unloading. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 36
Types of Transit Risks or Covers Exporters choose the transit policies or covers depending on risks covered by them. 1. Institute Cargo Clause (C) This policy covers total loss or damage to goods insured by fire or explosion, sinking or grounding of vessels, overturning or derailment of land - conveyance, collision, discharge of cargo at port of distress, general average sacrifice, jettison etc. 2. Institute Cargo Clause (B) This policy covers all risks of earlier policy, in addition loss or damage due to earthquake, volcanic eruption or lightning, washing overboard, entry of sea, lake or river water or loss due to dropping while loading or unloading. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 36
 3. Extraneous Risks The Insurance company may extend cover to Institute Cargo Clause (B) risks in addition to extraneous risks like TPND [ i. e. Theft, Pilferage & Non-Delivery], heating, sweating, leakage etc. on payment of extra premium. 4. All Risks Cover or Institute Cargo Clause (A) This policy covers all risks of loss or damage from factory/warehouse of exporter to final destination. Generally this policy is preferred by exporters. 5. War and S. R. C. C. Risk Cover This cover provides protection from damage and losses in cases of War, Seizure, Restraint and Civil commotion. 6. Insurance for Registered Articles This cover extends protection from physical loss, or damage to precious cargo like diamonds, costly stones etc. under 2/12/2018 Presentation 37 Institute Cargo Clauses by Prof. H. Ganguly. airfreights. (Air) for
3. Extraneous Risks The Insurance company may extend cover to Institute Cargo Clause (B) risks in addition to extraneous risks like TPND [ i. e. Theft, Pilferage & Non-Delivery], heating, sweating, leakage etc. on payment of extra premium. 4. All Risks Cover or Institute Cargo Clause (A) This policy covers all risks of loss or damage from factory/warehouse of exporter to final destination. Generally this policy is preferred by exporters. 5. War and S. R. C. C. Risk Cover This cover provides protection from damage and losses in cases of War, Seizure, Restraint and Civil commotion. 6. Insurance for Registered Articles This cover extends protection from physical loss, or damage to precious cargo like diamonds, costly stones etc. under 2/12/2018 Presentation 37 Institute Cargo Clauses by Prof. H. Ganguly. airfreights. (Air) for
 Step VIII. Export Credit Insurance Payment for exports are open to various type of risks like political risks in outbreak of wars, coup etc. , economic difficulties in drastic fall of Balance of Payment in addition to normal commercial risks of default, going bankrupt etc. Govt. of India has created Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India (ECGC) to provide insurance of export credit to exporters. ECGC extends following credit insurance covers : 1. Standard Policies -- to protect against short term credit risk. 2. Specific Policies – to protect against deferred payment risk in service, construction works and turn- key project exports. 3. Financial Guarantees – issued to Indian bankers to protect against loss on account of pre- and post-shipment support. 4. Special schemes – on confirmation of L/C against buyer’s 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. credit, lines of credit or overseas investment insurance. 38
Step VIII. Export Credit Insurance Payment for exports are open to various type of risks like political risks in outbreak of wars, coup etc. , economic difficulties in drastic fall of Balance of Payment in addition to normal commercial risks of default, going bankrupt etc. Govt. of India has created Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India (ECGC) to provide insurance of export credit to exporters. ECGC extends following credit insurance covers : 1. Standard Policies -- to protect against short term credit risk. 2. Specific Policies – to protect against deferred payment risk in service, construction works and turn- key project exports. 3. Financial Guarantees – issued to Indian bankers to protect against loss on account of pre- and post-shipment support. 4. Special schemes – on confirmation of L/C against buyer’s 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. credit, lines of credit or overseas investment insurance. 38
 ECGC operates these credit insurance as covers depending on viability of exporter or branch of bank. ECGC fixes a credit limit, within which the party has to keep their total liability at any point of time. The premium charged by ECGC depends on nature of risks, credit limit and past performance of exporter. 2/12/2018 Step IX. Central Excise Clearance Release of excisable goods from exporters’ factory or warehouse may be done after payment of central excise duty. Rebate may be claimed from office of actual export. The cargo is then sealed in presence of Superintendent or Inspector of Central Excise for export. Alternately, goods may be removed under Bond and selfsealed and self-certified for exporter. Goods may be examined at the place of export also. Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 39
ECGC operates these credit insurance as covers depending on viability of exporter or branch of bank. ECGC fixes a credit limit, within which the party has to keep their total liability at any point of time. The premium charged by ECGC depends on nature of risks, credit limit and past performance of exporter. 2/12/2018 Step IX. Central Excise Clearance Release of excisable goods from exporters’ factory or warehouse may be done after payment of central excise duty. Rebate may be claimed from office of actual export. The cargo is then sealed in presence of Superintendent or Inspector of Central Excise for export. Alternately, goods may be removed under Bond and selfsealed and self-certified for exporter. Goods may be examined at the place of export also. Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 39
 Step X. Shipment of Goods Those exporters who do not have their own Packing and Clearing departments may hand over consignments to Clearing & Forwarding Agents (C & F agents). The C&F agents carry out suitable packing of cargo, documentation and formalities for final shipment. Step XI. Shipment Advice to Importer After export is complete, exporter sends a fax of nonnegotiable copy of ‘Bill of Lading’ to importer containing relevant details with copy of Master document. Step XII. Negotiation of Documents for Payment Next the exporter presents Bill of Lading along with other documents to their banker for realisation of payment from overseas buyer as per terms of L/C. Subsequent to this, exporter 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 40 has to realise export benefits from Govt.
Step X. Shipment of Goods Those exporters who do not have their own Packing and Clearing departments may hand over consignments to Clearing & Forwarding Agents (C & F agents). The C&F agents carry out suitable packing of cargo, documentation and formalities for final shipment. Step XI. Shipment Advice to Importer After export is complete, exporter sends a fax of nonnegotiable copy of ‘Bill of Lading’ to importer containing relevant details with copy of Master document. Step XII. Negotiation of Documents for Payment Next the exporter presents Bill of Lading along with other documents to their banker for realisation of payment from overseas buyer as per terms of L/C. Subsequent to this, exporter 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 40 has to realise export benefits from Govt.
 VIII. Role of Clearing & Forwarding Agents Carrying out all operations in international trade may not be convenient for exporter, so use is made of Clearing & Forwarding Agent (CFA) also called Freight Forwarders to undertake following functions. * Advise on shipping route * Booking space on ship * Inland transportation * Insurance of cargo at warehouses * Shipping and custom formalities at port * Assisting exporter in filing claims etc. CFA operate for exporters on commission based on f. o. b. value of consignments. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 41
VIII. Role of Clearing & Forwarding Agents Carrying out all operations in international trade may not be convenient for exporter, so use is made of Clearing & Forwarding Agent (CFA) also called Freight Forwarders to undertake following functions. * Advise on shipping route * Booking space on ship * Inland transportation * Insurance of cargo at warehouses * Shipping and custom formalities at port * Assisting exporter in filing claims etc. CFA operate for exporters on commission based on f. o. b. value of consignments. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 41
 Documents for Export The exporter provides CFA with following documents along with export cargo to carry out port procedures and custom clearance of cargo for loading on ship or board of aircraft -- Original export order / contract -- Original Letter of Credit -- Commercial invoice -- Original and duplicate copy of GR form with IEC no. -- Requisite Certificate of origin -- Inspection / Quality control certificate -- Purchase memo (in case of merchant exporters) -- Railway/ Lorry Receipt of cargo -- Consular /Customs invoice -- ARE-1/ARE-2 forms -- Declaration by exporter (in three copies) -- Any other document needed by customs department. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 42
Documents for Export The exporter provides CFA with following documents along with export cargo to carry out port procedures and custom clearance of cargo for loading on ship or board of aircraft -- Original export order / contract -- Original Letter of Credit -- Commercial invoice -- Original and duplicate copy of GR form with IEC no. -- Requisite Certificate of origin -- Inspection / Quality control certificate -- Purchase memo (in case of merchant exporters) -- Railway/ Lorry Receipt of cargo -- Consular /Customs invoice -- ARE-1/ARE-2 forms -- Declaration by exporter (in three copies) -- Any other document needed by customs department. 2/12/2018 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly. 42
 Return Documents After loading the consignment ‘on board’ of ship, C&F agent gets ‘clean on board’ bill of lading( 3 negotiable and 10 non- negotiable copies ) from shipping company. Then C&F agent returns following documents to exporter -- Full set of ‘clean on board ‘ Bill of Lading -- Copies of commercial invoice attested by customs -- Duty Drawback copy of shipping bill -- Original export order/export contract -- Original Letter of credit -- Copies of consular invoice (if any) -- ARE-1 /ARE-2 forms -- GR form (duplicate). 2/12/2018 These documents are used by exporter to realise payment from importer and export-incentives from Govt. Presentation by Prof. ----H. Ganguly. 43
Return Documents After loading the consignment ‘on board’ of ship, C&F agent gets ‘clean on board’ bill of lading( 3 negotiable and 10 non- negotiable copies ) from shipping company. Then C&F agent returns following documents to exporter -- Full set of ‘clean on board ‘ Bill of Lading -- Copies of commercial invoice attested by customs -- Duty Drawback copy of shipping bill -- Original export order/export contract -- Original Letter of credit -- Copies of consular invoice (if any) -- ARE-1 /ARE-2 forms -- GR form (duplicate). 2/12/2018 These documents are used by exporter to realise payment from importer and export-incentives from Govt. Presentation by Prof. ----H. Ganguly. 43


