4d04c0262afe0234a85b30fd6f3598c9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Safety Management Systems
Safety Management Systems
 Safety Management Systems The Company West. Jet Culture Safety Management Plan Policies Organization Processes Training Communication SMS Benefits ($$$) Conclusion
Safety Management Systems The Company West. Jet Culture Safety Management Plan Policies Organization Processes Training Communication SMS Benefits ($$$) Conclusion
 Safety Management Systems West. Jet Snapshot • Ten years in operation • More than 43 million guests flown since 1996 • (average of 851, 043 guests/month in Q 4 2005) • Eight year average revenue growth of 54% • Nine year average growth: 50. 0% (RPM) / 47. 8% (ASM) • Fleet of 54 Boeing 737 NG aircraft (63 aircraft in 2006) • Over 5, 000 West. Jet employees
Safety Management Systems West. Jet Snapshot • Ten years in operation • More than 43 million guests flown since 1996 • (average of 851, 043 guests/month in Q 4 2005) • Eight year average revenue growth of 54% • Nine year average growth: 50. 0% (RPM) / 47. 8% (ASM) • Fleet of 54 Boeing 737 NG aircraft (63 aircraft in 2006) • Over 5, 000 West. Jet employees
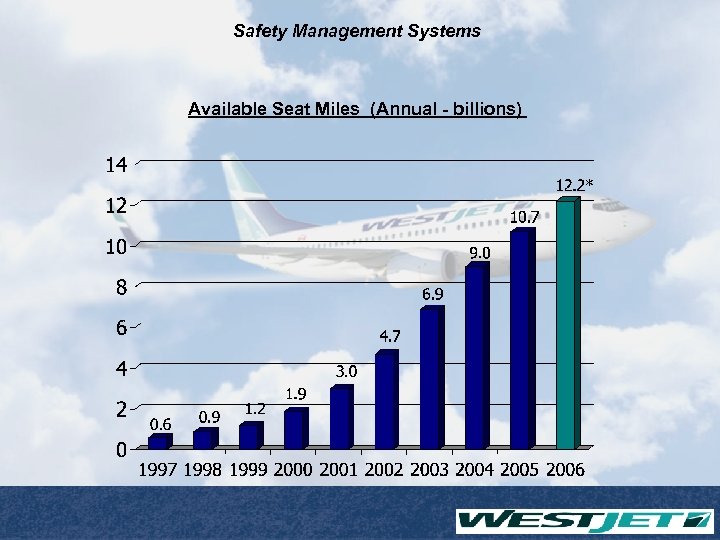 Safety Management Systems Available Seat Miles (Annual - billions)
Safety Management Systems Available Seat Miles (Annual - billions)
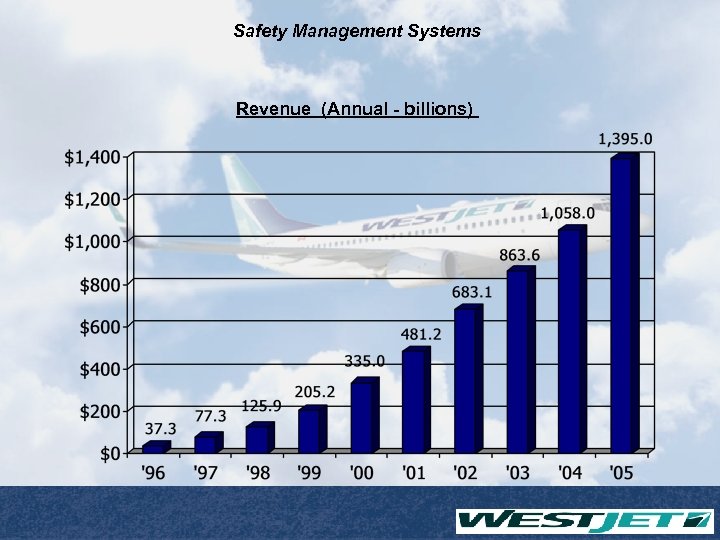 Safety Management Systems Revenue (Annual - billions)
Safety Management Systems Revenue (Annual - billions)
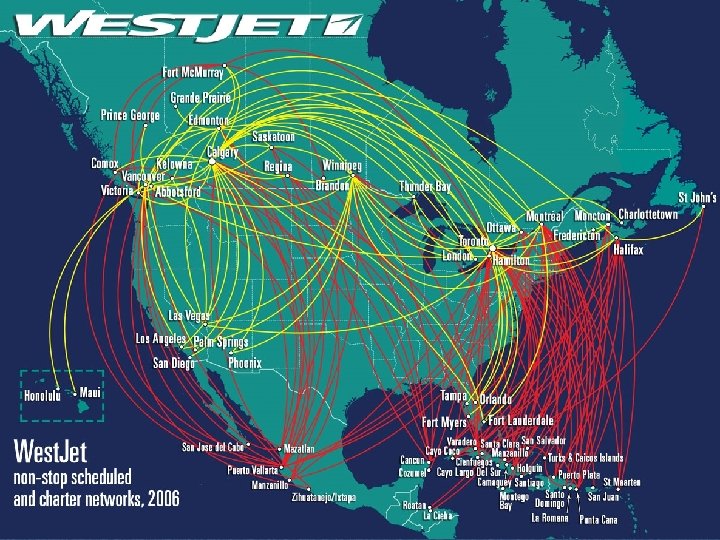 Safety Management Systems
Safety Management Systems
 Safety Management Systems Culture – Aligning Interests • “Turn employees into capitalists so they think and behave like owners” • Employee Share Purchase Plan • Dollar for dollar matching of employee contributions • 86% participation with average of 12% of base salary • Profit sharing - $73. 9 million distributed over nine years • Share options • 86. 6% outstanding held by pilots • 3. 7 million new grants to pilots in 2004
Safety Management Systems Culture – Aligning Interests • “Turn employees into capitalists so they think and behave like owners” • Employee Share Purchase Plan • Dollar for dollar matching of employee contributions • 86% participation with average of 12% of base salary • Profit sharing - $73. 9 million distributed over nine years • Share options • 86. 6% outstanding held by pilots • 3. 7 million new grants to pilots in 2004
 Safety Management Systems Culture – Aligning Interests • Culture of ownership, caring, empowerment, teamwork • West. Jet vocabulary: Guests, West. Jetters, Teams, Big Shots, Beanland, West. Jettitude • PACT – Pro-Active Communication Team • employee association • no unions • PACT and Management seek mutually beneficial solutions for: • the Company and its shareholders • the Employees • the Guests
Safety Management Systems Culture – Aligning Interests • Culture of ownership, caring, empowerment, teamwork • West. Jet vocabulary: Guests, West. Jetters, Teams, Big Shots, Beanland, West. Jettitude • PACT – Pro-Active Communication Team • employee association • no unions • PACT and Management seek mutually beneficial solutions for: • the Company and its shareholders • the Employees • the Guests
 Safety Management Systems Implementing the Regulations Transport Canada regulations apply to: • Aircraft Maintenance Organization Certificate • Air Operator Certificate West. Jet has made SMS a company-wide initiative • Maintenance • Flight Operations • Inflight • Airports • Occupational Safety & Health • Environment • Corporate Divisions
Safety Management Systems Implementing the Regulations Transport Canada regulations apply to: • Aircraft Maintenance Organization Certificate • Air Operator Certificate West. Jet has made SMS a company-wide initiative • Maintenance • Flight Operations • Inflight • Airports • Occupational Safety & Health • Environment • Corporate Divisions
 Safety Management Systems West. Jet differs from many airlines (perhaps your own) • • • Business model Growth Equipment type(s) Route structure Employee relations CULTURE Airlines will also differ in Safety Management Systems • common elements and components • different programs, processes and infrastructures
Safety Management Systems West. Jet differs from many airlines (perhaps your own) • • • Business model Growth Equipment type(s) Route structure Employee relations CULTURE Airlines will also differ in Safety Management Systems • common elements and components • different programs, processes and infrastructures
 Safety Management Systems Safety Management Plan Guiding document for implementation and operation of SMS • Policies • Safety Organization • Roles and Responsibilities • Processes • Audit • Training • Communication • Emergency Response
Safety Management Systems Safety Management Plan Guiding document for implementation and operation of SMS • Policies • Safety Organization • Roles and Responsibilities • Processes • Audit • Training • Communication • Emergency Response

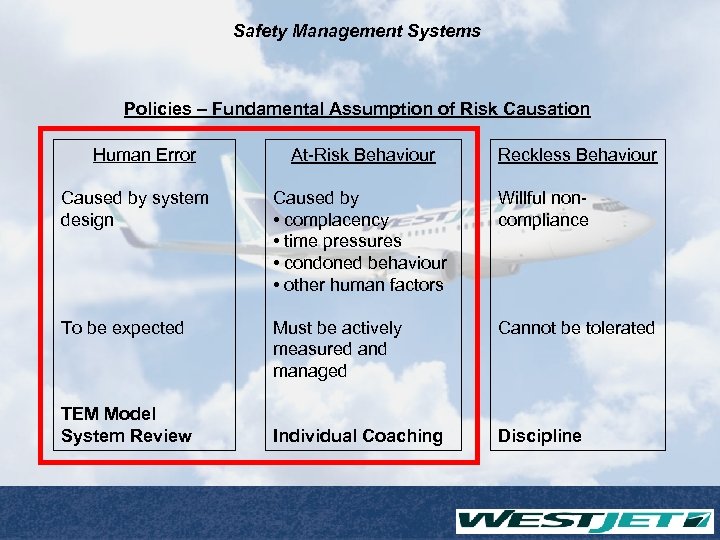 Safety Management Systems Policies – Fundamental Assumption of Risk Causation Human Error At-Risk Behaviour Reckless Behaviour Caused by system design Caused by • complacency • time pressures • condoned behaviour • other human factors Willful noncompliance To be expected Must be actively measured and managed Cannot be tolerated Individual Coaching Discipline TEM Model System Review
Safety Management Systems Policies – Fundamental Assumption of Risk Causation Human Error At-Risk Behaviour Reckless Behaviour Caused by system design Caused by • complacency • time pressures • condoned behaviour • other human factors Willful noncompliance To be expected Must be actively measured and managed Cannot be tolerated Individual Coaching Discipline TEM Model System Review
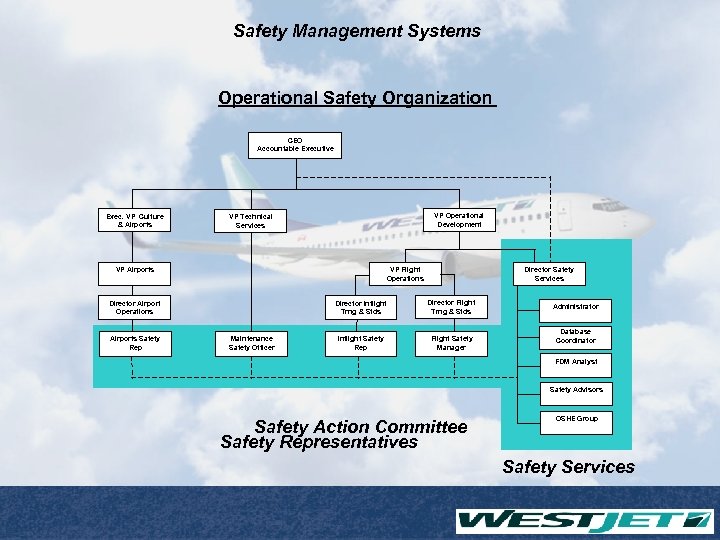 Safety Management Systems Operational Safety Organization CEO Accountable Executive Exec. VP Culture & Airports VP Operational Development VP Technical Services VP Airports Director Inflight Trng & Stds Director Airport Operations Airports Safety Rep Director Safety Services VP Flight Operations Maintenance Safety Officer Director Flight Trng & Stds Inflight Safety Rep Flight Safety Manager Administrator Database Coordinator FDM Analyst Safety Advisors Safety Action Committee Safety Representatives OSHE Group Safety Services
Safety Management Systems Operational Safety Organization CEO Accountable Executive Exec. VP Culture & Airports VP Operational Development VP Technical Services VP Airports Director Inflight Trng & Stds Director Airport Operations Airports Safety Rep Director Safety Services VP Flight Operations Maintenance Safety Officer Director Flight Trng & Stds Inflight Safety Rep Flight Safety Manager Administrator Database Coordinator FDM Analyst Safety Advisors Safety Action Committee Safety Representatives OSHE Group Safety Services
 Safety Management Systems Safety Department Mission Statement To support effective safety programs and proactive risk management by promoting safety as an inherent value of West. Jet’s culture
Safety Management Systems Safety Department Mission Statement To support effective safety programs and proactive risk management by promoting safety as an inherent value of West. Jet’s culture
 Safety Management Systems Safety Organization Accountable Executive Safety Management Committee (meets monthly*) Safety Action Committee (meets weekly*) Accountable Executive VP Technical Services VP Op. Development EVP People CFO EVP Culture & Airports EVP Marketing & Sales Director, Safety Maint. Safety Officer Manager, Flight Safety Airports Safety Advisor Inflight Safety Advisor SST Advisors SMEs
Safety Management Systems Safety Organization Accountable Executive Safety Management Committee (meets monthly*) Safety Action Committee (meets weekly*) Accountable Executive VP Technical Services VP Op. Development EVP People CFO EVP Culture & Airports EVP Marketing & Sales Director, Safety Maint. Safety Officer Manager, Flight Safety Airports Safety Advisor Inflight Safety Advisor SST Advisors SMEs
 Safety Management Systems Roles and Responsibilities • Accountable Executive • Senior Managers • Executive Vice Presidents, Directors • Managers and Supervisors • Front-line Employees • Safety Department • Safety Representatives • Safety Committees • Safety Action Committee, Safety Management Committee • Lead Investigator • Safety Review Teams
Safety Management Systems Roles and Responsibilities • Accountable Executive • Senior Managers • Executive Vice Presidents, Directors • Managers and Supervisors • Front-line Employees • Safety Department • Safety Representatives • Safety Committees • Safety Action Committee, Safety Management Committee • Lead Investigator • Safety Review Teams
 Safety Management Systems Safety Processes • Reactive and Proactive Processes • Hazard / Root Cause Analysis • Risk Assessment • Risk Mitigation • SMS Database • Safety Planning & Performance • Change Management • SMS Quality Assurance
Safety Management Systems Safety Processes • Reactive and Proactive Processes • Hazard / Root Cause Analysis • Risk Assessment • Risk Mitigation • SMS Database • Safety Planning & Performance • Change Management • SMS Quality Assurance
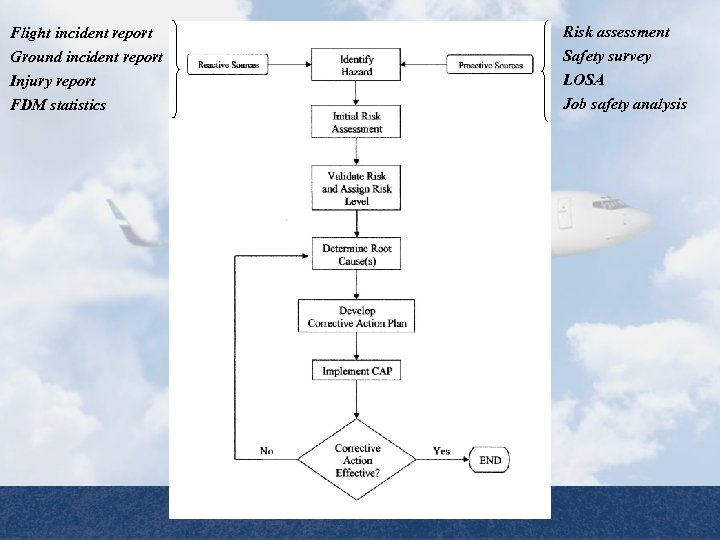 Flight incident report Ground incident report Injury report FDM statistics Safety Management Systems Basic Risk Management Process Risk assessment Safety survey LOSA Job safety analysis
Flight incident report Ground incident report Injury report FDM statistics Safety Management Systems Basic Risk Management Process Risk assessment Safety survey LOSA Job safety analysis
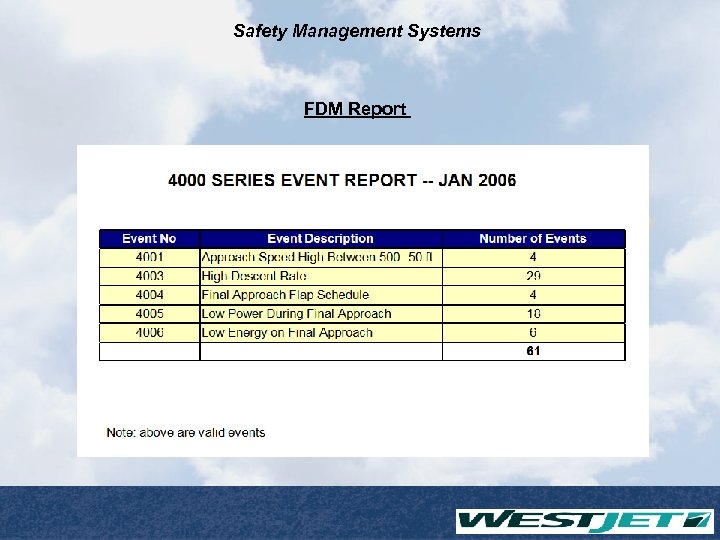 Safety Management Systems FDM Report
Safety Management Systems FDM Report
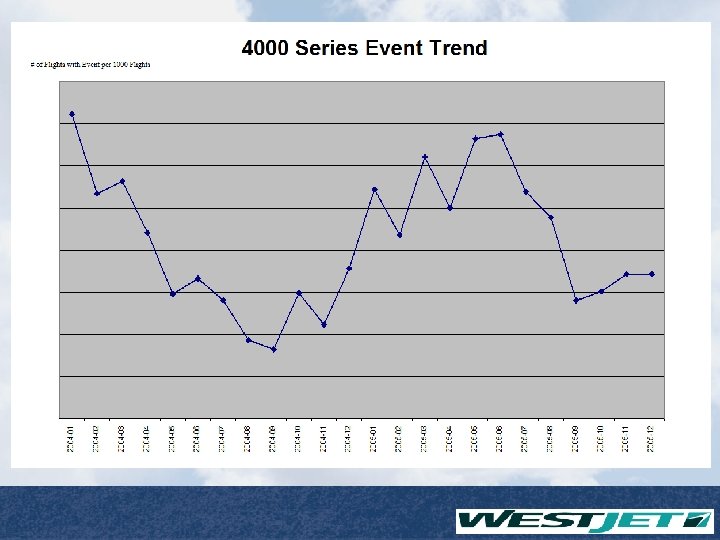 Safety Management Systems FDM Report
Safety Management Systems FDM Report
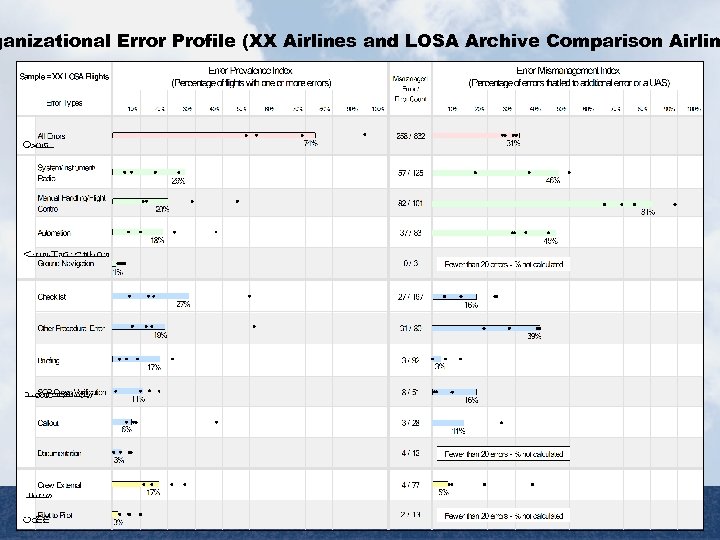 ganizational Error Profile (XX Airlines and LOSA Archive Comparison Airlin LOSA Report
ganizational Error Profile (XX Airlines and LOSA Archive Comparison Airlin LOSA Report
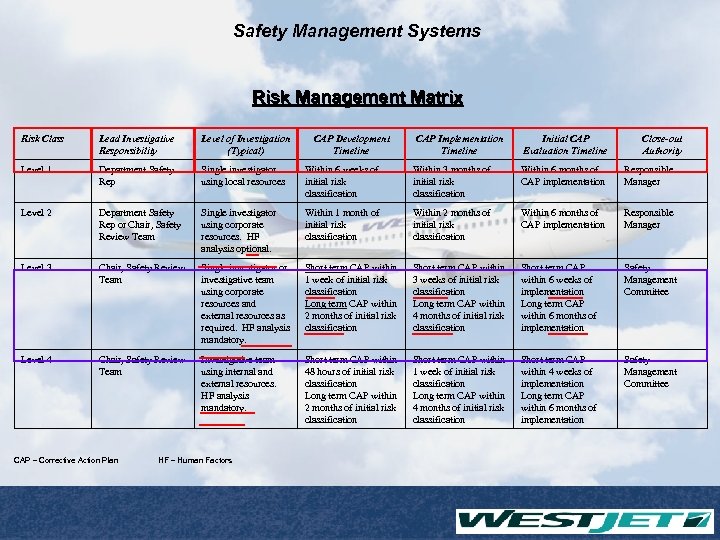 Safety Management Systems Risk Management Matrix Risk Class Lead Investigative Responsibility Level of Investigation (Typical) Level 1 Department Safety Rep Single investigator using local resources Within 6 weeks of initial risk classification Within 3 months of initial risk classification Within 6 months of CAP implementation Responsible Manager Level 2 Department Safety Rep or Chair, Safety Review Team Single investigator using corporate resources. HF analysis optional. Within 1 month of initial risk classification Within 2 months of initial risk classification Within 6 months of CAP implementation Responsible Manager Level 3 Chair, Safety Review Team Single investigator or investigative team using corporate resources and external resources as required. HF analysis mandatory. Short term CAP within 1 week of initial risk classification Long term CAP within 2 months of initial risk classification Short term CAP within 3 weeks of initial risk classification Long term CAP within 4 months of initial risk classification Short term CAP within 6 weeks of implementation Long term CAP within 6 months of implementation Safety Management Committee Level 4 Chair, Safety Review Team Investigative team using internal and external resources. HF analysis mandatory. Short term CAP within 48 hours of initial risk classification Long term CAP within 2 months of initial risk classification Short term CAP within 1 week of initial risk classification Long term CAP within 4 months of initial risk classification Short term CAP within 4 weeks of implementation Long term CAP within 6 months of implementation Safety Management Committee CAP – Corrective Action Plan HF – Human Factors CAP Development Timeline CAP Implementation Timeline Initial CAP Evaluation Timeline Close-out Authority
Safety Management Systems Risk Management Matrix Risk Class Lead Investigative Responsibility Level of Investigation (Typical) Level 1 Department Safety Rep Single investigator using local resources Within 6 weeks of initial risk classification Within 3 months of initial risk classification Within 6 months of CAP implementation Responsible Manager Level 2 Department Safety Rep or Chair, Safety Review Team Single investigator using corporate resources. HF analysis optional. Within 1 month of initial risk classification Within 2 months of initial risk classification Within 6 months of CAP implementation Responsible Manager Level 3 Chair, Safety Review Team Single investigator or investigative team using corporate resources and external resources as required. HF analysis mandatory. Short term CAP within 1 week of initial risk classification Long term CAP within 2 months of initial risk classification Short term CAP within 3 weeks of initial risk classification Long term CAP within 4 months of initial risk classification Short term CAP within 6 weeks of implementation Long term CAP within 6 months of implementation Safety Management Committee Level 4 Chair, Safety Review Team Investigative team using internal and external resources. HF analysis mandatory. Short term CAP within 48 hours of initial risk classification Long term CAP within 2 months of initial risk classification Short term CAP within 1 week of initial risk classification Long term CAP within 4 months of initial risk classification Short term CAP within 4 weeks of implementation Long term CAP within 6 months of implementation Safety Management Committee CAP – Corrective Action Plan HF – Human Factors CAP Development Timeline CAP Implementation Timeline Initial CAP Evaluation Timeline Close-out Authority
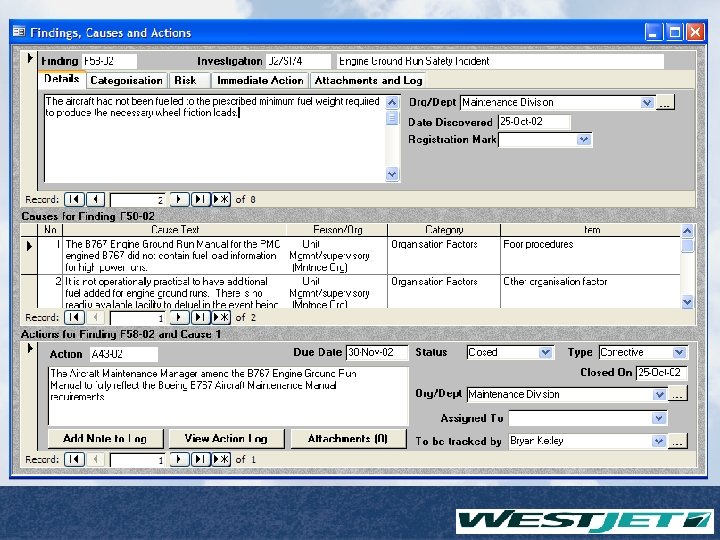 Safety Management Systems Database Findings / Causes / Actions Page
Safety Management Systems Database Findings / Causes / Actions Page
 Safety Management Systems Training must ensure: “… that personnel are trained and competent to perform their [safety management] duties…” Canadian Aviation Regulations 107. 03(d) Safety Management Plan specifies initial and recurrent training standards for • Safety Department • Senior Managers • Managers & Supervisors • Front line Employees “…as appropriate to the individual’s responsibilities in the safety management system. ” West. Jet Safety Management Plan Section 9
Safety Management Systems Training must ensure: “… that personnel are trained and competent to perform their [safety management] duties…” Canadian Aviation Regulations 107. 03(d) Safety Management Plan specifies initial and recurrent training standards for • Safety Department • Senior Managers • Managers & Supervisors • Front line Employees “…as appropriate to the individual’s responsibilities in the safety management system. ” West. Jet Safety Management Plan Section 9
 Safety Management Systems Training Initial, update and recurrent training covers (as required): Organization structure Human factors analysis Roles and responsibilities Risk classification system SMS principles Corrective action plans Company safety management plan Emergency response Regulatory requirements Occupational safety and health Documentation processes Corporate safety database Safety reporting systems Safety communication plans Investigation techniques Changes to SMS regulations Proactive risk assessment Annual safety performance reports
Safety Management Systems Training Initial, update and recurrent training covers (as required): Organization structure Human factors analysis Roles and responsibilities Risk classification system SMS principles Corrective action plans Company safety management plan Emergency response Regulatory requirements Occupational safety and health Documentation processes Corporate safety database Safety reporting systems Safety communication plans Investigation techniques Changes to SMS regulations Proactive risk assessment Annual safety performance reports
 Safety Management Systems Communication Safety Newsletter Corporate communications Executive presentations West. Net (company intranet) Base visits Indoctrination training Department meetings SAC, SMC meetings Jetsmarts (e-learning) Managers conference Job descriptions Performance appraisals
Safety Management Systems Communication Safety Newsletter Corporate communications Executive presentations West. Net (company intranet) Base visits Indoctrination training Department meetings SAC, SMC meetings Jetsmarts (e-learning) Managers conference Job descriptions Performance appraisals
 Safety Management Systems SMS VIDEO
Safety Management Systems SMS VIDEO
 Safety Management Systems
Safety Management Systems
 Safety Management Systems Communication • Easy to understand for ALL employees • Dynamic introduction to SMS fundamentals • focuses on proactive risk management • Features many employee groups: • Dispatch, Maintenance, Flight Crew, Scheduling Ramp Agents, CSAs, Training, FOQA You have many elements of SMS in place NOW
Safety Management Systems Communication • Easy to understand for ALL employees • Dynamic introduction to SMS fundamentals • focuses on proactive risk management • Features many employee groups: • Dispatch, Maintenance, Flight Crew, Scheduling Ramp Agents, CSAs, Training, FOQA You have many elements of SMS in place NOW
 Safety Management Systems Examples of SMS Savings Fuselage Ice Occurrence (Reactive Risk Assessment) Repairs & Downtime: $30, 000 / yr. Single Agent De-icing (Proactive Risk Assessment) Each Occurrence: $50, 000 / yr Workers Compensation Premiums (Integrated Risk Management) Forecast Annual Savings: Category A or B Occurrence $100, 000 - $500, 000 / yr $$$$$$
Safety Management Systems Examples of SMS Savings Fuselage Ice Occurrence (Reactive Risk Assessment) Repairs & Downtime: $30, 000 / yr. Single Agent De-icing (Proactive Risk Assessment) Each Occurrence: $50, 000 / yr Workers Compensation Premiums (Integrated Risk Management) Forecast Annual Savings: Category A or B Occurrence $100, 000 - $500, 000 / yr $$$$$$
 Safety Management Systems Summary Safety Management Systems will: • Formalize and document many current safety processes • Introduce new and improved safety programs • Force greater consistency and rigor in operational risk management • Bring new challenges • Evolve with new regulations, your company and the industry • Change corporate culture
Safety Management Systems Summary Safety Management Systems will: • Formalize and document many current safety processes • Introduce new and improved safety programs • Force greater consistency and rigor in operational risk management • Bring new challenges • Evolve with new regulations, your company and the industry • Change corporate culture
 Safety Management Systems
Safety Management Systems


