7671372b470caddc5bed1e164cabda60.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Safety Code 35 John Aldrich Ph. D FCCPM Regional Leader Clinical Physics Kevin Hammerstrom RTNM QC Coordinator Department of Radiology Vancouver Coastal Health University of British Columbia
Safety Code 35 John Aldrich Ph. D FCCPM Regional Leader Clinical Physics Kevin Hammerstrom RTNM QC Coordinator Department of Radiology Vancouver Coastal Health University of British Columbia
 Medical X-ray Safety Codes Safety Code 20 A (1976) Safety Code 35 (2008) (two drafts in 2005 and 2007) w Recommended safety procedures for the installation, use and control of x-ray equipment. Mainly concerned with the x-ray output parameters of the equipment w Only film processor QC defined w Comprehensive safety procedures for the installation, use and control of x-ray equipment. w Includes all x-ray systems w Increased emphasis on patient dose w 25% of the Code is concerned with QC of digital imaging systems
Medical X-ray Safety Codes Safety Code 20 A (1976) Safety Code 35 (2008) (two drafts in 2005 and 2007) w Recommended safety procedures for the installation, use and control of x-ray equipment. Mainly concerned with the x-ray output parameters of the equipment w Only film processor QC defined w Comprehensive safety procedures for the installation, use and control of x-ray equipment. w Includes all x-ray systems w Increased emphasis on patient dose w 25% of the Code is concerned with QC of digital imaging systems
 Safety Code 35 A 1. Responsibilities of owners and users (4) A 2. Procedures for minimizing staff dose (2) A 3. Procedures for minimizing patient dose (6) B 1. Facility shielding (3) B 2 -6. Equipment performance (15) C 1 -3. Quality Control (17) Appendices (30)
Safety Code 35 A 1. Responsibilities of owners and users (4) A 2. Procedures for minimizing staff dose (2) A 3. Procedures for minimizing patient dose (6) B 1. Facility shielding (3) B 2 -6. Equipment performance (15) C 1 -3. Quality Control (17) Appendices (30)
 Decoding the Code Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS w Handout includes all slides in our presentations w Attached sheets have all the tables enlarged w References are to details of the tests in the Code eg D 1 is the first daily test listed, W 1 – weekly, M 1 - monthly, Q 1 – quarterly, SY 1 – semiannually, Y 1 - Annual
Decoding the Code Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS w Handout includes all slides in our presentations w Attached sheets have all the tables enlarged w References are to details of the tests in the Code eg D 1 is the first daily test listed, W 1 – weekly, M 1 - monthly, Q 1 – quarterly, SY 1 – semiannually, Y 1 - Annual
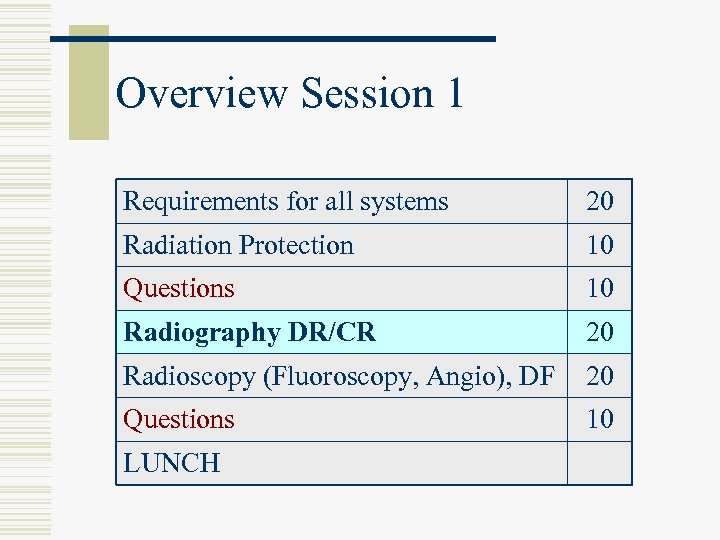
 Overview Session 1 Requirements for all systems 20 Radiation Protection 10 Questions 10 Radiography (Film/DR/CR) 20 Radioscopy (Fluoroscopy, Angio, DF) 20 Questions 10 LUNCH
Overview Session 1 Requirements for all systems 20 Radiation Protection 10 Questions 10 Radiography (Film/DR/CR) 20 Radioscopy (Fluoroscopy, Angio, DF) 20 Questions 10 LUNCH
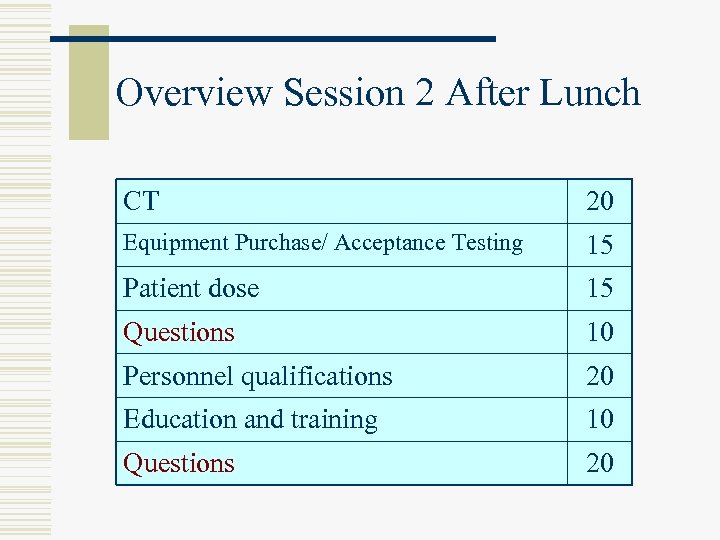 Overview Session 2 After Lunch CT 20 Equipment Purchase/ Acceptance Testing 15 Patient dose 15 Questions 10 Personnel qualifications 20 Education and training 10 Questions 20
Overview Session 2 After Lunch CT 20 Equipment Purchase/ Acceptance Testing 15 Patient dose 15 Questions 10 Personnel qualifications 20 Education and training 10 Questions 20
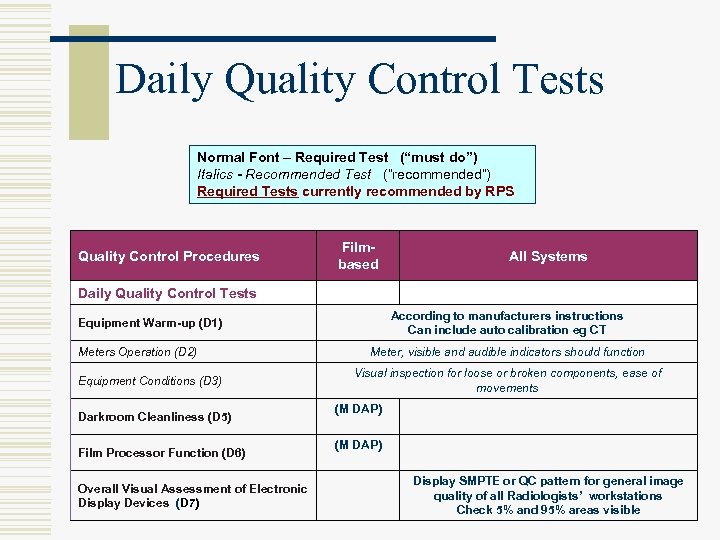 Daily Quality Control Tests Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS Quality Control Procedures Filmbased All Systems Daily Quality Control Tests According to manufacturers instructions Can include auto calibration eg CT Equipment Warm-up (D 1) Meters Operation (D 2) Equipment Conditions (D 3) Darkroom Cleanliness (D 5) Film Processor Function (D 6) Overall Visual Assessment of Electronic Display Devices (D 7) Meter, visible and audible indicators should function Visual inspection for loose or broken components, ease of movements (M DAP) Display SMPTE or QC pattern for general image quality of all Radiologists’ workstations Check 5% and 95% areas visible
Daily Quality Control Tests Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS Quality Control Procedures Filmbased All Systems Daily Quality Control Tests According to manufacturers instructions Can include auto calibration eg CT Equipment Warm-up (D 1) Meters Operation (D 2) Equipment Conditions (D 3) Darkroom Cleanliness (D 5) Film Processor Function (D 6) Overall Visual Assessment of Electronic Display Devices (D 7) Meter, visible and audible indicators should function Visual inspection for loose or broken components, ease of movements (M DAP) Display SMPTE or QC pattern for general image quality of all Radiologists’ workstations Check 5% and 95% areas visible
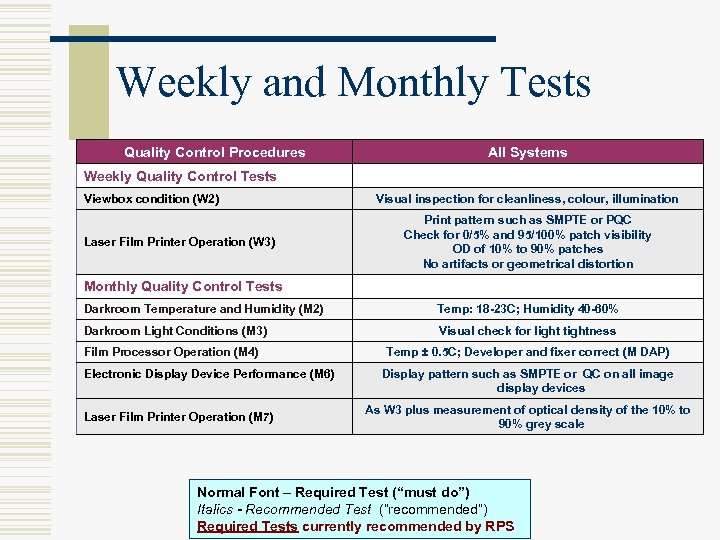 Weekly and Monthly Tests Quality Control Procedures All Systems Weekly Quality Control Tests Viewbox condition (W 2) Laser Film Printer Operation (W 3) Visual inspection for cleanliness, colour, illumination Print pattern such as SMPTE or PQC Check for 0/5% and 95/100% patch visibility OD of 10% to 90% patches No artifacts or geometrical distortion Monthly Quality Control Tests Darkroom Temperature and Humidity (M 2) Temp: 18 -23 C; Humidity 40 -60% Darkroom Light Conditions (M 3) Visual check for light tightness Film Processor Operation (M 4) Electronic Display Device Performance (M 6) Laser Film Printer Operation (M 7) Temp ± 0. 5 C; Developer and fixer correct (M DAP) Display pattern such as SMPTE or QC on all image display devices As W 3 plus measurement of optical density of the 10% to 90% grey scale Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS
Weekly and Monthly Tests Quality Control Procedures All Systems Weekly Quality Control Tests Viewbox condition (W 2) Laser Film Printer Operation (W 3) Visual inspection for cleanliness, colour, illumination Print pattern such as SMPTE or PQC Check for 0/5% and 95/100% patch visibility OD of 10% to 90% patches No artifacts or geometrical distortion Monthly Quality Control Tests Darkroom Temperature and Humidity (M 2) Temp: 18 -23 C; Humidity 40 -60% Darkroom Light Conditions (M 3) Visual check for light tightness Film Processor Operation (M 4) Electronic Display Device Performance (M 6) Laser Film Printer Operation (M 7) Temp ± 0. 5 C; Developer and fixer correct (M DAP) Display pattern such as SMPTE or QC on all image display devices As W 3 plus measurement of optical density of the 10% to 90% grey scale Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS
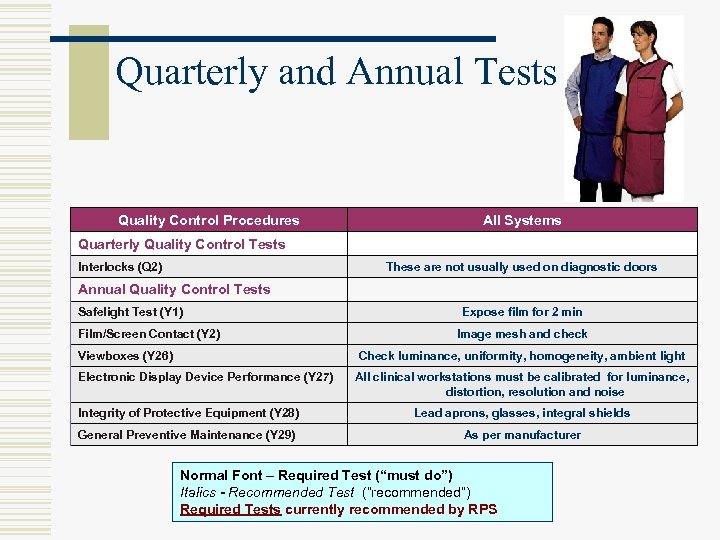 Quarterly and Annual Tests Quality Control Procedures All Systems Quarterly Quality Control Tests Interlocks (Q 2) These are not usually used on diagnostic doors Annual Quality Control Tests Safelight Test (Y 1) Film/Screen Contact (Y 2) Viewboxes (Y 26) Expose film for 2 min Image mesh and check Check luminance, uniformity, homogeneity, ambient light Electronic Display Device Performance (Y 27) All clinical workstations must be calibrated for luminance, distortion, resolution and noise Integrity of Protective Equipment (Y 28) Lead aprons, glasses, integral shields General Preventive Maintenance (Y 29) As per manufacturer Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS
Quarterly and Annual Tests Quality Control Procedures All Systems Quarterly Quality Control Tests Interlocks (Q 2) These are not usually used on diagnostic doors Annual Quality Control Tests Safelight Test (Y 1) Film/Screen Contact (Y 2) Viewboxes (Y 26) Expose film for 2 min Image mesh and check Check luminance, uniformity, homogeneity, ambient light Electronic Display Device Performance (Y 27) All clinical workstations must be calibrated for luminance, distortion, resolution and noise Integrity of Protective Equipment (Y 28) Lead aprons, glasses, integral shields General Preventive Maintenance (Y 29) As per manufacturer Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS
 Display QC w Daily (D 7) – for clinical interpretation n n Radiologist at each login Find suitable SMPTE test pattern Make accessible on PACS Test using various user logins/profiles Alert radiologists of requirement, frequency, and procedure
Display QC w Daily (D 7) – for clinical interpretation n n Radiologist at each login Find suitable SMPTE test pattern Make accessible on PACS Test using various user logins/profiles Alert radiologists of requirement, frequency, and procedure
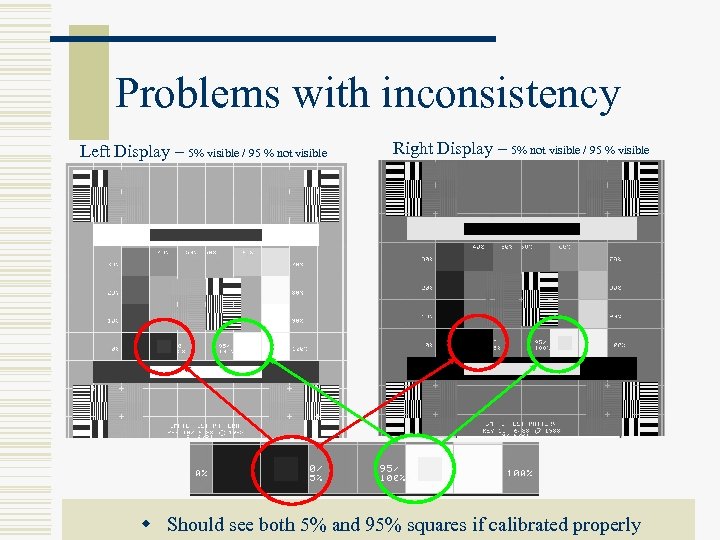 Problems with inconsistency Left Display – 5% visible / 95 % not visible Right Display – 5% not visible / 95 % visible w Should see both 5% and 95% squares if calibrated properly
Problems with inconsistency Left Display – 5% visible / 95 % not visible Right Display – 5% not visible / 95 % visible w Should see both 5% and 95% squares if calibrated properly
 Display QC w Monthly (M 6) n All displays Technologist l PACS administrator l Biomed l n SMPTE test pattern / test pattern generator / vendor
Display QC w Monthly (M 6) n All displays Technologist l PACS administrator l Biomed l n SMPTE test pattern / test pattern generator / vendor
 Display QC w Annually (Y 27) n Clinical interpretation and interventional use l l l n QC Coordinator PACS administrator Biomed SMPTE test pattern / test pattern generator / vendor QC software and photometer
Display QC w Annually (Y 27) n Clinical interpretation and interventional use l l l n QC Coordinator PACS administrator Biomed SMPTE test pattern / test pattern generator / vendor QC software and photometer
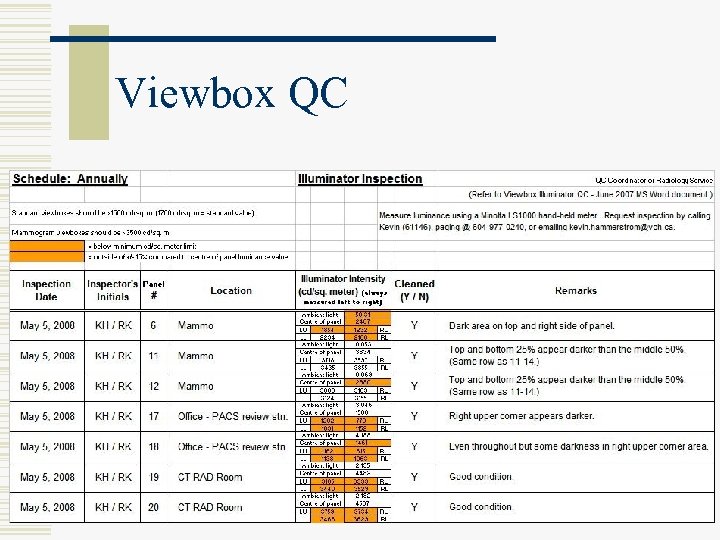
 Viewbox QC § Weekly visual inspection (W 2) § Cleanliness § Viewing area discolouration § Improper luminance § Clean, replace plastic or bulb if necessary § Technologists / Biomed / Plant services
Viewbox QC § Weekly visual inspection (W 2) § Cleanliness § Viewing area discolouration § Improper luminance § Clean, replace plastic or bulb if necessary § Technologists / Biomed / Plant services
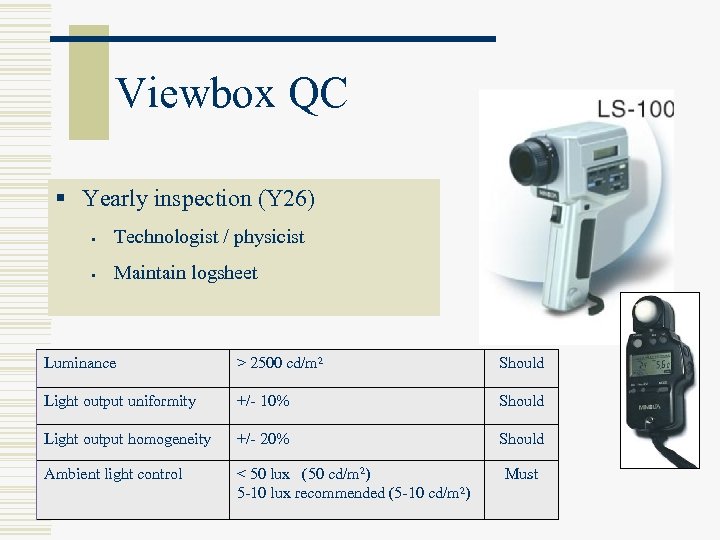 Viewbox QC § Yearly inspection (Y 26) § Technologist / physicist § Maintain logsheet Luminance > 2500 cd/m 2 Should Light output uniformity +/- 10% Should Light output homogeneity +/- 20% Should Ambient light control < 50 lux (50 cd/m 2) 5 -10 lux recommended (5 -10 cd/m 2) Must
Viewbox QC § Yearly inspection (Y 26) § Technologist / physicist § Maintain logsheet Luminance > 2500 cd/m 2 Should Light output uniformity +/- 10% Should Light output homogeneity +/- 20% Should Ambient light control < 50 lux (50 cd/m 2) 5 -10 lux recommended (5 -10 cd/m 2) Must
 Viewbox QC
Viewbox QC
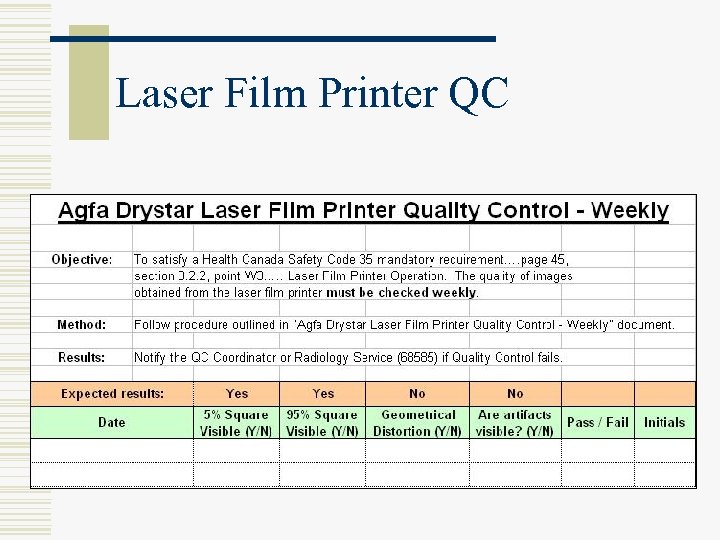
 Laser Film Printer QC § Weekly (W 3) § Use same viewbox panel § Print SMPTE from PACS workstation or from printer menu § View 5% and 95% grayscale squares § Maintain logsheet
Laser Film Printer QC § Weekly (W 3) § Use same viewbox panel § Print SMPTE from PACS workstation or from printer menu § View 5% and 95% grayscale squares § Maintain logsheet
 Laser Film Printer QC
Laser Film Printer QC
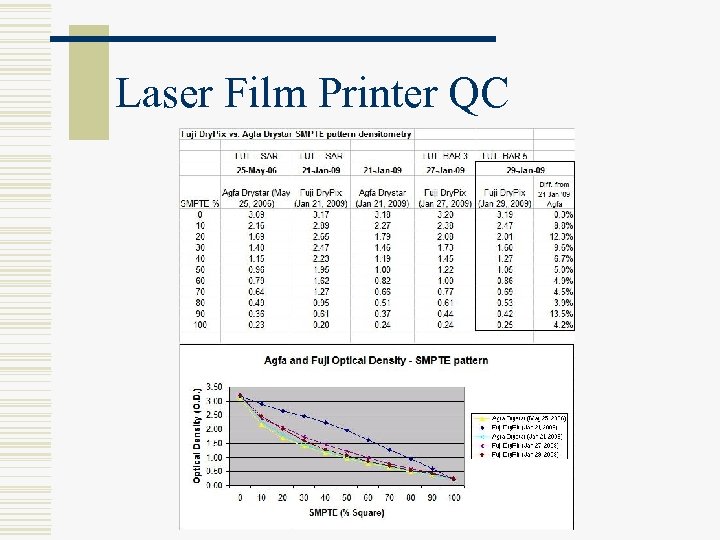
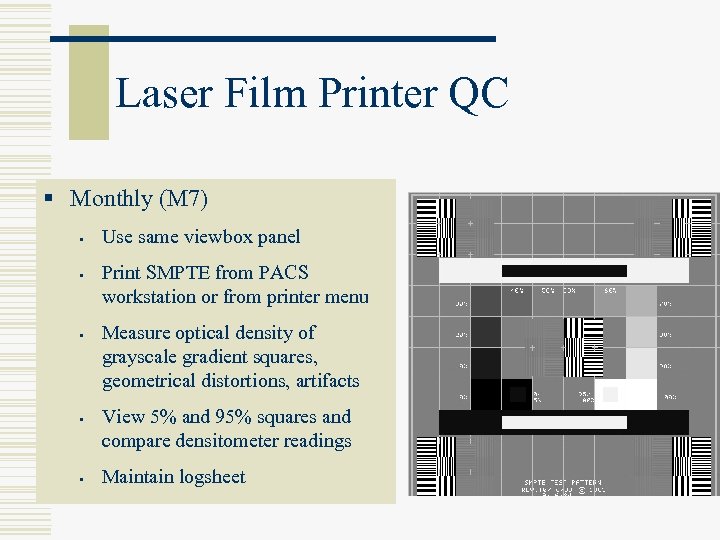 Laser Film Printer QC § Monthly (M 7) § § § Use same viewbox panel Print SMPTE from PACS workstation or from printer menu Measure optical density of grayscale gradient squares, geometrical distortions, artifacts View 5% and 95% squares and compare densitometer readings Maintain logsheet
Laser Film Printer QC § Monthly (M 7) § § § Use same viewbox panel Print SMPTE from PACS workstation or from printer menu Measure optical density of grayscale gradient squares, geometrical distortions, artifacts View 5% and 95% squares and compare densitometer readings Maintain logsheet
 Laser Film Printer QC
Laser Film Printer QC
 Overview Session 1 Requirements for all systems 20 Radiation Protection 10 Questions 10 Radiography DR/CR 20 Radioscopy (Fluoroscopy, Angio), DF 20 Questions 10 LUNCH
Overview Session 1 Requirements for all systems 20 Radiation Protection 10 Questions 10 Radiography DR/CR 20 Radioscopy (Fluoroscopy, Angio), DF 20 Questions 10 LUNCH
 Radiation Protection w Radiation Safety Officer (1. 4) w Room Shielding (5. 0) w Lead aprons (4. 1)
Radiation Protection w Radiation Safety Officer (1. 4) w Room Shielding (5. 0) w Lead aprons (4. 1)
 Radiation Safety Officer w There must be a Medical Physicist or Radiation Safety Officer to advise on all aspects of Radiation Safety n n Planning, registration, inspection Working conditions, procedures Classification of personnel, dosimetry Record keeping, investigations
Radiation Safety Officer w There must be a Medical Physicist or Radiation Safety Officer to advise on all aspects of Radiation Safety n n Planning, registration, inspection Working conditions, procedures Classification of personnel, dosimetry Record keeping, investigations
 Radiation Protection - Shielding w Design of Shielding n n Recommend NCRP 147 (2004) methods which are based on empirical data (although Appendix is NCRP 49 (1976) which will tend to overshield rooms) w Surveys of rooms must be done for new or altered rooms (equipment, use or vicinity Sec A 5) Design shielding Check lead installation Measure radiation in surrounding areas
Radiation Protection - Shielding w Design of Shielding n n Recommend NCRP 147 (2004) methods which are based on empirical data (although Appendix is NCRP 49 (1976) which will tend to overshield rooms) w Surveys of rooms must be done for new or altered rooms (equipment, use or vicinity Sec A 5) Design shielding Check lead installation Measure radiation in surrounding areas
 Lead Aprons Lead equivalence of aprons w SC 20 A n <150 k. Vp 0. 5 mm w SC 35 n n n < 100 k. Vp: 100< k. Vp <150: >150 k. Vp: 0. 25 mm 0. 35 mm 0. 5 mm
Lead Aprons Lead equivalence of aprons w SC 20 A n <150 k. Vp 0. 5 mm w SC 35 n n n < 100 k. Vp: 100< k. Vp <150: >150 k. Vp: 0. 25 mm 0. 35 mm 0. 5 mm
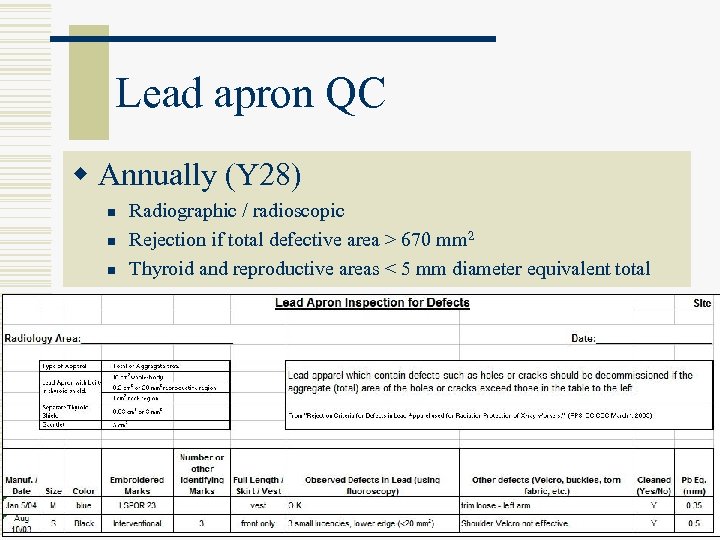 Lead apron QC w Annually (Y 28) n n n Radiographic / radioscopic Rejection if total defective area > 670 mm 2 Thyroid and reproductive areas < 5 mm diameter equivalent total
Lead apron QC w Annually (Y 28) n n n Radiographic / radioscopic Rejection if total defective area > 670 mm 2 Thyroid and reproductive areas < 5 mm diameter equivalent total
 Overview Session 1 Requirements for all systems 20 Radiation Protection 10 Questions 10 Radiography DR/CR 20 Radioscopy (Fluoroscopy, Angio), DF 20 Questions 10 LUNCH
Overview Session 1 Requirements for all systems 20 Radiation Protection 10 Questions 10 Radiography DR/CR 20 Radioscopy (Fluoroscopy, Angio), DF 20 Questions 10 LUNCH
 Overview Session 1 Requirements for all systems 20 Radiation Protection 10 Questions 10 Radiography DR/CR 20 Radioscopy (Fluoroscopy, Angio), DF 20 Questions 10 LUNCH
Overview Session 1 Requirements for all systems 20 Radiation Protection 10 Questions 10 Radiography DR/CR 20 Radioscopy (Fluoroscopy, Angio), DF 20 Questions 10 LUNCH
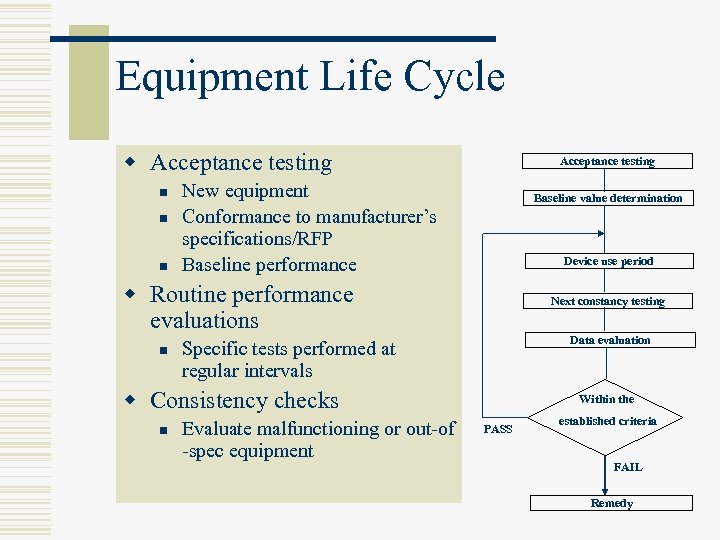 Equipment Life Cycle w Acceptance testing n n n Acceptance testing New equipment Conformance to manufacturer’s specifications/RFP Baseline performance Baseline value determination Device use period w Routine performance evaluations n Next constancy testing Data evaluation Specific tests performed at regular intervals w Consistency checks n Evaluate malfunctioning or out-of -spec equipment Within the PASS established criteria FAIL Remedy
Equipment Life Cycle w Acceptance testing n n n Acceptance testing New equipment Conformance to manufacturer’s specifications/RFP Baseline performance Baseline value determination Device use period w Routine performance evaluations n Next constancy testing Data evaluation Specific tests performed at regular intervals w Consistency checks n Evaluate malfunctioning or out-of -spec equipment Within the PASS established criteria FAIL Remedy
 Imaging QC Principles Proactive QC rather than Reactive QC w Test tool/phantom rated w Patient replaces the rated w System performance phantom clinical imaging. BEFORE clinical AFTER w Standard imaging parameters/conditions w Non-standard imaging parameters/conditions w Scheduled testing (Daily/Weekly) w Frequent testing (every patient) w Defined and objective approach would you Which acceptance/rejection criteria were a patient? ? subjective w Ill-defined and prefer if you acceptance/rejection criteria
Imaging QC Principles Proactive QC rather than Reactive QC w Test tool/phantom rated w Patient replaces the rated w System performance phantom clinical imaging. BEFORE clinical AFTER w Standard imaging parameters/conditions w Non-standard imaging parameters/conditions w Scheduled testing (Daily/Weekly) w Frequent testing (every patient) w Defined and objective approach would you Which acceptance/rejection criteria were a patient? ? subjective w Ill-defined and prefer if you acceptance/rejection criteria
 Radiographic Systems w Projection radiography n Film n Digital detectors (DR) n Computed radiography (CR)
Radiographic Systems w Projection radiography n Film n Digital detectors (DR) n Computed radiography (CR)
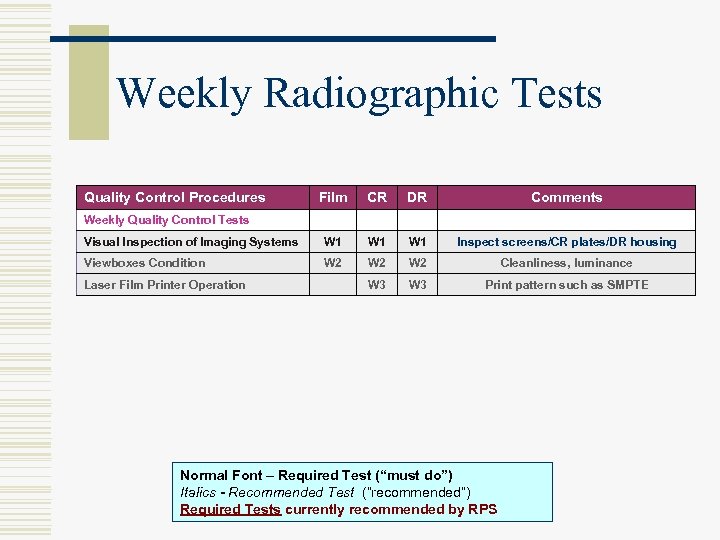 Weekly Radiographic Tests Quality Control Procedures Film CR DR Comments Visual Inspection of Imaging Systems W 1 W 1 Inspect screens/CR plates/DR housing Viewboxes Condition W 2 W 2 Cleanliness, luminance W 3 Print pattern such as SMPTE Weekly Quality Control Tests Laser Film Printer Operation Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS
Weekly Radiographic Tests Quality Control Procedures Film CR DR Comments Visual Inspection of Imaging Systems W 1 W 1 Inspect screens/CR plates/DR housing Viewboxes Condition W 2 W 2 Cleanliness, luminance W 3 Print pattern such as SMPTE Weekly Quality Control Tests Laser Film Printer Operation Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS
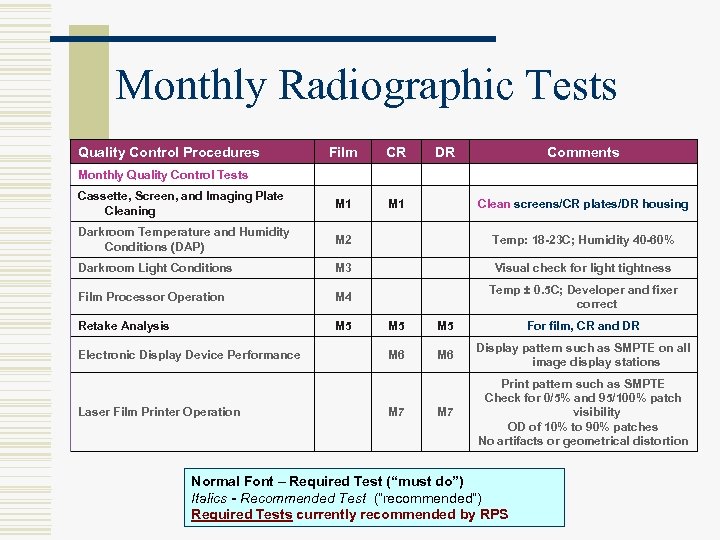 Monthly Radiographic Tests Quality Control Procedures Film CR DR Comments Cassette, Screen, and Imaging Plate Cleaning M 1 Darkroom Temperature and Humidity Conditions (DAP) M 2 Temp: 18 -23 C; Humidity 40 -60% Darkroom Light Conditions M 3 Visual check for light tightness Film Processor Operation M 4 Temp ± 0. 5 C; Developer and fixer correct Retake Analysis M 5 Monthly Quality Control Tests Electronic Display Device Performance Laser Film Printer Operation Clean screens/CR plates/DR housing M 5 For film, CR and DR M 6 Display pattern such as SMPTE on all image display stations M 7 Print pattern such as SMPTE Check for 0/5% and 95/100% patch visibility OD of 10% to 90% patches No artifacts or geometrical distortion M 7 Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS
Monthly Radiographic Tests Quality Control Procedures Film CR DR Comments Cassette, Screen, and Imaging Plate Cleaning M 1 Darkroom Temperature and Humidity Conditions (DAP) M 2 Temp: 18 -23 C; Humidity 40 -60% Darkroom Light Conditions M 3 Visual check for light tightness Film Processor Operation M 4 Temp ± 0. 5 C; Developer and fixer correct Retake Analysis M 5 Monthly Quality Control Tests Electronic Display Device Performance Laser Film Printer Operation Clean screens/CR plates/DR housing M 5 For film, CR and DR M 6 Display pattern such as SMPTE on all image display stations M 7 Print pattern such as SMPTE Check for 0/5% and 95/100% patch visibility OD of 10% to 90% patches No artifacts or geometrical distortion M 7 Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS
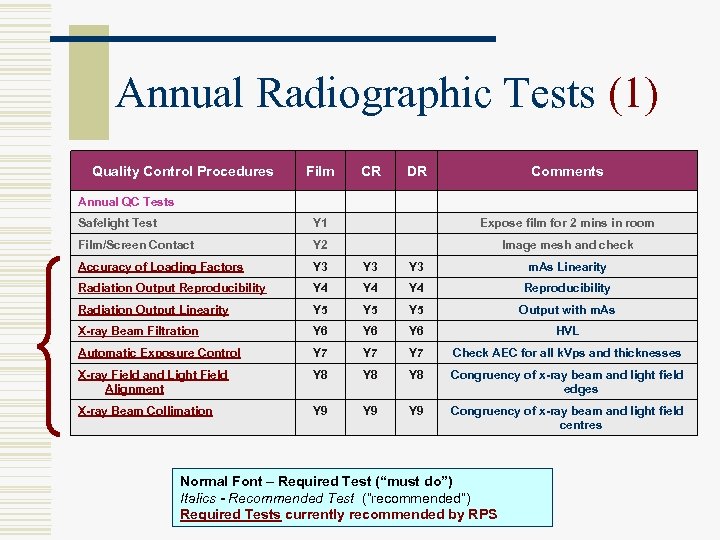 Annual Radiographic Tests (1) Quality Control Procedures Film CR DR Comments Annual QC Tests Safelight Test Y 1 Expose film for 2 mins in room Film/Screen Contact Y 2 Image mesh and check Accuracy of Loading Factors Y 3 Y 3 m. As Linearity Radiation Output Reproducibility Y 4 Y 4 Reproducibility Radiation Output Linearity Y 5 Y 5 Output with m. As X-ray Beam Filtration Y 6 Y 6 HVL Automatic Exposure Control Y 7 Y 7 Check AEC for all k. Vps and thicknesses X-ray Field and Light Field Alignment Y 8 Y 8 Congruency of x-ray beam and light field edges X-ray Beam Collimation Y 9 Y 9 Congruency of x-ray beam and light field centres Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS
Annual Radiographic Tests (1) Quality Control Procedures Film CR DR Comments Annual QC Tests Safelight Test Y 1 Expose film for 2 mins in room Film/Screen Contact Y 2 Image mesh and check Accuracy of Loading Factors Y 3 Y 3 m. As Linearity Radiation Output Reproducibility Y 4 Y 4 Reproducibility Radiation Output Linearity Y 5 Y 5 Output with m. As X-ray Beam Filtration Y 6 Y 6 HVL Automatic Exposure Control Y 7 Y 7 Check AEC for all k. Vps and thicknesses X-ray Field and Light Field Alignment Y 8 Y 8 Congruency of x-ray beam and light field edges X-ray Beam Collimation Y 9 Y 9 Congruency of x-ray beam and light field centres Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS
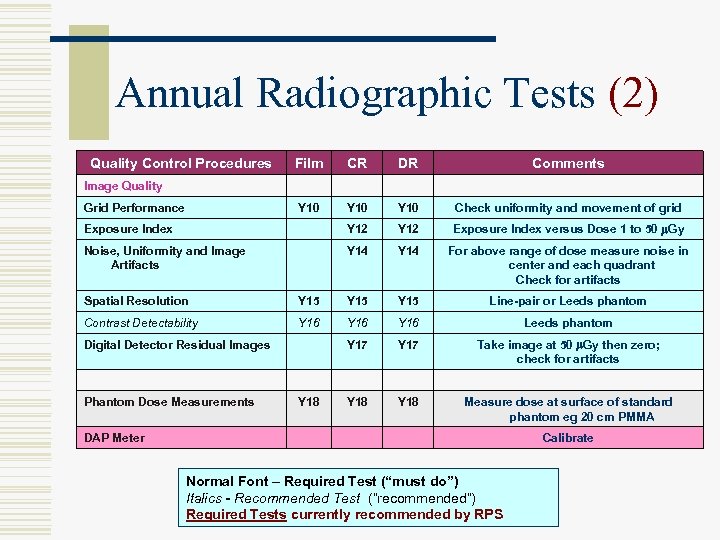 Annual Radiographic Tests (2) Quality Control Procedures Film CR DR Comments Y 10 Check uniformity and movement of grid Exposure Index Y 12 Exposure Index versus Dose 1 to 50 m. Gy Noise, Uniformity and Image Artifacts Y 14 For above range of dose measure noise in center and each quadrant Check for artifacts Image Quality Grid Performance Spatial Resolution Y 15 Line-pair or Leeds phantom Contrast Detectability Y 16 Leeds phantom Y 17 Take image at 50 m. Gy then zero; check for artifacts Y 18 Measure dose at surface of standard phantom eg 20 cm PMMA Digital Detector Residual Images Phantom Dose Measurements Y 18 DAP Meter Calibrate Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS
Annual Radiographic Tests (2) Quality Control Procedures Film CR DR Comments Y 10 Check uniformity and movement of grid Exposure Index Y 12 Exposure Index versus Dose 1 to 50 m. Gy Noise, Uniformity and Image Artifacts Y 14 For above range of dose measure noise in center and each quadrant Check for artifacts Image Quality Grid Performance Spatial Resolution Y 15 Line-pair or Leeds phantom Contrast Detectability Y 16 Leeds phantom Y 17 Take image at 50 m. Gy then zero; check for artifacts Y 18 Measure dose at surface of standard phantom eg 20 cm PMMA Digital Detector Residual Images Phantom Dose Measurements Y 18 DAP Meter Calibrate Normal Font – Required Test (“must do”) Italics - Recommended Test (“recommended”) Required Tests currently recommended by RPS
 Digital Imaging Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic… Arthur C Clarke 1961
Digital Imaging Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic… Arthur C Clarke 1961
 Digital X-ray Systems w Direct Radiography DR n Formation of image without a secondary read-out device w Computed Radiography CR n Use of storage phosphor plate usually in a cassette-based system
Digital X-ray Systems w Direct Radiography DR n Formation of image without a secondary read-out device w Computed Radiography CR n Use of storage phosphor plate usually in a cassette-based system
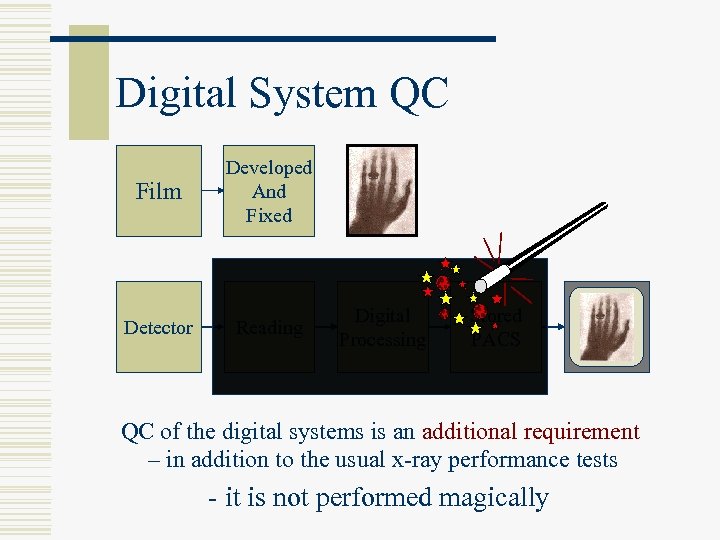 Digital System QC Film Developed And Fixed Detector Reading Digital Processing Stored PACS Viewed Display QC of the digital systems is an additional requirement – in addition to the usual x-ray performance tests - it is not performed magically
Digital System QC Film Developed And Fixed Detector Reading Digital Processing Stored PACS Viewed Display QC of the digital systems is an additional requirement – in addition to the usual x-ray performance tests - it is not performed magically
 DR, CR and DF – Extra QC n n n Dose Calibration Spatial Resolution Low Contrast Uniformity Artifacts
DR, CR and DF – Extra QC n n n Dose Calibration Spatial Resolution Low Contrast Uniformity Artifacts
 Dose Calibration w Each system should be calibrated according to the manufacturers protocol, as they are all slightly different w General set-up n n n Arrange for defined dose at surface of cassette at 80 k. Vp Expose and read image Record Exposure Index w The image can also be used to check for uniformity, linearity and artifacts
Dose Calibration w Each system should be calibrated according to the manufacturers protocol, as they are all slightly different w General set-up n n n Arrange for defined dose at surface of cassette at 80 k. Vp Expose and read image Record Exposure Index w The image can also be used to check for uniformity, linearity and artifacts
 Image Quality w All CR and some DR/DF manufacturers have custom Image Quality phantoms and automatic software to analyze image quality
Image Quality w All CR and some DR/DF manufacturers have custom Image Quality phantoms and automatic software to analyze image quality
 Resolution and Contrast w Any high contrast resolution phantom can be used to provide comparative information w Low contrast resolution is one of the most difficult parameters to measure. There are several phantoms and measurement is subjective, so consistent technique is essential w Image Noise is usually be a good indicator of consistency
Resolution and Contrast w Any high contrast resolution phantom can be used to provide comparative information w Low contrast resolution is one of the most difficult parameters to measure. There are several phantoms and measurement is subjective, so consistent technique is essential w Image Noise is usually be a good indicator of consistency
 Digital Radiography QC w Many DR systems require more frequent calibration of the uniformity eg every month n Flat field measurement (uniform Cu or. Al plate) Uniformity correction l Noise l Artifacts l n Contrast-detail and resolution phantom
Digital Radiography QC w Many DR systems require more frequent calibration of the uniformity eg every month n Flat field measurement (uniform Cu or. Al plate) Uniformity correction l Noise l Artifacts l n Contrast-detail and resolution phantom
 CR & DR QC • Weekly visual inspection (W 1) • Dust / dirt • Clean if necessary • Technologist • Monthly inspection / cleaning (M 1) • Dust / dirt / damage • Clean each IP. Replace damaged IPs. • Technologist • Maintain logsheet
CR & DR QC • Weekly visual inspection (W 1) • Dust / dirt • Clean if necessary • Technologist • Monthly inspection / cleaning (M 1) • Dust / dirt / damage • Clean each IP. Replace damaged IPs. • Technologist • Maintain logsheet
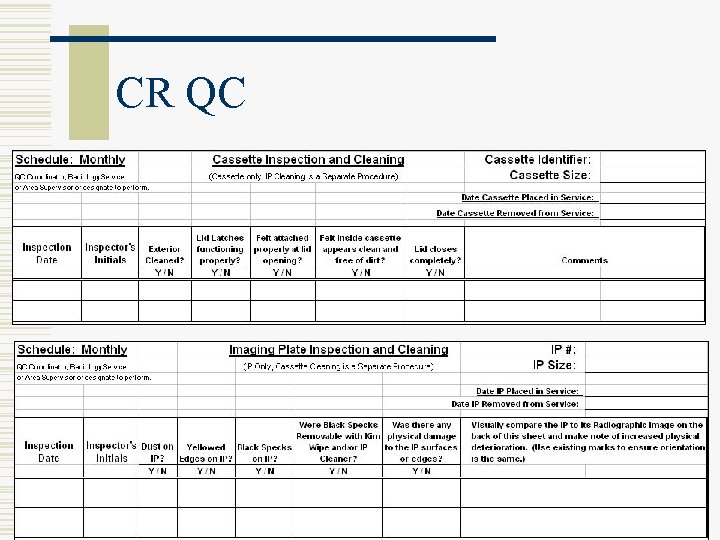 CR QC
CR QC


