3eb04719eda153f56d2deddd6ad13b5a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 131

Safety and Rules of the Lab

Safety Symbols • Know safety symbols • They appear in your laboratory activities • They will alert you to possible dangers • They will remind you to work carefully

Use Your Head • Exercise Caution and Good Judgment • Follow all instructions given by the teacher • Notify the teacher immediately regarding any accident or unsafe areas

Use Your Head • Read lab instructions ahead of time • Always follow lab procedures exactly • Never do an unauthorized experiment

Protect Yourself Eye Safety • Wear safety goggles when working with chemicals, flames, or heating devices • or if possibility of flying debris • If you wear contact lenses let your teacher know

Protect Yourself Eye Safety • In case of emergency in which a chemical goes into one’s eye, use the eyewash station (15 min. )

Protect Yourself Proper Attire • Keep all long hair tied back • Do not wear loose clothing that could catch on fire • Foot wear that completely covers the foot is required

Protect Yourself Hand Safety • If a chemical spills on your skin, notify the teacher and rinse with water for 15 minutes • Wash hands after every lab • Handle glassware, sharp tools and heated containers carefully

Protect Yourself Hand Safety

f e s o r o t h e r s h a r p o b j e c t s a l w a y s w a l k Sharp Objects • Always cut away from fingers and body • Always carry sharp objects with points and tips facing down and away • Never try to catch falling sharp instruments • Grasp sharp instruments only by the handles

f e s o r o t h e r s h a r p o b j e c t s a l w a y s w a l k Sharp Objects • Notify teacher if you get cut • Broken glass and sharp objects do not go in trash cans • Teacher will clean up broken glass

Electrical Safety • Only electrical plugs are to be placed into an electrical outlet • Unplug electrical equipment after use • Keep all electrical cords, wires, and appliances away from water

Physical Safety • Handle all equipment carefully • Do not place a cord where someone can trip over it • Push all stools in out of the way • Keep books picked up out of walking isles

Heating Safety • Tie back hair and loose clothes when working with open flames • Never look into a container as you are heating it • Never point the end of a test tube being heated at yourself or others • Never heat in a closed container

Heating Safety • Never leave a heat source unattended • Heated metal and glass looks cool, use tongs or gloves before handling • Do not place hot glassware directly on lab desk or in cold water

Chemical Safety • Read all labels twice before removing a chemical from the container • Only use the type and amount of chemical instructed to use • Never touch, taste, or smell a chemical unless instructed by the teacher • Never mix chemicals unless instructed to do so

Chemical Safety • Transfer chemicals carefully! • Keep lids on chemical containers when not in use • When diluting an acid, pour the acid into water • Consider all chemicals dangerous

Animal Safety • Only handle living organisms with teacher permission • Always treat living organisms humanely • Wash your hands after handling animals
Treatment of Specimen • Respect the life of all laboratory specimen • They gave their life for your education

Plant Safety • Do not eat any plants in lab • Wash your hands after handling plants • Tell your teacher of any plant allergies • Like any organism, plants should be considered possibly harmful

You Should Never… • Enter store room unless given permission • Take any chemicals from lab or store room • Touch any equipment, chemicals, or other materials until instructed to do so

You Should Never… • Eat or drink in the lab • Use lab glass-ware to eat or drink out of

You Should Never… • Engage in…. – practical jokes – horse play – rough house

In case of an emergency… • Know the locations of: – – fire extinguisher fire blanket body shower eyewash station – first aid kit • If you spill a harmful chemical on yourself or in your eyes, start rinsing immediately and send your partner to get teacher’s help

Remember to… • • Stay at your work station Maintain a clean work area Read and follow all directions Report any spills, accidents, or injury to the teacher immediately • Clean and put away all equipment at the end of the lab period • Dispose of waste products according to instruction


Dissection Terms • • Anterior: Towards the front Posterior: Towards the rear Ventral: Towards the belly Dorsal: Towards the backbone Superior: Towards the top Inferior: Towards the bottom Medial: Towards the middle Lateral: Towards the side
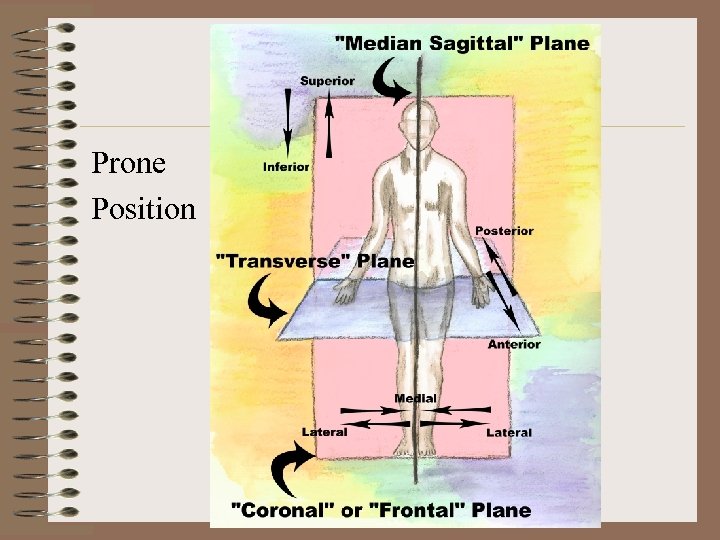
Prone Position

Scalpel

Probe
Dissecting Pins

Dissecting Pan


Earthworms • Terrestrial animals inhabiting the moist soil. • Usually found in the upper layer of soil to a depth of 30 -40 cm. • Nocturnal (active at night) • During rainy season they come out and crawl on the ground. • During winter they close the burrows by leaves and debris.

Earthworms Cont. • There about 500 species of earthworms. • Earthworms are hermaphroditic (have both male and female reproductive organs). • Some earthworms have the ability to regenerate their lower halves if they are cut off.
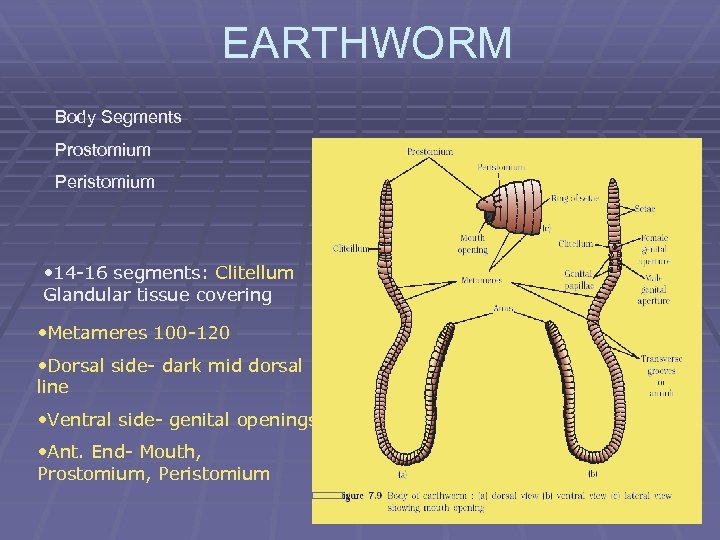
EARTHWORM Body Segments Prostomium Peristomium • 14 -16 segments: Clitellum Glandular tissue covering • Metameres 100 -120 • Dorsal side- dark mid dorsal line • Ventral side- genital openings • Ant. End- Mouth, Prostomium, Peristomium

Body apertures 1. Spermathecal Pores 2. Female genital Pores 3. Male genital pores 4. Nephridiopores 5. Dorsal pores 6. Anus
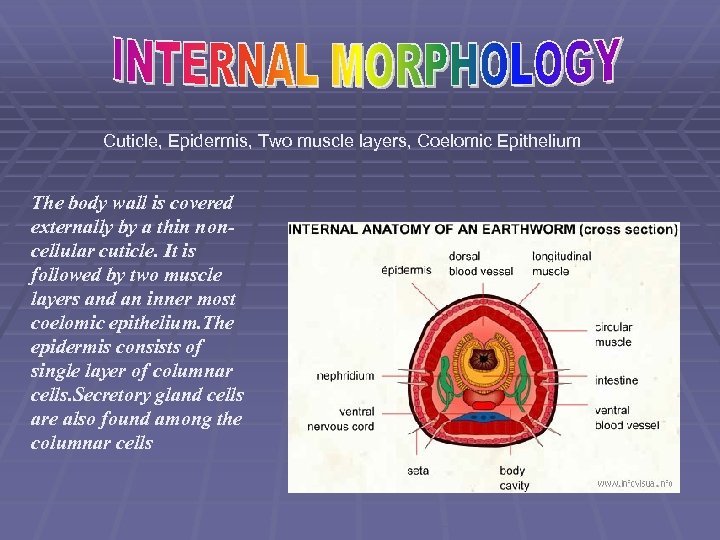
Cuticle, Epidermis, Two muscle layers, Coelomic Epithelium The body wall is covered externally by a thin noncellular cuticle. It is followed by two muscle layers and an inner most coelomic epithelium. The epidermis consists of single layer of columnar cells. Secretory gland cells are also found among the columnar cells
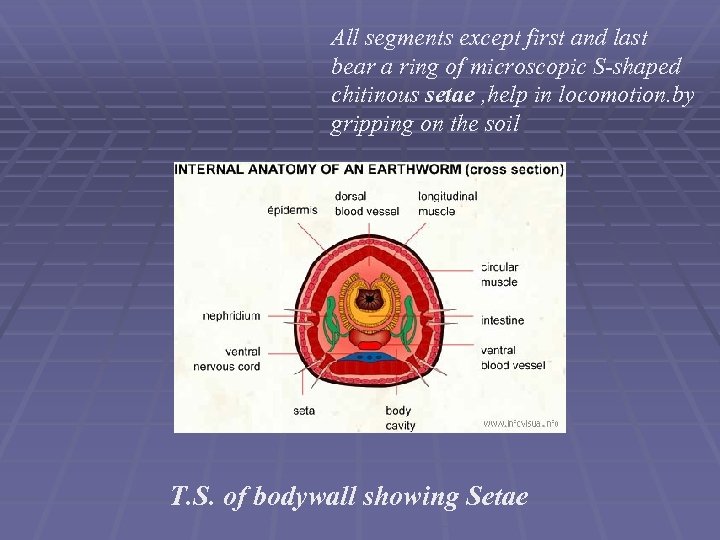
All segments except first and last bear a ring of microscopic S-shaped chitinous setae , help in locomotion. by gripping on the soil T. S. of bodywall showing Setae

Digestive system It is a straight tube and runs from the first to the last segments. It consists of mouth(peristomium), buccal cavity , pharynx, oesophagus, a muscular gizzard, stomach, intestine and anus

Circulatory system In earthworm , the circulation is closed type. The circulatory system consists of heart, blood vessels, capillaries and blood glands
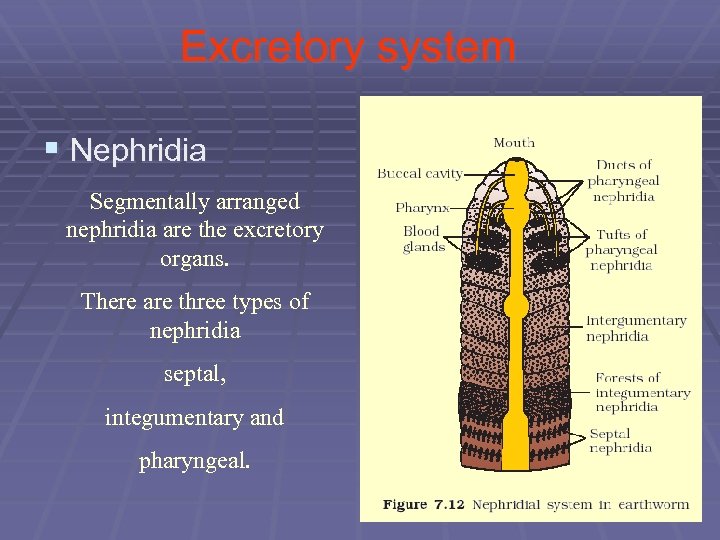
Excretory system § Nephridia Segmentally arranged nephridia are the excretory organs. There are three types of nephridia septal, integumentary and pharyngeal.

The nervous system consists of segmentally arranged ganglia and a ventral nerve cord. A ganglion is a mass of nerve cells. Nerve ring Ventral Nerve cord Sense Organs
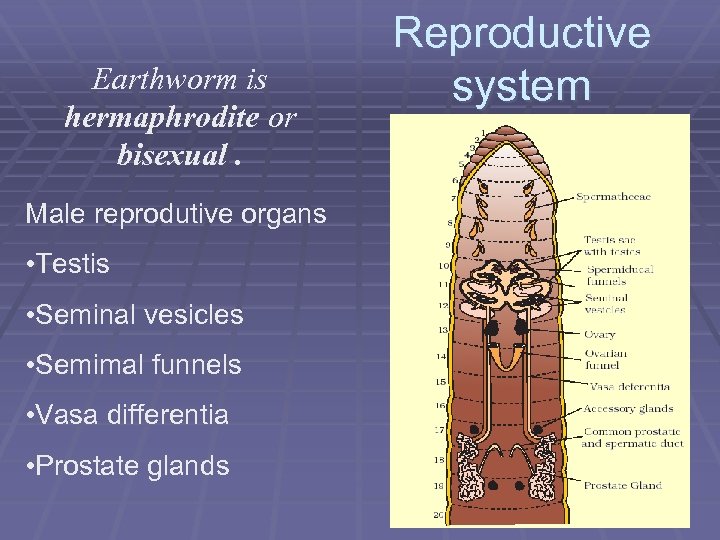
Earthworm is hermaphrodite or bisexual. Male reprodutive organs • Testis • Seminal vesicles • Semimal funnels • Vasa differentia • Prostate glands Reproductive system

Female reproductive system • Ovaries • Oviduccal funnels • Oviducts • Spermatheca surendranaduthila@gmail. com
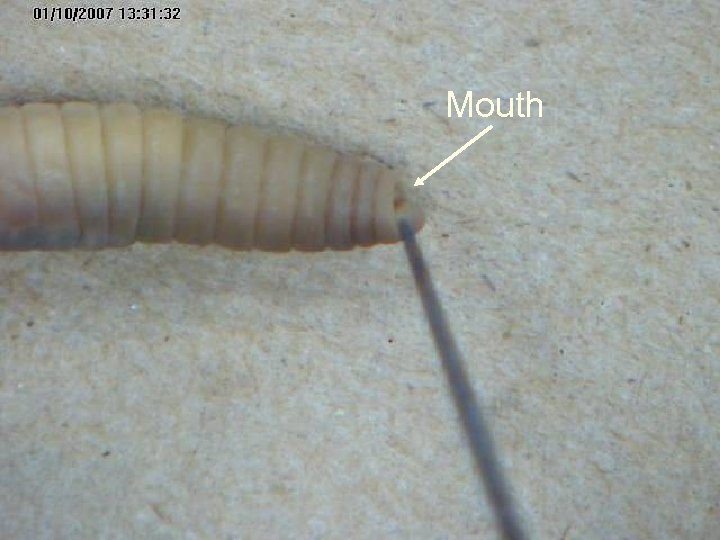

Mouth

Sperm Duct
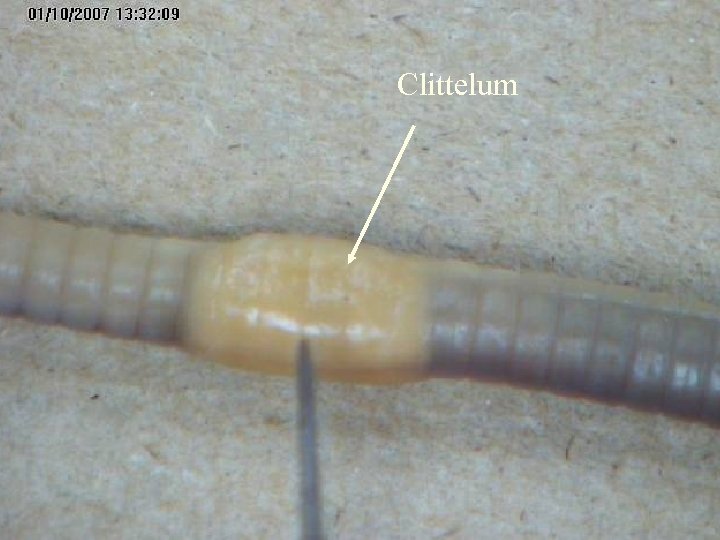
Clittelum

Mouth Pin your worm at the tip of the mouth and at its midpoint.

Continue your cut to the mouth Start your incision 2 cm behind the clittelum. Make sure not to cut too deeply.
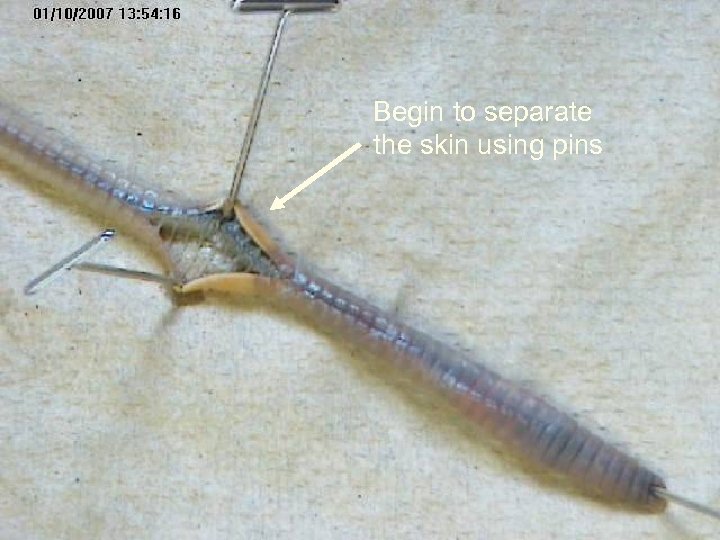
Begin to separate the skin using pins
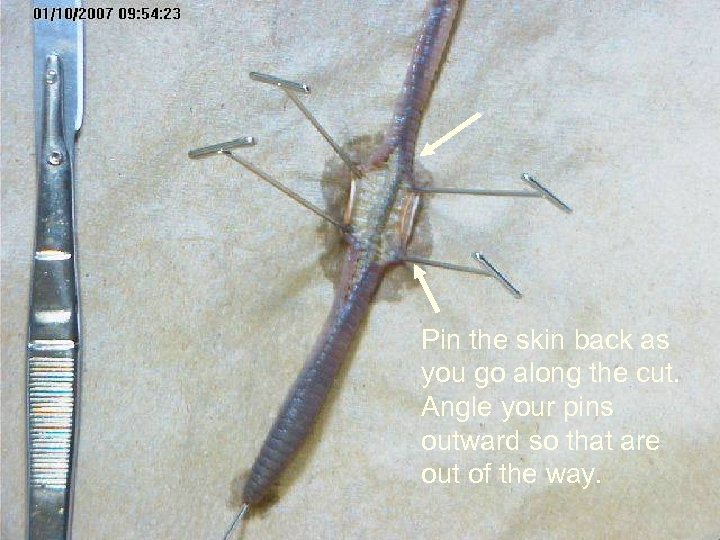

Pin the skin back as you go along the cut. Angle your pins outward so that are out of the way.
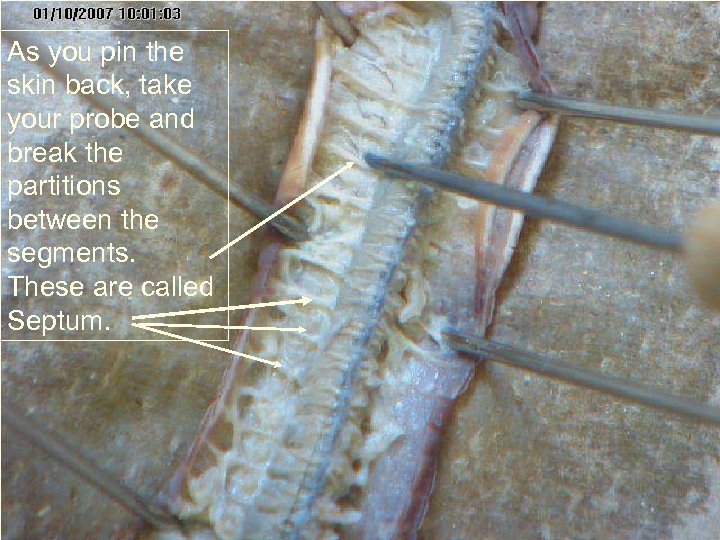
As you pin the skin back, take your probe and break the partitions between the segments. These are called Septum.

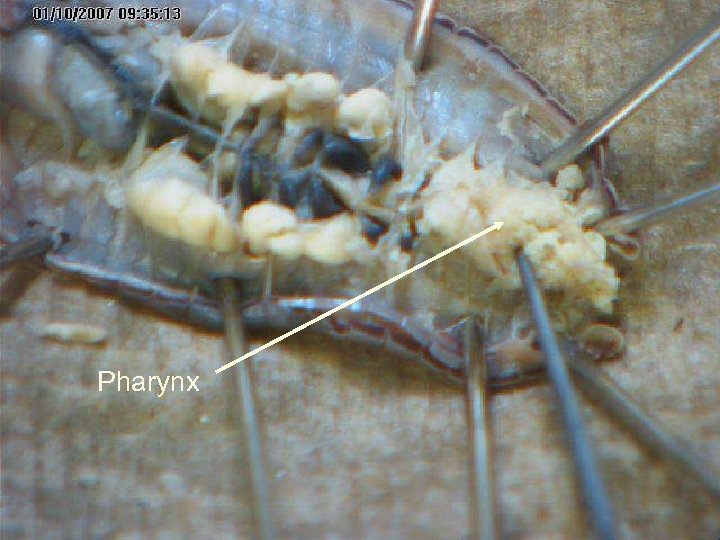
Pharynx

Aortic Arches – Earthworms have 5 pair of these simple hearts.
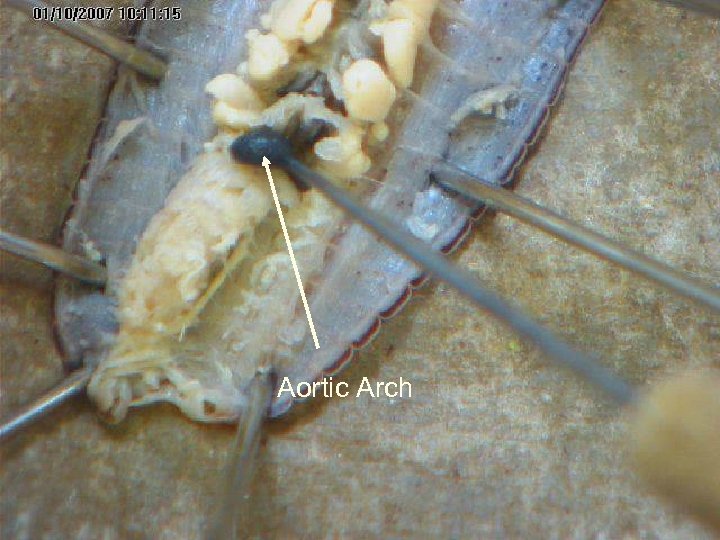
Aortic Arch
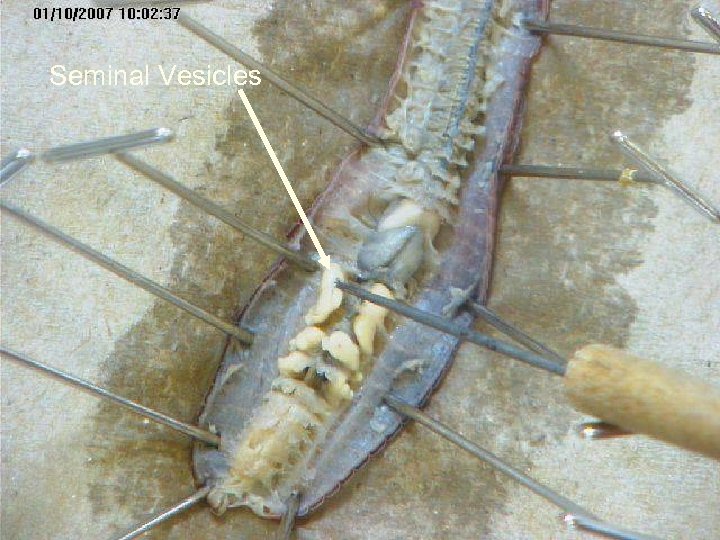

Seminal Vesicles

Seminal Receptacles
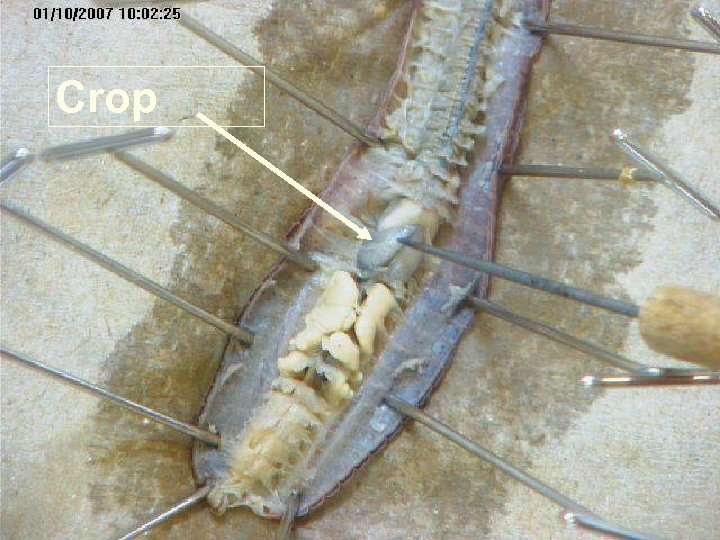
Crop
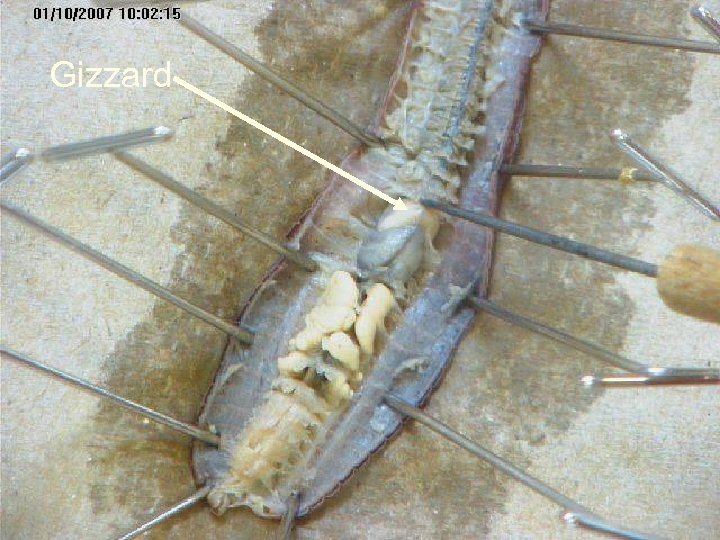

Gizzard
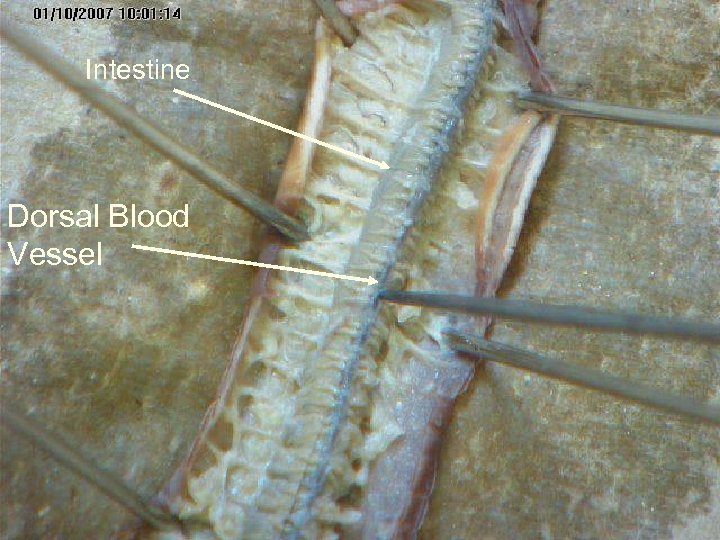
Intestine Dorsal Blood Vessel
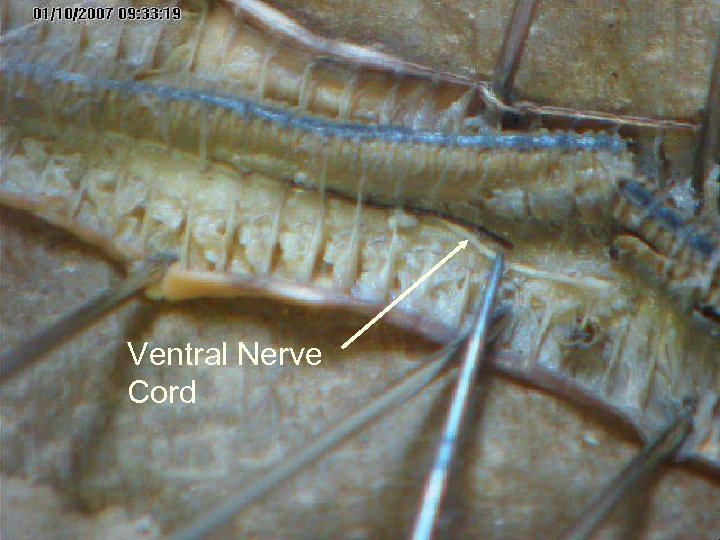
Ventral Nerve Cord
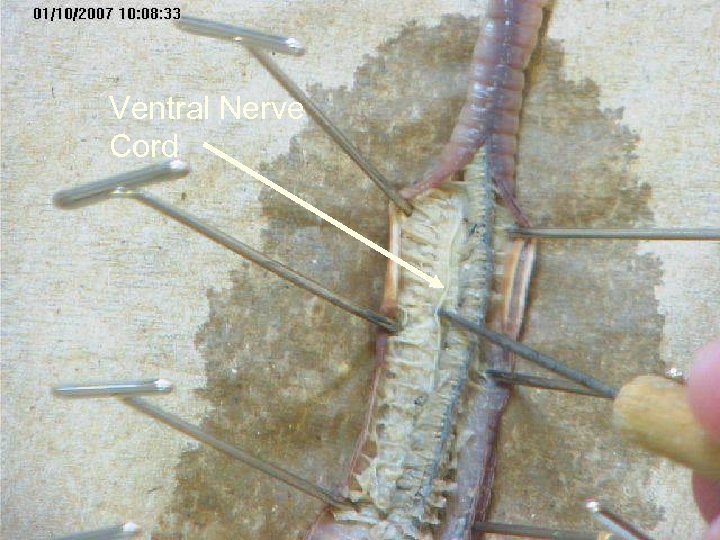
Ventral Nerve Cord
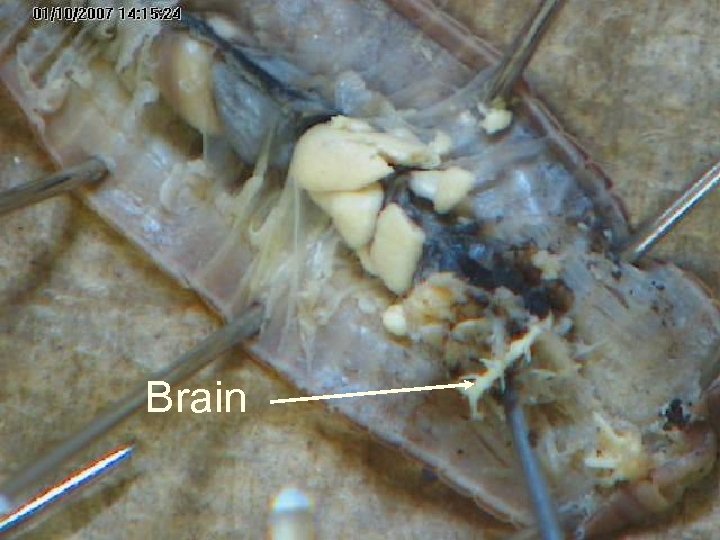
Brain
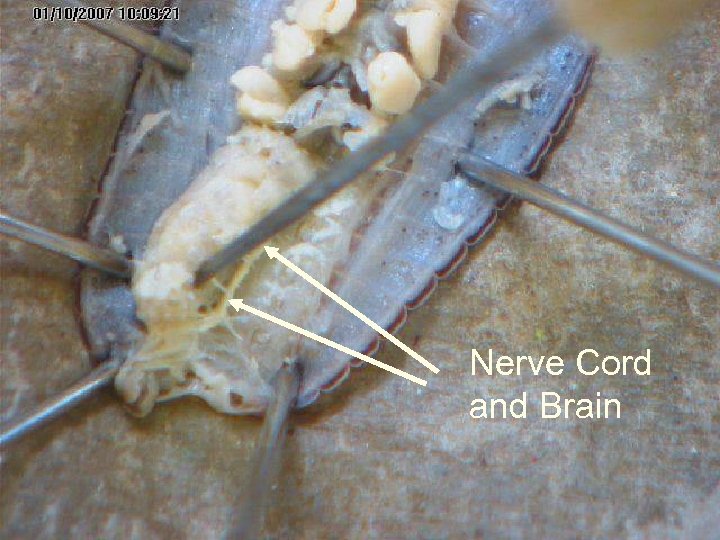
Nerve Cord and Brain
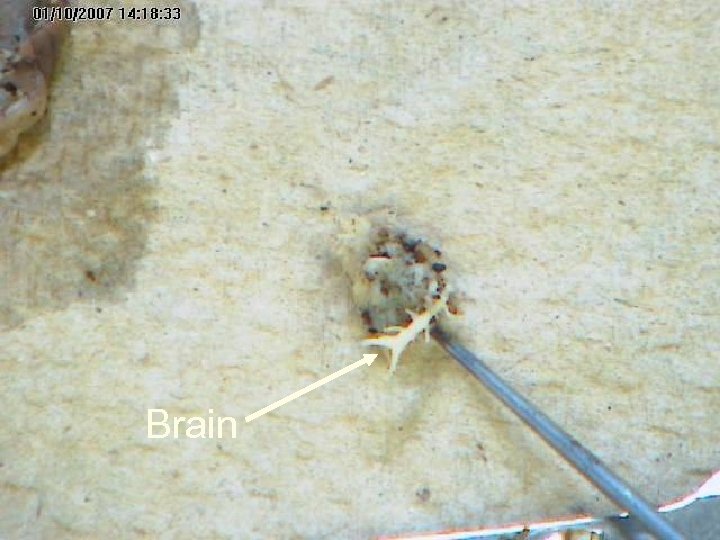
Brain

AMPHIBIAN CHARACTERISTICS Moist, thin skin without scales Aquatic larva changes to terrestrial adult Feet without claws Respiration with gills, lungs, skin, mouth Closed 2 loop circulation Ectothermic (cold blooded) Eggs without shells or multicellular membranes
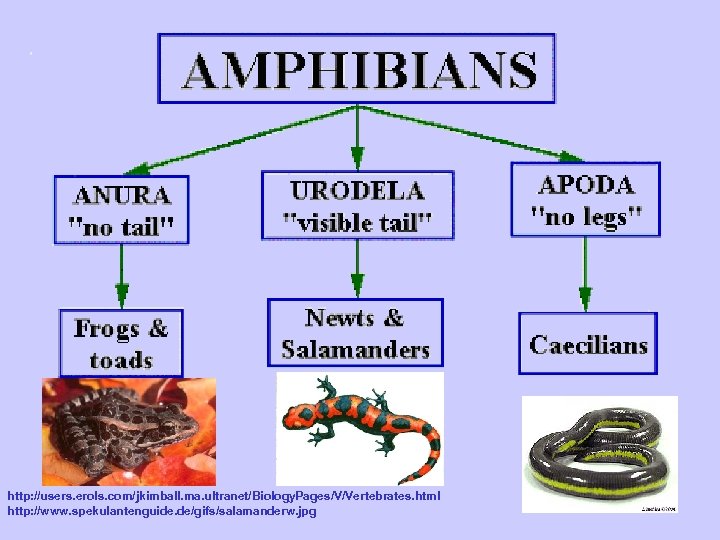
http: //users. erols. com/jkimball. ma. ultranet/Biology. Pages/V/Vertebrates. html http: //www. spekulantenguide. de/gifs/salamanderw. jpg

FROG LATIN meaning ANIMALIA KINGDOM _______ PHYLUM ______________ CHORDATA VERTEBRATA “backbone” SUBPHYLUM ______________ AMPHIBIA “double life” CLASS ________________ ANURA “without a tail” ORDER _______________

Thin, moist skin – no scales Mucous glands make it “slimy” Camouflage- for protection Some have poison glands http: //www-binf. bio. uu. nl/dutilh/hall/kikkers. html

http: //www. tvdsb. on. ca/westmin/science/snc 2 g 1/frogresp. htm BREATHING WITH LUNGS is called PULMONARY RESPIRATION
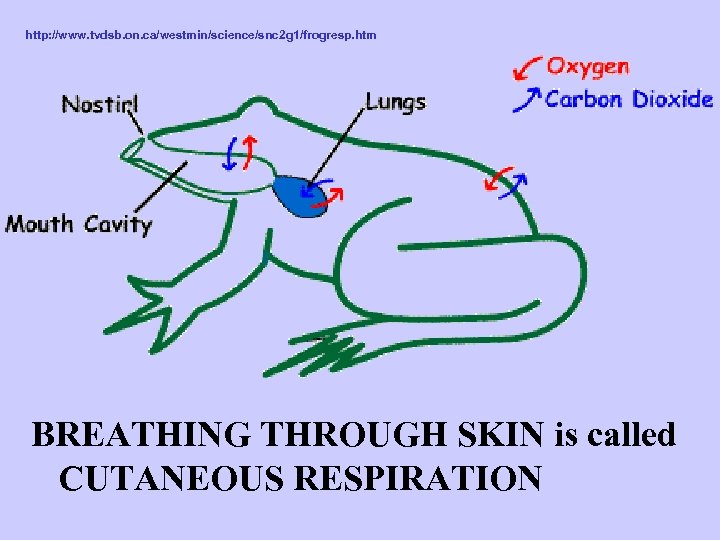
http: //www. tvdsb. on. ca/westmin/science/snc 2 g 1/frogresp. htm BREATHING THROUGH SKIN is called CUTANEOUS RESPIRATION

ECTOTHERMIC “cold blooded” Body temperature is dependent on surrounding environment http: //www. vanscyoc. net/randy/garden/wildlife/image 4. htm

HIBERNATION/ ESTIVATION FAT stored in FAT BODIES provides energy Images from: http: //www. enc. org/Classroom_Calendar/CC_Units/Unit_Images/185. jpg http: //www. reptilis. org/pyxi/image 5. htm
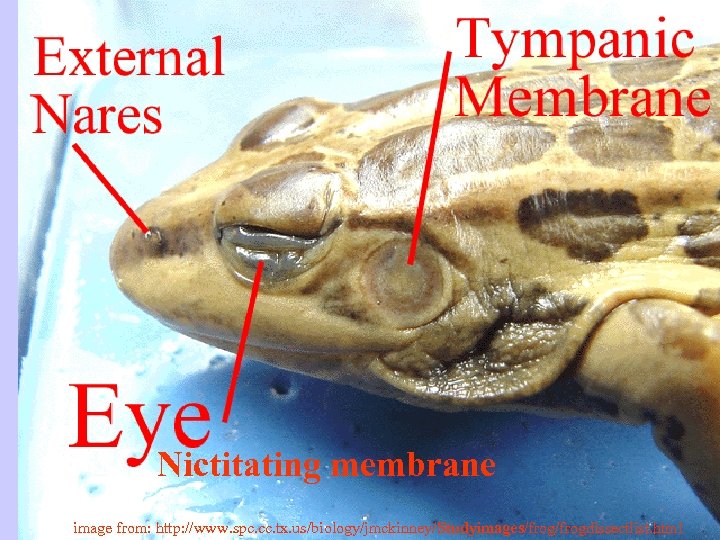
Nictitating membrane image from: http: //www. spc. cc. tx. us/biology/jmckinney/Studyimages/frogdissectlist. html
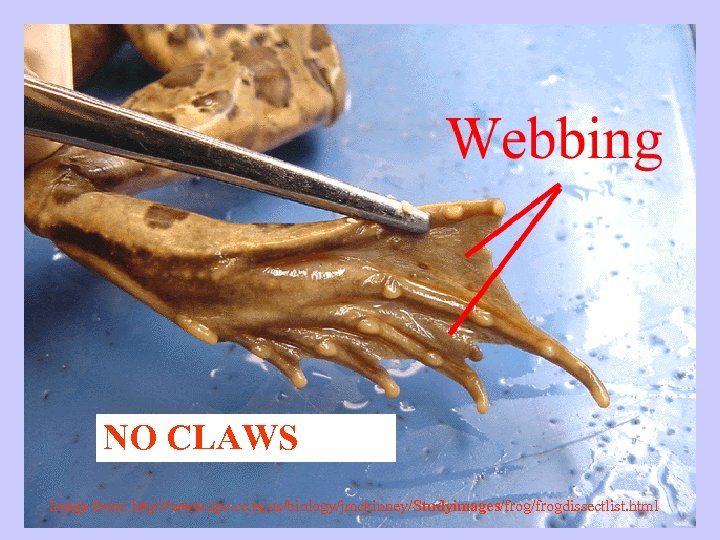
NO CLAWS image from: http: //www. spc. cc. tx. us/biology/jmckinney/Studyimages/frogdissectlist. html

EXIT OPENINGS DIGESTIVE WASTE (feces) = _________ ANUS Shared EXCRETORY & REPRODUCTIVE EXIT = _______________ UROGENITAL PORE (Urine & eggs or Urine & sperm)

EXIT OPENINGS OPENING SHARED BY EXCRETORY, REPRODUCTIVE, & DIGESTIVE = _______ VENT http: //www. student. loretto. org/zoology/Amphibians. htm
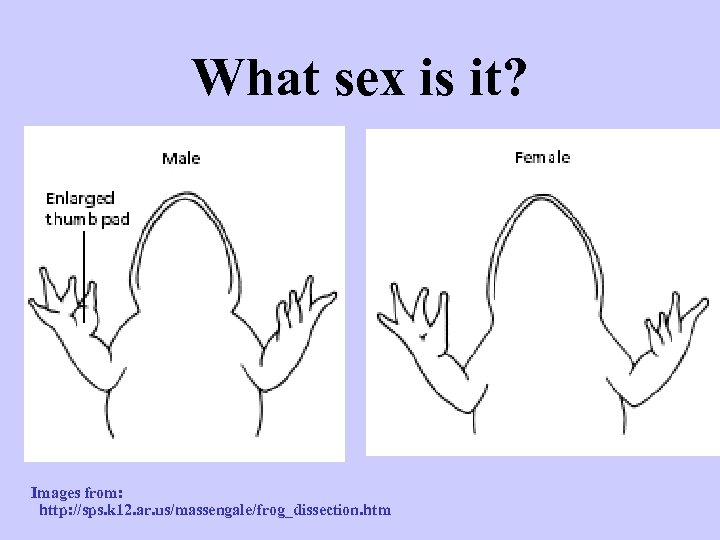
What sex is it? Images from: http: //sps. k 12. ar. us/massengale/frog_dissection. htm


Imagse from: http: //www. animationlibrary. com http: //www. geocities. com/animalbio/biology. htm TONGUE attached at front not back like yours!

Muscular Back of throat Pulls food into digestive system image from: http: //www. spc. cc. tx. us/biology/jmckinney/Studyimages/frogdissectlist. html
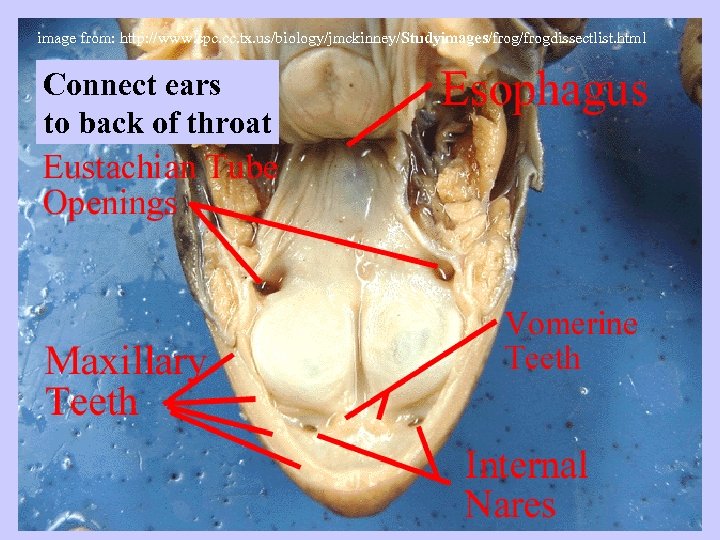
image from: http: //www. spc. cc. tx. us/biology/jmckinney/Studyimages/frogdissectlist. html Connect ears to back of throat

image from: http: //www. spc. cc. tx. us/biology/jmckinney/Studyimages/frogdissectlist. html GLOTTIS Opening to respiratory GULLET Opening to digestive
Images from: http: //sps. k 12. ar. us/massengale/frog_dissection. htm

Image from; http: //faculty. clintoncc. suny. edu/faculty/Michael. Gregory/files/Bio%20102%20 Laboratory/frog%20 dissection_files/frame. htm

Image from; http: //faculty. clintoncc. suny. edu/faculty/Michael. Gregory/files/Bio%20102%20 Laboratory/frog%20 dissection_files/frame. htm Females may have black & white eggs
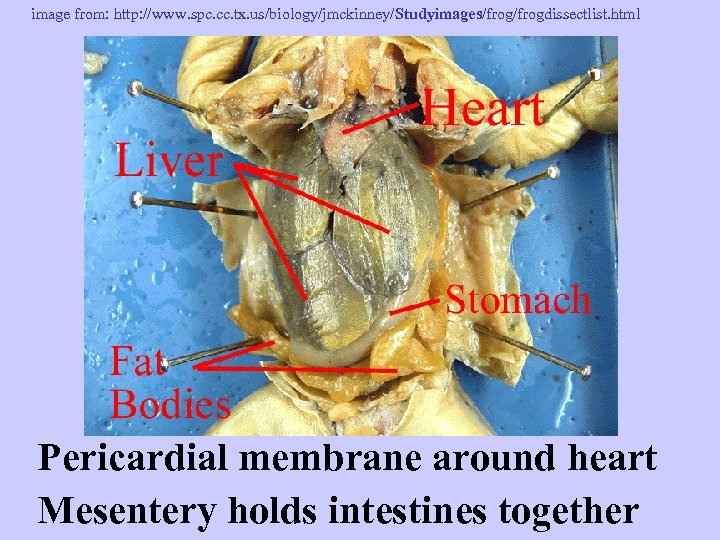
image from: http: //www. spc. cc. tx. us/biology/jmckinney/Studyimages/frogdissectlist. html Pericardial membrane around heart Mesentery holds intestines together
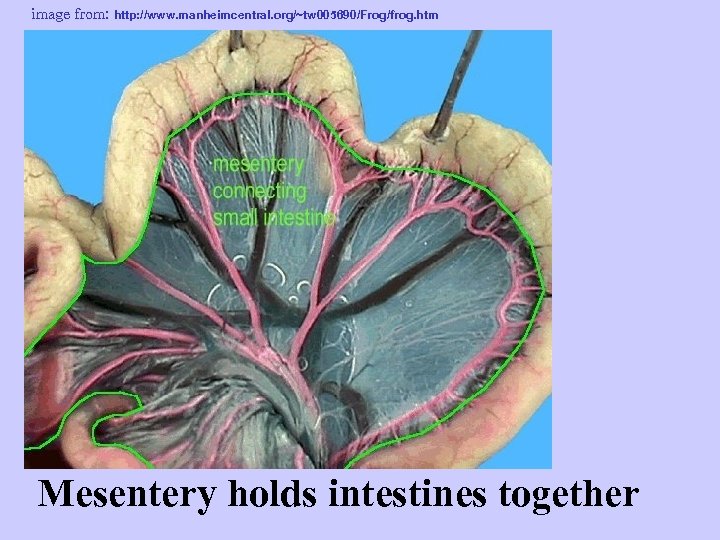
image from: http: //www. manheimcentral. org/~tw 005690/Frog/frog. htm Mesentery holds intestines together

FAT BODIES Store fat for energy during Hibernation Estivation Breeding Image from: http: //step. sdsc. edu/projects 95/Frog. Dissection/index. html
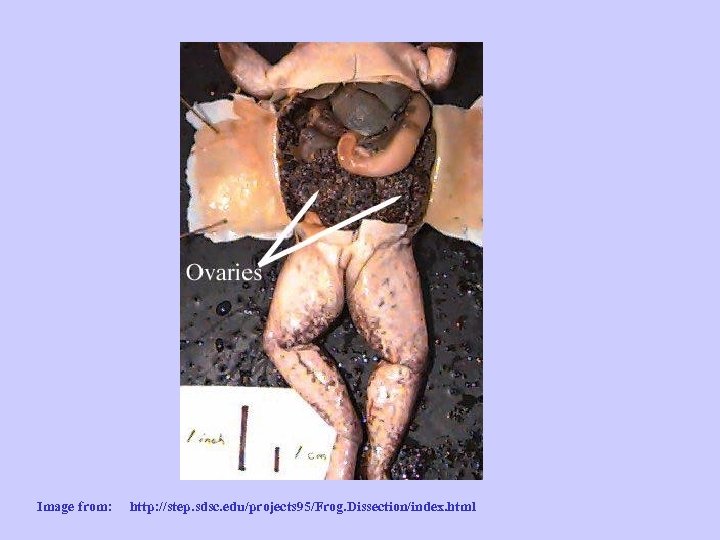
Image from: http: //step. sdsc. edu/projects 95/Frog. Dissection/index. html
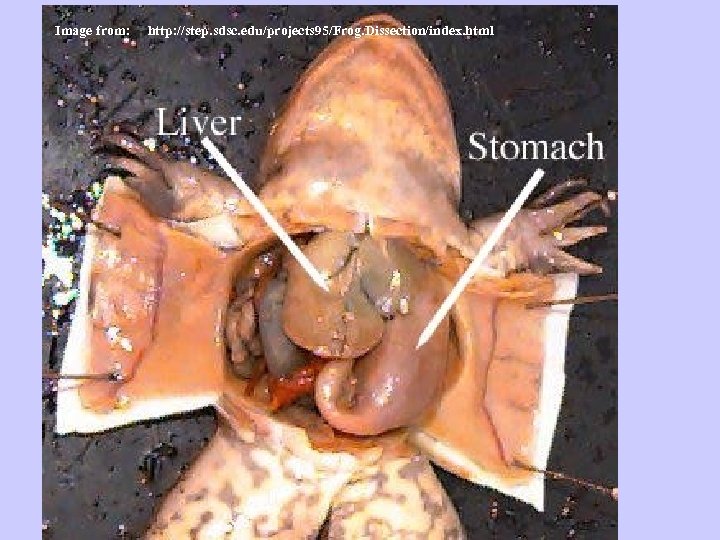
Image from: http: //step. sdsc. edu/projects 95/Frog. Dissection/index. html
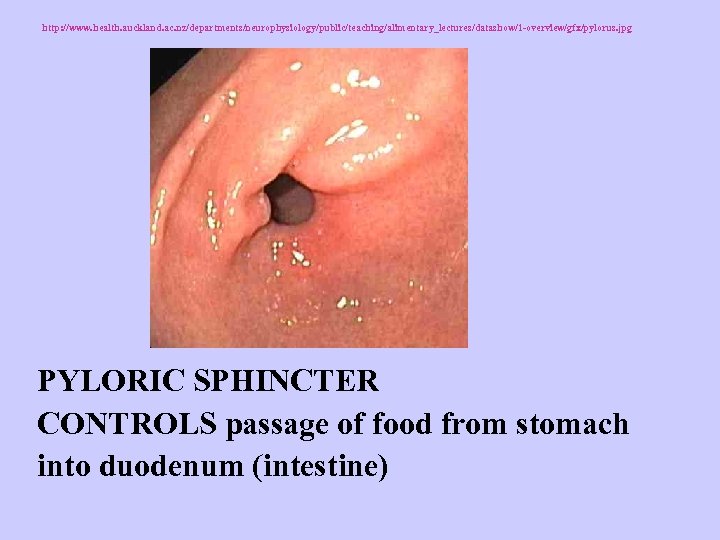
http: //www. health. auckland. ac. nz/departments/neurophysiology/public/teaching/alimentary_lectures/datashow/1 -overview/gfx/pylorus. jpg PYLORIC SPHINCTER CONTROLS passage of food from stomach into duodenum (intestine)
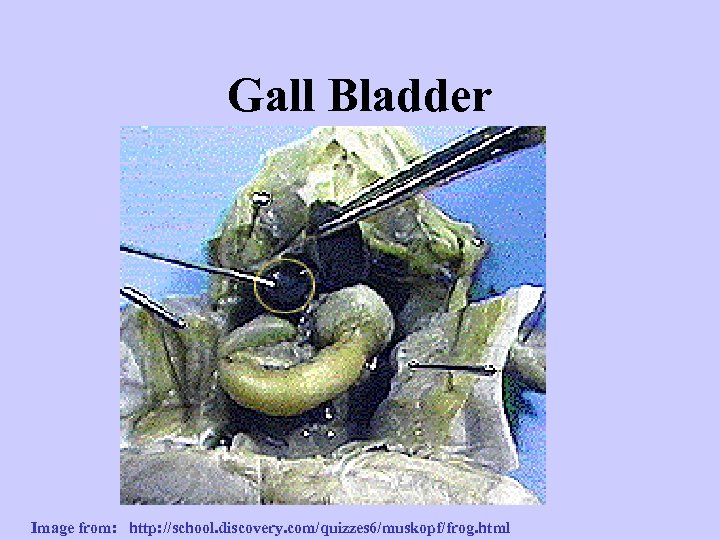
Gall Bladder Image from: http: //school. discovery. com/quizzes 6/muskopf/frog. html

STOMACH: Make acid and digestive enzymes Start digestion (grind up food) LIVER: Make bile Store glycogen Store vitamins Process toxins (including nitrogen waste) for kidneys GALL BLADDER Store bile
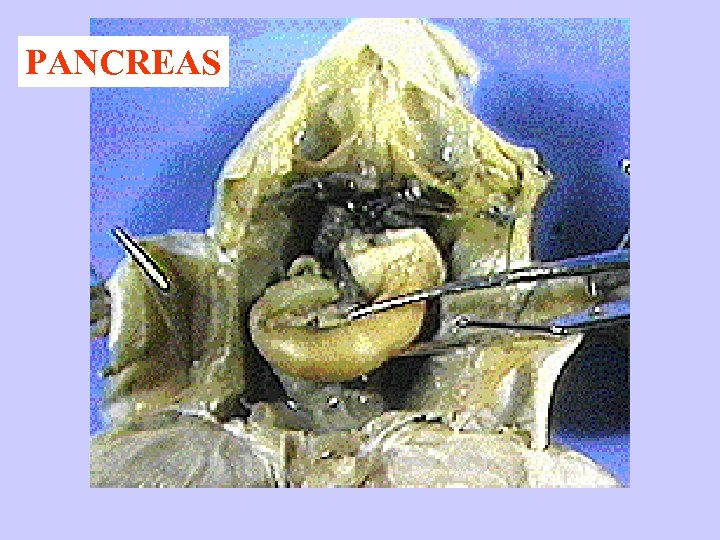
PANCREAS
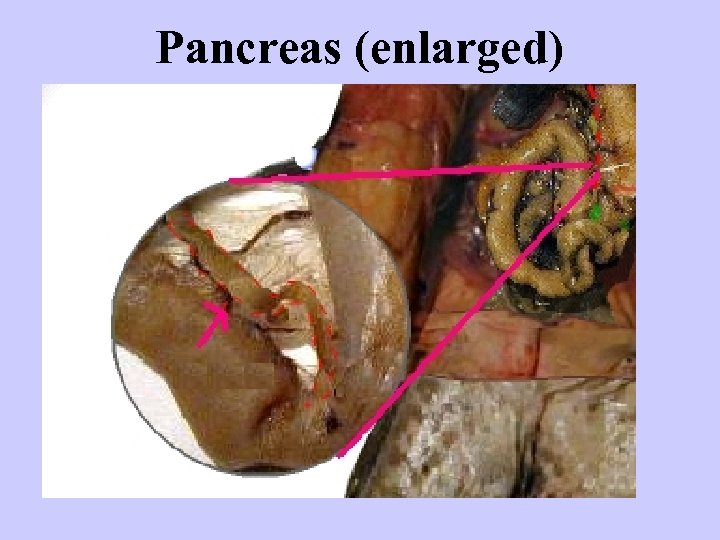
Pancreas (enlarged)

PANCREAS: Makes TRYPSIN, INSULIN, GLUCAGON TRYPSIN- breaks down proteins INSULIN- tells cells to store glucose from bloodstream as glycogen GLUCAGON- tells cells to release stored glucose to blood stream
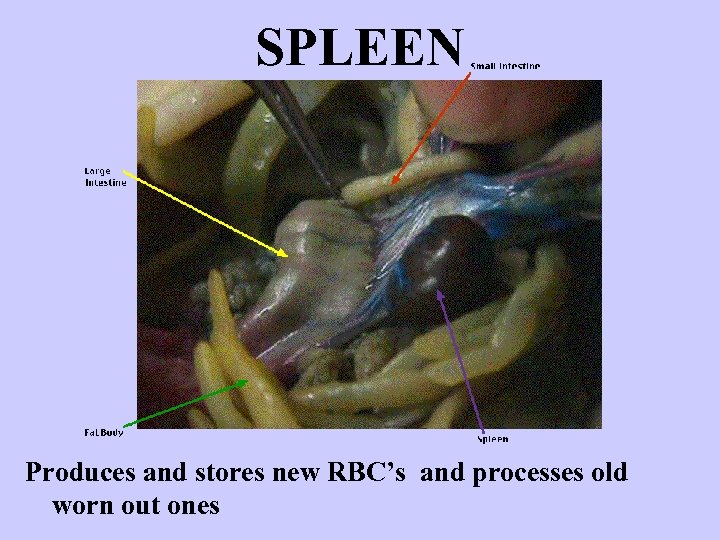
SPLEEN Produces and stores new RBC’s and processes old worn out ones
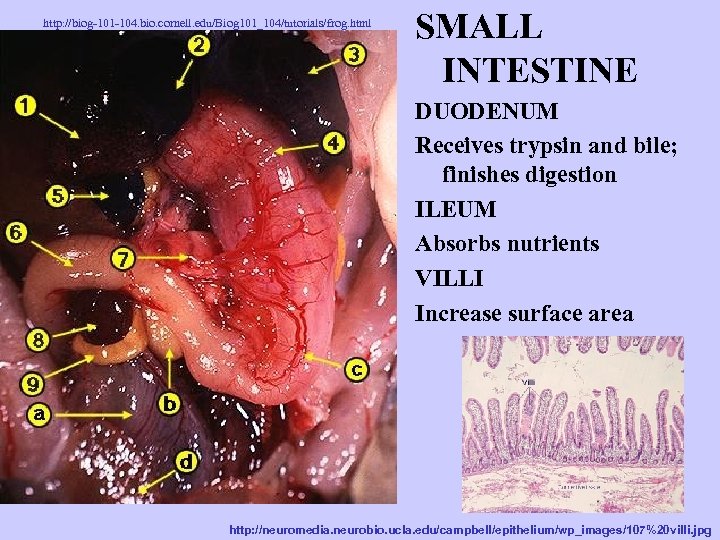
http: //biog-101 -104. bio. cornell. edu/Biog 101_104/tutorials/frog. html SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM Receives trypsin and bile; finishes digestion ILEUM Absorbs nutrients VILLI Increase surface area http: //neuromedia. neurobio. ucla. edu/campbell/epithelium/wp_images/107%20 villi. jpg

http: //www. flushing. k 12. mi. us/srhigh/tippettl/biology/frog/largeintestine. html LARGE INTESTINE Removes water from digestive waste; concentrates feces

10 Body Systems : __________ EXCRETORY Get rid of nitrogen waste made by cells Nitrogen waste has different chemical forms: AMMONIA ______ UREA _____ URIC ACID _______ MOST TOXIC made from ammonia by liver HUMANS AMPHIBIANS LEAST TOXIC needs the least water to dilute BIRDS, REPTILES FISH

ALL WASTE is NOT THE SAME! DIGESTIVE wasteleft over from undigested food travels through digestive system leaves through digestive system as feces EXCRETORY waste(Also called NITROGEN WASTE) made by cells from break down of proteins travels through blood stream leaves through excretory system as ammonia, urea, or uric acid
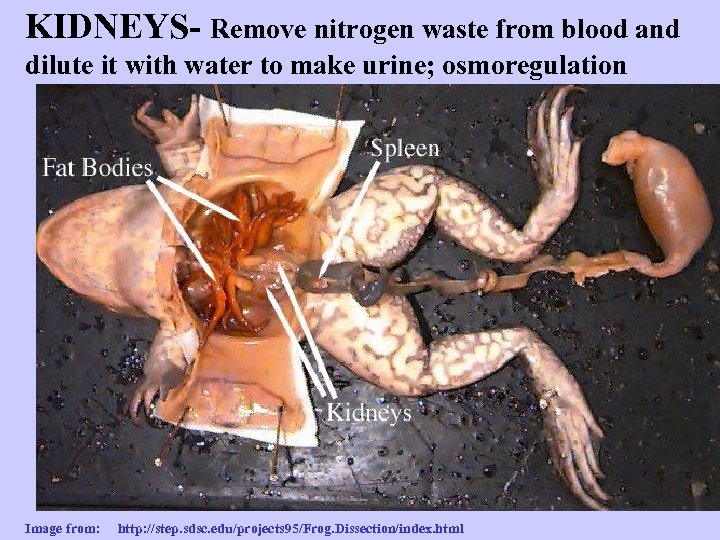
KIDNEYS- Remove nitrogen waste from blood and dilute it with water to make urine; osmoregulation Image from: http: //step. sdsc. edu/projects 95/Frog. Dissection/index. html
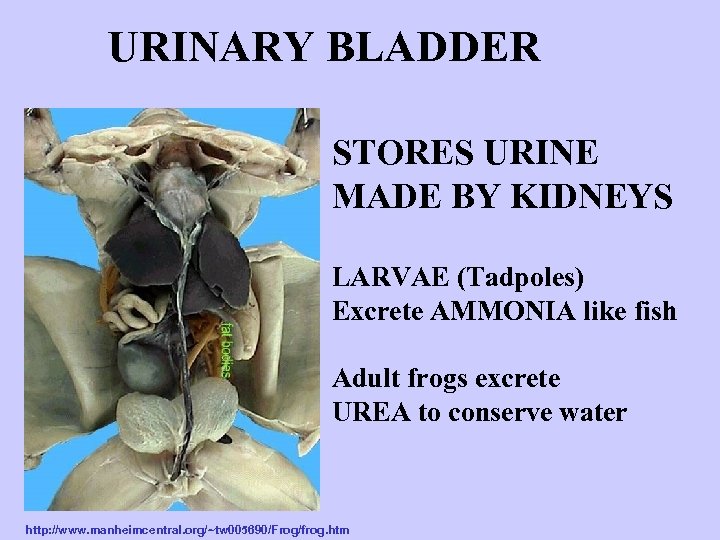
URINARY BLADDER STORES URINE MADE BY KIDNEYS LARVAE (Tadpoles) Excrete AMMONIA like fish Adult frogs excrete UREA to conserve water http: //www. manheimcentral. org/~tw 005690/Frog/frog. htm
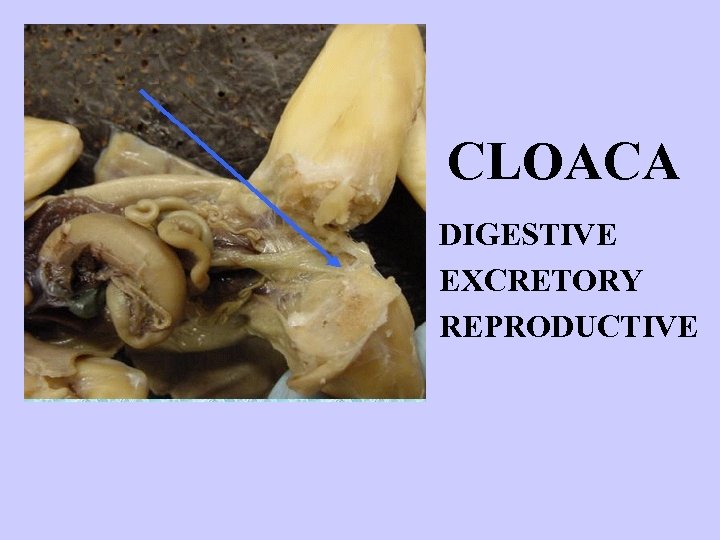
CLOACA DIGESTIVE EXCRETORY REPRODUCTIVE
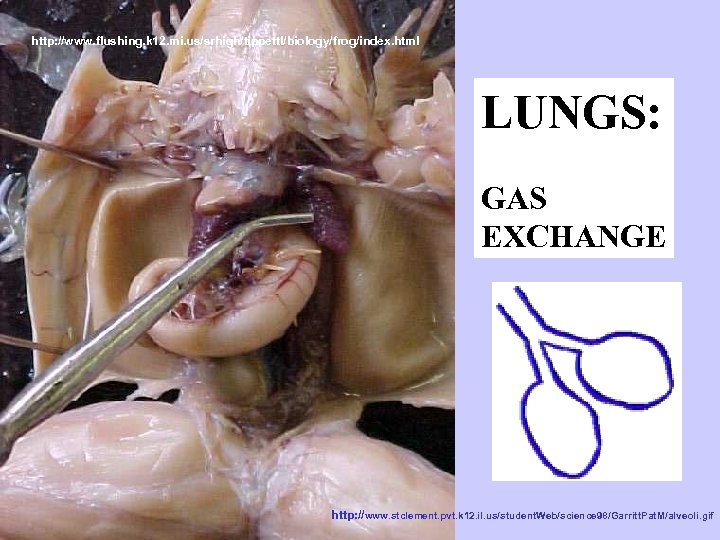
http: //www. flushing. k 12. mi. us/srhigh/tippettl/biology/frog/index. html LUNGS: GAS EXCHANGE http: //www. stclement. pvt. k 12. il. us/student. Web/science 98/Garritt. Pat. M/alveoli. gif

Larvae breathe with GILLS
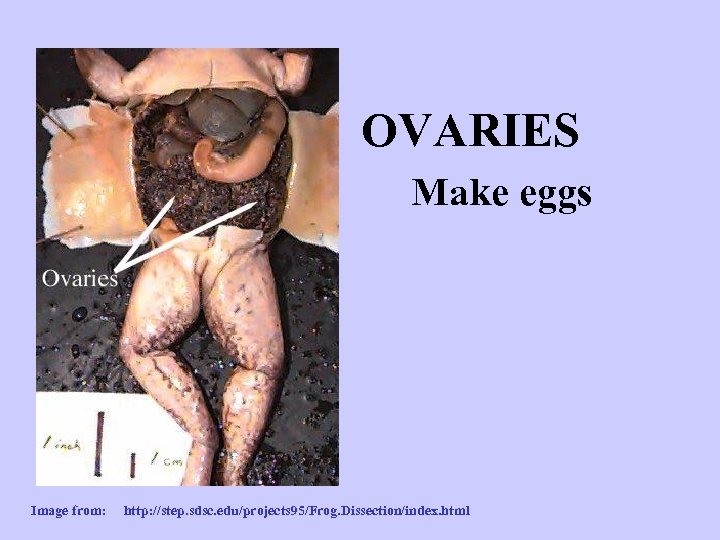
OVARIES Make eggs Image from: http: //step. sdsc. edu/projects 95/Frog. Dissection/index. html
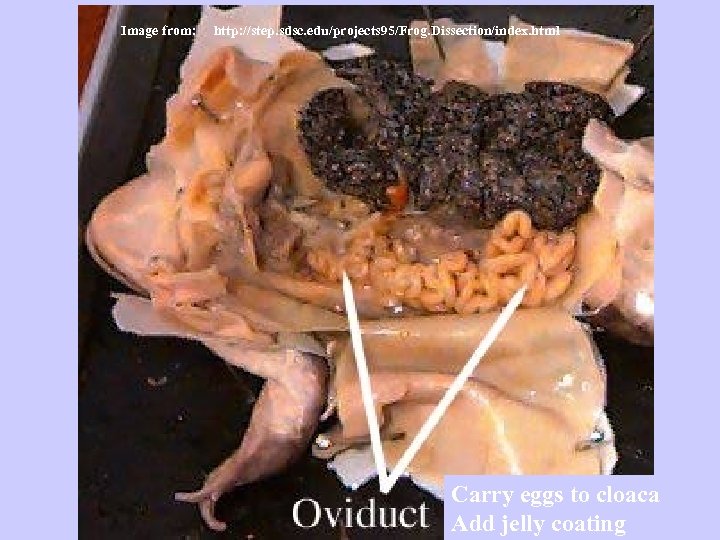
Image from: http: //step. sdsc. edu/projects 95/Frog. Dissection/index. html Carry eggs to cloaca Add jelly coating
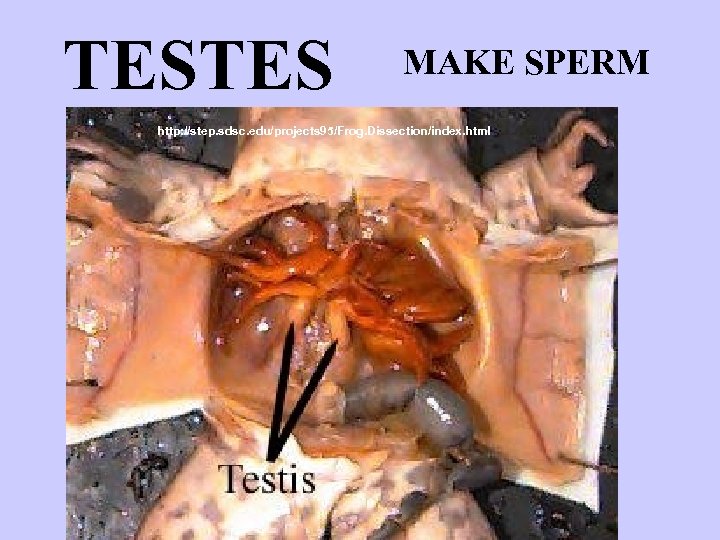
TESTES MAKE SPERM http: //step. sdsc. edu/projects 95/Frog. Dissection/index. html
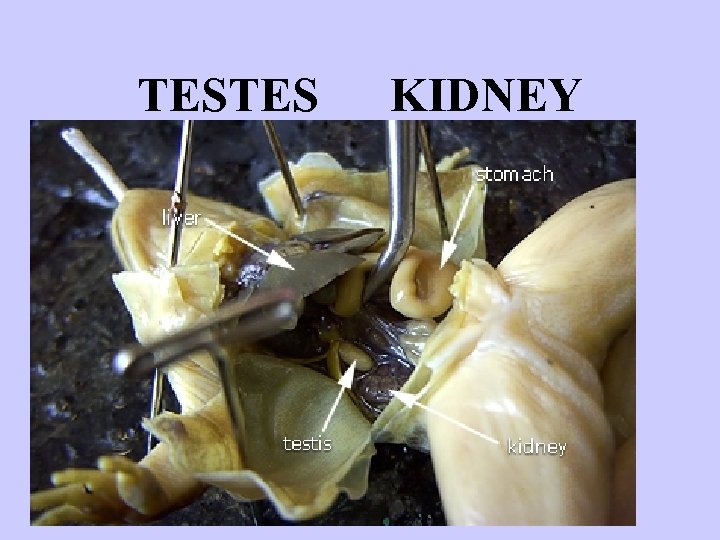
TESTES KIDNEY
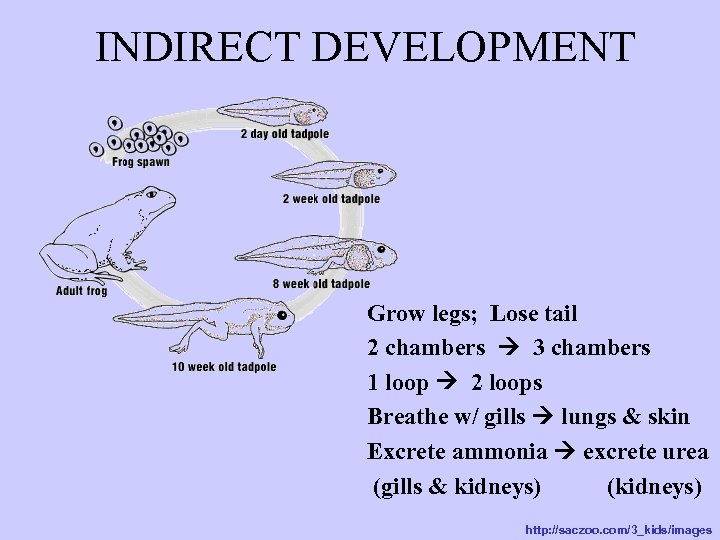
INDIRECT DEVELOPMENT Grow legs; Lose tail 2 chambers 3 chambers 1 loop 2 loops Breathe w/ gills lungs & skin Excrete ammonia excrete urea (gills & kidneys) (kidneys) http: //saczoo. com/3_kids/images

Ways tadpoles are like fish Have a LATERAL LINE Breathe with gills Excrete nitrogen waste as AMMONIA (with gills & kidneys) Have a 2 chamber heart Have a 1 loop circulatory system

HEART 3 chambered heart Right atrium Left atrium Ventricle Image from: http: //www. digitalfrog. com/resources/froggallery. html
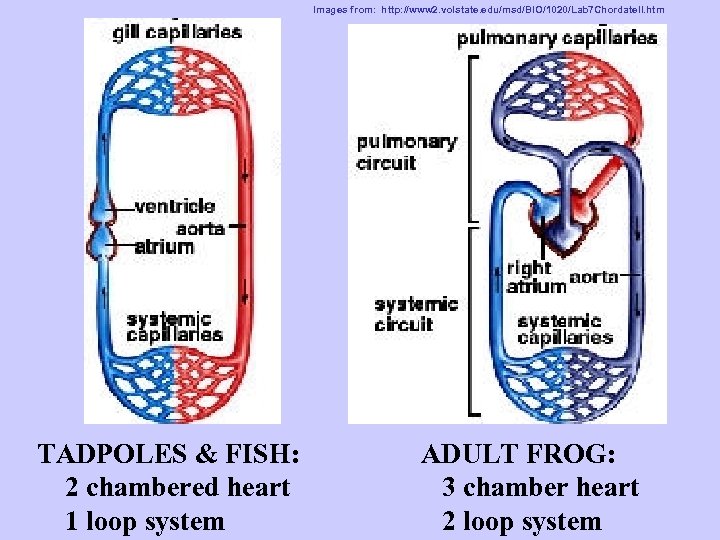
Images from: http: //www 2. volstate. edu/msd/BIO/1020/Lab 7 Chordate. II. htm TADPOLES & FISH: 2 chambered heart 1 loop system ADULT FROG: 3 chamber heart 2 loop system
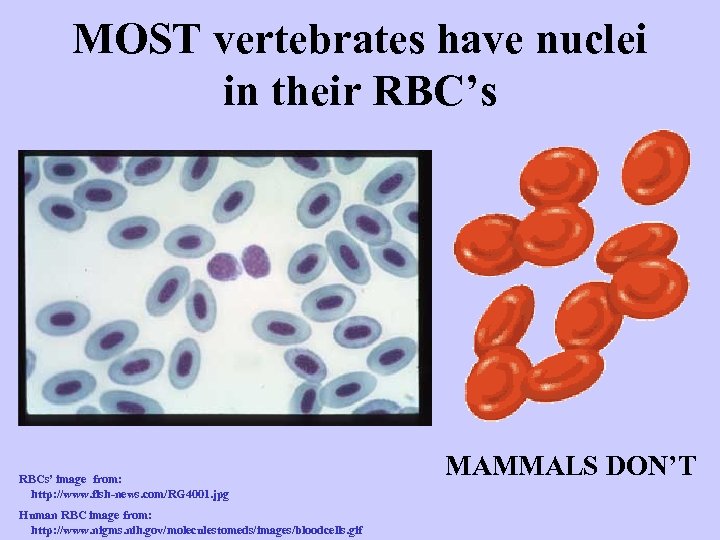
MOST vertebrates have nuclei in their RBC’s RBCs’ image from: http: //www. fish-news. com/RG 4001. jpg Human RBC image from: http: //www. nigms. nih. gov/moleculestomeds/images/bloodcells. gif MAMMALS DON’T
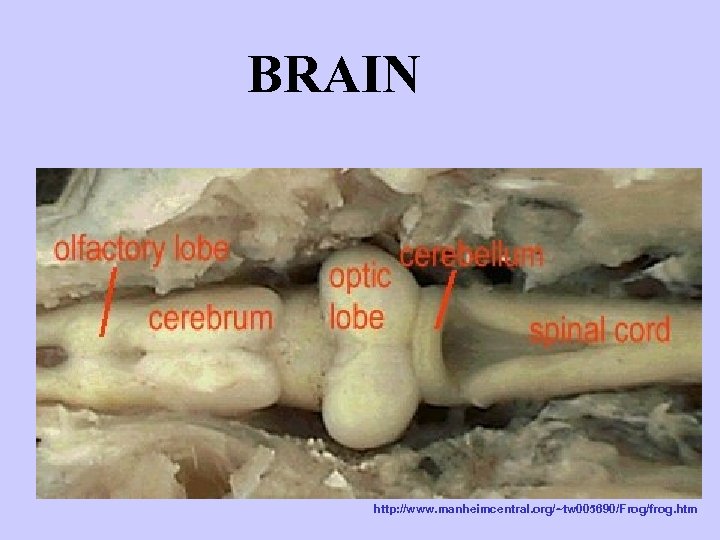
BRAIN http: //www. manheimcentral. org/~tw 005690/Frog/frog. htm

Yellow Perch This fish lives in ponds, lakes, and streams. They need water with lots of vegetation (plants). Often school (group together), especially in deep water. They come into shallow water to feed at dawn and dusk.

Yellow Perch Long fish for its size, growing up to 15 inches long. Yellowish in color, with five to eight dark bars going from its back almost to its belly. Its fins are olive colored, except for its pelvic (chest) fins, which are orange or red

Fish Anatomy Operculum: Gill covering (protects soft gill tissue and filaments). Swim Bladder: Air sac surrounded by muscles that contract and relax to keep the fish buoyant (floating). Lateral Line: Sense organ that detects vibrations in surrounding water. Fins: Aid swimming 4 Dorsal Fin: On Back (keep fish upright) 4 Caudal Fin: Tail (move forwards/backwards) 4 Pectoral Fin: Sides (move up/down)



Preparation & Examination Locate major external anatomical parts: 4 Dorsal Fin 4 Posterior Dorsal 4 Pectoral Fins 4 Pelvic Fins 4 Anal Fins 4 Caudal Fin 4 Gill Covers (operculum) 4 Lateral line - sensory organ of fish Remove several scales 4 Prepare a dry-mount of a scale. 4 Observe it under a microscope 4 What function do you think scales serve?

Dissection Remove operculum with scissors 4 Observe gill anatomy • Rakers - white, comb-like arches • Filaments - Red fingerlike projections With a scalpel, remove a section of the lateral line 4 What function does this organ serve? 4 Do you notice a concentration of nerve endings? Begin the main incision 4 Open the abdomen (below the gill) carefully with a scalpel 4 Cut with a scissors: remove a oval-shaped piece of skin (only skin) running from underneath the gills, to the anus, up to the lateral line, along the lateral line, to the gill, down to where you started the incision. Remove flap of skin (see diagram on next slide)

Main Incision Cut along the blue line. . . • Only cut through scales, muscles, and skin • Take special care not to cut too deep!

Anterior View 1. Gills 2. Heart 3. Liver 4. Pyloric caeca 5. Small intestine 6. Stomach 7. Swim bladder
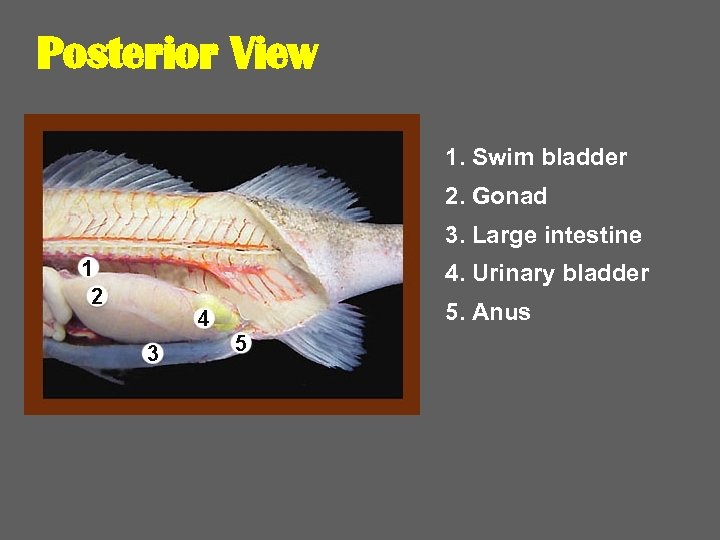
Posterior View 1. Swim bladder 2. Gonad 3. Large intestine 4. Urinary bladder 5. Anus
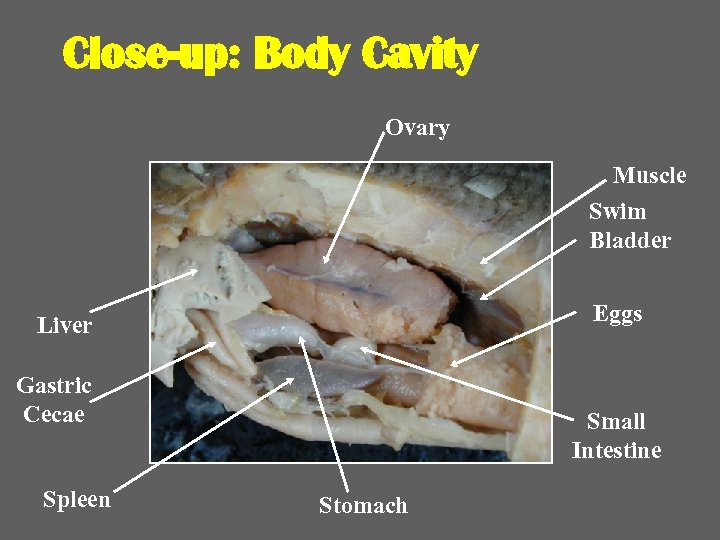
Close-up: Body Cavity Ovary Muscle Swim Bladder Eggs Liver Gastric Cecae Spleen Small Intestine Stomach

Can you identify the parts?
3eb04719eda153f56d2deddd6ad13b5a.ppt