1b072037eef264d5775634f652adbdf6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Safety and quality issues – studs and nuts Presentation API 6 A Winter meeting Feb. 2011 1 - 2010 -10 -19
Safety and quality issues – studs and nuts Presentation API 6 A Winter meeting Feb. 2011 1 - 2010 -10 -19
 Background • ASTM A 320 require studs of Grades L 7 and L 43 to be equipped with nuts confirming to Grade 4 or Grade 7 of ASTM A 194, i. e. high strength nuts to be equipped with high strength studs • ISO 10423/API 6 A allows for use of low strength nuts of type ASTM A 194 2 HM with high strength studs like ASTM A 320 Grade L 7/L 43 • The background for ISO 10423/API 6 A allowing for use of low strength nuts (2 HM) to high strength studs (L 7) is unknown (introduced in API 6 A 1985, 2 H was used before 1985). • Structural integrity of bolted connections with use of low strengths nuts raises is an issue that needs to be addressed • A technical note from Statoil on studs and nuts has been issued distributed to API 6 A, API 17 D, ASTM, ASME and ISO for comment. • SC 17 decided 18. January 2011 to monitor SC 6 and present the 2 HM issue at the SC 6 February 2011 meeting 2 2010 -10 -19
Background • ASTM A 320 require studs of Grades L 7 and L 43 to be equipped with nuts confirming to Grade 4 or Grade 7 of ASTM A 194, i. e. high strength nuts to be equipped with high strength studs • ISO 10423/API 6 A allows for use of low strength nuts of type ASTM A 194 2 HM with high strength studs like ASTM A 320 Grade L 7/L 43 • The background for ISO 10423/API 6 A allowing for use of low strength nuts (2 HM) to high strength studs (L 7) is unknown (introduced in API 6 A 1985, 2 H was used before 1985). • Structural integrity of bolted connections with use of low strengths nuts raises is an issue that needs to be addressed • A technical note from Statoil on studs and nuts has been issued distributed to API 6 A, API 17 D, ASTM, ASME and ISO for comment. • SC 17 decided 18. January 2011 to monitor SC 6 and present the 2 HM issue at the SC 6 February 2011 meeting 2 2010 -10 -19
 Example of 2 HM nut failure during shell test 3 2010 -10 -19
Example of 2 HM nut failure during shell test 3 2010 -10 -19
 Possible failure modes Stud tension failure Stud stripping Nut stripping Not acceptable failure mode in design codes 4 2010 -10 -19 Assumed failure mode in design codes
Possible failure modes Stud tension failure Stud stripping Nut stripping Not acceptable failure mode in design codes 4 2010 -10 -19 Assumed failure mode in design codes
 Why thread stripping is not acceptable? • Tensile failure of the stud is easily detected. • The initiation of stripping failure, though, is difficult to identify because the stripping develops gradually, some tension remains in the stud, and there is little or no visible damage. • Since replacement of damaged fasteners is essential for sound joints, tensile failure of the stud is desirable during overtightening during make-up or overloading in service. • Strongest stud to fail before weakest nut; checked by nut proof loading. 5 2010 -10 -19
Why thread stripping is not acceptable? • Tensile failure of the stud is easily detected. • The initiation of stripping failure, though, is difficult to identify because the stripping develops gradually, some tension remains in the stud, and there is little or no visible damage. • Since replacement of damaged fasteners is essential for sound joints, tensile failure of the stud is desirable during overtightening during make-up or overloading in service. • Strongest stud to fail before weakest nut; checked by nut proof loading. 5 2010 -10 -19
 ASTM A 320/A 194 requirements • Hardness requirements, HBmin − High strength assembly (L 43/7): Nut 7: − Low strength assembly (L 7 M/7 M: • Stud L 43: 250 Stud L 7 M: 200 Nut 7 M: 159 248 Proof load test load − High strength assembly (L 43/7): − Low strength assembly (L 7 M/7 M): • 6 1, 4 x tensile capacity of L 43 stud 1, 5 x tensile capacity of L 7 M stud No requirement for proof load of nuts when d > 1 ½ in. 2010 -10 -19
ASTM A 320/A 194 requirements • Hardness requirements, HBmin − High strength assembly (L 43/7): Nut 7: − Low strength assembly (L 7 M/7 M: • Stud L 43: 250 Stud L 7 M: 200 Nut 7 M: 159 248 Proof load test load − High strength assembly (L 43/7): − Low strength assembly (L 7 M/7 M): • 6 1, 4 x tensile capacity of L 43 stud 1, 5 x tensile capacity of L 7 M stud No requirement for proof load of nuts when d > 1 ½ in. 2010 -10 -19
 API 6 A requirements • Stud design capacity is based upon limit load • The nut limit load shall be higher than the stud limit load (only studs are checked) • Stud allowable loads: − 83 % of limit load for hydrostatic test • Proof load test load for diameter up to and including 1 ½ in. − High strength assembly (L 43/7): 1, 4 x tensile capacity of L 43 stud − Low strength assembly (L 7 M/7 M): 1, 5 x tensile capacity of L 7 M stud − “High” strength assembly (L 43/2 HM): 1, 5 x tensile capacity of L 7 M stud • • 7 No requirement for proof load of nuts when diameter is greater than 1 ½ in. API 6 A proof load test of nuts for “high” strength assemblies with 2 HM nuts is ≈20% less than required by ASTM A 320/A 194. 2010 -10 -19
API 6 A requirements • Stud design capacity is based upon limit load • The nut limit load shall be higher than the stud limit load (only studs are checked) • Stud allowable loads: − 83 % of limit load for hydrostatic test • Proof load test load for diameter up to and including 1 ½ in. − High strength assembly (L 43/7): 1, 4 x tensile capacity of L 43 stud − Low strength assembly (L 7 M/7 M): 1, 5 x tensile capacity of L 7 M stud − “High” strength assembly (L 43/2 HM): 1, 5 x tensile capacity of L 7 M stud • • 7 No requirement for proof load of nuts when diameter is greater than 1 ½ in. API 6 A proof load test of nuts for “high” strength assemblies with 2 HM nuts is ≈20% less than required by ASTM A 320/A 194. 2010 -10 -19
 Calculation of 2 HM nut capacities • API 6 A and ASME VIII Div. 2/3 limit load − Worst case dimensional tolerances nut/stud − Coefficient of thread friction equal to zero − Minimum specified yield strength 60 ksi (HB 159 ≈ Su = 80 ksi) • • Nut capacity formulas established based upon formulas in VDI 2230 Part 1 and non-linear FEA • FEA results validated with 1 ¼” L 7/7 tests and 2 ¼” 2 HM nut testing • 8 Non-linear 2 D FEA performed for 2 ¼” and 1 ¼” stud/nut assemblies Calculation model also validated with 1 3/8” and 1 ½” 2 HM nut testing 2010 -10 -19
Calculation of 2 HM nut capacities • API 6 A and ASME VIII Div. 2/3 limit load − Worst case dimensional tolerances nut/stud − Coefficient of thread friction equal to zero − Minimum specified yield strength 60 ksi (HB 159 ≈ Su = 80 ksi) • • Nut capacity formulas established based upon formulas in VDI 2230 Part 1 and non-linear FEA • FEA results validated with 1 ¼” L 7/7 tests and 2 ¼” 2 HM nut testing • 8 Non-linear 2 D FEA performed for 2 ¼” and 1 ¼” stud/nut assemblies Calculation model also validated with 1 3/8” and 1 ½” 2 HM nut testing 2010 -10 -19
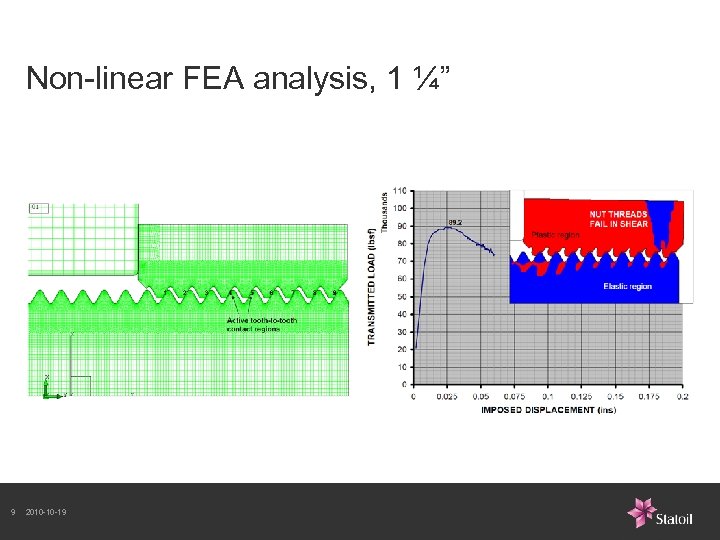 Non-linear FEA analysis, 1 ¼” 9 2010 -10 -19
Non-linear FEA analysis, 1 ¼” 9 2010 -10 -19
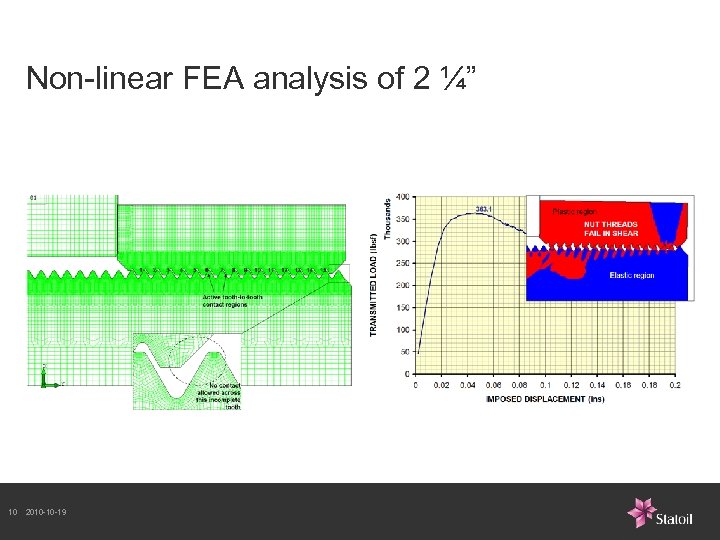 Non-linear FEA analysis of 2 ¼” 10 2010 -10 -19
Non-linear FEA analysis of 2 ¼” 10 2010 -10 -19
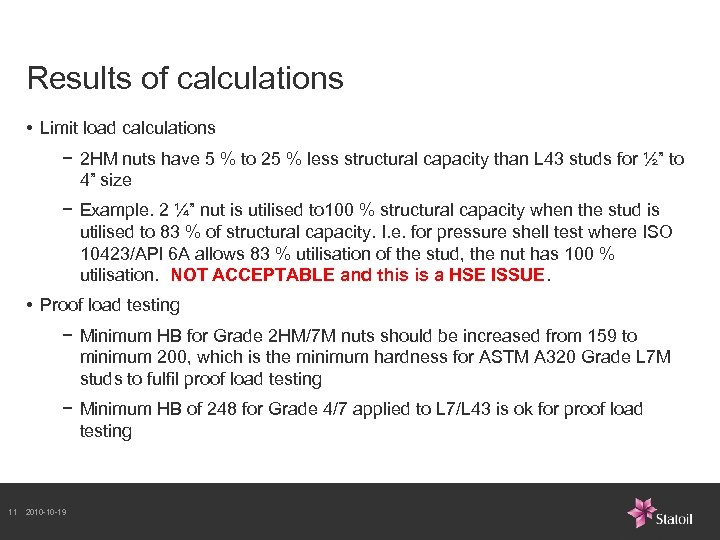 Results of calculations • Limit load calculations − 2 HM nuts have 5 % to 25 % less structural capacity than L 43 studs for ½” to 4” size − Example. 2 ¼” nut is utilised to 100 % structural capacity when the stud is utilised to 83 % of structural capacity. I. e. for pressure shell test where ISO 10423/API 6 A allows 83 % utilisation of the stud, the nut has 100 % utilisation. NOT ACCEPTABLE and this is a HSE ISSUE. • Proof load testing − Minimum HB for Grade 2 HM/7 M nuts should be increased from 159 to minimum 200, which is the minimum hardness for ASTM A 320 Grade L 7 M studs to fulfil proof load testing − Minimum HB of 248 for Grade 4/7 applied to L 7/L 43 is ok for proof load testing 11 2010 -10 -19
Results of calculations • Limit load calculations − 2 HM nuts have 5 % to 25 % less structural capacity than L 43 studs for ½” to 4” size − Example. 2 ¼” nut is utilised to 100 % structural capacity when the stud is utilised to 83 % of structural capacity. I. e. for pressure shell test where ISO 10423/API 6 A allows 83 % utilisation of the stud, the nut has 100 % utilisation. NOT ACCEPTABLE and this is a HSE ISSUE. • Proof load testing − Minimum HB for Grade 2 HM/7 M nuts should be increased from 159 to minimum 200, which is the minimum hardness for ASTM A 320 Grade L 7 M studs to fulfil proof load testing − Minimum HB of 248 for Grade 4/7 applied to L 7/L 43 is ok for proof load testing 11 2010 -10 -19
 Conclusions • API 6 A/ISO 10423 − Nuts is assumed to have higher structural capacities than studs, however, calculations shows that 2 HM nuts has less 5% to 25% less structural capacity than L 7/L 43 studs, hence, derating have to be considered − Nut proof load test of nuts for “high” strength assemblies (L 7/L 43 studs) with 2 HM nuts is ≈20% less than required by ASTM A 320/A 194 • ASTM A 194 − Minimum hardness of nuts should be the same as for studs, i. e. the 2 HM/7 M nut minimum HB hardness should be 200 when used with L 7 M studs • General − Studs shall be equipped with heavy hex nuts with a grade of steel or minimum hardness similar to that of the studs. − Low strength nuts like 2 HM shall not be used in combination with high strength studs like L 7/L 43 – STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY AND SAFETY CONCERN 12 2010 -10 -19
Conclusions • API 6 A/ISO 10423 − Nuts is assumed to have higher structural capacities than studs, however, calculations shows that 2 HM nuts has less 5% to 25% less structural capacity than L 7/L 43 studs, hence, derating have to be considered − Nut proof load test of nuts for “high” strength assemblies (L 7/L 43 studs) with 2 HM nuts is ≈20% less than required by ASTM A 320/A 194 • ASTM A 194 − Minimum hardness of nuts should be the same as for studs, i. e. the 2 HM/7 M nut minimum HB hardness should be 200 when used with L 7 M studs • General − Studs shall be equipped with heavy hex nuts with a grade of steel or minimum hardness similar to that of the studs. − Low strength nuts like 2 HM shall not be used in combination with high strength studs like L 7/L 43 – STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY AND SAFETY CONCERN 12 2010 -10 -19
 API 6 A – Quality issues of closure bolting • No traceability between heat treatment batch and material certificate • No NDT (MPI/DP/UT/RT) • No dimensional control • Low sampling rate, e. g. hardness testing of Grade 7 nuts: 1 of 800 • No proof load testing for nuts when d> 1 ½” • The studs (nuts) are the governing structural component for all API BX type flanged connections and not the flange • Not consistent quality requirements of fasteners compared with forged flanges/components as fasteners are the governing (critical) structural component in the API BX type flanged connection 13 2010 -10 -19
API 6 A – Quality issues of closure bolting • No traceability between heat treatment batch and material certificate • No NDT (MPI/DP/UT/RT) • No dimensional control • Low sampling rate, e. g. hardness testing of Grade 7 nuts: 1 of 800 • No proof load testing for nuts when d> 1 ½” • The studs (nuts) are the governing structural component for all API BX type flanged connections and not the flange • Not consistent quality requirements of fasteners compared with forged flanges/components as fasteners are the governing (critical) structural component in the API BX type flanged connection 13 2010 -10 -19
 Thank you Presentation title: Safety and quality issues – studs and nuts Presenters name: Finn Kirkemo Presenters title: Technical Advisor E-mail address: fkir@statoil. com, tel: +47 901 27 901 www. statoil. com 14 2010 -10 -19
Thank you Presentation title: Safety and quality issues – studs and nuts Presenters name: Finn Kirkemo Presenters title: Technical Advisor E-mail address: fkir@statoil. com, tel: +47 901 27 901 www. statoil. com 14 2010 -10 -19


