66c4d75bfc054746c77bab09c3559c62.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 Safeguarding Adults P 1 - Protection Practitioner Level February 2015 www. devon. gov. uk/index/socialcarehealth/ scwd/scwd-safeguarding-adults. htm
Safeguarding Adults P 1 - Protection Practitioner Level February 2015 www. devon. gov. uk/index/socialcarehealth/ scwd/scwd-safeguarding-adults. htm
 Housekeeping Toilets Mobile Phones / Devices Fire Procedure Breaks Smoking Finishing Time
Housekeeping Toilets Mobile Phones / Devices Fire Procedure Breaks Smoking Finishing Time
 Training Transfer Getting learning into practice • “ 50% of learning fails to transfer to the workplace” (Sak, 2002) • “The ultimate test of effective training is whether it benefits service users” (Horwath and Morrison, 1999)
Training Transfer Getting learning into practice • “ 50% of learning fails to transfer to the workplace” (Sak, 2002) • “The ultimate test of effective training is whether it benefits service users” (Horwath and Morrison, 1999)
 Ground Rules Safeguarding is a dynamic world and we continue to learn about how to prevent people from being harmed on both a strategic / organisational level and as individual practitioners. Safeguarding is about partnership, it is not about blame. All agencies and individuals need to take responsibility, to reflect and learn to safeguard people who may be vulnerable.
Ground Rules Safeguarding is a dynamic world and we continue to learn about how to prevent people from being harmed on both a strategic / organisational level and as individual practitioners. Safeguarding is about partnership, it is not about blame. All agencies and individuals need to take responsibility, to reflect and learn to safeguard people who may be vulnerable.
 Ground Rules Confidentiality within the group will be respected but may need to be broken if a disclosure of unsafe practice, abuse or neglect is made during the course – this will usually be discussed with you first.
Ground Rules Confidentiality within the group will be respected but may need to be broken if a disclosure of unsafe practice, abuse or neglect is made during the course – this will usually be discussed with you first.
 Introductions • Name • Place and nature of work • What do you want to know by the end of today’s session?
Introductions • Name • Place and nature of work • What do you want to know by the end of today’s session?
 At the end of the session you will: • be aware of the legal framework • ask the ‘right’ questions and gather initial information in order to undertake an initial risk assessment • take any required protective action to promote the safety and well being of the person • take or make appropriate safeguarding referrals • recognise when other agencies may need to be involved e. g. the Police, CQC, and refer to other sources of investigation where required (preservation of evidence) • have reflected on your practice in safeguarding • be clear about your role in the safeguarding process
At the end of the session you will: • be aware of the legal framework • ask the ‘right’ questions and gather initial information in order to undertake an initial risk assessment • take any required protective action to promote the safety and well being of the person • take or make appropriate safeguarding referrals • recognise when other agencies may need to be involved e. g. the Police, CQC, and refer to other sources of investigation where required (preservation of evidence) • have reflected on your practice in safeguarding • be clear about your role in the safeguarding process
 Care Act • Comes into force on the 1 st April 2015 • Revokes, repeals and cancels many laws and guidance including No Secrets • Clarifies and consolidates good practice • Not just about health or social care – promotes wider partnership working and responsibilities • Promotes - Prevent, Reduce, Delay • Many chapters relevant to SA Agenda
Care Act • Comes into force on the 1 st April 2015 • Revokes, repeals and cancels many laws and guidance including No Secrets • Clarifies and consolidates good practice • Not just about health or social care – promotes wider partnership working and responsibilities • Promotes - Prevent, Reduce, Delay • Many chapters relevant to SA Agenda
 14. Adult safeguarding This chapter covers: • • Adult safeguarding – what it is and why it matters; • • Abuse and neglect: • • Understanding what they are and spotting the signs; • • Reporting and responding to abuse and neglect; • • Carers and adult safeguarding; • • Adult safeguarding procedures; • • Local authority’s role and multi-agency working; • • Criminal offences and adult safeguarding; • • Safeguarding enquiries; • • Safeguarding Adults Boards; • • Safeguarding Adults Reviews; • • Information sharing, confidentiality and record keeping; • • Roles, responsibilities and training in local authorities, the NHS and other agencies PREVENT, REDUCE, DELAY 9
14. Adult safeguarding This chapter covers: • • Adult safeguarding – what it is and why it matters; • • Abuse and neglect: • • Understanding what they are and spotting the signs; • • Reporting and responding to abuse and neglect; • • Carers and adult safeguarding; • • Adult safeguarding procedures; • • Local authority’s role and multi-agency working; • • Criminal offences and adult safeguarding; • • Safeguarding enquiries; • • Safeguarding Adults Boards; • • Safeguarding Adults Reviews; • • Information sharing, confidentiality and record keeping; • • Roles, responsibilities and training in local authorities, the NHS and other agencies PREVENT, REDUCE, DELAY 9
 Key Changes /points • It changes the language of safeguarding adults – NOT Vulnerable • The guidance repeatedly highlights the importance of person centred practice, the Mental Capacity Act and Advocacy in individual cases. • It also emphasises strategies for prevention at both operational and inter agency strategic levels of working. • Commitment to ‘Making Safeguarding Personal’ and Making Every Adult Matter 10
Key Changes /points • It changes the language of safeguarding adults – NOT Vulnerable • The guidance repeatedly highlights the importance of person centred practice, the Mental Capacity Act and Advocacy in individual cases. • It also emphasises strategies for prevention at both operational and inter agency strategic levels of working. • Commitment to ‘Making Safeguarding Personal’ and Making Every Adult Matter 10
 Key Changes /points • Includes more detailed and explicit references to carers, including the risks that they can face and support they may need as well as the risks that they can present. • Roles and responsibilities of partner organisations • Serious case reviews become Serious • Roles and responsibilities of SA Board members and Safeguarding Adults Boards 11
Key Changes /points • Includes more detailed and explicit references to carers, including the risks that they can face and support they may need as well as the risks that they can present. • Roles and responsibilities of partner organisations • Serious case reviews become Serious • Roles and responsibilities of SA Board members and Safeguarding Adults Boards 11
 Safeguarding Duties The safeguarding duties apply to an adult who: has needs for care and support (whether or not the local authority is meeting any of those needs) and; is experiencing, or at risk of, abuse or neglect; and as a result of those care and support needs is unable to protect themselves from either the risk of, or the experience of abuse or neglect. 12 Care Act 14. 20
Safeguarding Duties The safeguarding duties apply to an adult who: has needs for care and support (whether or not the local authority is meeting any of those needs) and; is experiencing, or at risk of, abuse or neglect; and as a result of those care and support needs is unable to protect themselves from either the risk of, or the experience of abuse or neglect. 12 Care Act 14. 20
 Safeguarding Duties Local authority statutory adult safeguarding duties apply equally to those adults with care and support needs regardless of whether those needs are being met, regardless of whether the adult lacks mental capacity or not, and regardless of setting, other than prisons and approved premises Care Act 14. 60
Safeguarding Duties Local authority statutory adult safeguarding duties apply equally to those adults with care and support needs regardless of whether those needs are being met, regardless of whether the adult lacks mental capacity or not, and regardless of setting, other than prisons and approved premises Care Act 14. 60
 Make Enquiry • Adult safeguarding means protecting a person’s right to live in safety, free from abuse and neglect. The Care Act requires that each local authority must: • make enquiries, or ensure others do so, if it believes an adult is, or is at risk of, abuse or neglect (see paragraphs 14. 36 to 14. 75). An enquiry should establish whether any action needs to be taken to stop prevent abuse or neglect, and if so, by whom; Mr A Care Act 14. 10
Make Enquiry • Adult safeguarding means protecting a person’s right to live in safety, free from abuse and neglect. The Care Act requires that each local authority must: • make enquiries, or ensure others do so, if it believes an adult is, or is at risk of, abuse or neglect (see paragraphs 14. 36 to 14. 75). An enquiry should establish whether any action needs to be taken to stop prevent abuse or neglect, and if so, by whom; Mr A Care Act 14. 10
 Categories of abuse • • • Physical abuse Domestic violence Sexual abuse Psychological abuse Financial or material abuse Modern slavery – encompasses slavery, human trafficking, forced labour and domestic servitude. Traffickers and slave masters use whatever means they have at their disposal to coerce, deceive and force individuals into a life of abuse, servitude and inhumane treatment. Care Act 14. 17
Categories of abuse • • • Physical abuse Domestic violence Sexual abuse Psychological abuse Financial or material abuse Modern slavery – encompasses slavery, human trafficking, forced labour and domestic servitude. Traffickers and slave masters use whatever means they have at their disposal to coerce, deceive and force individuals into a life of abuse, servitude and inhumane treatment. Care Act 14. 17
 Categories of abuse • Discriminatory abuse • Organisational abuse – including neglect and poor care practice within an institution or specific care setting such as a hospital or care home, for example, or in relation to care provided in one’s own home. • Neglect and acts of omission • Self-neglect – this covers a wide range of behaviour neglecting to care for one’s personal hygiene, health or surroundings and includes behaviour such as hoarding Care Act 14. 17
Categories of abuse • Discriminatory abuse • Organisational abuse – including neglect and poor care practice within an institution or specific care setting such as a hospital or care home, for example, or in relation to care provided in one’s own home. • Neglect and acts of omission • Self-neglect – this covers a wide range of behaviour neglecting to care for one’s personal hygiene, health or surroundings and includes behaviour such as hoarding Care Act 14. 17
 Patterns of abuse vary and include: • serial abusing in which the perpetrator seeks out and ‘grooms’ individuals. • long-term abuse in the context of an ongoing family relationship such as domestic violence between spouses or generations or persistent psychological abuse; • opportunistic abuse such as theft occurring because money or jewellery has been left lying around.
Patterns of abuse vary and include: • serial abusing in which the perpetrator seeks out and ‘grooms’ individuals. • long-term abuse in the context of an ongoing family relationship such as domestic violence between spouses or generations or persistent psychological abuse; • opportunistic abuse such as theft occurring because money or jewellery has been left lying around.
 Six key principles underpin all adult safeguarding work • Empowerment “I am asked what I want as the outcomes from the safeguarding process and these directly inform what happens. ” • Prevention “I receive clear and simple information about what abuse is, how to recognise the signs and what I can do to seek help. ” • Proportionality “I am sure that the professionals will work in my interest, as I see them and they will only get involved as much as needed. ” • Protection “I get help and support to report abuse and neglect. I get help so that I am able to take part in the safeguarding process to the extent to which I want. ” • Partnership “I know that staff treat any personal and sensitive information in confidence, only sharing what is helpful and necessary. I am confident that professionals will work together and with me to get the best result for me. ” • Accountability “I understand the role of everyone involved in my life and so do they. ”
Six key principles underpin all adult safeguarding work • Empowerment “I am asked what I want as the outcomes from the safeguarding process and these directly inform what happens. ” • Prevention “I receive clear and simple information about what abuse is, how to recognise the signs and what I can do to seek help. ” • Proportionality “I am sure that the professionals will work in my interest, as I see them and they will only get involved as much as needed. ” • Protection “I get help and support to report abuse and neglect. I get help so that I am able to take part in the safeguarding process to the extent to which I want. ” • Partnership “I know that staff treat any personal and sensitive information in confidence, only sharing what is helpful and necessary. I am confident that professionals will work together and with me to get the best result for me. ” • Accountability “I understand the role of everyone involved in my life and so do they. ”
 • • • Empowerment Prevention Proportionality Protection Partnership Accountability What outcomes should individuals experience from the safeguarding process? What can YOU do?
• • • Empowerment Prevention Proportionality Protection Partnership Accountability What outcomes should individuals experience from the safeguarding process? What can YOU do?
 Because you said something. . .
Because you said something. . .
 Small Group Discussion In groups have a look at the following scenarios : - • The man in the park • The two brothers • The couple in the conservatory What did you actually observe What’s the worst case scenario or possible least harmful scenario? What could / should / might be done (immediate short/long term)?
Small Group Discussion In groups have a look at the following scenarios : - • The man in the park • The two brothers • The couple in the conservatory What did you actually observe What’s the worst case scenario or possible least harmful scenario? What could / should / might be done (immediate short/long term)?
 Feedback – the man in the park
Feedback – the man in the park
 Hate Crime “Any criminal offence, which is perceived, by the victim or any other person, to be motivated by hostility or prejudice based on a person’s difference or perceived difference. ” CPS Police also record incidents which are not crimes. Care Act 14. 70
Hate Crime “Any criminal offence, which is perceived, by the victim or any other person, to be motivated by hostility or prejudice based on a person’s difference or perceived difference. ” CPS Police also record incidents which are not crimes. Care Act 14. 70
 Disability Hate Crime Better understanding of disability hate crime and of impact on victims Offender(s) often known to victim Likely to increase in severity or frequency • EHRC / Do. H / Home Office / Regional projects • Neighbourhood harm register • Enhanced sentencing
Disability Hate Crime Better understanding of disability hate crime and of impact on victims Offender(s) often known to victim Likely to increase in severity or frequency • EHRC / Do. H / Home Office / Regional projects • Neighbourhood harm register • Enhanced sentencing
 Mate Crime “When someone befriends a vulnerable person in order to exploit them. ” www. arcuk. org. uk/safetynet Miss Y
Mate Crime “When someone befriends a vulnerable person in order to exploit them. ” www. arcuk. org. uk/safetynet Miss Y
 Grooming Process • Choose a vulnerable adult with whom they have (or can manipulate) a relationship of authority • Develop a special relationship with the adult • Get the victim’s support network to trust them or isolate the victim (threat, inducement, deception) • Slowly introduce low level behaviour in order to desensitise or normalise • Introduce the target behaviour
Grooming Process • Choose a vulnerable adult with whom they have (or can manipulate) a relationship of authority • Develop a special relationship with the adult • Get the victim’s support network to trust them or isolate the victim (threat, inducement, deception) • Slowly introduce low level behaviour in order to desensitise or normalise • Introduce the target behaviour
 Forced Marriage www. forcedtomarry. com
Forced Marriage www. forcedtomarry. com
 Radicalisation to Support or Commit Terrorism Nicky Reilly attempted to detonate an improvised explosive device at a restaurant in Exeter in May 2008. Was radicalised through contact with people on the internet. Known to have mental health issues and learning difficulties. Building Partnerships, Staying Safe The health sector contribution to the Prevent strategy: guidance for healthcare organisations Police found weapons and explosives at the home of Michael Piggin. He has Asperger syndrome and had been repeatedly bullied at school. He had become involved with a far right extremist group, the EDL.
Radicalisation to Support or Commit Terrorism Nicky Reilly attempted to detonate an improvised explosive device at a restaurant in Exeter in May 2008. Was radicalised through contact with people on the internet. Known to have mental health issues and learning difficulties. Building Partnerships, Staying Safe The health sector contribution to the Prevent strategy: guidance for healthcare organisations Police found weapons and explosives at the home of Michael Piggin. He has Asperger syndrome and had been repeatedly bullied at school. He had become involved with a far right extremist group, the EDL.
 Police involvement • 101 OR 999 http: //www. devon-cornwall. police. uk/ • PCSO’s • Police officers • Neighbourhood beat managers • Specialist officers – public protection unit
Police involvement • 101 OR 999 http: //www. devon-cornwall. police. uk/ • PCSO’s • Police officers • Neighbourhood beat managers • Specialist officers – public protection unit
 • Making Every Adult Matter MEAM Project is also creating ways of improving multi agency assessment and support provided to people with complex needs and chaotic life styles at risk from self neglect and other types of harm. 30
• Making Every Adult Matter MEAM Project is also creating ways of improving multi agency assessment and support provided to people with complex needs and chaotic life styles at risk from self neglect and other types of harm. 30
 Scams www. thinkjessica. com www. stoploansharks. org. uk
Scams www. thinkjessica. com www. stoploansharks. org. uk
 Trading Standards May be able to help: • If you’ve been misled by the trader into buying something you wouldn’t have bought if you had been given all the information beforehand • If the trader has made false claims about goods or services which you have found out not to be true • If you’ve been sold fake or counterfeit goods • If the trader has used aggressive selling techniques or persuaded you to buy something you wouldn't necessarily have bought if you had a free choice scamsteamadmin@eastsussex. co. uk
Trading Standards May be able to help: • If you’ve been misled by the trader into buying something you wouldn’t have bought if you had been given all the information beforehand • If the trader has made false claims about goods or services which you have found out not to be true • If you’ve been sold fake or counterfeit goods • If the trader has used aggressive selling techniques or persuaded you to buy something you wouldn't necessarily have bought if you had a free choice scamsteamadmin@eastsussex. co. uk
 Feedback – the two brothers Miss P
Feedback – the two brothers Miss P
 Domestic Abuse • Incident or pattern of incidents of controlling, coercive or threatening behaviour, violence or abuse. . . by someone who is or has been an intimate partner or family member regardless of gender or sexuality • Includes: psychological, physical, sexual, financial, emotional abuse; so called ‘honour’ based violence; Female Genital Mutilation; forced marriage The Home Office 2013
Domestic Abuse • Incident or pattern of incidents of controlling, coercive or threatening behaviour, violence or abuse. . . by someone who is or has been an intimate partner or family member regardless of gender or sexuality • Includes: psychological, physical, sexual, financial, emotional abuse; so called ‘honour’ based violence; Female Genital Mutilation; forced marriage The Home Office 2013
 Devon Domestic Abuse Support Services www. new. devon. gov. uk/dsva
Devon Domestic Abuse Support Services www. new. devon. gov. uk/dsva
 Feedback – the couple in the conservatory
Feedback – the couple in the conservatory
 Carers and Safeguarding Carers are more likely to perpetrate abuse (intentional or not) if the carer: • Has unmet or unrecognised needs • Is themselves vulnerable • Has unwillingly had to change his or her lifestyle or feels unappreciated or exploited • Is being abused by the vulnerable person • Has little insight or understanding of the person’s condition or needs • Is feeling isolated, undervalued or stigmatised • Has other responsibilities ADASS (July 2011)
Carers and Safeguarding Carers are more likely to perpetrate abuse (intentional or not) if the carer: • Has unmet or unrecognised needs • Is themselves vulnerable • Has unwillingly had to change his or her lifestyle or feels unappreciated or exploited • Is being abused by the vulnerable person • Has little insight or understanding of the person’s condition or needs • Is feeling isolated, undervalued or stigmatised • Has other responsibilities ADASS (July 2011)
 Woman in the hospital & woman in the care home What might be happening (best Case Scenario / worst scenario)? What could / might be done (short/long term)?
Woman in the hospital & woman in the care home What might be happening (best Case Scenario / worst scenario)? What could / might be done (short/long term)?
 Advocacy • arrange, where appropriate, for an independent advocate to represent and support an adult who is the subject of a safeguarding enquiry or Safeguarding Adult Review where the adult has ‘substantial difficulty’ in being involved in the process and where there is no
Advocacy • arrange, where appropriate, for an independent advocate to represent and support an adult who is the subject of a safeguarding enquiry or Safeguarding Adult Review where the adult has ‘substantial difficulty’ in being involved in the process and where there is no
 New Statutory Advocacy • The Act requires local authorities to involve people in assessments, care and support planning, and reviews. • In order to facilitate the involvement and engagement of people who would otherwise have difficulty, it introduces a new requirement to arrange independent advocacy for people… • A) who have substantial difficulty in being involved/ engaged in these processes and • B) where there is no one available to help facilitate this involvement and engagement. 40
New Statutory Advocacy • The Act requires local authorities to involve people in assessments, care and support planning, and reviews. • In order to facilitate the involvement and engagement of people who would otherwise have difficulty, it introduces a new requirement to arrange independent advocacy for people… • A) who have substantial difficulty in being involved/ engaged in these processes and • B) where there is no one available to help facilitate this involvement and engagement. 40
 Substantial difficulty • Where a person has substantial difficulty in engaging with the assessment process – Is there anyone appropriate who can support the person be fully involved? • Maybe a carer (who is not professionally engaged or remunerated), a family member or friend. • If there is no one appropriate, then the local authority must arrange for an independent advocate. 41
Substantial difficulty • Where a person has substantial difficulty in engaging with the assessment process – Is there anyone appropriate who can support the person be fully involved? • Maybe a carer (who is not professionally engaged or remunerated), a family member or friend. • If there is no one appropriate, then the local authority must arrange for an independent advocate. 41
 What is the purpose of making an alert? • To support the person to keep them safe now and in the future and to lead the life of their choice • To share information about risk so that others can decide on the next actions that might be needed • To collect national information / data
What is the purpose of making an alert? • To support the person to keep them safe now and in the future and to lead the life of their choice • To share information about risk so that others can decide on the next actions that might be needed • To collect national information / data
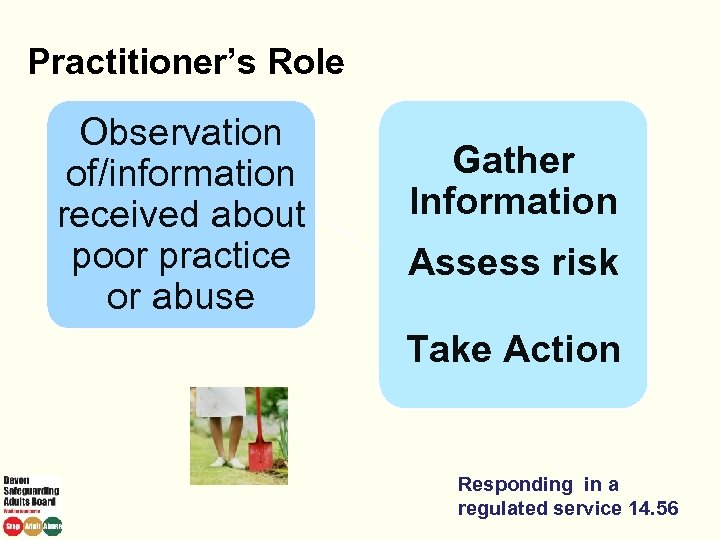 Practitioner’s Role Observation of/information received about poor practice or abuse Gather Information Assess risk Take Action Responding in a regulated service 14. 56
Practitioner’s Role Observation of/information received about poor practice or abuse Gather Information Assess risk Take Action Responding in a regulated service 14. 56
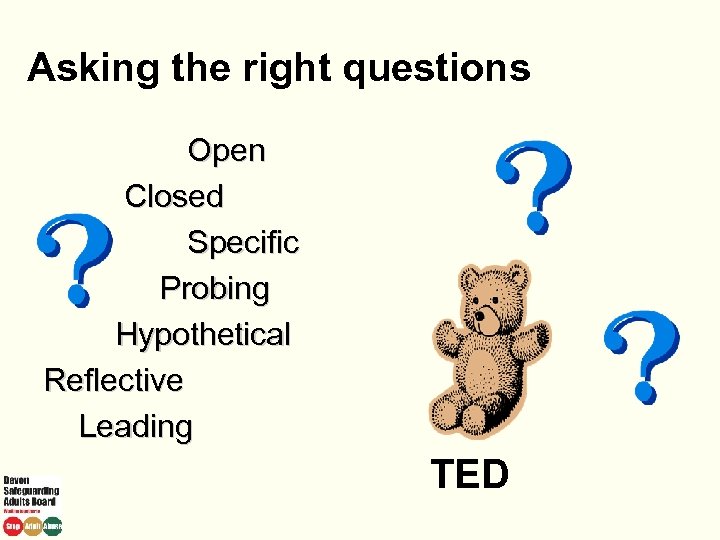 Asking the right questions Open Closed Specific Probing Hypothetical Reflective Leading TED
Asking the right questions Open Closed Specific Probing Hypothetical Reflective Leading TED
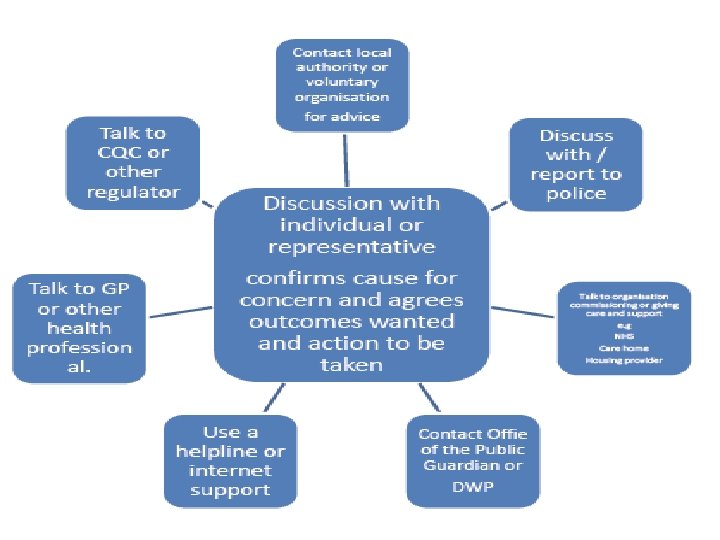
 Gaining Consent You should seek consent to share Information unless doing so would: • Place a child at increased risk of significant harm • Place and adult at increased risk of serious harm • Prejudice the prevention, detection or prosecution of a serious crime • Lead to unjustified delay in making enquiries about significant harm or serious harm
Gaining Consent You should seek consent to share Information unless doing so would: • Place a child at increased risk of significant harm • Place and adult at increased risk of serious harm • Prejudice the prevention, detection or prosecution of a serious crime • Lead to unjustified delay in making enquiries about significant harm or serious harm
 Gaining Consent You can share information without consent: • In the best interest of a person lacking capacity (to understand the risks they face or capacity to understand the safeguarding process) • In the public interest (You are trying to balance a person’s right to privacy with their right to life, right to be free from torture, inhuman and degrading treatment, right to liberty and right to autonomy. )
Gaining Consent You can share information without consent: • In the best interest of a person lacking capacity (to understand the risks they face or capacity to understand the safeguarding process) • In the public interest (You are trying to balance a person’s right to privacy with their right to life, right to be free from torture, inhuman and degrading treatment, right to liberty and right to autonomy. )
 Objectives of an enquiry • 14. 78. The objectives of an enquiry into abuse or neglect are to: • • • establish facts; • • • ascertain the adult’s views and wishes; • • • assess the needs of the adult for protection, support and redress and how they might be met; • • • protect from the abuse and neglect, in accordance with the wishes of the adult; • • • make decisions as to what follow-up action should be taken with regard to the person or organisation responsible for the abuse or neglect; and • • enable the adult to achieve resolution and recovery.
Objectives of an enquiry • 14. 78. The objectives of an enquiry into abuse or neglect are to: • • • establish facts; • • • ascertain the adult’s views and wishes; • • • assess the needs of the adult for protection, support and redress and how they might be met; • • • protect from the abuse and neglect, in accordance with the wishes of the adult; • • • make decisions as to what follow-up action should be taken with regard to the person or organisation responsible for the abuse or neglect; and • • enable the adult to achieve resolution and recovery.
 When should an enquiry take place? 14. 77. Local authorities must make enquiries, or cause another agency to do so, whenever abuse or neglect are suspected in relation to an adult and the local authority thinks it necessary to enable it to decide what (if any) action is needed to help and protect the adult. The scope of that enquiry, who leads it and its nature, and how long it takes, will depend on the particular circumstances. It will usually start with asking the adult their view and wishes which will often determine what next steps to take.
When should an enquiry take place? 14. 77. Local authorities must make enquiries, or cause another agency to do so, whenever abuse or neglect are suspected in relation to an adult and the local authority thinks it necessary to enable it to decide what (if any) action is needed to help and protect the adult. The scope of that enquiry, who leads it and its nature, and how long it takes, will depend on the particular circumstances. It will usually start with asking the adult their view and wishes which will often determine what next steps to take.
 Multi-agency Process Devon Care Direct on 0345 1551 007 Torbay Single Point of Contact on 01803 219741 or safeguarding. alertstct@nhs. net Plymouth Adult Protection Team on 01752 668000 or adultpro@plymouth. gov. uk
Multi-agency Process Devon Care Direct on 0345 1551 007 Torbay Single Point of Contact on 01803 219741 or safeguarding. alertstct@nhs. net Plymouth Adult Protection Team on 01752 668000 or adultpro@plymouth. gov. uk
 Process • The Care Act becomes law on the 1 st April 2015 • Until advised otherwise by the safeguarding adults board all processes remain the same
Process • The Care Act becomes law on the 1 st April 2015 • Until advised otherwise by the safeguarding adults board all processes remain the same
 Child Protection www. devon. gov. uk/childprotection • If you are concerned about a child or young person in Devon contact the MASH on 0345 155 1071 or email mashsecure@devon. gcsx. gov. uk and give as much information as you can.
Child Protection www. devon. gov. uk/childprotection • If you are concerned about a child or young person in Devon contact the MASH on 0345 155 1071 or email mashsecure@devon. gcsx. gov. uk and give as much information as you can.
 Prevention is Better Than Cure Keep the course in context. Whilst there are some very worrying situations occurring everyday there is also good practice. Remember to vigilant and deal with things at the earliest opportunity. Doing nothing isn’t an option. What will you do now?
Prevention is Better Than Cure Keep the course in context. Whilst there are some very worrying situations occurring everyday there is also good practice. Remember to vigilant and deal with things at the earliest opportunity. Doing nothing isn’t an option. What will you do now?
 Reference Sources • www. devon. gov. uk • https: //www. gov. uk/government/uploads/s ystem/uploads/attachment_data/file/36610 4/43380_23902777_Care_Act_Book. pdf • http: //www. careknowledge. com • www. meam. org. uk • www. scie. org. uk • www. ripfa. org. uk • www. careknowledge. com
Reference Sources • www. devon. gov. uk • https: //www. gov. uk/government/uploads/s ystem/uploads/attachment_data/file/36610 4/43380_23902777_Care_Act_Book. pdf • http: //www. careknowledge. com • www. meam. org. uk • www. scie. org. uk • www. ripfa. org. uk • www. careknowledge. com
 Final Questions?
Final Questions?


