7f1af925cc1626c9e0b12e3a6eab04b6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Safe Anticoagulation Management using Point of Care Dr. Tony Avades Sr. Consultant / Head of Chemistry, Endocrinology and POCT Sections DLMP Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Safe Anticoagulation Management using Point of Care Dr. Tony Avades Sr. Consultant / Head of Chemistry, Endocrinology and POCT Sections DLMP Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 Point of Care testing (POCT) • Tests that are performed at the bedside. . near patient. . physician office = Point of care • Many diagnostic tests evolved from Point of care • Example is urine test at the bedside> moved to>>side room>>moved inside the lab Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Point of Care testing (POCT) • Tests that are performed at the bedside. . near patient. . physician office = Point of care • Many diagnostic tests evolved from Point of care • Example is urine test at the bedside> moved to>>side room>>moved inside the lab Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 Point of Care Testing • POCT tests designed to be used at or near the site where the patient is located, that do not require permanent dedicated space, are performed outside the physical facilities of the clinical laboratories and that is performed by non-laboratory personnel. College of American Pathologists (CAP) Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Point of Care Testing • POCT tests designed to be used at or near the site where the patient is located, that do not require permanent dedicated space, are performed outside the physical facilities of the clinical laboratories and that is performed by non-laboratory personnel. College of American Pathologists (CAP) Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 POCT and Technology • New technological innovation is delivering – Improved – Simple – Shorter analysis time – Smaller Devices • Laboratory concerns – Non-lab personnel carrying out lab work – Quality Assurance – Encroaching on the lab territory Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology 4 Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
POCT and Technology • New technological innovation is delivering – Improved – Simple – Shorter analysis time – Smaller Devices • Laboratory concerns – Non-lab personnel carrying out lab work – Quality Assurance – Encroaching on the lab territory Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology 4 Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 Evolution of healthcare and laboratory tests Home Doctors clinic Future for health care provider and POCT Hospital Reversal of Centralization as it could prolong the diagnostic decision and care delivery But more costly and non-economically from a lab standard Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section 5
Evolution of healthcare and laboratory tests Home Doctors clinic Future for health care provider and POCT Hospital Reversal of Centralization as it could prolong the diagnostic decision and care delivery But more costly and non-economically from a lab standard Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section 5
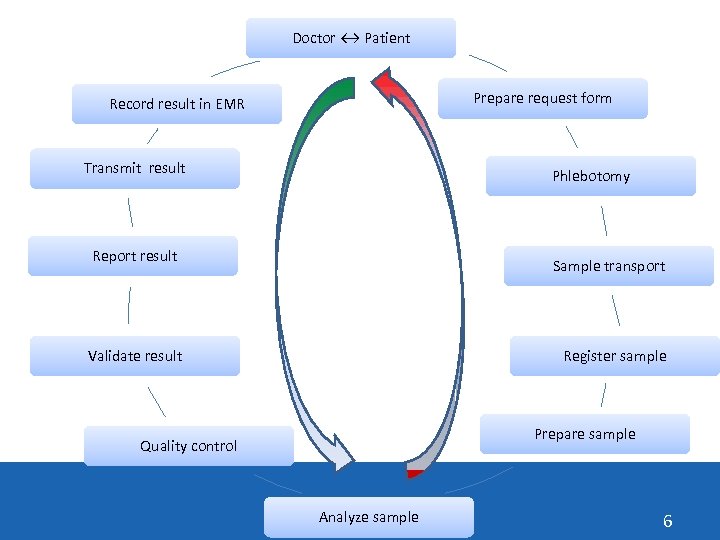 Doctor ↔ Patient Prepare request form Record result in EMR Transmit result Phlebotomy Report result Sample transport Register sample Validate result Prepare sample Quality control Analyze sample 6
Doctor ↔ Patient Prepare request form Record result in EMR Transmit result Phlebotomy Report result Sample transport Register sample Validate result Prepare sample Quality control Analyze sample 6
 Management of POCT • • • Developing POCT Guidelines and Policy Establish POCT Committee Procuring equipment and Middleware Evaluating equipment Establish Quality assurance program Maintenance and Inventory Control Preparing documentation Training and certifying staff Audit and accreditation Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Management of POCT • • • Developing POCT Guidelines and Policy Establish POCT Committee Procuring equipment and Middleware Evaluating equipment Establish Quality assurance program Maintenance and Inventory Control Preparing documentation Training and certifying staff Audit and accreditation Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 POCT HMC Policy 7211 • The policy is formulated for all Hamad Medical Corporation services and staff for the establishment of a safe and functional POCT program. • It covers all laboratory tests and services approved by the POCT Committee. Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
POCT HMC Policy 7211 • The policy is formulated for all Hamad Medical Corporation services and staff for the establishment of a safe and functional POCT program. • It covers all laboratory tests and services approved by the POCT Committee. Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 The availability of the result within minutes of asking the clinical question would improves the outcome BUT should ensure safety and manage risk Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
The availability of the result within minutes of asking the clinical question would improves the outcome BUT should ensure safety and manage risk Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
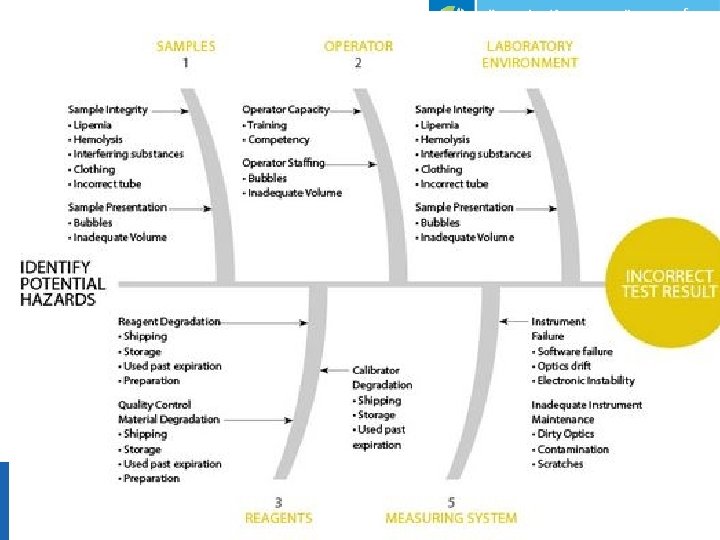
 Risks of Point of Care • Risk is the chance of suffering harm or error and it can be estimated from the probability of the event and the severity of the harm. • Safe POCT is achieved by application of the approved policy, procedures and practices to the task of analysing, evaluation, controlling and monitoring risk. • Risk management of POCT activities is by validating the tests before use, trouble shooting of failed QC, performing maintenance, ensuring operators are trained, inventory control. Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Risks of Point of Care • Risk is the chance of suffering harm or error and it can be estimated from the probability of the event and the severity of the harm. • Safe POCT is achieved by application of the approved policy, procedures and practices to the task of analysing, evaluation, controlling and monitoring risk. • Risk management of POCT activities is by validating the tests before use, trouble shooting of failed QC, performing maintenance, ensuring operators are trained, inventory control. Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 Main risks of POCT • Unqualified lab users-Nurses – Have minimum lab skills perform POCT testing – They are focused on patient care • Quality Control – A liquid sample of known concentration – Preferably two levels are used to prove stability of the testing. – It detects systemic error not random error Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Main risks of POCT • Unqualified lab users-Nurses – Have minimum lab skills perform POCT testing – They are focused on patient care • Quality Control – A liquid sample of known concentration – Preferably two levels are used to prove stability of the testing. – It detects systemic error not random error Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 Role of POCT co-ordiator • • • Training Competency assessment Quality control, internal and external Writing and reviewing the Operating procedures Devices and inventory control Ensuring Results are – reported with an appropriate units and reference ranges – documented with patient record which are accessible by all care giver Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Role of POCT co-ordiator • • • Training Competency assessment Quality control, internal and external Writing and reviewing the Operating procedures Devices and inventory control Ensuring Results are – reported with an appropriate units and reference ranges – documented with patient record which are accessible by all care giver Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section


 Ideal POCT Device Simple to use Minimal steps Robust to storage and transporation (reagent) Produce results concordant with a reference lab method • Safe to use • • Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Ideal POCT Device Simple to use Minimal steps Robust to storage and transporation (reagent) Produce results concordant with a reference lab method • Safe to use • • Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 Anti Coagulation POCT • PT/INR • ACT • TEG Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Anti Coagulation POCT • PT/INR • ACT • TEG Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 The need for anticoagulant Clotting is associated with disease conditions Ø Artificial heart valve replacement Ø Myocardial Ischaemia Ø Atrial fibrillation (AF) Ø Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Ø Pulmonary embolus Ø Hereditary disorders ~ deficiencies in blood proteins or production of antibodies that cause the blood to clot or prevent the blood from clotting Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
The need for anticoagulant Clotting is associated with disease conditions Ø Artificial heart valve replacement Ø Myocardial Ischaemia Ø Atrial fibrillation (AF) Ø Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Ø Pulmonary embolus Ø Hereditary disorders ~ deficiencies in blood proteins or production of antibodies that cause the blood to clot or prevent the blood from clotting Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 Prothrombin time • Prothrombin Time is a measure of how quickly blood clots. • The ideal target International Normalized Ratio (INR) range will vary from person to person depending on a variety of factors such as; • Reason for taking anticoagulants • Medical conditions • Other issues. • The traditional way to run a PT-INR test is to have blood drawn and sent to a lab, where the test is conducted Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Prothrombin time • Prothrombin Time is a measure of how quickly blood clots. • The ideal target International Normalized Ratio (INR) range will vary from person to person depending on a variety of factors such as; • Reason for taking anticoagulants • Medical conditions • Other issues. • The traditional way to run a PT-INR test is to have blood drawn and sent to a lab, where the test is conducted Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 PT/INR • Measure of the extrinsic pathway • POCT devices strips containing thromboplastin reagents (variable sources) • Fresh whole blood • Clot detection – The lab uses either optical or mechanical means – POCT • Capillary or pump-induced movement • Oscillation change of a magnetic particle • Electro-current by alteration of fluorescence Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
PT/INR • Measure of the extrinsic pathway • POCT devices strips containing thromboplastin reagents (variable sources) • Fresh whole blood • Clot detection – The lab uses either optical or mechanical means – POCT • Capillary or pump-induced movement • Oscillation change of a magnetic particle • Electro-current by alteration of fluorescence Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
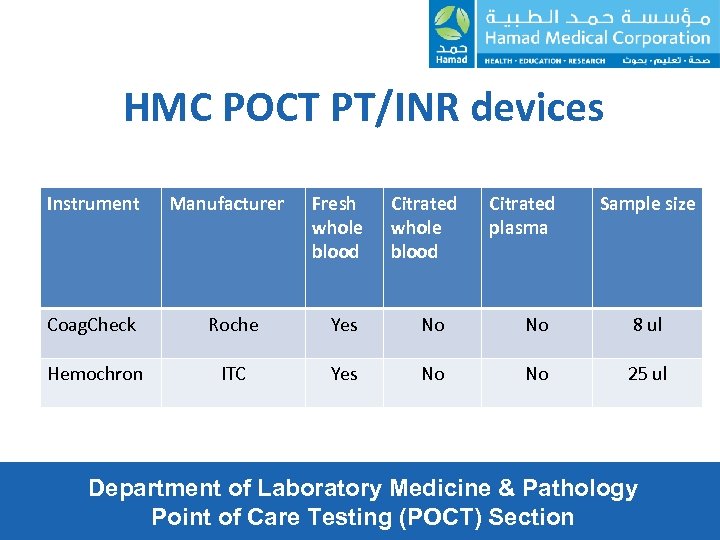 HMC POCT PT/INR devices Instrument Manufacturer Fresh whole blood Citrated plasma Sample size Coag. Check Roche Yes No No 8 ul Hemochron ITC Yes No No 25 ul Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
HMC POCT PT/INR devices Instrument Manufacturer Fresh whole blood Citrated plasma Sample size Coag. Check Roche Yes No No 8 ul Hemochron ITC Yes No No 25 ul Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
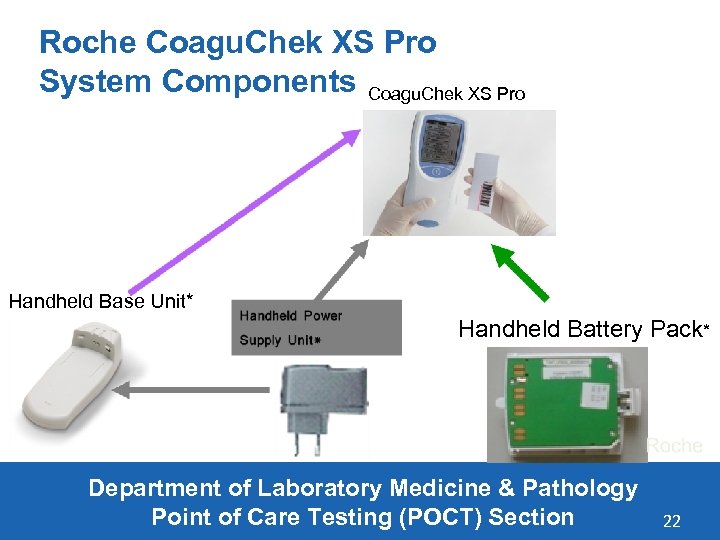 Roche Coagu. Chek XS Pro System Components Coagu. Chek XS Pro Handheld Base Unit* Handheld Battery Pack* Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section 22
Roche Coagu. Chek XS Pro System Components Coagu. Chek XS Pro Handheld Base Unit* Handheld Battery Pack* Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section 22
 Principle • The Coagu. Chek test strip contains recombinant thromboplastin reagent. • When the whole blood sample is applied, the reagent is solved an electrochemical reaction takes place which is transformed into a clotting time value being displayed on the meter screen in INR values. • The international sensitivity index (ISI) for the system has been established as 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Principle • The Coagu. Chek test strip contains recombinant thromboplastin reagent. • When the whole blood sample is applied, the reagent is solved an electrochemical reaction takes place which is transformed into a clotting time value being displayed on the meter screen in INR values. • The international sensitivity index (ISI) for the system has been established as 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 Self-monitoring • Evidence for its effectiveness continues to accumulate • The consequence of glucose on health because of wrong POCT results is minimal compared to wrong coagulation which could be lethal • The risk is much higher for self-monitoring for coagulation Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology 24 Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Self-monitoring • Evidence for its effectiveness continues to accumulate • The consequence of glucose on health because of wrong POCT results is minimal compared to wrong coagulation which could be lethal • The risk is much higher for self-monitoring for coagulation Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology 24 Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 Hemochron Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Hemochron Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
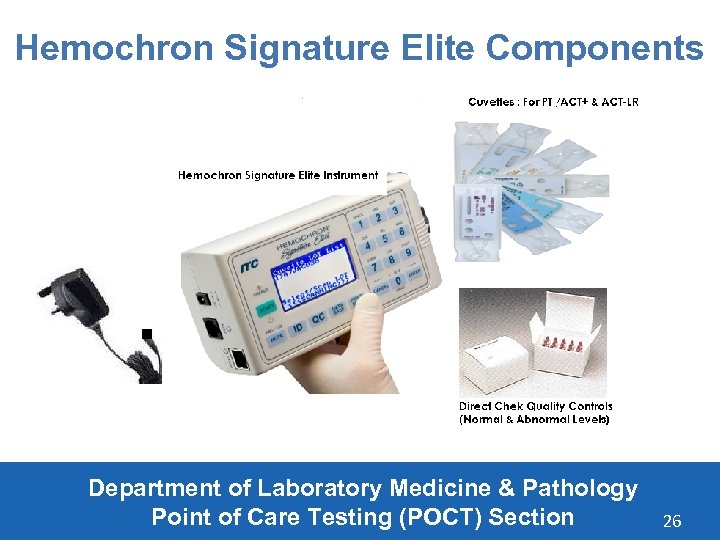 Hemochron Signature Elite Components Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section 26
Hemochron Signature Elite Components Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section 26
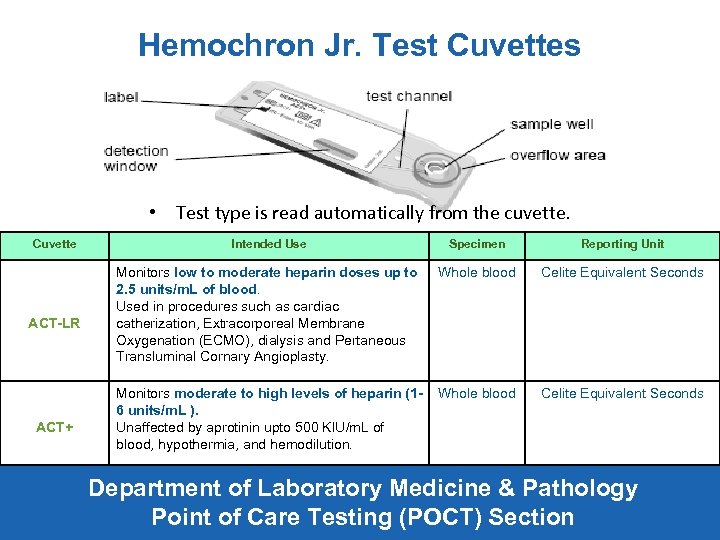 Hemochron Jr. Test Cuvettes • Test type is read automatically from the cuvette. Cuvette ACT-LR ACT+ Intended Use Specimen Reporting Unit Monitors low to moderate heparin doses up to 2. 5 units/m. L of blood. Used in procedures such as cardiac catherization, Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO), dialysis and Pertaneous Transluminal Cornary Angioplasty. Whole blood Celite Equivalent Seconds Monitors moderate to high levels of heparin (16 units/m. L ). Unaffected by aprotinin upto 500 KIU/m. L of blood, hypothermia, and hemodilution. Whole blood Celite Equivalent Seconds Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Hemochron Jr. Test Cuvettes • Test type is read automatically from the cuvette. Cuvette ACT-LR ACT+ Intended Use Specimen Reporting Unit Monitors low to moderate heparin doses up to 2. 5 units/m. L of blood. Used in procedures such as cardiac catherization, Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO), dialysis and Pertaneous Transluminal Cornary Angioplasty. Whole blood Celite Equivalent Seconds Monitors moderate to high levels of heparin (16 units/m. L ). Unaffected by aprotinin upto 500 KIU/m. L of blood, hypothermia, and hemodilution. Whole blood Celite Equivalent Seconds Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 ACT • Coagulation initiated by an activator • Strong activator celite (or kaolin) • Clot detection is change in pump driven blood movement • Results in seconds Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
ACT • Coagulation initiated by an activator • Strong activator celite (or kaolin) • Clot detection is change in pump driven blood movement • Results in seconds Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 Why use ACT • Monitoring hemostatsis for heparin anticoagulant therapy Bleeding clotting Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Why use ACT • Monitoring hemostatsis for heparin anticoagulant therapy Bleeding clotting Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 Advantages of ACT • Rapid TAT • Rapidly and easily adjust anticoagulant dose • Heparin – half life varies by patient – Dose required varies by patient – Potency varies by different lot • Direct thrombin inhibitors – very short half life – Require immediate intervention – No antidote available Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Advantages of ACT • Rapid TAT • Rapidly and easily adjust anticoagulant dose • Heparin – half life varies by patient – Dose required varies by patient – Potency varies by different lot • Direct thrombin inhibitors – very short half life – Require immediate intervention – No antidote available Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 ACT • • Cardiac surgery Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) Interventional cardiology ECMO Critical care Interventional radiology Electrophysiology Vascular surgery Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
ACT • • Cardiac surgery Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) Interventional cardiology ECMO Critical care Interventional radiology Electrophysiology Vascular surgery Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 • • APTT ACT Activated clotting time • Activated partial thromboplastin time POC Only Low, moderate or high • Laboratory dose heparin • Low dose heparin only System dependent • System dependent upper limit Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
• • APTT ACT Activated clotting time • Activated partial thromboplastin time POC Only Low, moderate or high • Laboratory dose heparin • Low dose heparin only System dependent • System dependent upper limit Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 Challenges • Variation in tests results based on the device used • INR corrects for variation, not with ACT • End-user knowledge of the pre-analytical variables- Training – Sample type: cap avoid messaging, arterial or venous avoid trauma – Size: – timing of collection-immediately • Quality assurances Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
Challenges • Variation in tests results based on the device used • INR corrects for variation, not with ACT • End-user knowledge of the pre-analytical variables- Training – Sample type: cap avoid messaging, arterial or venous avoid trauma – Size: – timing of collection-immediately • Quality assurances Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
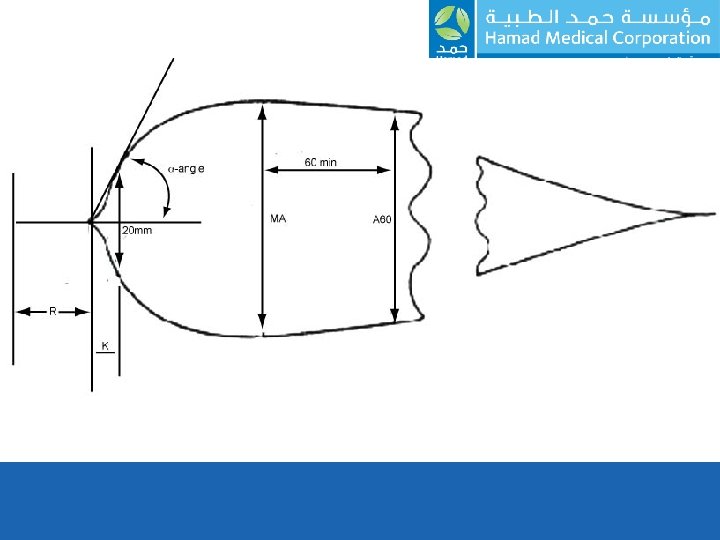
 Thromboelastograph (TEG) • TEG measures viscoelastic properties (viscosity) of whole blood. • The clot viscoelasticity depends on – Fibrinogen – Platelets – Coagulation – Fibrinolytic proteins
Thromboelastograph (TEG) • TEG measures viscoelastic properties (viscosity) of whole blood. • The clot viscoelasticity depends on – Fibrinogen – Platelets – Coagulation – Fibrinolytic proteins
 TEG TEG- abnormal hemostasis and fibronolysis • Hepatic disease • Cardiac Surgery • ECMO • Assessment of bleeding peri-operatively and following trauma Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
TEG TEG- abnormal hemostasis and fibronolysis • Hepatic disease • Cardiac Surgery • ECMO • Assessment of bleeding peri-operatively and following trauma Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 NICE guidelines on TEG • Viscoelastometric POC MAY be useful to help determine if bleeding is because of a problem with the blood’s ability to clot, or because of a surgical bleed. This helps the right treatment to stop the bleeding. • Using these systems MAY mean that patients are less likely to need a blood transfusion during surgery or need more operations to investigate further bleeding. • TEG is recommended to help monitor blood clotting during and after heart surgery by healthcare professionals who have had appropriate training NICE August 2014 Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
NICE guidelines on TEG • Viscoelastometric POC MAY be useful to help determine if bleeding is because of a problem with the blood’s ability to clot, or because of a surgical bleed. This helps the right treatment to stop the bleeding. • Using these systems MAY mean that patients are less likely to need a blood transfusion during surgery or need more operations to investigate further bleeding. • TEG is recommended to help monitor blood clotting during and after heart surgery by healthcare professionals who have had appropriate training NICE August 2014 Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
 THANK YOU Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section
THANK YOU Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology Point of Care Testing (POCT) Section


