saas_and_cloud_computing.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 31

Saa. S and Cloud Computing Internet Technologies Nurbek Saparkhojayev

The challenge Add new services for your users quickly and cost effectively

Expand your Infrastructure! Buy new servers, increase your software costs, provision more datacenter capacity!!

Look to the cloud! Pay for the bandwidth and server resources that you need. When your push is done then turn the whole thing off!

What is the cloud? • IT as a service • Cloud allows access to services without user technical knowledge or control of supporting infrastructure • Best described in terms of what happened to mechanical power over 100 yrs ago • Now computers are simple devices connected to the larger cloud • Data processing, storage and software applications that used to run locally are now being supplied by big central computing stations. They're becoming, in essence, computing utilities. What is Cloud Computing?

UNCLASSIFIED What is Cloud Computing? Multiple Choice: Cloud Computing is… a) A way to access applications hosted on the web through your web browser (Software as a Service -Saa. S) b) A pay-as-you-go model for IT resources accessed over the Internet (Platform as a Service – Paa. S) c) Use of commodity computers, distributed throughout an internet, to perform parallel processing, distributed storage, indexing and mining of data d) Gartner: “Cloud computing is a style of computing where massively scalable IT-related capabilities are provided ‘as a service’ across the Internet to multiple external customers” e) An IT buzzword that assures potential clients that your product is on the cutting edge of technology f) All of the above UNCLASSIFIED 6

UNCLASSIFIED Coud Deployment Models: • Internal (private) cloud. The cloud infrastructure is operated within the consumer’s organization. • Community cloud. The cloud infrastructure is jointly owned by several organizations and supports a specific community that has shared concerns (e. g. , mission, security requirements, policy, and compliance considerations). • Public cloud. The cloud infrastructure is owned by an organization selling cloud services to the general public or to a large industry group. • Hybrid cloud. The cloud infrastructure is a composition of two or more clouds (internal, community, or public) that remain unique entities but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that enables data and application NIST working definitions portability. UNCLASSIFIED 7
Saa. S Software as a Service Paa. S Platform as a Service Iaa. S Infrastructure as a Service

Saa. S Software as a Service

Saa. S Software delivery model • Increasingly popular with SMEs • No hardware or software to manage • Service delivered through a browser

Saa. S Advantages • • • Pay per use Instant Scalability Security Reliability APIs

Google App Engine Exposes the Google Infrastructure to the outside world Big. Table Python Language runtime Access to some google api’s (authentication , image manipulation) APIs The Python Runtime, The Python environment in which your app runs; CGI, sandbox features, application caching, logging Datastore API, Big. Table – Google’s Database Images API, the image data manipulation service Mail API, sending email from your app Memcache API, the distributed memory cache URL Fetch API, accessing other Internet hosts from your app Users API, integrating your app with Google Accounts You should expect to see more API’s exposed. More specifically the Google API’s for Docs , GWT , etc

App Engine - offering Claim to Fame Free (to start with) Big. Table ( a real winner) Essentially a good way to get into the google world and potentially get acquired by google

Saa. S Examples • • CRM Financial Planning Human Resources Word processing Commercial Services: • Salesforce. com • emailcloud

Paa. S Platform as a Service
Platform delivery model Paa. S • Platforms are built upon Infrastructure, which is expensive • Estimating demand is not a science! • Platform management is not fun!
Popular services Paa. S • Storage • Database • Scalability
Advantages Paa. S • • • Pay per use Instant Scalability Security Reliability APIs

Examples Paa. S • Google App Engine • Mosso • AWS: S 3

Iaa. S Infrastructure as a Service
Computer infrastructure delivery model Access to infrastructure stack: Iaa. S – Full OS access – Firewalls – Routers – Load balancing
Advantages Iaa. S • • • Pay per use Instant Scalability Security Reliability APIs
Examples • Flexiscale • AWS: EC 2 Iaa. S
Saa. S Software as a Service Paa. S Platform as a Service Iaa. S Infrastructure as a Service
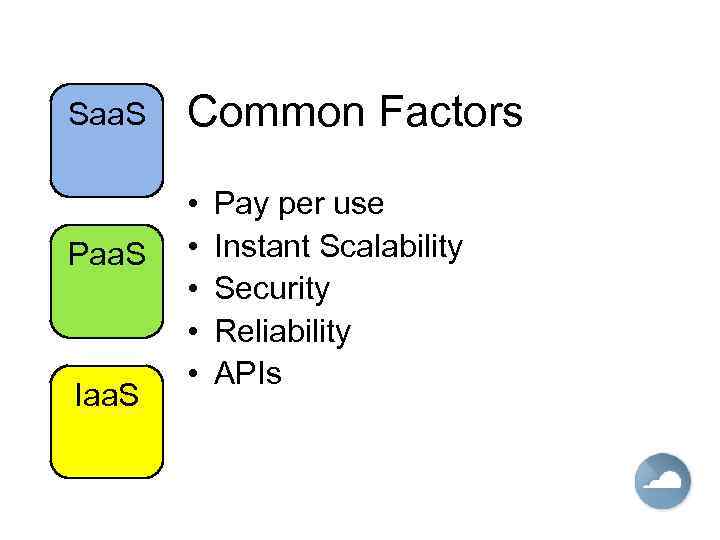
Saa. S Paa. S Iaa. S Common Factors • • • Pay per use Instant Scalability Security Reliability APIs
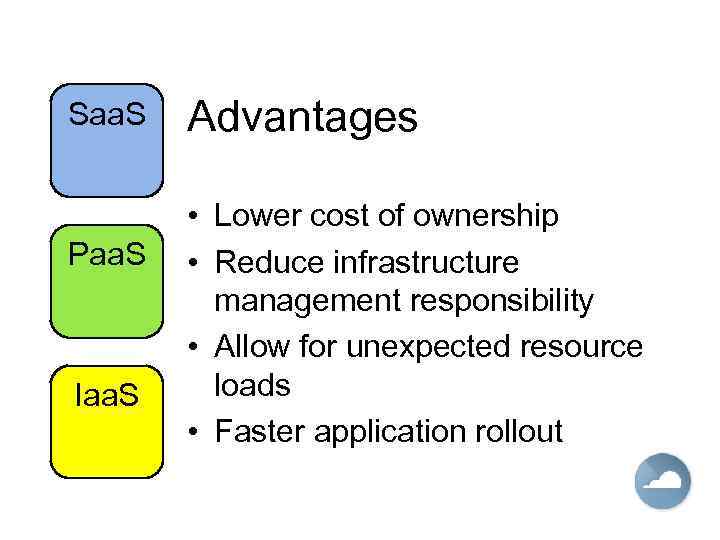
Saa. S Paa. S Iaa. S Advantages • Lower cost of ownership • Reduce infrastructure management responsibility • Allow for unexpected resource loads • Faster application rollout
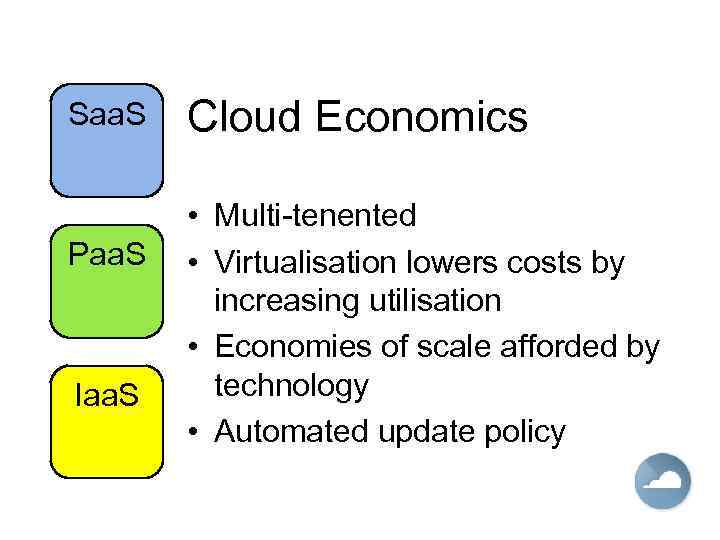
Saa. S Paa. S Iaa. S Cloud Economics • Multi-tenented • Virtualisation lowers costs by increasing utilisation • Economies of scale afforded by technology • Automated update policy
Examples of usage

Saa. S • Your current CRM package is not managing the load or you simply don’t want to host it in-house…. use a Saa. S provider such as Salesforce. com • Your email is hosted on an exchange server in your office and it is very slow…outsource this using Hosted Exchange.

• You need to host a large file (5 Mb) on your website and make it available for 35, 000 users for only two months duration. Use Cloud Front from Amazon. Paa. S • You want to start storage services on your network for a large number of files and you do not have the storage capacity…use Amazon S 3.

• You want to run a batch job but you don’t have the infrastructure necessary to run it in a timely manner. Use Amazon EC 2. • You want to host a website, but only for a few days. Use Flexiscale. Iaa. S
saas_and_cloud_computing.pptx