 S Y S T E M S D E S I G N A L Y S I S Chapter 1 Introduction Jerry Post Copyright © 1997 1
S Y S T E M S D E S I G N A L Y S I S Chapter 1 Introduction Jerry Post Copyright © 1997 1
 S Purpose of This Class Y S Ø Systems development and programming is hard. T Ø Many failures in the past and recently. E v Over budget. M v Over schedule. S v Total failure/not completed. D E S I G N Ø Teamwork v Large projects require teams of MIS workers. v Need to split project into pieces, coordinate workers. v Need to share and communicate. v Need to control and evaluate progress. Ø Design characteristics, tips, and tricks. v Planning and scheduling. v Tools. 2
S Purpose of This Class Y S Ø Systems development and programming is hard. T Ø Many failures in the past and recently. E v Over budget. M v Over schedule. S v Total failure/not completed. D E S I G N Ø Teamwork v Large projects require teams of MIS workers. v Need to split project into pieces, coordinate workers. v Need to share and communicate. v Need to control and evaluate progress. Ø Design characteristics, tips, and tricks. v Planning and scheduling. v Tools. 2
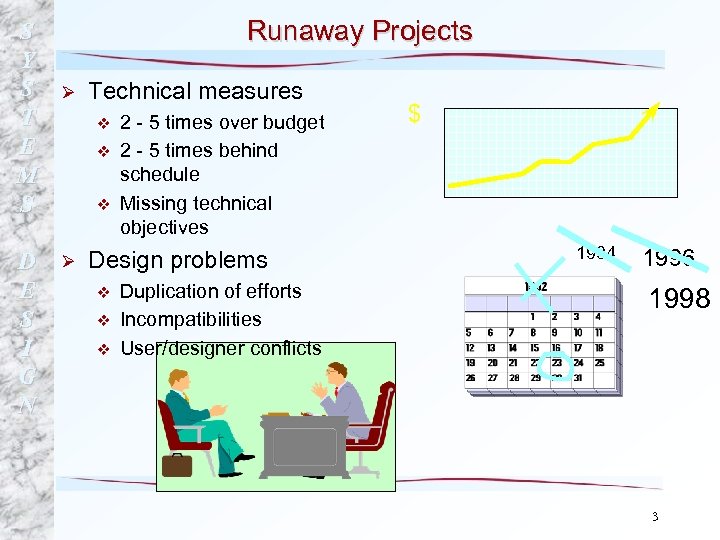 S Y S T E M S D E S I G N Runaway Projects Ø Technical measures v v v Ø 2 - 5 times over budget 2 - 5 times behind schedule Missing technical objectives Design problems v v v Duplication of efforts Incompatibilities User/designer conflicts $ 1994 1996 1998 3
S Y S T E M S D E S I G N Runaway Projects Ø Technical measures v v v Ø 2 - 5 times over budget 2 - 5 times behind schedule Missing technical objectives Design problems v v v Duplication of efforts Incompatibilities User/designer conflicts $ 1994 1996 1998 3
 S Project Success and Failure Y Ø Reasons for Success S Ø Reasons for Failure v Lack of user input v User Involvement T v Incomplete requirements v Executive management E support v Changing requirements and M specifications v Clear requirements S v Lack of executive support v Proper planning D E S I G N v Lack of technical skills v Realistic expectations 4
S Project Success and Failure Y Ø Reasons for Success S Ø Reasons for Failure v Lack of user input v User Involvement T v Incomplete requirements v Executive management E support v Changing requirements and M specifications v Clear requirements S v Lack of executive support v Proper planning D E S I G N v Lack of technical skills v Realistic expectations 4
 S Development Trends Y Ø New tools S Ø Development problems. v Don’t meet deadlines. v Project management T v Go over budget. v Groupware for sharing E v Can’t control large projects. v CASE: Computer-aided M software engineering v Programmers are expensive. S v Database management D E S I G N Ø You can buy really good software today. v Transaction processing. v Common applications. Ø How long does software last? v Outdated? Functions and needs change. v Depends on hardware. systems v Powerful languages (Visual Basic) Ø The Internet! v User Interface! Ø A new way of looking at development: object-oriented design 5
S Development Trends Y Ø New tools S Ø Development problems. v Don’t meet deadlines. v Project management T v Go over budget. v Groupware for sharing E v Can’t control large projects. v CASE: Computer-aided M software engineering v Programmers are expensive. S v Database management D E S I G N Ø You can buy really good software today. v Transaction processing. v Common applications. Ø How long does software last? v Outdated? Functions and needs change. v Depends on hardware. systems v Powerful languages (Visual Basic) Ø The Internet! v User Interface! Ø A new way of looking at development: object-oriented design 5
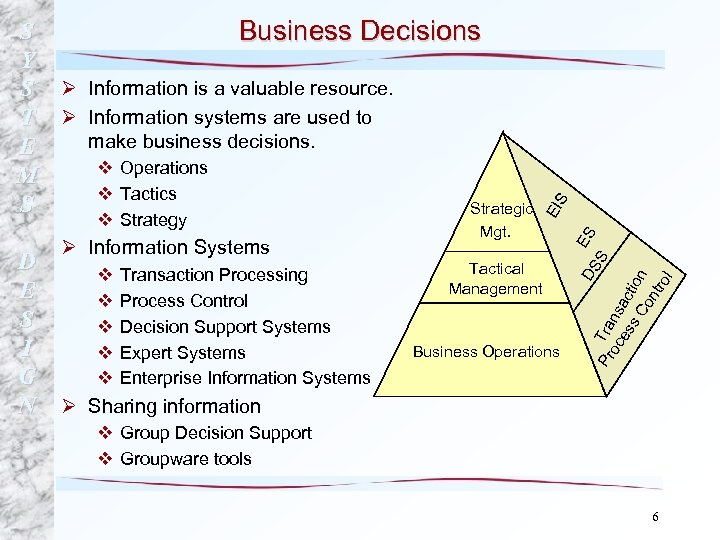 v v v Transaction Processing Process Control Decision Support Systems Expert Systems Enterprise Information Systems S Tactical Management Business Operations Pr Tra oc ns es ac s C tion on tro l D E S I G N Ø Information Systems Mgt. DS ES S v Strategy EI S Business Decisions Y S Ø Information is a valuable resource. T Ø Information systems are used to make business decisions. E v Operations M v Tactics S Strategic Ø Sharing information v Group Decision Support v Groupware tools 6
v v v Transaction Processing Process Control Decision Support Systems Expert Systems Enterprise Information Systems S Tactical Management Business Operations Pr Tra oc ns es ac s C tion on tro l D E S I G N Ø Information Systems Mgt. DS ES S v Strategy EI S Business Decisions Y S Ø Information is a valuable resource. T Ø Information systems are used to make business decisions. E v Operations M v Tactics S Strategic Ø Sharing information v Group Decision Support v Groupware tools 6
 S The Role of the Analyst Y S Ø Analyze and Design Systems v Identify problems, opportunities, T objectives. E v Analyze information flows. M v Design computerized systems to S solve problems. D E S I G N Ø Ø Problem solving. Communication. Change agent. Control, planning, and structure. 7
S The Role of the Analyst Y S Ø Analyze and Design Systems v Identify problems, opportunities, T objectives. E v Analyze information flows. M v Design computerized systems to S solve problems. D E S I G N Ø Ø Problem solving. Communication. Change agent. Control, planning, and structure. 7
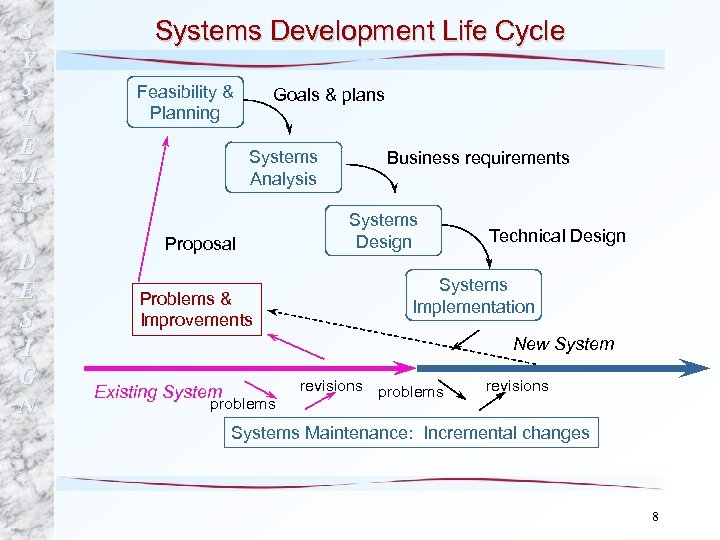 S Y S T E M S D E S I G N Systems Development Life Cycle Feasibility & Planning Goals & plans Systems Analysis Proposal Problems & Improvements Business requirements Systems Design Technical Design Systems Implementation New System Existing System problems revisions Systems Maintenance: Incremental changes 8
S Y S T E M S D E S I G N Systems Development Life Cycle Feasibility & Planning Goals & plans Systems Analysis Proposal Problems & Improvements Business requirements Systems Design Technical Design Systems Implementation New System Existing System problems revisions Systems Maintenance: Incremental changes 8
 S Design Stages Y Ø Physical Design S Ø Initiation v Scope v Table definitions T v Feasibility v Application development E v Cost & Time estimates v Data storage M v Security S Ø Requirements Analysis v User Views & Needs D E S I G N ü Forms ü Reports v Processes & Events v Objects & Attributes Ø Conceptual Design v Models ü Data flow diagram ü Entity Relationships ü Objects v Procedures Ø Implementation v v Training Purchases Data conversion Installation Ø Evaluation & Review v User feedback 9
S Design Stages Y Ø Physical Design S Ø Initiation v Scope v Table definitions T v Feasibility v Application development E v Cost & Time estimates v Data storage M v Security S Ø Requirements Analysis v User Views & Needs D E S I G N ü Forms ü Reports v Processes & Events v Objects & Attributes Ø Conceptual Design v Models ü Data flow diagram ü Entity Relationships ü Objects v Procedures Ø Implementation v v Training Purchases Data conversion Installation Ø Evaluation & Review v User feedback 9
 S SDLC Strengths and Weaknesses Y Ø Disadvantages S Ø Advantages v Control & targets v Increased costs T v Formality v Increased time E v Financial controls v Hard for DSS M v User input v Requires definitions up front S D E S I G N v Documentation v Testing v Ease of maintenance v Rigid 10
S SDLC Strengths and Weaknesses Y Ø Disadvantages S Ø Advantages v Control & targets v Increased costs T v Formality v Increased time E v Financial controls v Hard for DSS M v User input v Requires definitions up front S D E S I G N v Documentation v Testing v Ease of maintenance v Rigid 10
 S Computer Assisted Software Engineering Y Ø CASE tool possibilities Ø Case complications S v Personal productivity v Expensive T ü Diagrams v No standards E ü Store & Search v Complex software, learning v Team productivity M v Team must follow methodology. ü Sharing up-to-date changes S Ø CASE Levels D E S I G N ü One shared source of data ü Communication v Development ü Reverse engineering ü Automated programming v Maintenance ü Complete records for future ü Diagrams and context ü Reverse engineering v Upper: front-end v Lower: back-end Ø CASE tool examples v IEF v Oracle ü Designer 2000 ü Developer 2000 v Rational Rose 11
S Computer Assisted Software Engineering Y Ø CASE tool possibilities Ø Case complications S v Personal productivity v Expensive T ü Diagrams v No standards E ü Store & Search v Complex software, learning v Team productivity M v Team must follow methodology. ü Sharing up-to-date changes S Ø CASE Levels D E S I G N ü One shared source of data ü Communication v Development ü Reverse engineering ü Automated programming v Maintenance ü Complete records for future ü Diagrams and context ü Reverse engineering v Upper: front-end v Lower: back-end Ø CASE tool examples v IEF v Oracle ü Designer 2000 ü Developer 2000 v Rational Rose 11


