712c1621dab936dc090172d1c787bead.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
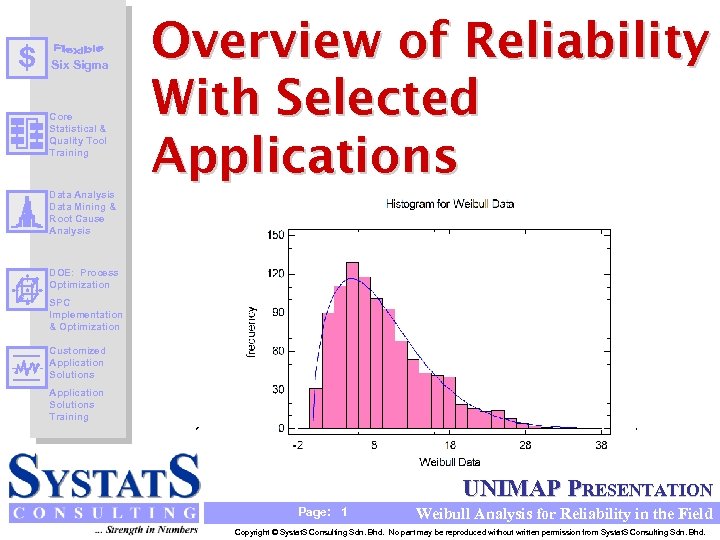 S Six Sigma Core Statistical & Quality Tool Training Overview of Reliability With Selected Applications Data Analysis Data Mining & Root Cause Analysis DOE: Process Optimization SPC Implementation & Optimization Customized Application Solutions Training UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 1 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
S Six Sigma Core Statistical & Quality Tool Training Overview of Reliability With Selected Applications Data Analysis Data Mining & Root Cause Analysis DOE: Process Optimization SPC Implementation & Optimization Customized Application Solutions Training UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 1 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 Agenda • Measuring Reliability: – Reliability Fn, Hazard Fn Bath Tub Curve, MTTF • • • Applications in the Field Weibull Analysis Fitting a Weibull Distribution What Can You Do with the Weibull Fit? Exercises UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 2 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Agenda • Measuring Reliability: – Reliability Fn, Hazard Fn Bath Tub Curve, MTTF • • • Applications in the Field Weibull Analysis Fitting a Weibull Distribution What Can You Do with the Weibull Fit? Exercises UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 2 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 What is Reliability? • What do you look for when purchasing a new PC? A new or used Car? A new Phone? – – – Price Features Brand/Reputation Style/Color Functionality / Reliability • How do we translate this VOC (Voice of the Customer) into technical specifications? – In order for the PC to work what components need to work? • Motherboard, connectors, fan, CPU cooler, thermal compound, RAM, video card, sound card, DVD-RW, hard drive, modem, mouse, monitor, operating system, processor, cables, case, etc. – In order for the components to work, what processes need to work? – In order for the processes to work, what controls need to be in place? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 3 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
What is Reliability? • What do you look for when purchasing a new PC? A new or used Car? A new Phone? – – – Price Features Brand/Reputation Style/Color Functionality / Reliability • How do we translate this VOC (Voice of the Customer) into technical specifications? – In order for the PC to work what components need to work? • Motherboard, connectors, fan, CPU cooler, thermal compound, RAM, video card, sound card, DVD-RW, hard drive, modem, mouse, monitor, operating system, processor, cables, case, etc. – In order for the components to work, what processes need to work? – In order for the processes to work, what controls need to be in place? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 3 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
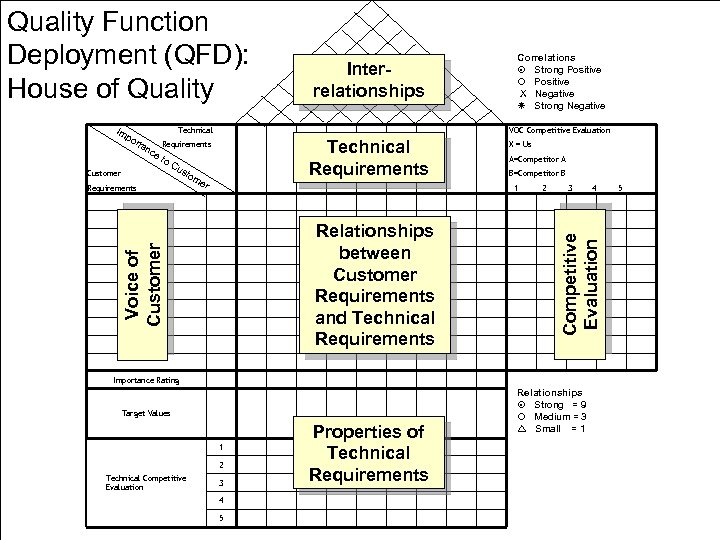 Quality Function Deployment (QFD): House of Quality Technical po rta nc VOC Competitive Evaluation Technical Requirements et o. C us Customer tom er X = Us A=Competitor A B=Competitor B 1 Relationships between Customer Requirements and Technical Requirements Voice of Customer Requirements Correlations Strong Positive X Negative Strong Negative 2 3 4 5 Competitive Evaluation Im Interrelationships Importance Rating Target Values 1 2 Technical Competitive Evaluation 3 4 5 Properties of Technical Requirements Page: 4 Relationships Strong = 9 Medium = 3 Small = 1 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Quality Function Deployment (QFD): House of Quality Technical po rta nc VOC Competitive Evaluation Technical Requirements et o. C us Customer tom er X = Us A=Competitor A B=Competitor B 1 Relationships between Customer Requirements and Technical Requirements Voice of Customer Requirements Correlations Strong Positive X Negative Strong Negative 2 3 4 5 Competitive Evaluation Im Interrelationships Importance Rating Target Values 1 2 Technical Competitive Evaluation 3 4 5 Properties of Technical Requirements Page: 4 Relationships Strong = 9 Medium = 3 Small = 1 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
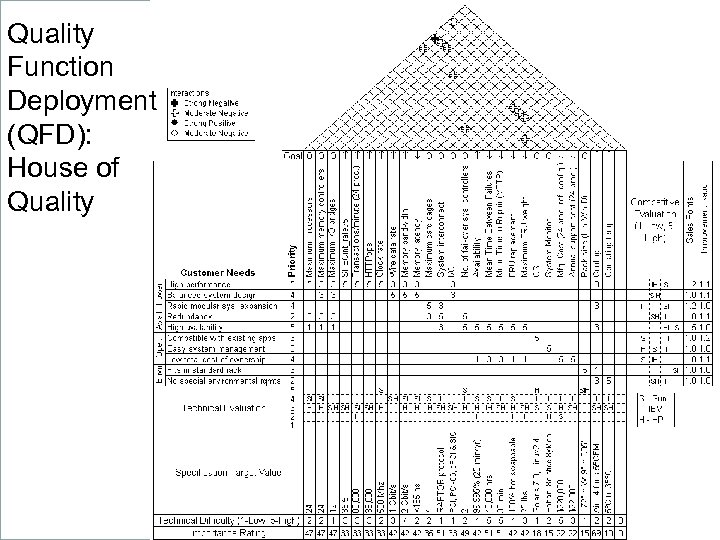 Quality Function Deployment (QFD): House of Quality UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 5 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Quality Function Deployment (QFD): House of Quality UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 5 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
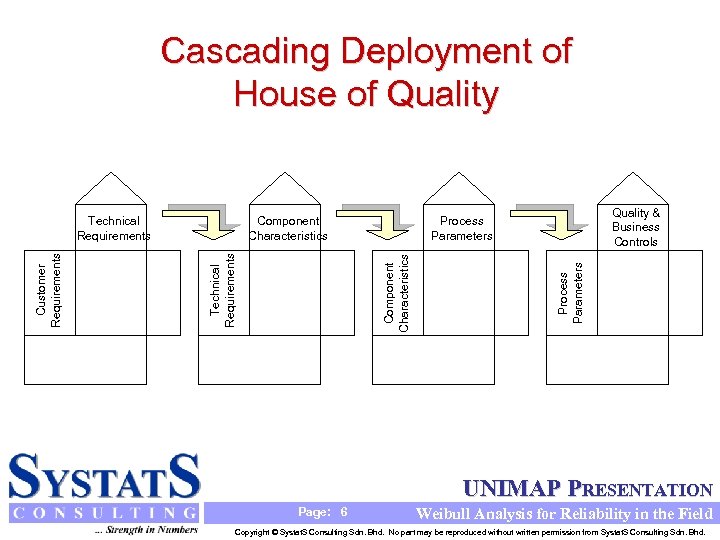 Cascading Deployment of House of Quality & Business Controls Component Characteristics Process Parameters Component Characteristics Technical Requirements Customer Requirements Technical Requirements UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 6 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Cascading Deployment of House of Quality & Business Controls Component Characteristics Process Parameters Component Characteristics Technical Requirements Customer Requirements Technical Requirements UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 6 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
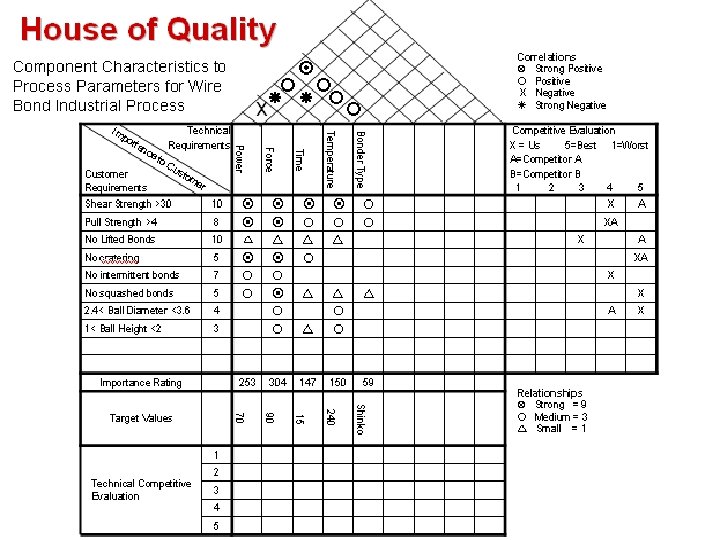 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 7 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 7 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
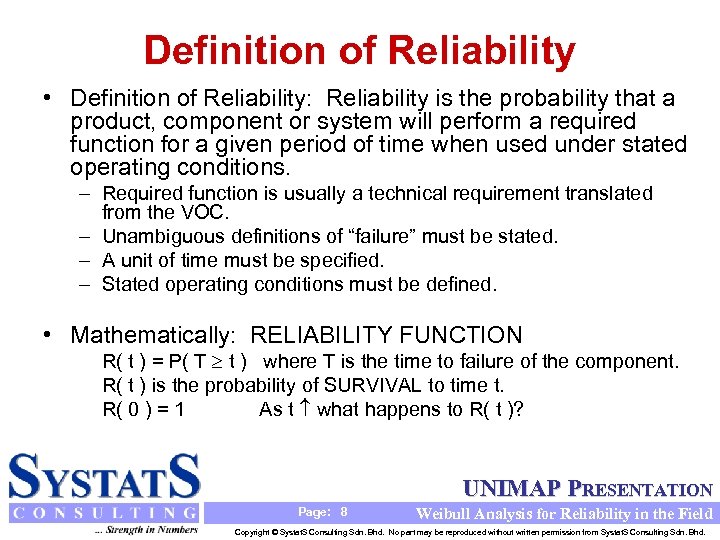 Definition of Reliability • Definition of Reliability: Reliability is the probability that a product, component or system will perform a required function for a given period of time when used under stated operating conditions. – Required function is usually a technical requirement translated from the VOC. – Unambiguous definitions of “failure” must be stated. – A unit of time must be specified. – Stated operating conditions must be defined. • Mathematically: RELIABILITY FUNCTION R( t ) = P( T t ) where T is the time to failure of the component. R( t ) is the probability of SURVIVAL to time t. R( 0 ) = 1 As t what happens to R( t )? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 8 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Definition of Reliability • Definition of Reliability: Reliability is the probability that a product, component or system will perform a required function for a given period of time when used under stated operating conditions. – Required function is usually a technical requirement translated from the VOC. – Unambiguous definitions of “failure” must be stated. – A unit of time must be specified. – Stated operating conditions must be defined. • Mathematically: RELIABILITY FUNCTION R( t ) = P( T t ) where T is the time to failure of the component. R( t ) is the probability of SURVIVAL to time t. R( 0 ) = 1 As t what happens to R( t )? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 8 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 Applications of Reliability • Improvement – System, Component or Process Design: Series vs Parallel, Redundancy, Stand-by Systems – Reliability Growth Testing / FMEA – Burn-In Testing • Characterization – Product Testing / Accelerated Life Testing – Reliability Demonstration for Qualification & Dispositioning – Design Life & Reliability Allocation: Setting Component Reliability Goals to Support Overall Product Reliability Goals – Economic Analysis: Warranty Costs • Control – Matrix Monitors – Maintainability & Availability: PM Schedules, Spare Part Analysis, Repair vs Replace Decisions UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 9 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Applications of Reliability • Improvement – System, Component or Process Design: Series vs Parallel, Redundancy, Stand-by Systems – Reliability Growth Testing / FMEA – Burn-In Testing • Characterization – Product Testing / Accelerated Life Testing – Reliability Demonstration for Qualification & Dispositioning – Design Life & Reliability Allocation: Setting Component Reliability Goals to Support Overall Product Reliability Goals – Economic Analysis: Warranty Costs • Control – Matrix Monitors – Maintainability & Availability: PM Schedules, Spare Part Analysis, Repair vs Replace Decisions UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 9 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
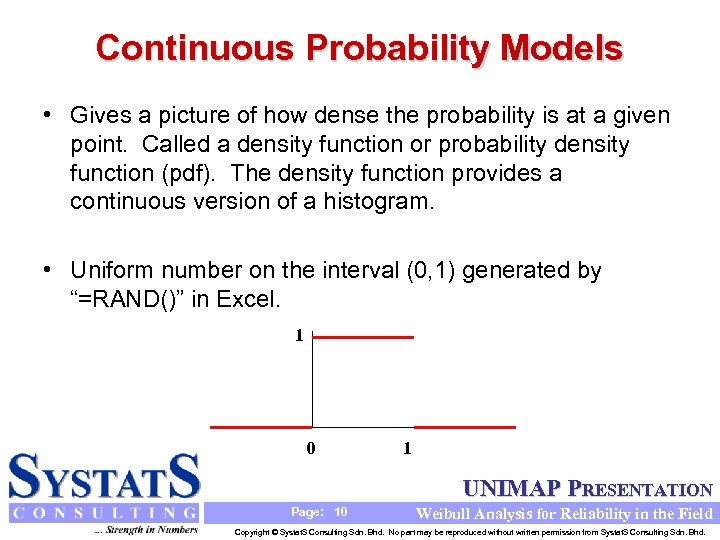 Continuous Probability Models • Gives a picture of how dense the probability is at a given point. Called a density function or probability density function (pdf). The density function provides a continuous version of a histogram. • Uniform number on the interval (0, 1) generated by “=RAND()” in Excel. 1 0 1 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 10 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Continuous Probability Models • Gives a picture of how dense the probability is at a given point. Called a density function or probability density function (pdf). The density function provides a continuous version of a histogram. • Uniform number on the interval (0, 1) generated by “=RAND()” in Excel. 1 0 1 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 10 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
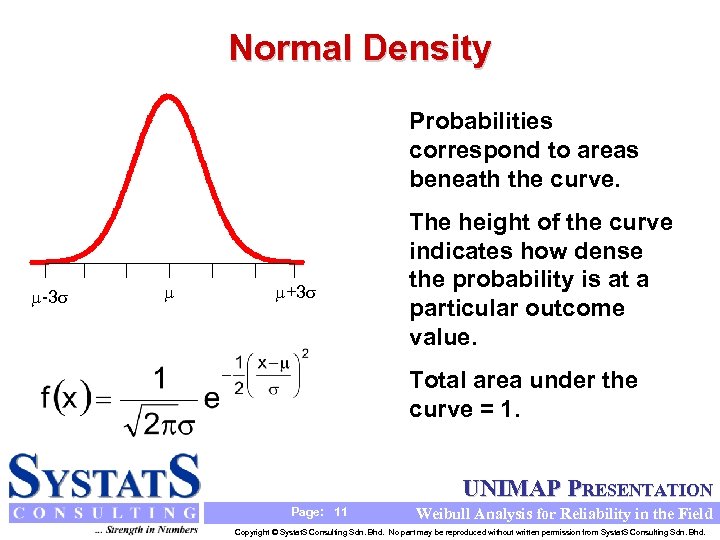 Normal Density Probabilities correspond to areas beneath the curve. -3 +3 The height of the curve indicates how dense the probability is at a particular outcome value. Total area under the curve = 1. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 11 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Normal Density Probabilities correspond to areas beneath the curve. -3 +3 The height of the curve indicates how dense the probability is at a particular outcome value. Total area under the curve = 1. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 11 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 Cumulative Density =NORMDIST(x, , , 1) =0. 15865526 -3 +3 =NORMINV(0. 158655, 0, 1) Page: 12 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Cumulative Density =NORMDIST(x, , , 1) =0. 15865526 -3 +3 =NORMINV(0. 158655, 0, 1) Page: 12 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
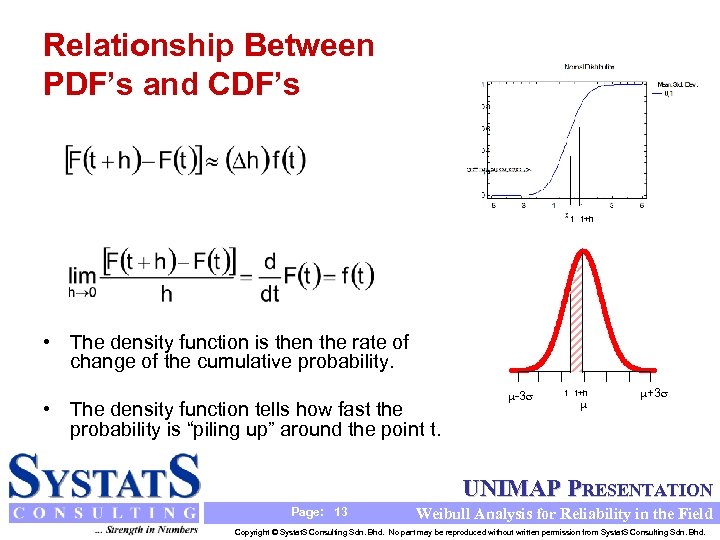 Relationship Between PDF’s and CDF’s t t+h • The density function is then the rate of change of the cumulative probability. • The density function tells how fast the probability is “piling up” around the point t. -3 t t+h +3 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 13 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Relationship Between PDF’s and CDF’s t t+h • The density function is then the rate of change of the cumulative probability. • The density function tells how fast the probability is “piling up” around the point t. -3 t t+h +3 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 13 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
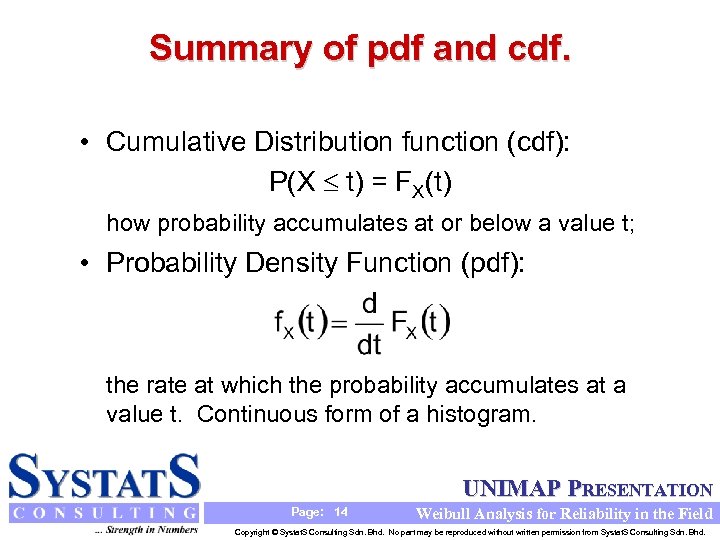 Summary of pdf and cdf. • Cumulative Distribution function (cdf): P(X t) = FX(t) how probability accumulates at or below a value t; • Probability Density Function (pdf): the rate at which the probability accumulates at a value t. Continuous form of a histogram. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 14 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Summary of pdf and cdf. • Cumulative Distribution function (cdf): P(X t) = FX(t) how probability accumulates at or below a value t; • Probability Density Function (pdf): the rate at which the probability accumulates at a value t. Continuous form of a histogram. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 14 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
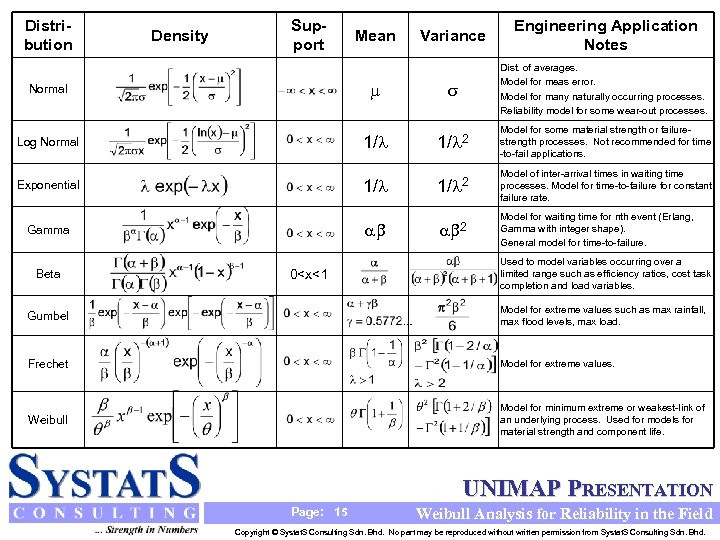 Distribution Variance Engineering Application Notes Dist. of averages. Model for meas error. Model for many naturally occurring processes. Reliability model for some wear-out processes. Log Normal 1/ 2 Model for some material strength or failurestrength processes. Not recommended for time -to-fail applications. Exponential 1/ 2 Model of inter-arrival times in waiting time processes. Model for time-to-failure for constant failure rate. 2 Model for waiting time for nth event (Erlang, Gamma with integer shape). General model for time-to-failure. Density Support Normal Gamma Beta 0
Distribution Variance Engineering Application Notes Dist. of averages. Model for meas error. Model for many naturally occurring processes. Reliability model for some wear-out processes. Log Normal 1/ 2 Model for some material strength or failurestrength processes. Not recommended for time -to-fail applications. Exponential 1/ 2 Model of inter-arrival times in waiting time processes. Model for time-to-failure for constant failure rate. 2 Model for waiting time for nth event (Erlang, Gamma with integer shape). General model for time-to-failure. Density Support Normal Gamma Beta 0
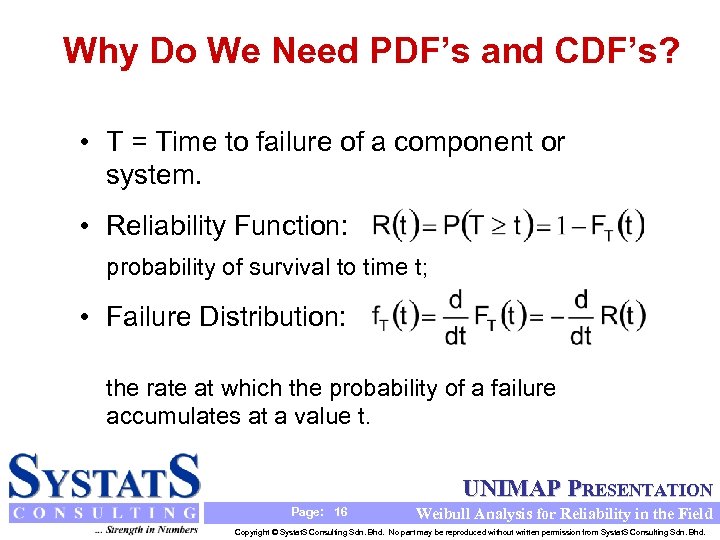 Why Do We Need PDF’s and CDF’s? • T = Time to failure of a component or system. • Reliability Function: probability of survival to time t; • Failure Distribution: the rate at which the probability of a failure accumulates at a value t. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 16 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Why Do We Need PDF’s and CDF’s? • T = Time to failure of a component or system. • Reliability Function: probability of survival to time t; • Failure Distribution: the rate at which the probability of a failure accumulates at a value t. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 16 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
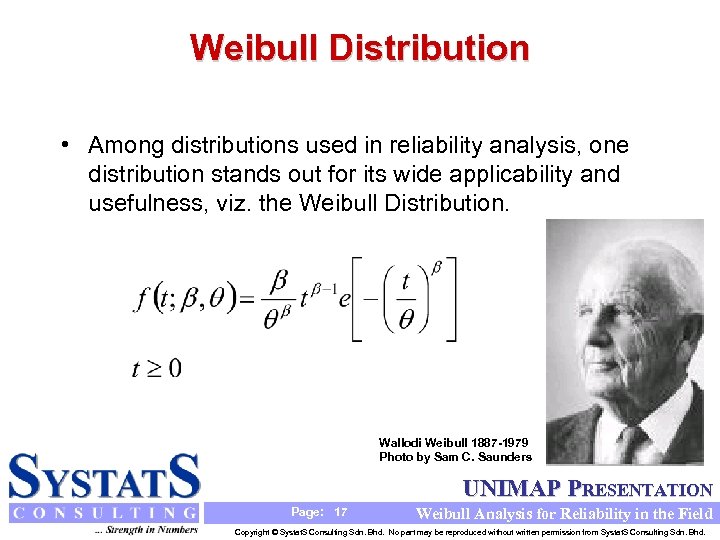 Weibull Distribution • Among distributions used in reliability analysis, one distribution stands out for its wide applicability and usefulness, viz. the Weibull Distribution. Wallodi Weibull 1887 -1979 Photo by Sam C. Saunders UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 17 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Weibull Distribution • Among distributions used in reliability analysis, one distribution stands out for its wide applicability and usefulness, viz. the Weibull Distribution. Wallodi Weibull 1887 -1979 Photo by Sam C. Saunders UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 17 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
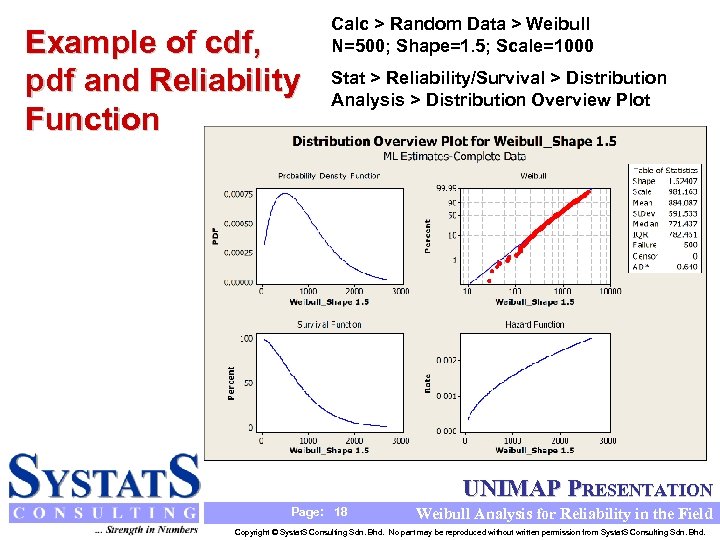 Example of cdf, pdf and Reliability Function Calc > Random Data > Weibull N=500; Shape=1. 5; Scale=1000 Stat > Reliability/Survival > Distribution Analysis > Distribution Overview Plot UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 18 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Example of cdf, pdf and Reliability Function Calc > Random Data > Weibull N=500; Shape=1. 5; Scale=1000 Stat > Reliability/Survival > Distribution Analysis > Distribution Overview Plot UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 18 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
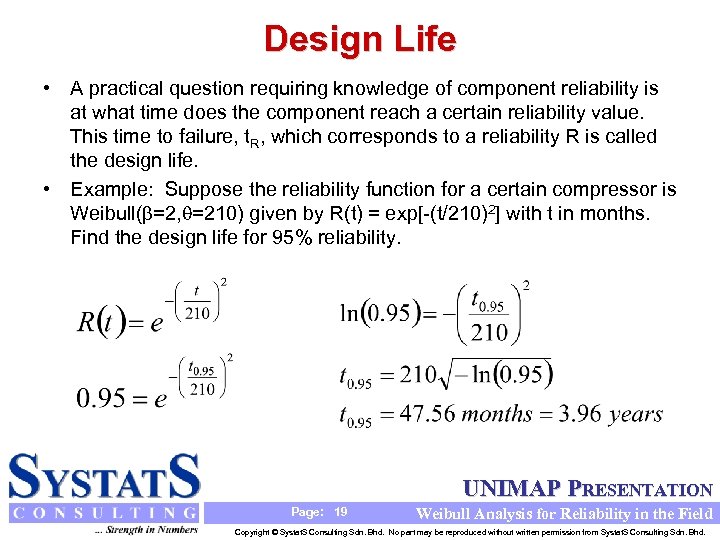 Design Life • A practical question requiring knowledge of component reliability is at what time does the component reach a certain reliability value. This time to failure, t. R, which corresponds to a reliability R is called the design life. • Example: Suppose the reliability function for a certain compressor is Weibull( =2, =210) given by R(t) = exp[-(t/210)2] with t in months. Find the design life for 95% reliability. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 19 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Design Life • A practical question requiring knowledge of component reliability is at what time does the component reach a certain reliability value. This time to failure, t. R, which corresponds to a reliability R is called the design life. • Example: Suppose the reliability function for a certain compressor is Weibull( =2, =210) given by R(t) = exp[-(t/210)2] with t in months. Find the design life for 95% reliability. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 19 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
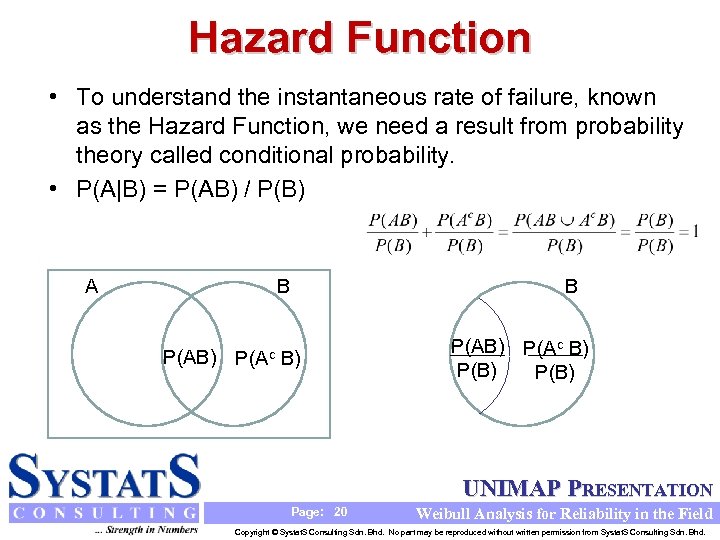 Hazard Function • To understand the instantaneous rate of failure, known as the Hazard Function, we need a result from probability theory called conditional probability. • P(A|B) = P(AB) / P(B) A B B P(AB) P(Ac B) P(B) UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 20 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Hazard Function • To understand the instantaneous rate of failure, known as the Hazard Function, we need a result from probability theory called conditional probability. • P(A|B) = P(AB) / P(B) A B B P(AB) P(Ac B) P(B) UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 20 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
![Hazard Function • Conditional probability of a failure during time [t, t+ t] per Hazard Function • Conditional probability of a failure during time [t, t+ t] per](https://present5.com/presentation/712c1621dab936dc090172d1c787bead/image-21.jpg) Hazard Function • Conditional probability of a failure during time [t, t+ t] per unit of time (failure rate): • Instantaneous hazard rate or failure rate function: UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 21 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Hazard Function • Conditional probability of a failure during time [t, t+ t] per unit of time (failure rate): • Instantaneous hazard rate or failure rate function: UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 21 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
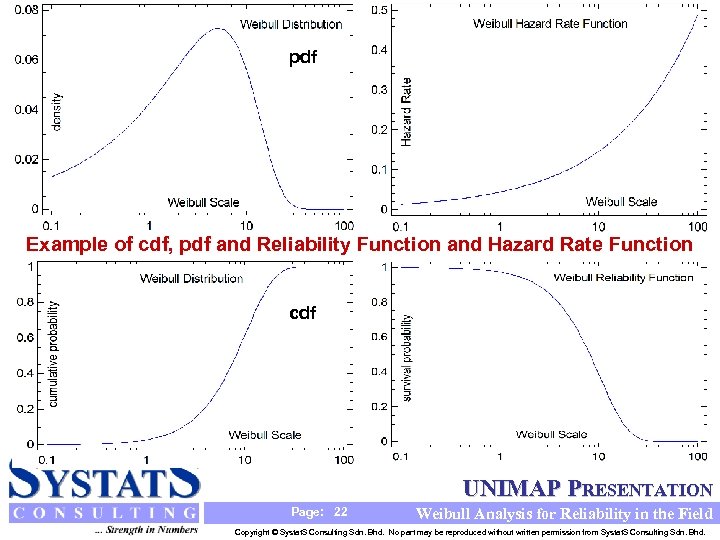 pdf Example of cdf, pdf and Reliability Function and Hazard Rate Function cdf UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 22 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
pdf Example of cdf, pdf and Reliability Function and Hazard Rate Function cdf UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 22 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
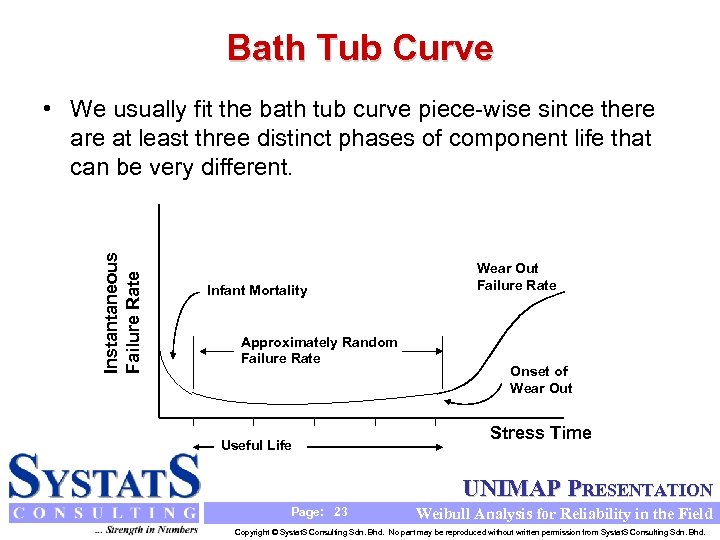 Bath Tub Curve Instantaneous Failure Rate • We usually fit the bath tub curve piece-wise since there at least three distinct phases of component life that can be very different. Infant Mortality Approximately Random Failure Rate Useful Life Wear Out Failure Rate Onset of Wear Out Stress Time UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 23 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Bath Tub Curve Instantaneous Failure Rate • We usually fit the bath tub curve piece-wise since there at least three distinct phases of component life that can be very different. Infant Mortality Approximately Random Failure Rate Useful Life Wear Out Failure Rate Onset of Wear Out Stress Time UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 23 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
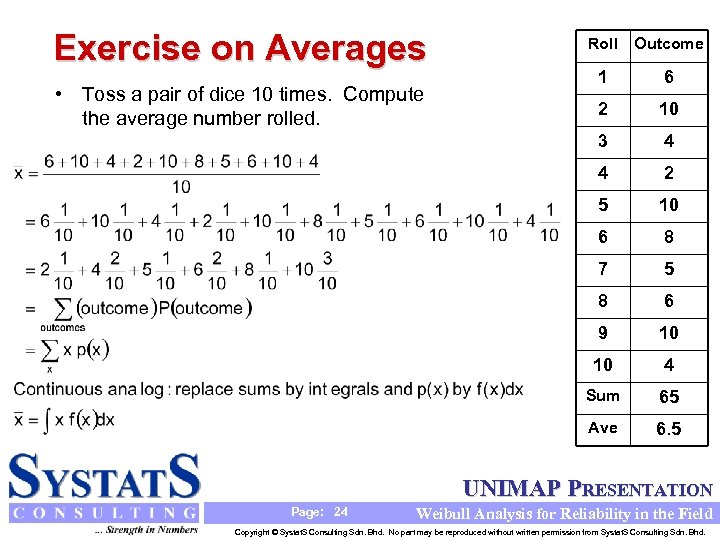 Exercise on Averages Roll Outcome • Toss a pair of dice 10 times. Compute the average number rolled. 1 6 2 10 3 4 4 2 5 10 6 8 7 5 8 6 9 10 10 4 Sum 65 Ave 6. 5 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 24 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Exercise on Averages Roll Outcome • Toss a pair of dice 10 times. Compute the average number rolled. 1 6 2 10 3 4 4 2 5 10 6 8 7 5 8 6 9 10 10 4 Sum 65 Ave 6. 5 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 24 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
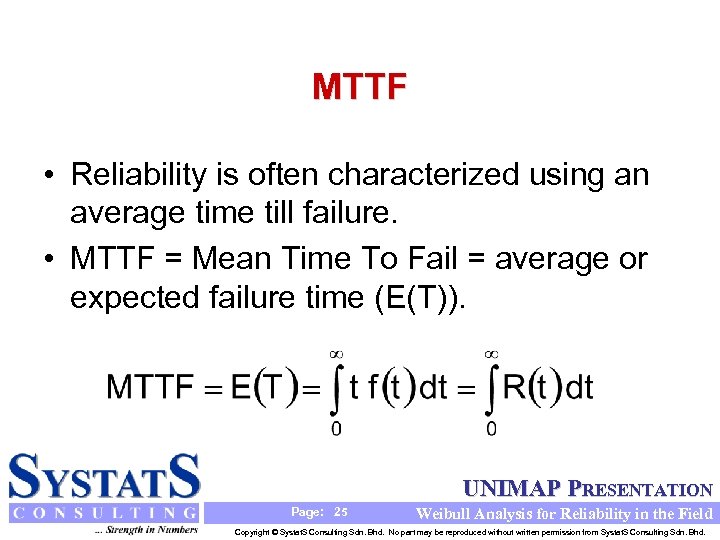 MTTF • Reliability is often characterized using an average time till failure. • MTTF = Mean Time To Fail = average or expected failure time (E(T)). UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 25 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
MTTF • Reliability is often characterized using an average time till failure. • MTTF = Mean Time To Fail = average or expected failure time (E(T)). UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 25 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 Example Suppose a manufacturer of monitors performs reliability testing and finds the reliability function is Weibull( =1, =25000), R(t)=exp(-t/25000) where t is in hours of use and 25000=MTTF. A Weibull( =1, ) is also called an Exponential( ). 1. 2. 3. Assume employees will use the monitor for an average of 6 hours per day. Find the reliability after the first year (assume the monitor is used every day of the year). Estimate the warranty cost per unit for a 1 year warranty if each repair averages $200. What MTTF goal is needed in order to reduce the warranty cost below $10 per monitor? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 26 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Example Suppose a manufacturer of monitors performs reliability testing and finds the reliability function is Weibull( =1, =25000), R(t)=exp(-t/25000) where t is in hours of use and 25000=MTTF. A Weibull( =1, ) is also called an Exponential( ). 1. 2. 3. Assume employees will use the monitor for an average of 6 hours per day. Find the reliability after the first year (assume the monitor is used every day of the year). Estimate the warranty cost per unit for a 1 year warranty if each repair averages $200. What MTTF goal is needed in order to reduce the warranty cost below $10 per monitor? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 26 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 1. Assume employees will use the monitor for an average of 6 hours per day. Find the reliability after the first year (assume the monitor is used every day of the year). R(365 6) = exp[-(365 6)/25000] = 0. 916 2. Estimate the warranty cost per unit for a 1 year warranty if each repair averages $200(1 -0. 916) = $16. 77 3. What MTTF goal is needed in order to reduce the warranty cost below $10 per monitor? $200(1 -R(365 6)) < $10 $200 {1 -exp[-(365*6)/ ]} < $10 > (365 6)/(-ln(1 -10/200)) = 42, 695. 64 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 27 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
1. Assume employees will use the monitor for an average of 6 hours per day. Find the reliability after the first year (assume the monitor is used every day of the year). R(365 6) = exp[-(365 6)/25000] = 0. 916 2. Estimate the warranty cost per unit for a 1 year warranty if each repair averages $200(1 -0. 916) = $16. 77 3. What MTTF goal is needed in order to reduce the warranty cost below $10 per monitor? $200(1 -R(365 6)) < $10 $200 {1 -exp[-(365*6)/ ]} < $10 > (365 6)/(-ln(1 -10/200)) = 42, 695. 64 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 27 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 Overview of Weibull Analysis • Weibull Analysis generally refers to a graphical analysis to fit a member of the Weibull family of distributions to a set of life data for the purpose of predicting and modeling important life characteristics of the product such as reliability, conditional probability of failure, mean time to failure and failure rate. • Advantages: – Failure rate can assume a variety of types: decreasing, constant or increasing. – Can be used with small sample sizes. – Data analysis is relatively easy to perform and interpret. – Can provide clues for the physics-of-failure. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 28 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Overview of Weibull Analysis • Weibull Analysis generally refers to a graphical analysis to fit a member of the Weibull family of distributions to a set of life data for the purpose of predicting and modeling important life characteristics of the product such as reliability, conditional probability of failure, mean time to failure and failure rate. • Advantages: – Failure rate can assume a variety of types: decreasing, constant or increasing. – Can be used with small sample sizes. – Data analysis is relatively easy to perform and interpret. – Can provide clues for the physics-of-failure. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 28 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 Overview of Weibull Analysis • Weibull analysis has been used extensively to study material, mechanical, chemical, electrical and electronic properties as well as being used in medical research, calibration and measurement. It can provide insights for: – Product Design – Quality Control – Maintenance and replacement strategies – Spare parts planning – Warranty analysis – Meteorological phenomena such as lightning strikes, storm intensity & number, snowfall, wind gusts and rainfall, etc. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 29 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Overview of Weibull Analysis • Weibull analysis has been used extensively to study material, mechanical, chemical, electrical and electronic properties as well as being used in medical research, calibration and measurement. It can provide insights for: – Product Design – Quality Control – Maintenance and replacement strategies – Spare parts planning – Warranty analysis – Meteorological phenomena such as lightning strikes, storm intensity & number, snowfall, wind gusts and rainfall, etc. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 29 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 History of Weibull Analysis • • • The Weibull distribution was originally developed by Fisher and Tippet in 1928 as an asymptotic extreme value distribution. Professor Weibull derived the distribution in 1939 from analysis of material breaking strength. Waloddi Weibull (1887 -1979) graduated from the Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm in 1924 and earned his doctorate in physics from the University of Uppsalla in 1932. Weibull worked in the Royal Swedish Coast Guard studying the effects of underwater explosions and the lifetime of components especially metallurgical failures. Weibull produced his landmark paper in 1951, “A Statistical Distribution Function of Wide Applicability, ” Journal of Applied Mechanics, 18, 293297. Professor Weibull proposed to analyze life data by selecting a suitable distribution from the broad family of distributions, fit parameters and use the models for failure analysis. Professor Weibull received the Gold Medal in 1972 from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers for his pioneering work in fracture, fatigue and reliability. U. S. Air Force funded Professor Weibull’s research through 1975. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 30 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
History of Weibull Analysis • • • The Weibull distribution was originally developed by Fisher and Tippet in 1928 as an asymptotic extreme value distribution. Professor Weibull derived the distribution in 1939 from analysis of material breaking strength. Waloddi Weibull (1887 -1979) graduated from the Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm in 1924 and earned his doctorate in physics from the University of Uppsalla in 1932. Weibull worked in the Royal Swedish Coast Guard studying the effects of underwater explosions and the lifetime of components especially metallurgical failures. Weibull produced his landmark paper in 1951, “A Statistical Distribution Function of Wide Applicability, ” Journal of Applied Mechanics, 18, 293297. Professor Weibull proposed to analyze life data by selecting a suitable distribution from the broad family of distributions, fit parameters and use the models for failure analysis. Professor Weibull received the Gold Medal in 1972 from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers for his pioneering work in fracture, fatigue and reliability. U. S. Air Force funded Professor Weibull’s research through 1975. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 30 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
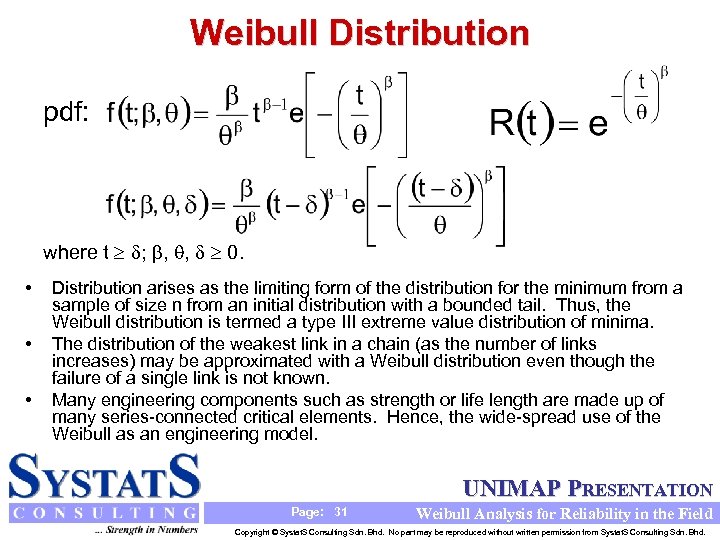 Weibull Distribution pdf: where t ; , , 0. • • • Distribution arises as the limiting form of the distribution for the minimum from a sample of size n from an initial distribution with a bounded tail. Thus, the Weibull distribution is termed a type III extreme value distribution of minima. The distribution of the weakest link in a chain (as the number of links increases) may be approximated with a Weibull distribution even though the failure of a single link is not known. Many engineering components such as strength or life length are made up of many series-connected critical elements. Hence, the wide-spread use of the Weibull as an engineering model. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 31 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Weibull Distribution pdf: where t ; , , 0. • • • Distribution arises as the limiting form of the distribution for the minimum from a sample of size n from an initial distribution with a bounded tail. Thus, the Weibull distribution is termed a type III extreme value distribution of minima. The distribution of the weakest link in a chain (as the number of links increases) may be approximated with a Weibull distribution even though the failure of a single link is not known. Many engineering components such as strength or life length are made up of many series-connected critical elements. Hence, the wide-spread use of the Weibull as an engineering model. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 31 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
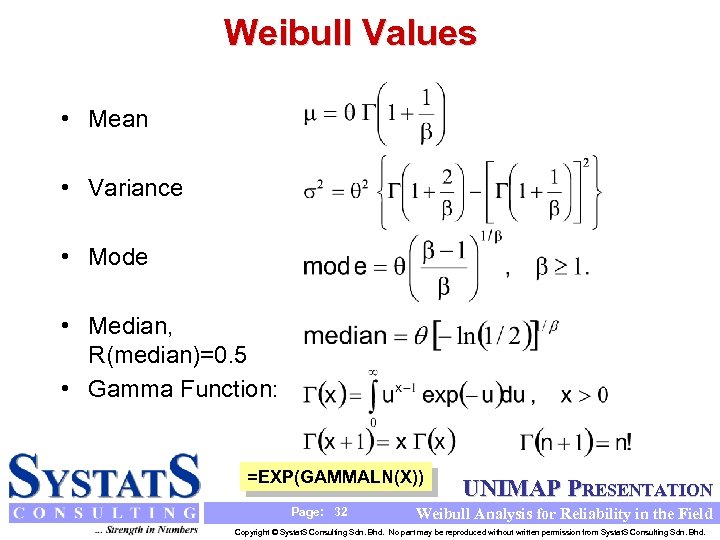 Weibull Values • Mean • Variance • Mode • Median, R(median)=0. 5 • Gamma Function: =EXP(GAMMALN(X)) Page: 32 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Weibull Values • Mean • Variance • Mode • Median, R(median)=0. 5 • Gamma Function: =EXP(GAMMALN(X)) Page: 32 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
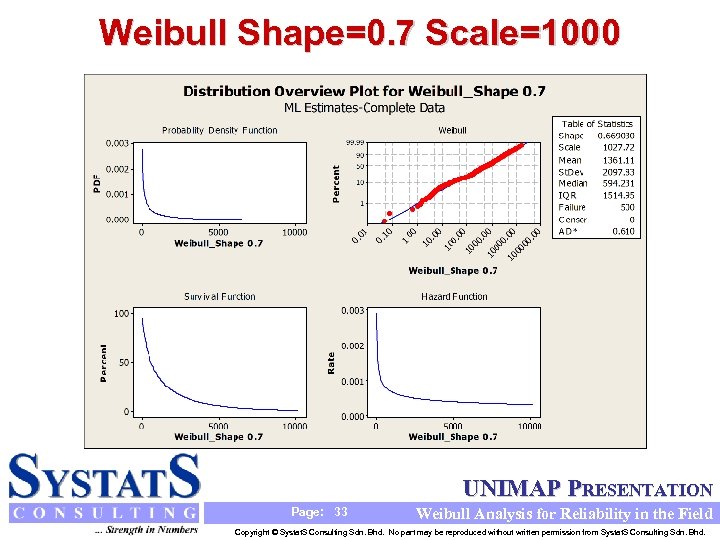 Weibull Shape=0. 7 Scale=1000 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 33 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Weibull Shape=0. 7 Scale=1000 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 33 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
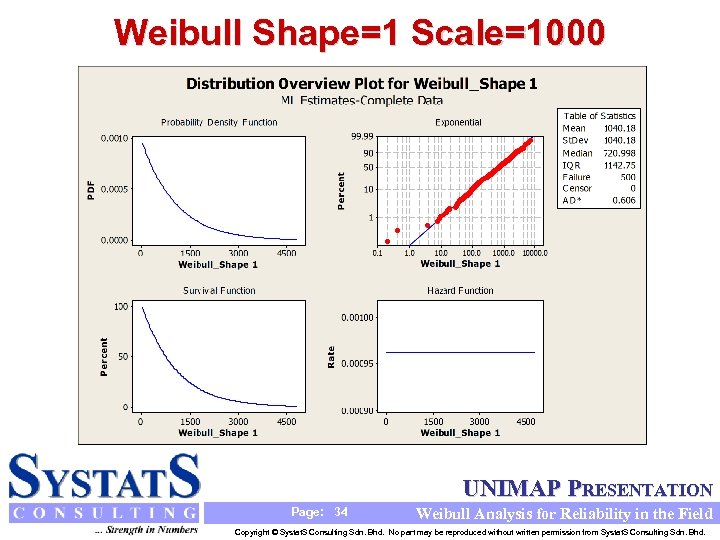 Weibull Shape=1 Scale=1000 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 34 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Weibull Shape=1 Scale=1000 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 34 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
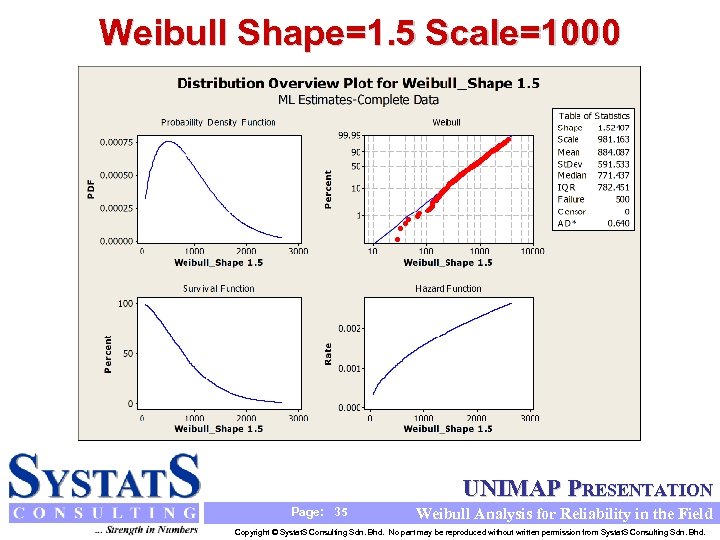 Weibull Shape=1. 5 Scale=1000 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 35 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Weibull Shape=1. 5 Scale=1000 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 35 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
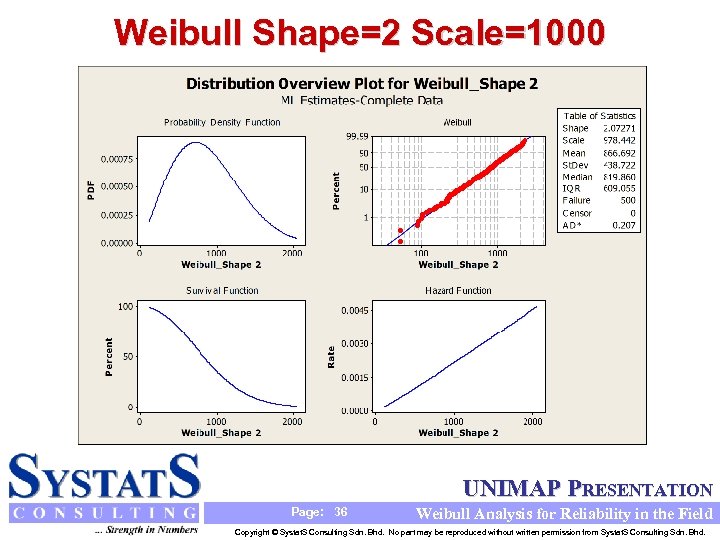 Weibull Shape=2 Scale=1000 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 36 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Weibull Shape=2 Scale=1000 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 36 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
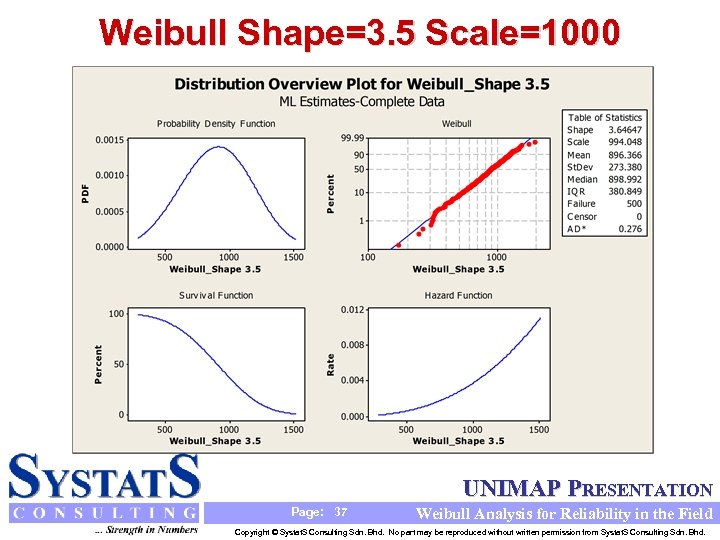 Weibull Shape=3. 5 Scale=1000 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 37 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Weibull Shape=3. 5 Scale=1000 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 37 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
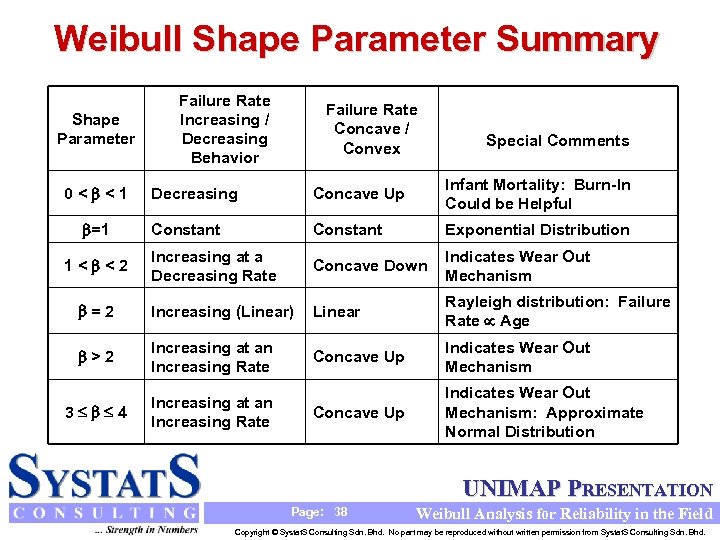 Weibull Shape Parameter Summary Shape Parameter Failure Rate Increasing / Decreasing Behavior Failure Rate Concave / Convex Special Comments Decreasing Concave Up Infant Mortality: Burn-In Could be Helpful Constant Exponential Distribution Increasing at a Decreasing Rate Concave Down Indicates Wear Out Mechanism =2 Increasing (Linear) Linear Rayleigh distribution: Failure Rate Age >2 Increasing at an Increasing Rate Concave Up Indicates Wear Out Mechanism 3 4 Increasing at an Increasing Rate Concave Up Indicates Wear Out Mechanism: Approximate Normal Distribution 0< <1 =1 1< <2 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 38 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Weibull Shape Parameter Summary Shape Parameter Failure Rate Increasing / Decreasing Behavior Failure Rate Concave / Convex Special Comments Decreasing Concave Up Infant Mortality: Burn-In Could be Helpful Constant Exponential Distribution Increasing at a Decreasing Rate Concave Down Indicates Wear Out Mechanism =2 Increasing (Linear) Linear Rayleigh distribution: Failure Rate Age >2 Increasing at an Increasing Rate Concave Up Indicates Wear Out Mechanism 3 4 Increasing at an Increasing Rate Concave Up Indicates Wear Out Mechanism: Approximate Normal Distribution 0< <1 =1 1< <2 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 38 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
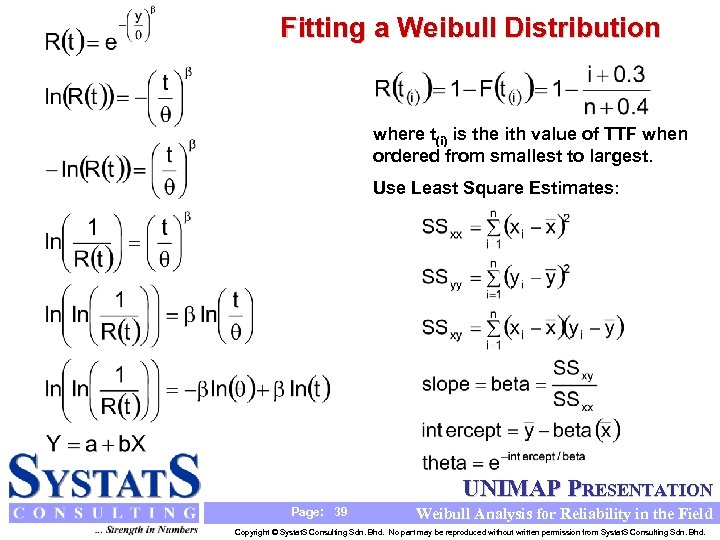 Fitting a Weibull Distribution where t(i) is the ith value of TTF when ordered from smallest to largest. Use Least Square Estimates: UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 39 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Fitting a Weibull Distribution where t(i) is the ith value of TTF when ordered from smallest to largest. Use Least Square Estimates: UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 39 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 What Can You Do with the Weibull Fit? • • • Calculate Design Life Calculate Warranty Costs Set Reliability Growth Goals Recommend Burn-In Set PM Schedules Set Spare Parts Levels UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 40 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
What Can You Do with the Weibull Fit? • • • Calculate Design Life Calculate Warranty Costs Set Reliability Growth Goals Recommend Burn-In Set PM Schedules Set Spare Parts Levels UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 40 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
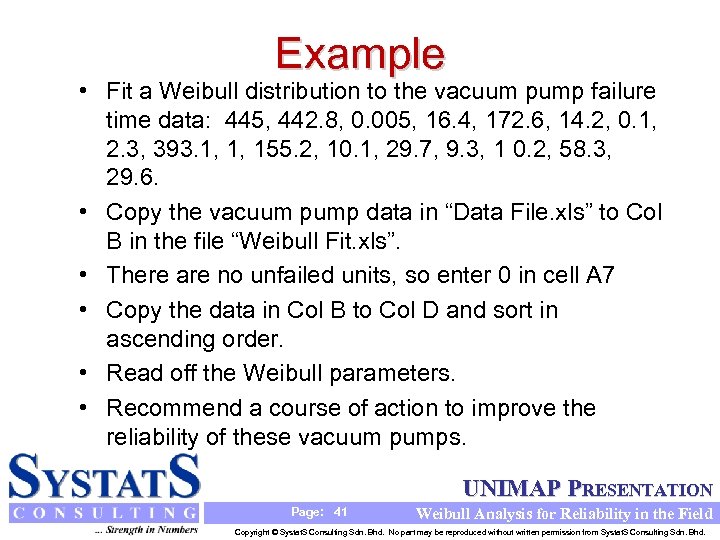 Example • Fit a Weibull distribution to the vacuum pump failure time data: 445, 442. 8, 0. 005, 16. 4, 172. 6, 14. 2, 0. 1, 2. 3, 393. 1, 1, 155. 2, 10. 1, 29. 7, 9. 3, 1 0. 2, 58. 3, 29. 6. • Copy the vacuum pump data in “Data File. xls” to Col B in the file “Weibull Fit. xls”. • There are no unfailed units, so enter 0 in cell A 7 • Copy the data in Col B to Col D and sort in ascending order. • Read off the Weibull parameters. • Recommend a course of action to improve the reliability of these vacuum pumps. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 41 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Example • Fit a Weibull distribution to the vacuum pump failure time data: 445, 442. 8, 0. 005, 16. 4, 172. 6, 14. 2, 0. 1, 2. 3, 393. 1, 1, 155. 2, 10. 1, 29. 7, 9. 3, 1 0. 2, 58. 3, 29. 6. • Copy the vacuum pump data in “Data File. xls” to Col B in the file “Weibull Fit. xls”. • There are no unfailed units, so enter 0 in cell A 7 • Copy the data in Col B to Col D and sort in ascending order. • Read off the Weibull parameters. • Recommend a course of action to improve the reliability of these vacuum pumps. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 41 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
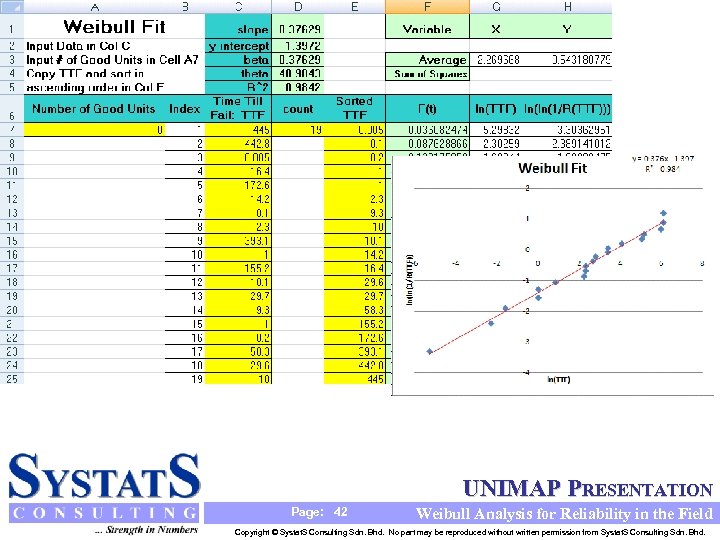 UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 42 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 42 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
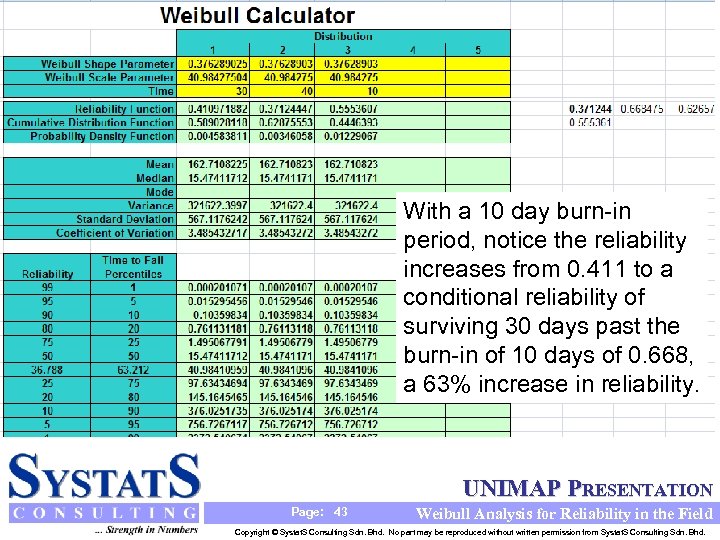 With a 10 day burn-in period, notice the reliability increases from 0. 411 to a conditional reliability of surviving 30 days past the burn-in of 10 days of 0. 668, a 63% increase in reliability. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 43 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
With a 10 day burn-in period, notice the reliability increases from 0. 411 to a conditional reliability of surviving 30 days past the burn-in of 10 days of 0. 668, a 63% increase in reliability. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 43 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
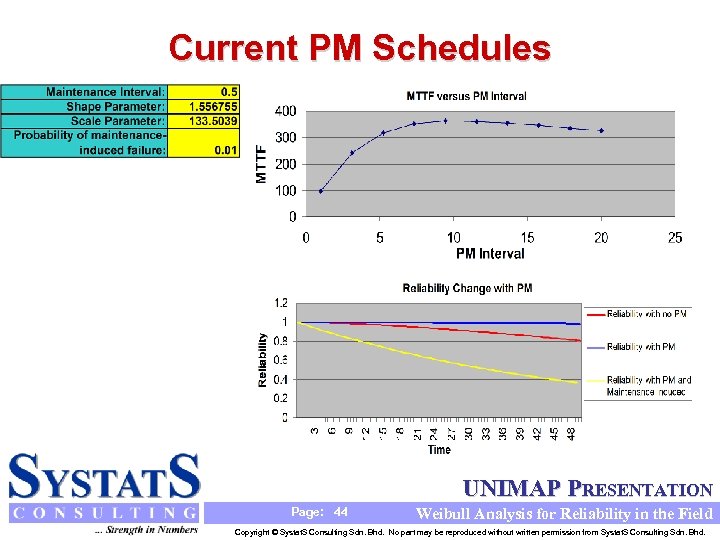 Current PM Schedules UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 44 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Current PM Schedules UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 44 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
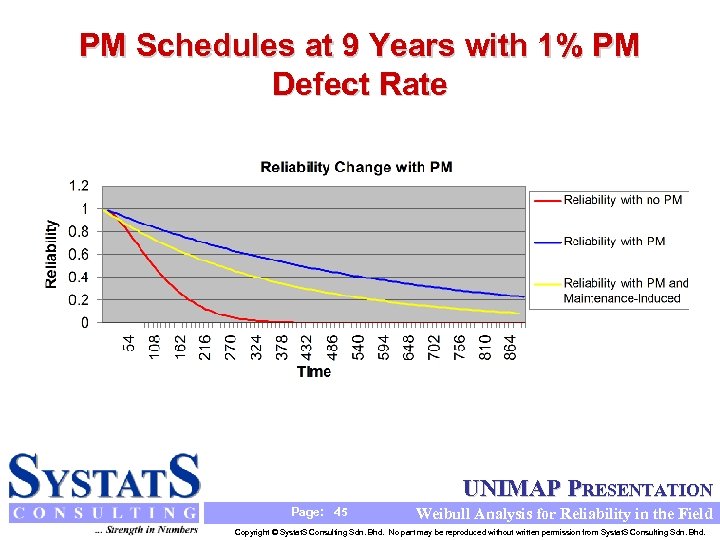 PM Schedules at 9 Years with 1% PM Defect Rate UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 45 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
PM Schedules at 9 Years with 1% PM Defect Rate UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 45 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
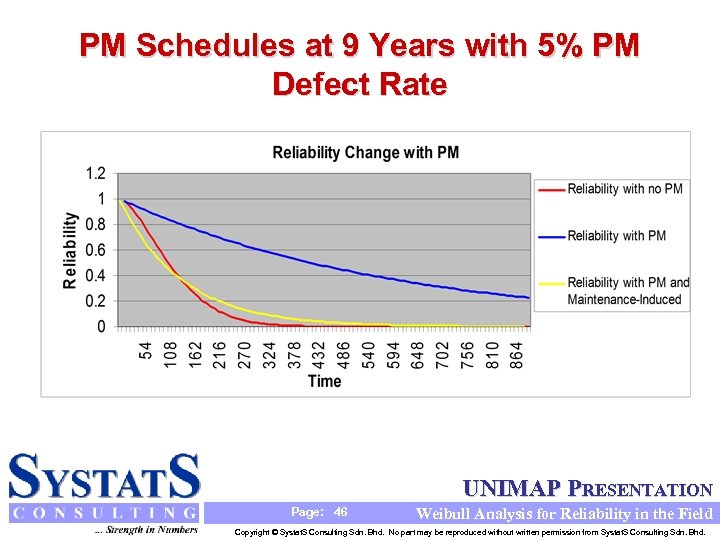 PM Schedules at 9 Years with 5% PM Defect Rate UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 46 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
PM Schedules at 9 Years with 5% PM Defect Rate UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 46 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
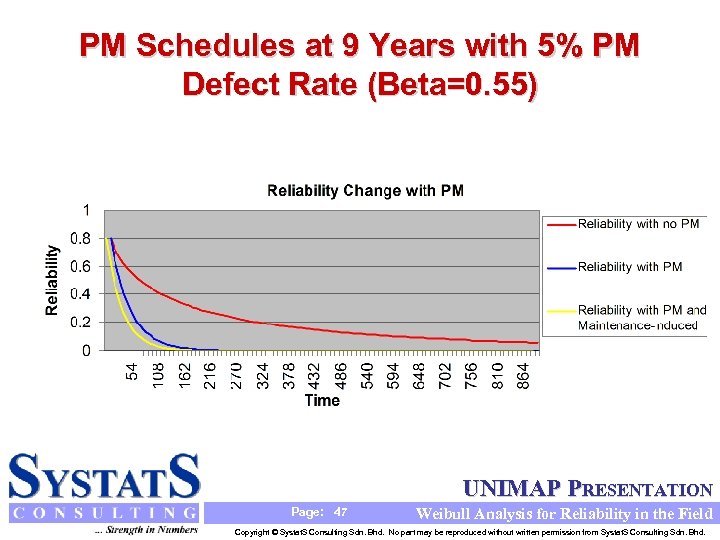 PM Schedules at 9 Years with 5% PM Defect Rate (Beta=0. 55) UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 47 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
PM Schedules at 9 Years with 5% PM Defect Rate (Beta=0. 55) UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 47 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 Summary: Applications of Reliability • Improvement – System, Component or Process Design: Series vs Parallel, Redundancy, Stand-by Systems – Reliability Growth Testing / FMEA – Burn-In Testing • Characterization – Product Testing / Accelerated Life Testing – Reliability Demonstration for Qualification & Dispositioning – Design Life & Reliability Allocation: Setting Component Reliability Goals to Support Overall Product Reliability Goals – Economic Analysis: Warranty Costs • Control – Matrix Monitors – Maintainability & Availability: PM Schedules, Spare Part Analysis, Repair vs Replace Decisions UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 48 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Summary: Applications of Reliability • Improvement – System, Component or Process Design: Series vs Parallel, Redundancy, Stand-by Systems – Reliability Growth Testing / FMEA – Burn-In Testing • Characterization – Product Testing / Accelerated Life Testing – Reliability Demonstration for Qualification & Dispositioning – Design Life & Reliability Allocation: Setting Component Reliability Goals to Support Overall Product Reliability Goals – Economic Analysis: Warranty Costs • Control – Matrix Monitors – Maintainability & Availability: PM Schedules, Spare Part Analysis, Repair vs Replace Decisions UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 48 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 Exercises 1. The time to fail for a fluorescent light in an office building is Weibull( =1, =320 days) given by R(t) = exp[-t/320] with t in days. a) Find the design life for 95% reliability. b) Suppose a warranty of 30 days is planned to be offered. What fraction of lights will fail this warranty period? c) If the cost of a warranty failure is RM 20. 00, find the expected cost per unit for a failure. d) What does the parameter need to be in order for the design life to equal 30 days? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 49 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Exercises 1. The time to fail for a fluorescent light in an office building is Weibull( =1, =320 days) given by R(t) = exp[-t/320] with t in days. a) Find the design life for 95% reliability. b) Suppose a warranty of 30 days is planned to be offered. What fraction of lights will fail this warranty period? c) If the cost of a warranty failure is RM 20. 00, find the expected cost per unit for a failure. d) What does the parameter need to be in order for the design life to equal 30 days? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 49 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 Exercises 2. Suppose the reliability function for a certain turbine blade is Weibull( =0. 5, =10000 days) given by R(t) = exp[-(t/10000)0. 5] with t in days. a) Find the reliability after 365 days. b) Find the design life for 95% reliability. c) Suppose a burn-in of 150 days is planned. Calculate P(T>365+150). Calculate P(T>150). d) The company who supplies the blades would like to offer a 365 day warranty. It needs the reliability 365 days after any burn-in to be at least 90%. Compute the conditional probability that the blade will survive 365+150 days given that it has survived 150 days. Hint: P(T>365+150 | T>150) = P({T>365+150} {T>150}) / P(T>150) = P(T>365+150)/ P(T>150). Can this burn-in achieve a 90% reliability at a warranty period of 365 days? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 50 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Exercises 2. Suppose the reliability function for a certain turbine blade is Weibull( =0. 5, =10000 days) given by R(t) = exp[-(t/10000)0. 5] with t in days. a) Find the reliability after 365 days. b) Find the design life for 95% reliability. c) Suppose a burn-in of 150 days is planned. Calculate P(T>365+150). Calculate P(T>150). d) The company who supplies the blades would like to offer a 365 day warranty. It needs the reliability 365 days after any burn-in to be at least 90%. Compute the conditional probability that the blade will survive 365+150 days given that it has survived 150 days. Hint: P(T>365+150 | T>150) = P({T>365+150} {T>150}) / P(T>150) = P(T>365+150)/ P(T>150). Can this burn-in achieve a 90% reliability at a warranty period of 365 days? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 50 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 Exercises 3. Fit a Weibull distribution to the rubber seal failure time data in months. There are 52 other seals currently in use which have not failed. a) b) c) d) Copy the seal data in “Weibull Fit. xls: sheet: Rubber Seal TTF” to Cells B 7: B 33 in the file “Weibull Fit. xls: sheet: Weibull Fit”. Input the number of good units into cell A 7 of “Weibull Fit. xls: sheet: Weibull Fit”. Copy the data in Col B to Col D and sort in ascending order. What is the Weibull shape parameter? What is the Weibull scale parameter? Is there a wear-out mechanism or infant mortality mechanism for these seals? What is the design life for this rubber seal? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 51 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Exercises 3. Fit a Weibull distribution to the rubber seal failure time data in months. There are 52 other seals currently in use which have not failed. a) b) c) d) Copy the seal data in “Weibull Fit. xls: sheet: Rubber Seal TTF” to Cells B 7: B 33 in the file “Weibull Fit. xls: sheet: Weibull Fit”. Input the number of good units into cell A 7 of “Weibull Fit. xls: sheet: Weibull Fit”. Copy the data in Col B to Col D and sort in ascending order. What is the Weibull shape parameter? What is the Weibull scale parameter? Is there a wear-out mechanism or infant mortality mechanism for these seals? What is the design life for this rubber seal? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 51 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
![Exercises 4. Show that the median of the Weibull distribution is median= [-ln(1 -1/2)]1/. Exercises 4. Show that the median of the Weibull distribution is median= [-ln(1 -1/2)]1/.](https://present5.com/presentation/712c1621dab936dc090172d1c787bead/image-52.jpg) Exercises 4. Show that the median of the Weibull distribution is median= [-ln(1 -1/2)]1/. 5. A set of 16 fuel pumps are put on test with 16 failures: 0. 01, 0. 3, 0. 4, 2. 0, 2. 1, 4. 6, 18. 6, 20. 1, 28. 4, 32. 9, 59. 4, 310. 4, 345. 3, 786. 2, 885. 7, 890. 0. a) Fit a Weibull distribution and find the fitted shape and scale parameters. b) What is the reliability at the end of a 50 day warranty period? c) Calculate the warranty cost for an average repair cost of $30. 00 and warranty period of 50 days. e) If a 10 day burn-in is made on the fuel pumps, then the reliability would be calculated using conditional probability as R( 50|10) = P( t>50 | t>10 ) = P( t>50 and t>10 )/P( t>10 ) = P( t>50 )/P( t>10 ) = R(50)/R(10). What is the conditional reliability by using a burn-in period of 10 hours and find the decrease in warranty costs. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 52 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Exercises 4. Show that the median of the Weibull distribution is median= [-ln(1 -1/2)]1/. 5. A set of 16 fuel pumps are put on test with 16 failures: 0. 01, 0. 3, 0. 4, 2. 0, 2. 1, 4. 6, 18. 6, 20. 1, 28. 4, 32. 9, 59. 4, 310. 4, 345. 3, 786. 2, 885. 7, 890. 0. a) Fit a Weibull distribution and find the fitted shape and scale parameters. b) What is the reliability at the end of a 50 day warranty period? c) Calculate the warranty cost for an average repair cost of $30. 00 and warranty period of 50 days. e) If a 10 day burn-in is made on the fuel pumps, then the reliability would be calculated using conditional probability as R( 50|10) = P( t>50 | t>10 ) = P( t>50 and t>10 )/P( t>10 ) = P( t>50 )/P( t>10 ) = R(50)/R(10). What is the conditional reliability by using a burn-in period of 10 hours and find the decrease in warranty costs. UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 52 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
 Lab Exercise • Take two different diameter wires. Bend each diameter wire and count the number of bends until breakage. Take at least 20 observations of breakage counts for each wire diameter. • Fit a Weibull distribution for each diameter type. • Are the two shape parameters different? Which diameter wire has the larger MTTF? Why? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 53 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.
Lab Exercise • Take two different diameter wires. Bend each diameter wire and count the number of bends until breakage. Take at least 20 observations of breakage counts for each wire diameter. • Fit a Weibull distribution for each diameter type. • Are the two shape parameters different? Which diameter wire has the larger MTTF? Why? UNIMAP PRESENTATION Page: 53 Weibull Analysis for Reliability in the Field Copyright © Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd. No part may be reproduced without written permission from Systat. S Consulting Sdn. Bhd.


