f8849870d81a6e0fa63ac9223ec59791.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
s IP Network Engineering Challenges Dr. Thomas Bauschert Senior Consultant Network Planning and Design Siemens AG, München Email: thomas. bauschert@icn. siemens. de IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 1

s Outline • Network Architecture • IP Traffic Specification • IP Network Dimensioning • IP Traffic Engineering and Qo. S Provisioning • Further important Engineering Issues • Special Topic: MPLS - Diff. Serv: Combination of Traffic Engineering and Qo. S Provisioning IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 2
s Network Architecture IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 3
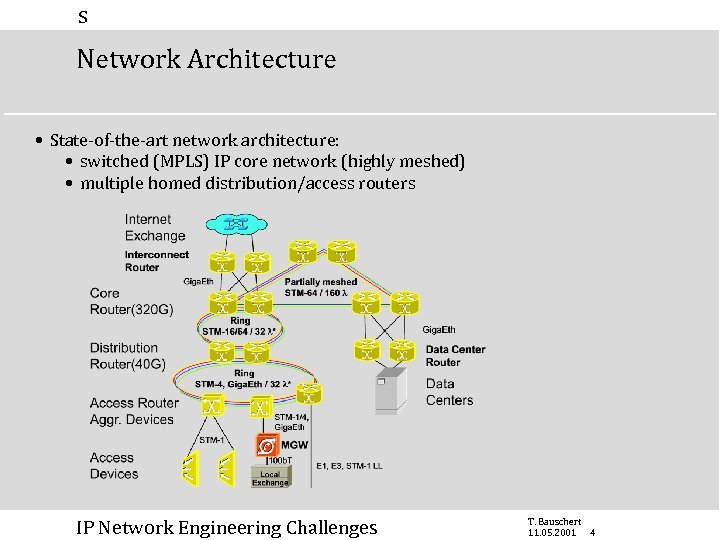
s Network Architecture • State-of-the-art network architecture: • switched (MPLS) IP core network (highly meshed) • multiple homed distribution/access routers IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 4
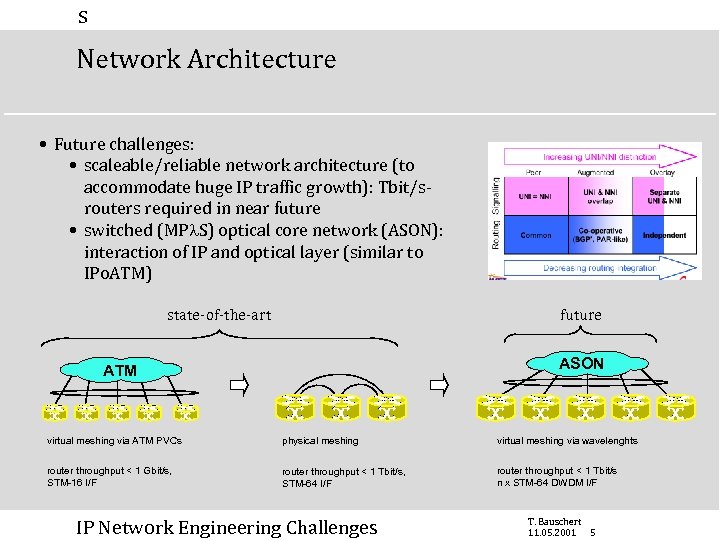
s Network Architecture • Future challenges: • scaleable/reliable network architecture (to accommodate huge IP traffic growth): Tbit/srouters required in near future • switched (MP S) optical core network (ASON): interaction of IP and optical layer (similar to IPo. ATM) state-of-the-art future ASON ATM virtual meshing via ATM PVCs physical meshing virtual meshing via wavelenghts router throughput < 1 Gbit/s, STM-16 I/F router throughput < 1 Tbit/s, STM-64 I/F router throughput < 1 Tbit/s n x STM-64 DWDM I/F IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 5

s IP Traffic Specification IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 6
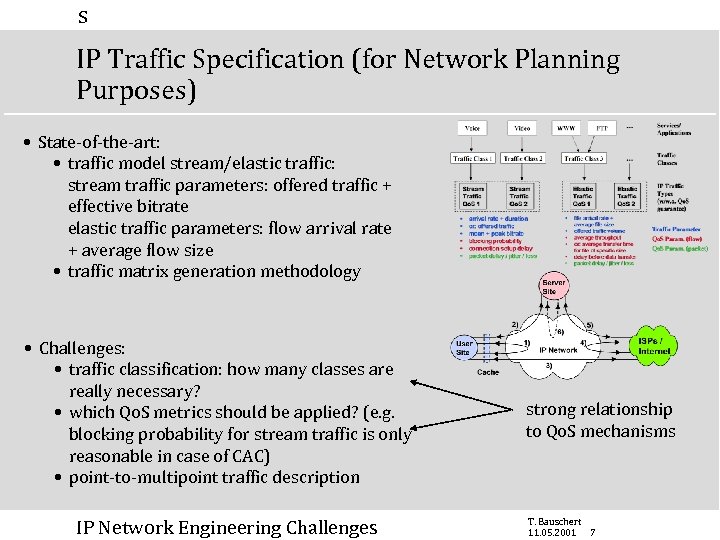
s IP Traffic Specification (for Network Planning Purposes) • State-of-the-art: • traffic model stream/elastic traffic: stream traffic parameters: offered traffic + effective bitrate elastic traffic parameters: flow arrival rate + average flow size • traffic matrix generation methodology • Challenges: • traffic classification: how many classes are really necessary? • which Qo. S metrics should be applied? (e. g. blocking probability for stream traffic is only reasonable in case of CAC) • point-to-multipoint traffic description IP Network Engineering Challenges strong relationship to Qo. S mechanisms T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 7
s IP Network Dimensioning IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 8
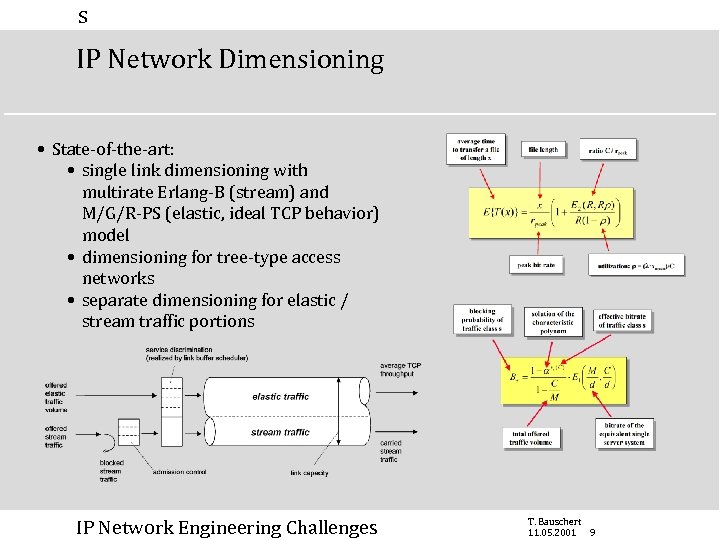
s IP Network Dimensioning • State-of-the-art: • single link dimensioning with multirate Erlang-B (stream) and M/G/R-PS (elastic, ideal TCP behavior) model • dimensioning for tree-type access networks • separate dimensioning for elastic / stream traffic portions IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 9
s IP Network Dimensioning • Challenges: • link dimensioning model improvements: - dimensioning formula for short flows - M/G/R-PS extension for multiple rpeak - consideration of Qo. S mechanisms and multiple Qo. S levels • network dimensioning algorithm (similar to the well-known unified algorithm for PSTN and ATM networks) with following features: - integrated (IGP) routing optimization - consideration of constraints imposed by TE and Qo. S mechanisms like MPLS, OMP, Diff. Serv - multiple load period dimensioning - point-to-any dimensioning (for Diff. Serv networks) - consideration of restoration capabilities (e. g. via MPLS) - dimensioning for multiple Qo. S metrics • integration of dimensioning algorithm and TE system in automated planning and engineering system IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 10

s IP Traffic Engineering and Qo. S Provisioning IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 11
s IP Traffic Engineering and Qo. S Provisioning • State-of-the-art: • separate application of Traffic Engineering and Qo. S mechanisms (multipath routing (OMP), MPLS LSP adaption, Diff. Serv, Int. Serv) in IP networks • Challenges: • performance evaluation of TE / Qo. S mechanisms • use of TE for fast load adaption and restoration • development of optimum TE control algorithm (objectives/constraints of TE? ) • information exchange/interaction of TE mechanism and routing • combination of different mechanisms: MPLS-OMP, MPLS-DS - requires protocol enhancements > new IETF drafts - driver: search for optimum tradeoff between overprovisioning and complexity - strong relationship to SLA formulation - will admission control be really neccessary? • end-to-end Qo. S provisioning: reasonable scenarios IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 12

s Further important Engineering Issues IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 13
s Further important Engineering Issues • Optimization tasks concerning routing protocols: • IGP (OSPF, ISIS) design / optimization rules • EGP (BGP-4) design / optimization rules (e. g. application and # of route reflectors, confederations etc. ) • traffic induced by routing protocol • performance evaluation of routing protocols • Optimization of Data Center (server site) locations • Engineering of Data Centers IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 14

s Special Topic: MPLS-Diff. Serv* *partially taken from MPLS 2000 Conference material IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 15
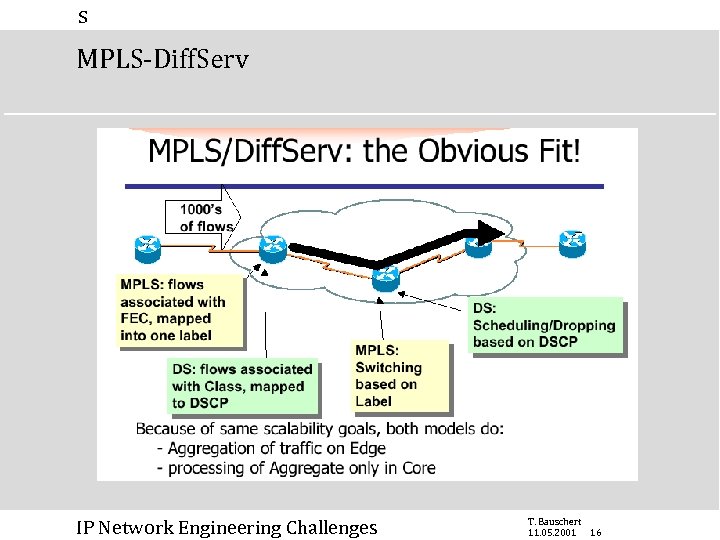
s MPLS-Diff. Serv IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 16
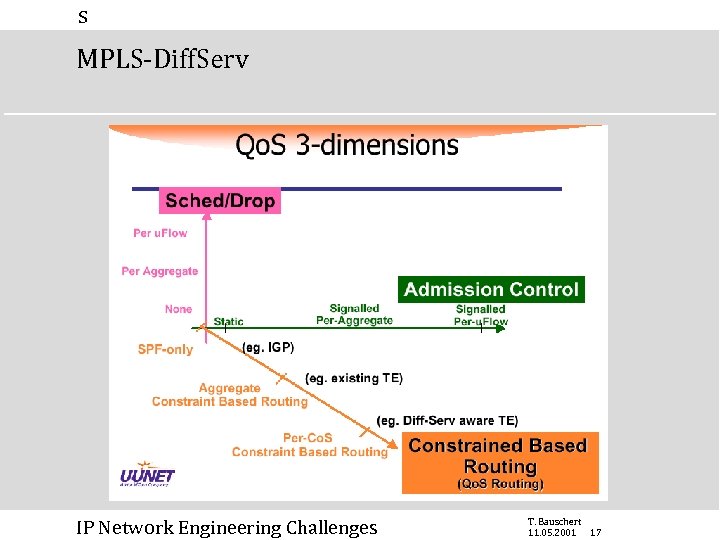
s MPLS-Diff. Serv IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 17
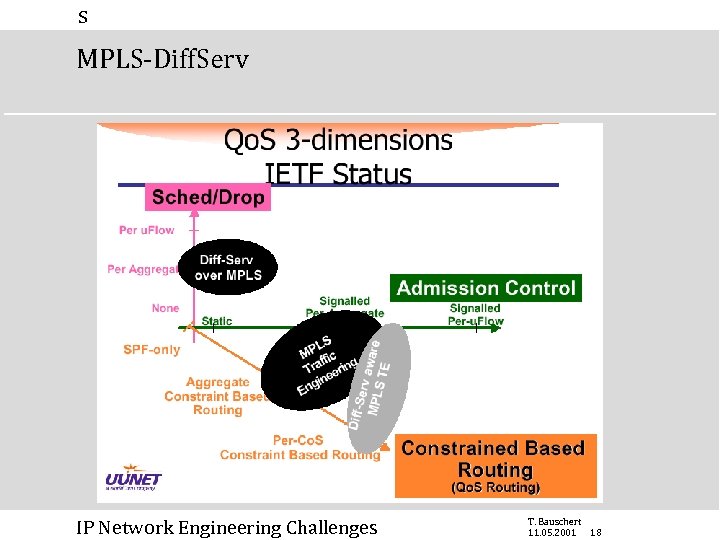
s MPLS-Diff. Serv IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 18
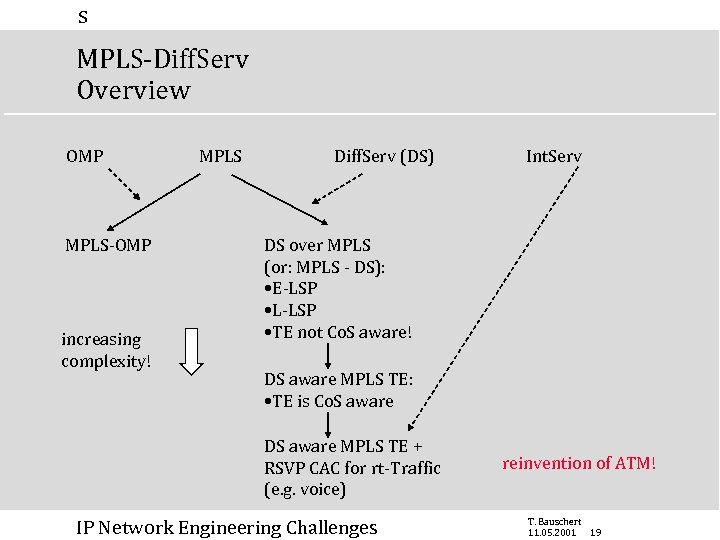
s MPLS-Diff. Serv Overview OMP MPLS-OMP increasing complexity! MPLS Diff. Serv (DS) Int. Serv DS over MPLS (or: MPLS - DS): • E-LSP • L-LSP • TE not Co. S aware! DS aware MPLS TE: • TE is Co. S aware DS aware MPLS TE + RSVP CAC for rt-Traffic (e. g. voice) IP Network Engineering Challenges reinvention of ATM! T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 19

s MPLS-Diff. Serv IETF Drafts MPLS TE: • “Requirements for Traffic Engineering Over MPLS” RFC 2702, Informational RFC • “RSVP-TE: Extensions to RSVP for LSP Tunnels” draft-ietf-mpls-rsvp-lsp-tunnel-07. txt, Aug 2000 • “Constraint-Based LSP Setup using LDP” draft-ietf-mpls-cr-ldp-04. txt, Jul 2000 • “Extensions to ISIS for TE” draft-ietf-isis-traffic-03. txt, Sept 2000 • “TE extensions to OSPF” draft-katz-yeung-ospf-traffic-03. txt, Oct 2000 DS over MPLS: • “MPLS Support of Diff-Serv” draft-ietf-mpls-diff-ext-07. txt, Aug 2000 DS aware MPLS TE: • “Requirements for support of Diff-Serv-aware MPLS Traffic Engineering” draft-lefaucheur-diff-te-reqts-00. txt, Jul 2000 • “Extensions to IS-IS, OSPF, RSVP and CR-LDP for support of Diff-Serv-aware MPLS TE” draft-lefaucheur-diff-te-ext-00. txt, Jul 2000 IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 20
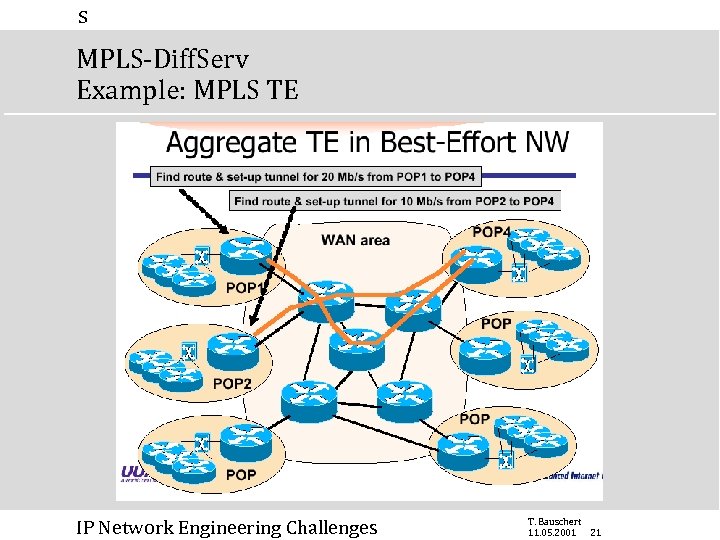
s MPLS-Diff. Serv Example: MPLS TE IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 21
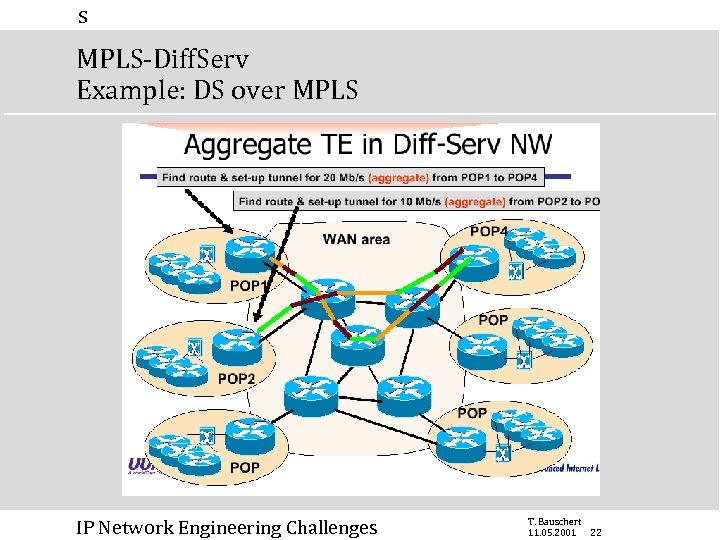
s MPLS-Diff. Serv Example: DS over MPLS IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 22
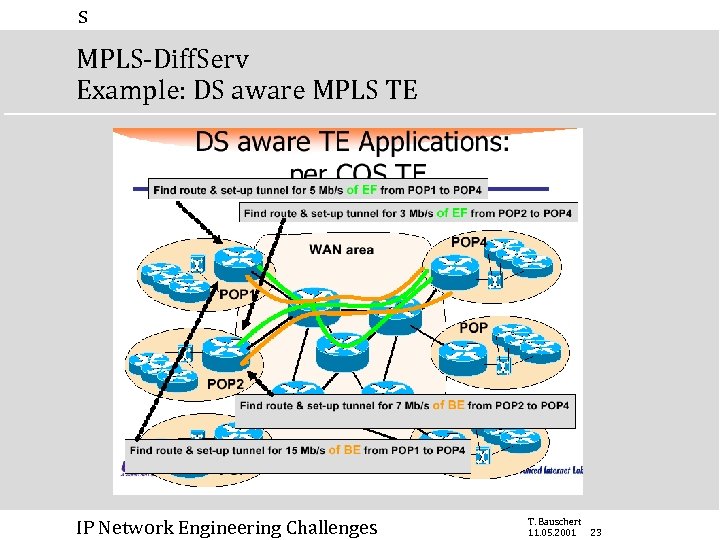
s MPLS-Diff. Serv Example: DS aware MPLS TE IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 23
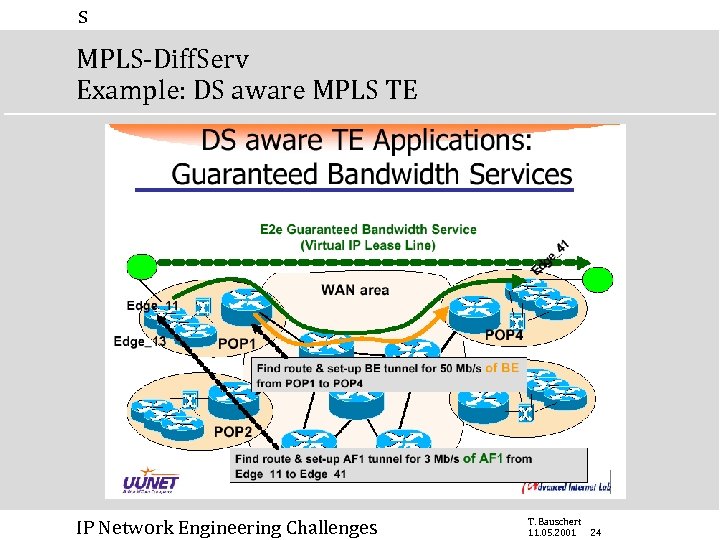
s MPLS-Diff. Serv Example: DS aware MPLS TE IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 24
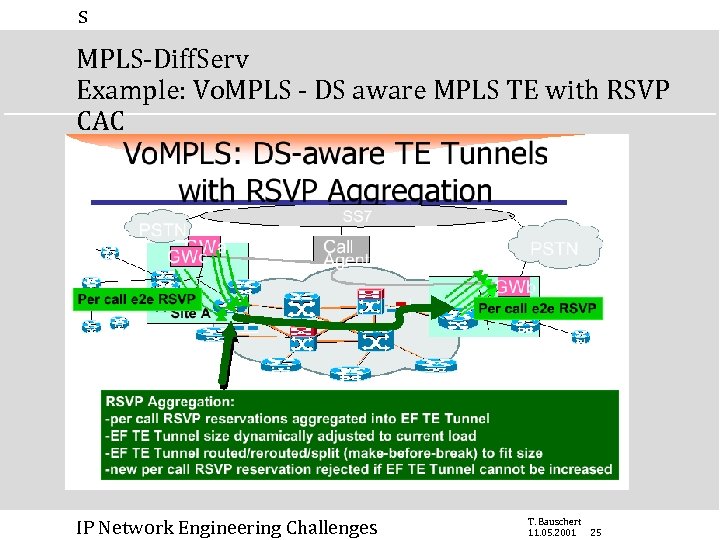
s MPLS-Diff. Serv Example: Vo. MPLS - DS aware MPLS TE with RSVP CAC IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 25
s MPLS-Diff. Serv Vo. MPLS: DS aware MPLS TE with RSVP CAC n “ultimate Qo. S” solution for Vo. MPLS: n Qo. S never degrades n automatic/dynamic traffic engineering of voice (exceeds today’s TDM TE capabilities) n n n excess calls get rejected if/when EF-capacity exceeded traffic patterns do not have to be known before This level of sophistication is only useful in some environments n Under construction at IETF IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 26
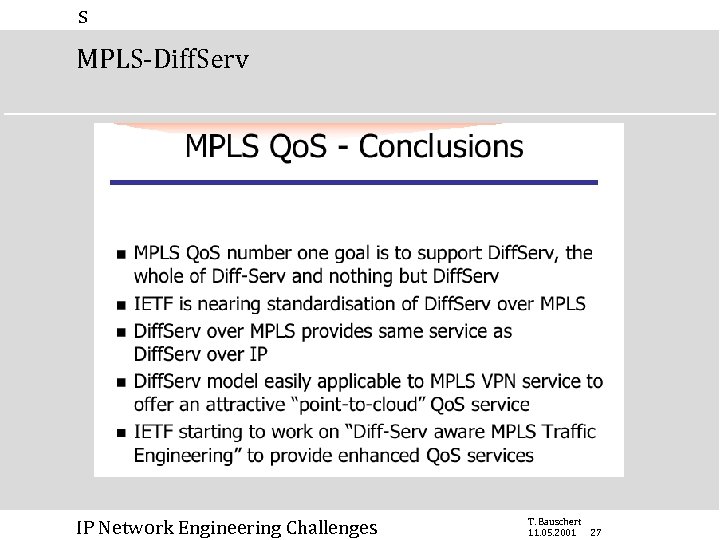
s MPLS-Diff. Serv IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 27
s Additional Slides IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 28
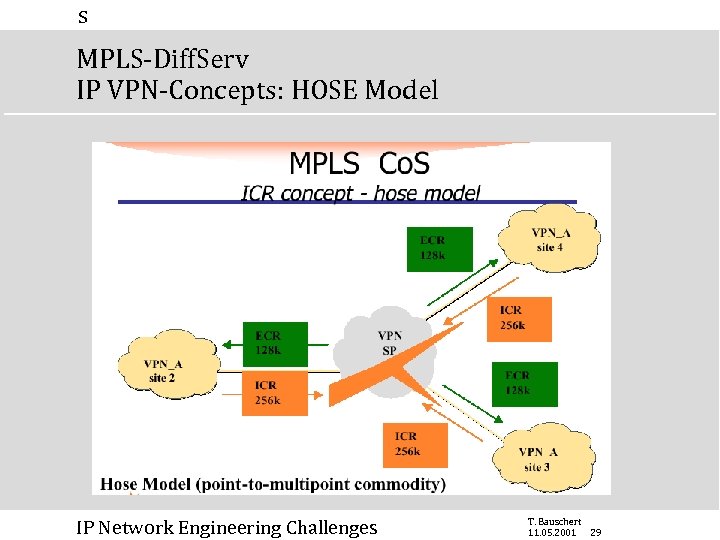
s MPLS-Diff. Serv IP VPN-Concepts: HOSE Model IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 29
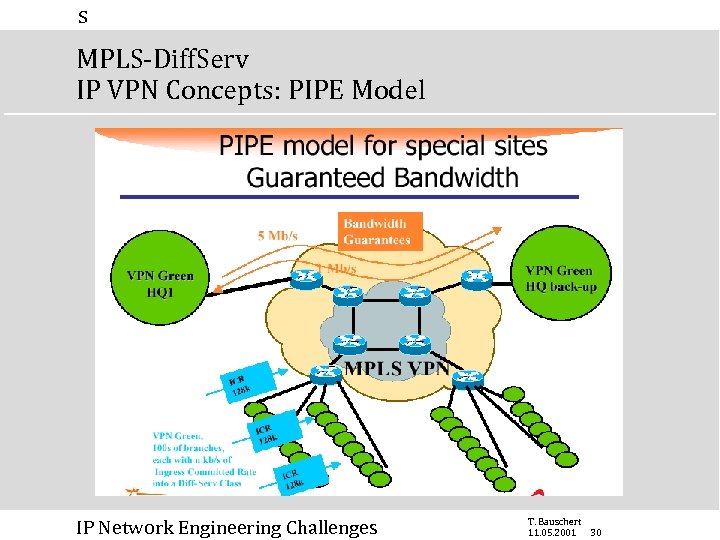
s MPLS-Diff. Serv IP VPN Concepts: PIPE Model IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 30
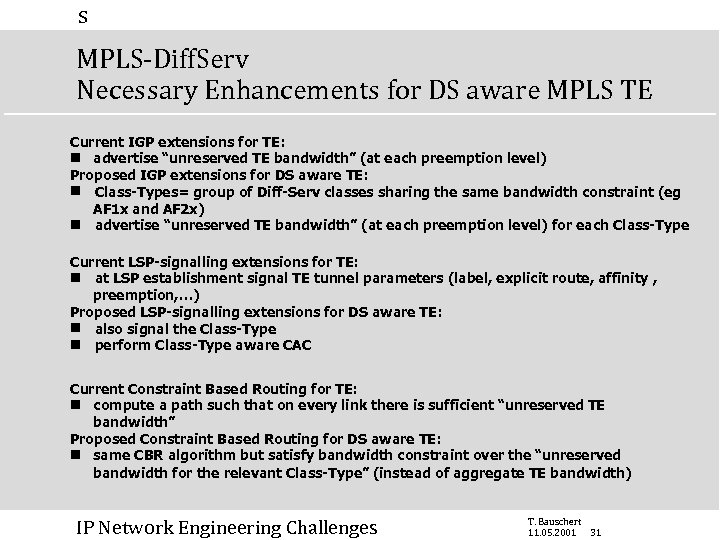
s MPLS-Diff. Serv Necessary Enhancements for DS aware MPLS TE Current IGP extensions for TE: n advertise “unreserved TE bandwidth” (at each preemption level) Proposed IGP extensions for DS aware TE: n Class-Types= group of Diff-Serv classes sharing the same bandwidth constraint (eg AF 1 x and AF 2 x) n advertise “unreserved TE bandwidth” (at each preemption level) for each Class-Type Current LSP-signalling extensions for TE: n at LSP establishment signal TE tunnel parameters (label, explicit route, affinity , preemption, …) Proposed LSP-signalling extensions for DS aware TE: n also signal the Class-Type n perform Class-Type aware CAC Current Constraint Based Routing for TE: n compute a path such that on every link there is sufficient “unreserved TE bandwidth” Proposed Constraint Based Routing for DS aware TE: n same CBR algorithm but satisfy bandwidth constraint over the “unreserved bandwidth for the relevant Class-Type” (instead of aggregate TE bandwidth) IP Network Engineering Challenges T. Bauschert 11. 05. 2001 31
f8849870d81a6e0fa63ac9223ec59791.ppt