4c042b3ea354637282fe567d1f793abd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 S 8 CG 2 The student will analyze the role of the legislative branch in Georgia state government. a. Explain the qualifications, term, election, and duties of members of the General Assembly. b. Describe the organization of the General Assembly, with emphasis on leadership and the committee system. c. Trace the steps in the legislative process for a bill to become a law in Georgia. 1
S 8 CG 2 The student will analyze the role of the legislative branch in Georgia state government. a. Explain the qualifications, term, election, and duties of members of the General Assembly. b. Describe the organization of the General Assembly, with emphasis on leadership and the committee system. c. Trace the steps in the legislative process for a bill to become a law in Georgia. 1
 Essential. Questions. What does the Legislative Branch do for Georgia? 1. What are the qualification, terms, and duties of the General Assembly? 2. What is the role of the General Assembly? 3. To what extent does the Legislative Branch influence our state government? Click to See Pictures of the Georgia Capitol 2
Essential. Questions. What does the Legislative Branch do for Georgia? 1. What are the qualification, terms, and duties of the General Assembly? 2. What is the role of the General Assembly? 3. To what extent does the Legislative Branch influence our state government? Click to See Pictures of the Georgia Capitol 2
 State Government: The Legislative Branch In Georgia, our legislative branch is called the General. Assembly. . General Assembly The General Assembly is The General made up ofis made Assembly two parts. up of two parts. The Role of the General Assembly is to write and pass laws that are just for the state of The General Assembly writes and passes laws that are just for the Georgia. state of Georgia.
State Government: The Legislative Branch In Georgia, our legislative branch is called the General. Assembly. . General Assembly The General Assembly is The General made up ofis made Assembly two parts. up of two parts. The Role of the General Assembly is to write and pass laws that are just for the state of The General Assembly writes and passes laws that are just for the Georgia. state of Georgia.
 State Government: The Legislative Branch HOW DO LEGISLATORS GAIN THEIR POWER? In Georgia, our legislative branch is called the • Members of the General Assembly. are elected by the House and the Senate voters in their district. Theq Each district contains the same number of people. General Assembly is made up of two parts. WHAT DOES THEIR WORK YEAR LOOK LIKE? • 40 Day Session, beginning on 2 nd Monday in January • Sitting on committees (year round) The General Assembly writes and passes laws that are just for the state of Georgia.
State Government: The Legislative Branch HOW DO LEGISLATORS GAIN THEIR POWER? In Georgia, our legislative branch is called the • Members of the General Assembly. are elected by the House and the Senate voters in their district. Theq Each district contains the same number of people. General Assembly is made up of two parts. WHAT DOES THEIR WORK YEAR LOOK LIKE? • 40 Day Session, beginning on 2 nd Monday in January • Sitting on committees (year round) The General Assembly writes and passes laws that are just for the state of Georgia.
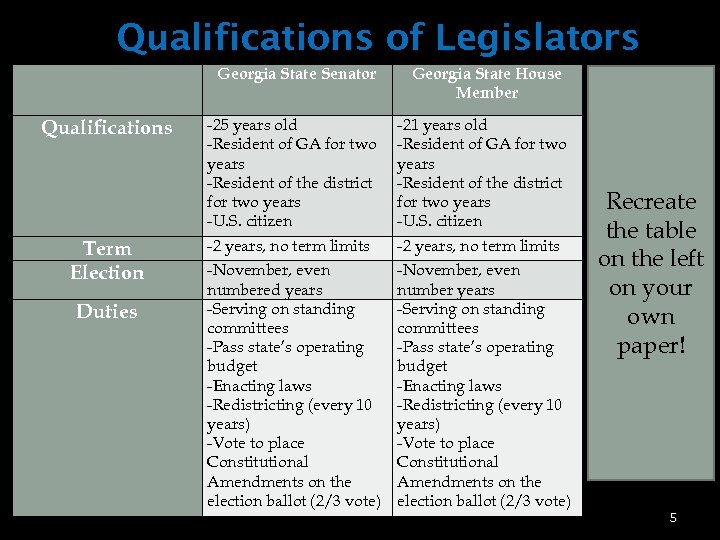 Qualifications of Legislators Qualifications . Term Election Duties Georgia State Senator Georgia State House Member -25 years old -Resident of GA for two years -Resident of the district for two years -U. S. citizen -21 years old -Resident of GA for two years -Resident of the district for two years -U. S. citizen -2 years, no term limits -November, even numbered years -Serving on standing committees -Pass state’s operating budget -Enacting laws -Redistricting (every 10 years) -Vote to place Constitutional Amendments on the election ballot (2/3 vote) -2 years, no term limits -November, even number years -Serving on standing committees -Pass state’s operating budget -Enacting laws -Redistricting (every 10 years) -Vote to place Constitutional Amendments on the election ballot (2/3 vote) Recreate the table on the left on your own paper! 5
Qualifications of Legislators Qualifications . Term Election Duties Georgia State Senator Georgia State House Member -25 years old -Resident of GA for two years -Resident of the district for two years -U. S. citizen -21 years old -Resident of GA for two years -Resident of the district for two years -U. S. citizen -2 years, no term limits -November, even numbered years -Serving on standing committees -Pass state’s operating budget -Enacting laws -Redistricting (every 10 years) -Vote to place Constitutional Amendments on the election ballot (2/3 vote) -2 years, no term limits -November, even number years -Serving on standing committees -Pass state’s operating budget -Enacting laws -Redistricting (every 10 years) -Vote to place Constitutional Amendments on the election ballot (2/3 vote) Recreate the table on the left on your own paper! 5
 GEORGIA’s HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES Made up of 180 members Presided over (headed by) the Speaker of the House Elected by all members of the House Historically is a member of the majority party (but doesn’t have to be) 6
GEORGIA’s HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES Made up of 180 members Presided over (headed by) the Speaker of the House Elected by all members of the House Historically is a member of the majority party (but doesn’t have to be) 6
 GEORGIA’s House of Representatives The Majority Party is the political party with the most members in the house. The Minority Party has the fewest members. Majority Leader: responsible for making sure its members vote for the bills & the agenda that the MAJORITY PARTY favors Minority Leader: responsible for making sure its members vote for the bills & the agenda that the MINORITY PARTY favors Floor Leader: promote interest of the Governor on the House floor 7
GEORGIA’s House of Representatives The Majority Party is the political party with the most members in the house. The Minority Party has the fewest members. Majority Leader: responsible for making sure its members vote for the bills & the agenda that the MAJORITY PARTY favors Minority Leader: responsible for making sure its members vote for the bills & the agenda that the MINORITY PARTY favors Floor Leader: promote interest of the Governor on the House floor 7
 GEORGIA’s Senate Made up of 56 members Presided over by the Lieutenant Governor AKA - “President of the Senate” GA’s Lieutenant Governor – Casey Cagle (R) Elected directly by voters therefore can be member of minority party Does NOT have a vote in the Senate 2 nd in charge - President Pro Tempore Leader of Senate’s majority party 8
GEORGIA’s Senate Made up of 56 members Presided over by the Lieutenant Governor AKA - “President of the Senate” GA’s Lieutenant Governor – Casey Cagle (R) Elected directly by voters therefore can be member of minority party Does NOT have a vote in the Senate 2 nd in charge - President Pro Tempore Leader of Senate’s majority party 8
 DIFFERENCES b/w GEORGIA’s SENATE and the HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES For the most part, the two houses operate in much the same. In Georgia, except for two things: the fashion our legislative branch is called General Assembly. 1. Only the H. o. R. can write appropriations (spending) bills 2. The General Only the is made can confirm appointments Assembly Senate byup of two parts. to the executive branch the Governor made Both houses can propose/pass bills and all bills must be approved by BOTH houses before heading The General Assembly writes and passes laws that are just for the to Governor state of Georgia.
DIFFERENCES b/w GEORGIA’s SENATE and the HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES For the most part, the two houses operate in much the same. In Georgia, except for two things: the fashion our legislative branch is called General Assembly. 1. Only the H. o. R. can write appropriations (spending) bills 2. The General Only the is made can confirm appointments Assembly Senate byup of two parts. to the executive branch the Governor made Both houses can propose/pass bills and all bills must be approved by BOTH houses before heading The General Assembly writes and passes laws that are just for the to Governor state of Georgia.
 JOB DESCRIPTION OF PRESIDING OFFICERS (Lieutenant Governor & Speaker of the House) Appoints committees and the chairpersons Assigns bills to committees Can determine order of business Controls debates Rules out proposed amendments to bills Enforces rules for procedure for the General Assemble Controls meeting times Orders roll call votes, if needed 10
JOB DESCRIPTION OF PRESIDING OFFICERS (Lieutenant Governor & Speaker of the House) Appoints committees and the chairpersons Assigns bills to committees Can determine order of business Controls debates Rules out proposed amendments to bills Enforces rules for procedure for the General Assemble Controls meeting times Orders roll call votes, if needed 10
 COMMITTEE SYSTEM Most work for both houses is conducted within the COMMITTEE SYSTEM. Standing Committees: permanent committees with specific focuses (IE: agriculture, education, etc. ) H. O. R. – 36 standing committees SENATE – 26 standing committees Each member of H. O. R & SENATE must serve on at least 2 -3 standing committees Committees have the power to CREATE – AMEND – CHANGE - KILL legislation. 11
COMMITTEE SYSTEM Most work for both houses is conducted within the COMMITTEE SYSTEM. Standing Committees: permanent committees with specific focuses (IE: agriculture, education, etc. ) H. O. R. – 36 standing committees SENATE – 26 standing committees Each member of H. O. R & SENATE must serve on at least 2 -3 standing committees Committees have the power to CREATE – AMEND – CHANGE - KILL legislation. 11
 COMMITTEE SYSTEM FOUR MAIN TYPES OF COMMITTEES: 1. Standing Committees: permanent committees/continue through all legislative sessions 2. Ad Hoc Committees: created for special purposes 3. Joint Committees: made up of members of both the SENATE and H. O. R. 4. Conference Committees: needed when H. O. R. and SENATE create different versions of same bill – members create compromise b/w the two before it becomes bill 12
COMMITTEE SYSTEM FOUR MAIN TYPES OF COMMITTEES: 1. Standing Committees: permanent committees/continue through all legislative sessions 2. Ad Hoc Committees: created for special purposes 3. Joint Committees: made up of members of both the SENATE and H. O. R. 4. Conference Committees: needed when H. O. R. and SENATE create different versions of same bill – members create compromise b/w the two before it becomes bill 12
 VIDEOS Watch the following videos: 1. How a Bill Becomes a Law http: //www. schooltube. com/video/fcde 4 d 15 a 9 276 c 9 a 09 d 3/ 13
VIDEOS Watch the following videos: 1. How a Bill Becomes a Law http: //www. schooltube. com/video/fcde 4 d 15 a 9 276 c 9 a 09 d 3/ 13


