6f5f9ff9aa966384a51f5874975fb78a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 s 10 Security 1
s 10 Security 1
 The Tension z. Security vs. ease of use: the more security measures added, the more difficult a site is to use, and the slower it becomes z. Security vs. desire of individuals to act anonymously 2
The Tension z. Security vs. ease of use: the more security measures added, the more difficult a site is to use, and the slower it becomes z. Security vs. desire of individuals to act anonymously 2
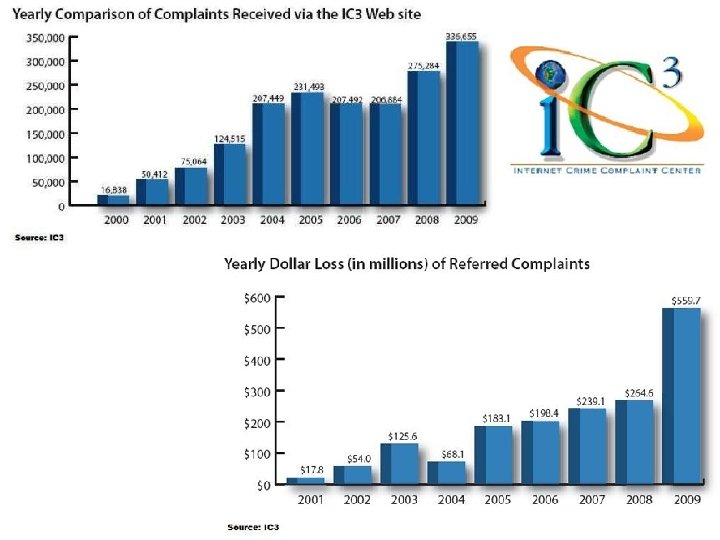
 FBI 2007 INTERNET FRAUD 2009 Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC 3) Cyber Crime up 23% Over $500 million • The highest median dollar losses came from check fraud confidence fraud, and Nigerian (West African 419) "advance fee" scams. 3
FBI 2007 INTERNET FRAUD 2009 Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC 3) Cyber Crime up 23% Over $500 million • The highest median dollar losses came from check fraud confidence fraud, and Nigerian (West African 419) "advance fee" scams. 3
 4
4
 world relies on physical security Ecommerce world - reliance on electronic means to protect data, communications & transactions. THREE TYPES OF SECURITY DIMENSIONS 1. 2. 3. Infrastructure security (hard/software Transactions security (web/moving) Data/information security (message itself) 5
world relies on physical security Ecommerce world - reliance on electronic means to protect data, communications & transactions. THREE TYPES OF SECURITY DIMENSIONS 1. 2. 3. Infrastructure security (hard/software Transactions security (web/moving) Data/information security (message itself) 5
 Do you see a Role for Laws and Public Policy z New laws have granted local and national authorities new tools and mechanisms for identifying, tracing and prosecuting cybercriminals y y y National Infrastructure Protection Center – unit within National Cyber Security Division of Department of Homeland Security whose mission is to identify and combat threats against U. S. technology and telecommunications infrastructure USA Patriot Act Homeland Security Act z Government policies and controls on encryption software 6
Do you see a Role for Laws and Public Policy z New laws have granted local and national authorities new tools and mechanisms for identifying, tracing and prosecuting cybercriminals y y y National Infrastructure Protection Center – unit within National Cyber Security Division of Department of Homeland Security whose mission is to identify and combat threats against U. S. technology and telecommunications infrastructure USA Patriot Act Homeland Security Act z Government policies and controls on encryption software 6
 n n n n n Malicious code (viruses, worms, Trojans) Unwanted programs (spyware, browser parasites) Phishing/identity theft Hacking and cybervandalism Credit card fraud/theft Spoofing (pharming)/spam (junk) Web sites Sniffing Insider attacks Poorly designed server and client software Do. S and d. Do. S attacks
n n n n n Malicious code (viruses, worms, Trojans) Unwanted programs (spyware, browser parasites) Phishing/identity theft Hacking and cybervandalism Credit card fraud/theft Spoofing (pharming)/spam (junk) Web sites Sniffing Insider attacks Poorly designed server and client software Do. S and d. Do. S attacks
 Malicious Code Viruses: Have ability to replicate and spread to other files; most also deliver a “payload” of some sort (destructive or benign); include macro viruses, file-infecting viruses, and script viruses n Worms: Designed to spread from computer to computer n Trojan horse: Appears to be benign, but then does something other than expected n Bots: Can be covertly installed on computer; responds to external commands sent by the attacker n
Malicious Code Viruses: Have ability to replicate and spread to other files; most also deliver a “payload” of some sort (destructive or benign); include macro viruses, file-infecting viruses, and script viruses n Worms: Designed to spread from computer to computer n Trojan horse: Appears to be benign, but then does something other than expected n Bots: Can be covertly installed on computer; responds to external commands sent by the attacker n
 Unwanted Programs n Installed without the user’s informed consent n Browser parasites: Can monitor and change settings of a user’s browser n Adware: Calls for unwanted pop-up ads n Spyware: Can be used to obtain information, such as a user’s keystrokes, e-mail, IMs, etc. Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
Unwanted Programs n Installed without the user’s informed consent n Browser parasites: Can monitor and change settings of a user’s browser n Adware: Calls for unwanted pop-up ads n Spyware: Can be used to obtain information, such as a user’s keystrokes, e-mail, IMs, etc. Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Phishing and Identity Theft n Any deceptive, online attempt by a third party to obtain confidential information for financial gain Most popular type: e-mail scam letter n One of fastest growing forms of e-commerce crime n n Many of you have gotten the “we are upgrading our server or the “I am the wife of Amad who. . ” Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
Phishing and Identity Theft n Any deceptive, online attempt by a third party to obtain confidential information for financial gain Most popular type: e-mail scam letter n One of fastest growing forms of e-commerce crime n n Many of you have gotten the “we are upgrading our server or the “I am the wife of Amad who. . ” Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Hacking and Cybervandalism Hacker: Individual who intends to gain unauthorized access to computer systems Cracker: Hacker with criminal intent (two terms often used interchangeably) Cybervandalism: Intentionally disrupting, defacing or destroying a Web site Types of hackers include: White hats n Black hats n Grey hats n
Hacking and Cybervandalism Hacker: Individual who intends to gain unauthorized access to computer systems Cracker: Hacker with criminal intent (two terms often used interchangeably) Cybervandalism: Intentionally disrupting, defacing or destroying a Web site Types of hackers include: White hats n Black hats n Grey hats n
 ZEUS INTERNATIONAL OPERATION 2007 “WEAPON OF CHOICE” CYBER BANK ROBBERS $70 MILLION BUST OCT 201 CAN BE BOUGHT ON WEB LOSSES TO 200 m SMALL/ MEDIUM BUSINESSES LIMITED PROTECTIONS RUSSIAN AUTHOR A-Z BUSINESS LICENSING AGREEMENTS -TECH SUPPORT – TARGETS SPECIFIC BANKS – CAPTURES YOUR INFO AND SENDS TO SERVER - CAN DISPLAY THEIR PAGE TO ASK FOR MORE INFORMATION
ZEUS INTERNATIONAL OPERATION 2007 “WEAPON OF CHOICE” CYBER BANK ROBBERS $70 MILLION BUST OCT 201 CAN BE BOUGHT ON WEB LOSSES TO 200 m SMALL/ MEDIUM BUSINESSES LIMITED PROTECTIONS RUSSIAN AUTHOR A-Z BUSINESS LICENSING AGREEMENTS -TECH SUPPORT – TARGETS SPECIFIC BANKS – CAPTURES YOUR INFO AND SENDS TO SERVER - CAN DISPLAY THEIR PAGE TO ASK FOR MORE INFORMATION
 YATCHWORLD. COM n Spoofing (Pharming) & Spam (Junk) Web Sites Misrepresenting oneself by using fake e-mail addresses or masquerading as someone else n Threatens integrity of site; authenticity n n Spam (Junk) Web sites n Use domain names similar to legitimate one, redirect traffic to spammer-redirection domains
YATCHWORLD. COM n Spoofing (Pharming) & Spam (Junk) Web Sites Misrepresenting oneself by using fake e-mail addresses or masquerading as someone else n Threatens integrity of site; authenticity n n Spam (Junk) Web sites n Use domain names similar to legitimate one, redirect traffic to spammer-redirection domains
 Other Security Threats tjmax Sniffing: Type of eavesdropping program that monitors information traveling over a network; enables hackers to steal proprietary information from anywhere on a network n Insider jobs: Single largest financial threat n Poorly designed server and client software: Increase in complexity of software programs has contributed to increase is vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit n
Other Security Threats tjmax Sniffing: Type of eavesdropping program that monitors information traveling over a network; enables hackers to steal proprietary information from anywhere on a network n Insider jobs: Single largest financial threat n Poorly designed server and client software: Increase in complexity of software programs has contributed to increase is vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit n
 Do. S and DDo. S Attacks n Denial of service (Do. S) attack n n Hackers flood Web site with useless traffic to inundate and overwhelm network Distributed denial of service (DDo. S) attack n Hackers use numerous computers to attack target network from numerous launch points
Do. S and DDo. S Attacks n Denial of service (Do. S) attack n n Hackers flood Web site with useless traffic to inundate and overwhelm network Distributed denial of service (DDo. S) attack n Hackers use numerous computers to attack target network from numerous launch points
 IS THE THREAT TO NATION’S SECURITY Why did it prove to be so effective against Estonia? What are botnets? Why are they used in DDo. S attacks? ATTACK ON ESTONIA MAY 9, 10 2007 n Denial of service (Do. S) attack n n Hackers flood Web site with useless traffic to inundate and overwhelm network Distributed denial of service (DDo. S) attack n Hackers use numerous computers to attack target network from numerous launch points
IS THE THREAT TO NATION’S SECURITY Why did it prove to be so effective against Estonia? What are botnets? Why are they used in DDo. S attacks? ATTACK ON ESTONIA MAY 9, 10 2007 n Denial of service (Do. S) attack n n Hackers flood Web site with useless traffic to inundate and overwhelm network Distributed denial of service (DDo. S) attack n Hackers use numerous computers to attack target network from numerous launch points
 IT’S A CYBER WAR OUT THERE 45, 000 computers infected by STUXNET AUGUST, 2010 INDUSTRIAL SIEMANS CONTROL COMPUTER INFRASTRUCTURE – POWER, PIPELINES 60% OF COMPUTERS IN IRAN
IT’S A CYBER WAR OUT THERE 45, 000 computers infected by STUXNET AUGUST, 2010 INDUSTRIAL SIEMANS CONTROL COMPUTER INFRASTRUCTURE – POWER, PIPELINES 60% OF COMPUTERS IN IRAN
 DESIGN A SYSTEM TO SEND A SECURE MESSGE z. WHAT ARE YOUR INFRASTRUCTURE NEEDS? z. WHAT DOES THE SOFTWARE DO? z. WHAT TYPES OF SECURITY ARE THERE IN YOUR SYSTEM? z. HOW ARE COMPUTERS LINKED? z. HOW DO YOU KNOW WHO YOU ARE “TALKING” TO? 18
DESIGN A SYSTEM TO SEND A SECURE MESSGE z. WHAT ARE YOUR INFRASTRUCTURE NEEDS? z. WHAT DOES THE SOFTWARE DO? z. WHAT TYPES OF SECURITY ARE THERE IN YOUR SYSTEM? z. HOW ARE COMPUTERS LINKED? z. HOW DO YOU KNOW WHO YOU ARE “TALKING” TO? 18
 SECURTY NEEDS: y. Authentication: y A way to verify user’s identity before payments are made y. Integrity: y. Ensuring that information will not be accidentally or maliciously altered or destroyed, usually during transmission 19
SECURTY NEEDS: y. Authentication: y A way to verify user’s identity before payments are made y. Integrity: y. Ensuring that information will not be accidentally or maliciously altered or destroyed, usually during transmission 19
 SECURTY NEEDS: Encryption: y making messages indecipherable except by those who have an authorized decryption key y. Non-repudiation: y Merchants protection - customer’s unjustifiable denial of placed orders customers protection -against merchants’ unjustifiable denial of payments 20
SECURTY NEEDS: Encryption: y making messages indecipherable except by those who have an authorized decryption key y. Non-repudiation: y Merchants protection - customer’s unjustifiable denial of placed orders customers protection -against merchants’ unjustifiable denial of payments 20
 Securing Channels of Communication z Secure Sockets Layer (SSL): Most common form used to establish a secure negotiated session (client-server session in which URL of requested document, along with contents, is encrypted) Part on customers’ PC – so no special software needed z Secure Electronic Transaction (SET): More complicated comprehensive security protocol provides privacy, authenticity, integrity, repudiation – must install “Digital Wallet” z S-HTTP: Alternative method; provides a secure message-oriented communications protocol designed for use in conjunction with HTTP z Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Allow remote users to securely access internal networks via the Internet, using Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocols 21
Securing Channels of Communication z Secure Sockets Layer (SSL): Most common form used to establish a secure negotiated session (client-server session in which URL of requested document, along with contents, is encrypted) Part on customers’ PC – so no special software needed z Secure Electronic Transaction (SET): More complicated comprehensive security protocol provides privacy, authenticity, integrity, repudiation – must install “Digital Wallet” z S-HTTP: Alternative method; provides a secure message-oriented communications protocol designed for use in conjunction with HTTP z Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Allow remote users to securely access internal networks via the Internet, using Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocols 21
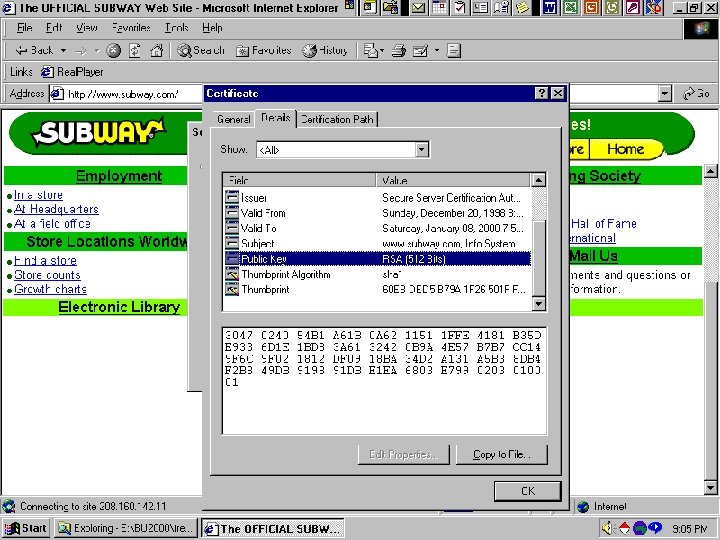
 ENCRYPTON WHAT ARE THE 2 TYPES 1. PRIVATE/SECRET KEY Some believe penetrable. Maybe secure “enoug 2. PUBLIC KEY Most popular algorithm is RSA (Rivest, Shamir and Adelman) Various key sizes (e. g. 1, 024 bits) Most secure - Never known to be broken (to date) 22
ENCRYPTON WHAT ARE THE 2 TYPES 1. PRIVATE/SECRET KEY Some believe penetrable. Maybe secure “enoug 2. PUBLIC KEY Most popular algorithm is RSA (Rivest, Shamir and Adelman) Various key sizes (e. g. 1, 024 bits) Most secure - Never known to be broken (to date) 22
 Digital Envelopes z. Addresses weaknesses of public key encryption (computationally slow, decreases transmission speed, increases processing time) and symmetric key encryption (faster, but more secure) z. Uses symmetric key encryption to encrypt document but public key encryption to encrypt and send symmetric key 23
Digital Envelopes z. Addresses weaknesses of public key encryption (computationally slow, decreases transmission speed, increases processing time) and symmetric key encryption (faster, but more secure) z. Uses symmetric key encryption to encrypt document but public key encryption to encrypt and send symmetric key 23
 Certificate Security Schemes y. Identifying the holder of a public key (Key-Exchange) Issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA) Name : “Dr. Kip” key-Exchange Key : Signature Key : Serial # : 29483756 Other Data : 10236283025273 Class of certificate Dates valid Issuing authority digital signature Expires : 6/18/03 Signed : KB’s Signature 24
Certificate Security Schemes y. Identifying the holder of a public key (Key-Exchange) Issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA) Name : “Dr. Kip” key-Exchange Key : Signature Key : Serial # : 29483756 Other Data : 10236283025273 Class of certificate Dates valid Issuing authority digital signature Expires : 6/18/03 Signed : KB’s Signature 24
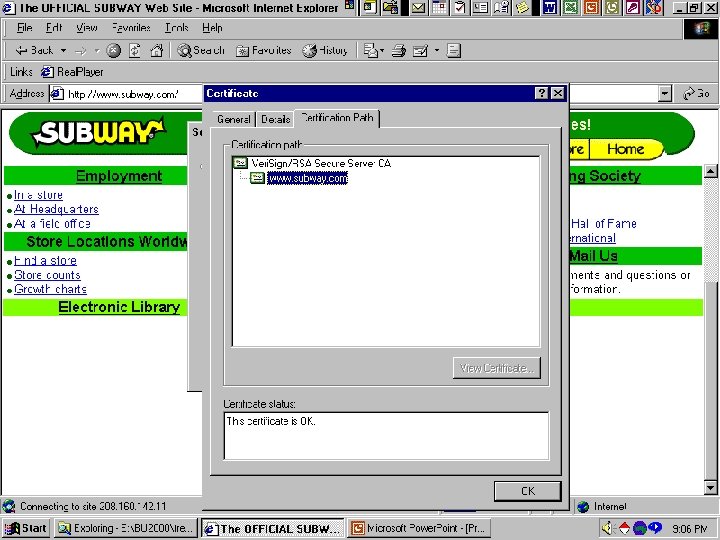
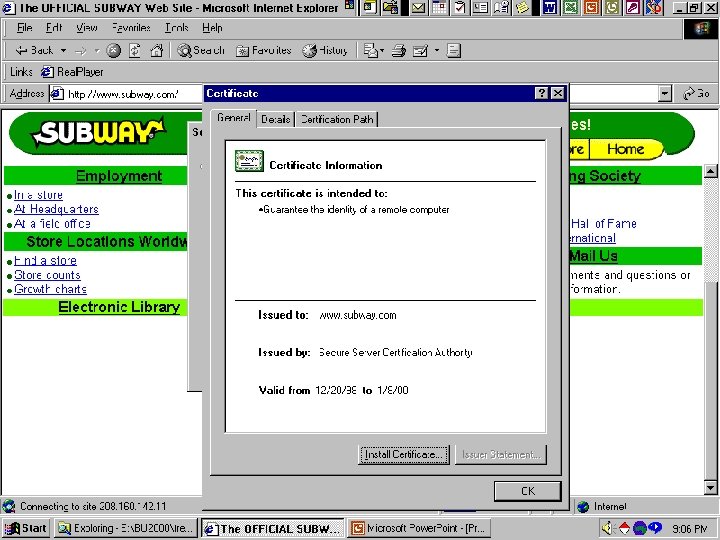
 Digital Certificates & Certifying Authorities y. Digital Certificates x 3 RD Party-Verify holder of a public & private key is who they claim to be z Certifying Authorities (CAs) y. Maintain responsibility for checking user’s identity y. Verifying validity of digital certificates y. Issue digital certificates y. Verify the information creates a certificate that contains the applicant’s public key along with identifying information y. Uses their private key to encrypt certificate and sends the signed certificate to applicant 25
Digital Certificates & Certifying Authorities y. Digital Certificates x 3 RD Party-Verify holder of a public & private key is who they claim to be z Certifying Authorities (CAs) y. Maintain responsibility for checking user’s identity y. Verifying validity of digital certificates y. Issue digital certificates y. Verify the information creates a certificate that contains the applicant’s public key along with identifying information y. Uses their private key to encrypt certificate and sends the signed certificate to applicant 25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29


