bfc3706f55d30981a05eab611bb3aa6c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Ruthenium based non platinum catalysts for oxygen reduction in acid solution Alex Schechter Ariel University Center ISRAEL הכנס ה-7 למקורות אנרגיה מתקדמים 26 January 2011 אוניברסיטת ת"א

Methanol fueled Electric vehicle Fuel cell
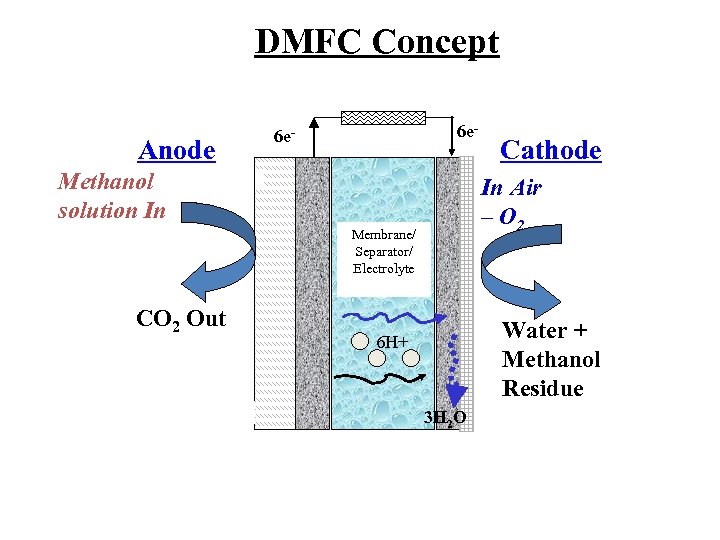
DMFC Concept Anode 6 e- Methanol solution In In Air – O 2 Membrane/ Separator/ Electrolyte CO 2 Out Cathode Water + Methanol Residue 6 H+ 3 H 2 O
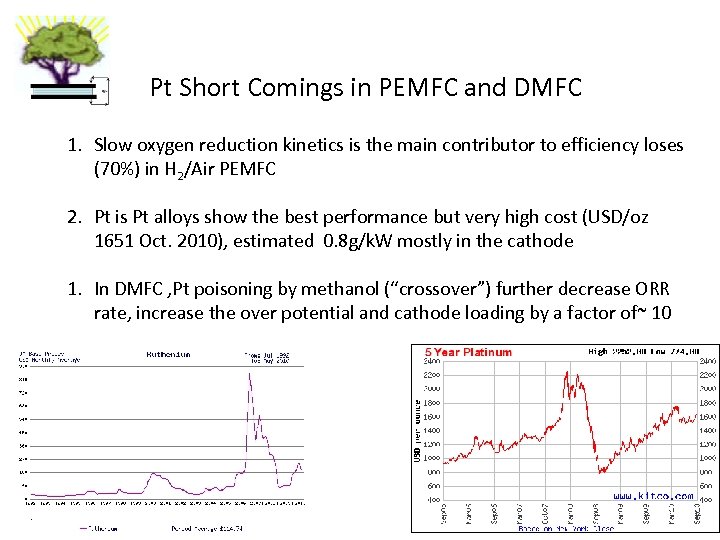
Pt Short Comings in PEMFC and DMFC 1. Slow oxygen reduction kinetics is the main contributor to efficiency loses (70%) in H 2/Air PEMFC 2. Pt is Pt alloys show the best performance but very high cost (USD/oz 1651 Oct. 2010), estimated 0. 8 g/k. W mostly in the cathode 1. In DMFC , Pt poisoning by methanol (“crossover”) further decrease ORR rate, increase the over potential and cathode loading by a factor of~ 10
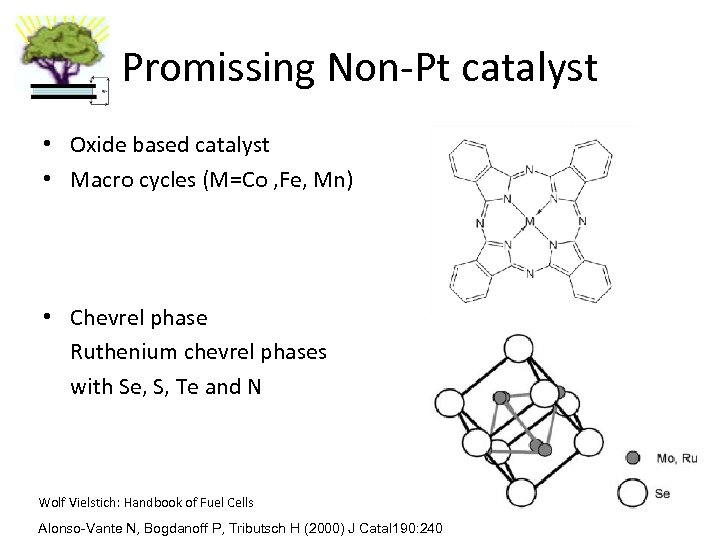
Promissing Non-Pt catalyst • Oxide based catalyst • Macro cycles (M=Co , Fe, Mn) • Chevrel phase Ruthenium chevrel phases with Se, S, Te and N Wolf Vielstich: Handbook of Fuel Cells Alonso-Vante N, Bogdanoff P, Tributsch H (2000) J Catal 190: 240
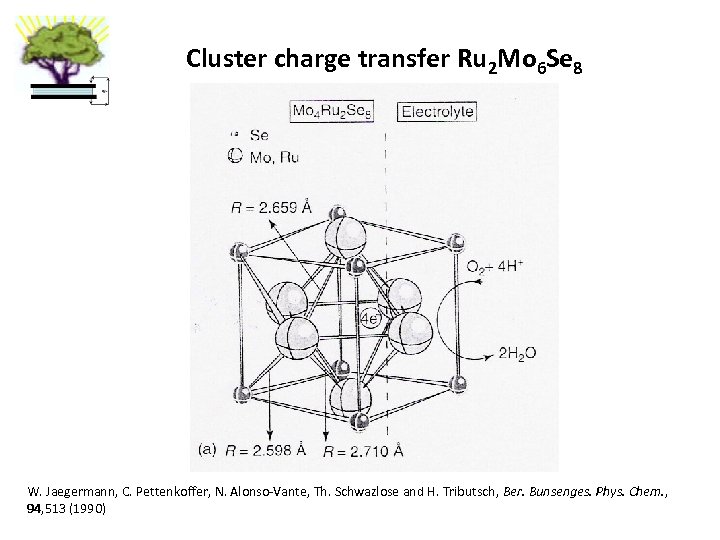
Cluster charge transfer Ru 2 Mo 6 Se 8 W. Jaegermann, C. Pettenkoffer, N. Alonso-Vante, Th. Schwazlose and H. Tributsch, Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. , 94, 513 (1990)
Conventional Synthesis methods of Rux. Ly (L=S, Se, Te) Precursors • Ru 3 CO 12, Ru. Cl 3 • Elemental S/Se/Te powder Methods • Reflux 12 -48 hours in Xylene or ethylene glycol • Thermolysis 1200 -1700ºC
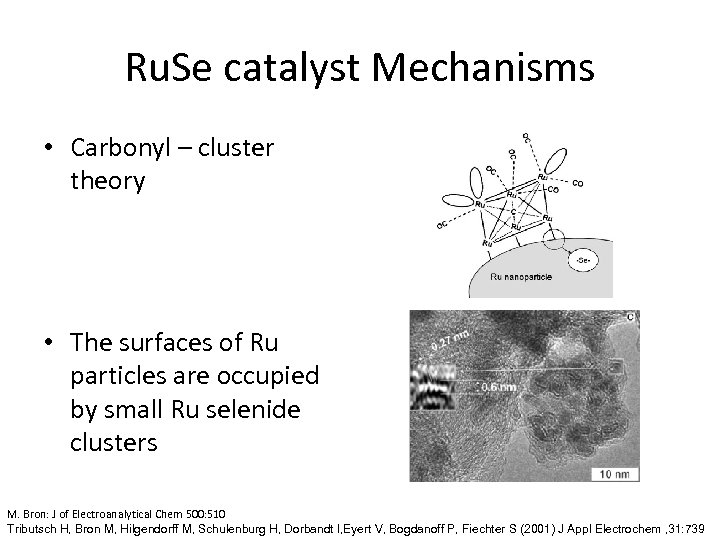
Ru. Se catalyst Mechanisms • Carbonyl – cluster theory • The surfaces of Ru particles are occupied by small Ru selenide clusters M. Bron: J of Electroanalytical Chem 500: 510 Tributsch H, Bron M, Hilgendorff M, Schulenburg H, Dorbandt I, Eyert V, Bogdanoff P, Fiechter S (2001) J Appl Electrochem , 31: 739

Objectives 1. Find an effective method of preparing Rux. Sey 2. Characterize these materials 3. Study oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) on Rux. Sey in aspects related to fuel cells

Microwave Synthesis of Nano-Catalysts C 2 H 4(OH)2 C 2 H 4(OH)O· + H· H· H+ + e. Ru 3+ +3 e- Ru Eo= 0. 703 V H 2 Se. O 3 + 4 H+ + 4 e- Se + 3 H 2 O Eo= 0. 74 V

Electron Microscopy of Rux. Sey HRSEM Ru. Cl 3 : elemental Se powder 2: 1 (molar) TEM
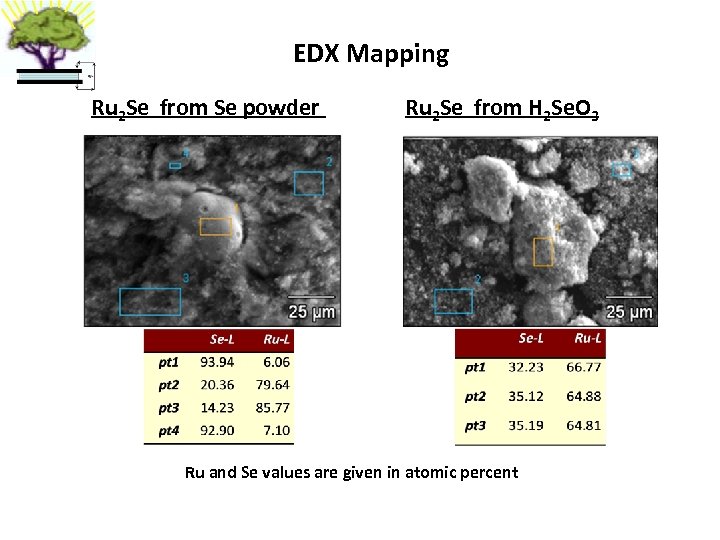
EDX Mapping Ru 2 Se from Se powder Ru 2 Se from H 2 Se. O 3 Ru and Se values are given in atomic percent
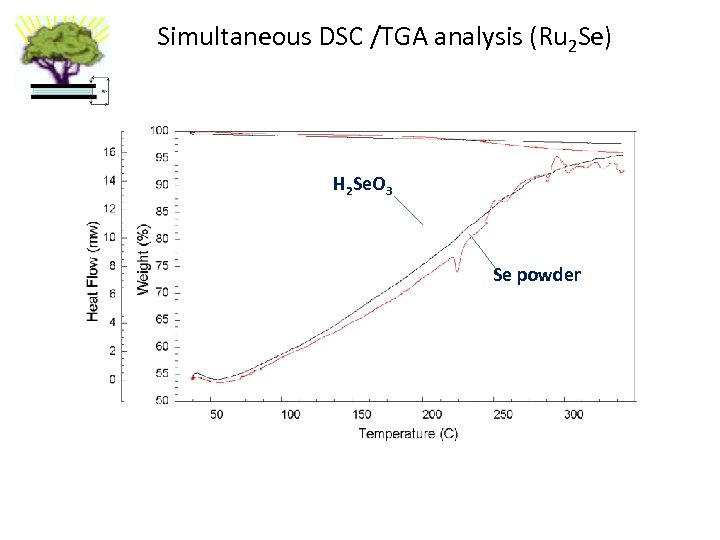
Simultaneous DSC /TGA analysis (Ru 2 Se) H 2 Se. O 3 Se powder
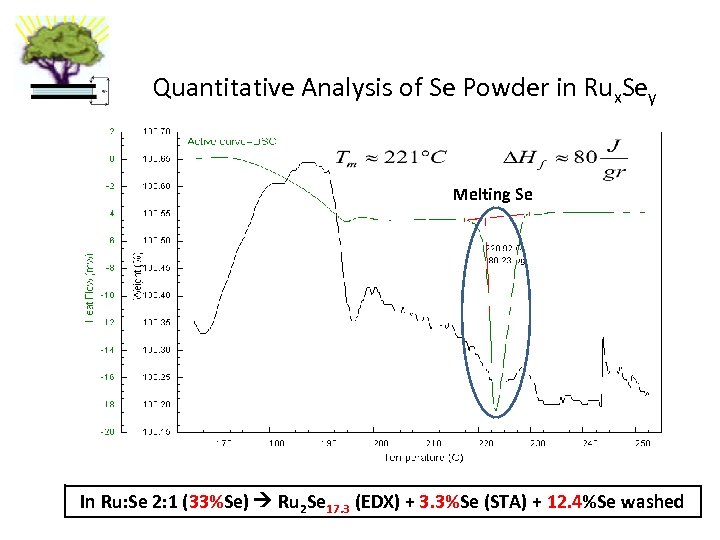
Quantitative Analysis of Se Powder in Rux. Sey Melting Se 3. 3% elemental Se In Ru: Se 2: 1 (33%Se) Ru 2 Se 17. 3 (EDX) + 3. 3%Se (STA) + 12. 4%Se washed
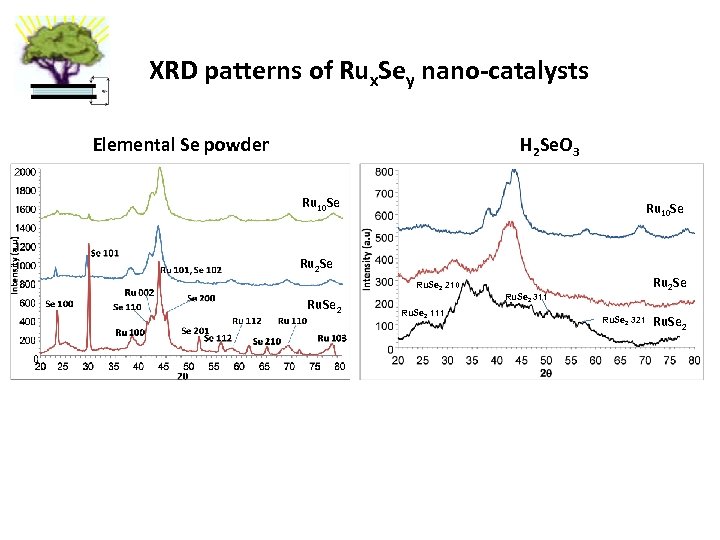
XRD patterns of Rux. Sey nano-catalysts Elemental Se powder H 2 Se. O 3 Ru 10 Se Ru 2 Se Ru. Se 2 210 Ru. Se 2 111 Ru 2 Se Ru. Se 2 311 Ru. Se 2 321 Ru. Se 2
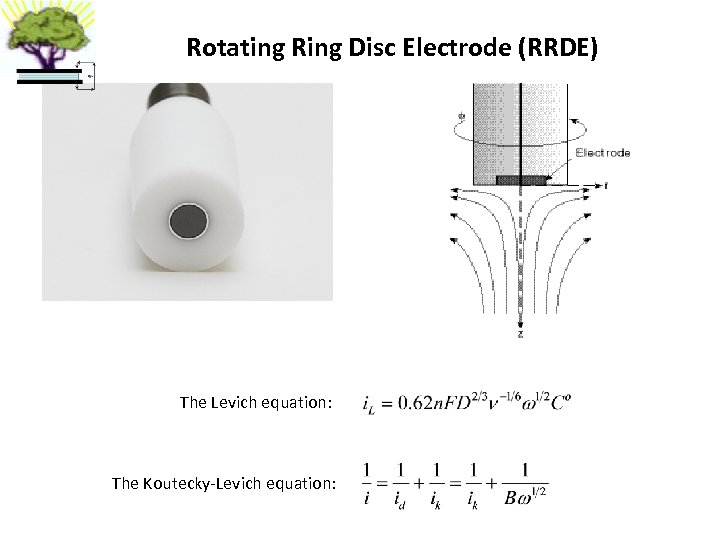
Rotating Ring Disc Electrode (RRDE) The Levich equation: The Koutecky-Levich equation:
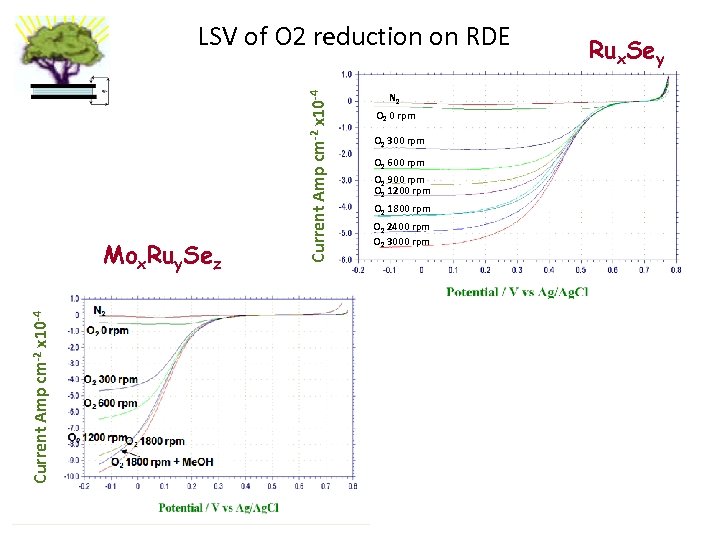
Current Amp cm-2 x 10 -4 Mox. Ruy. Sez Current Amp cm-2 x 10 -4 LSV of O 2 reduction on RDE N 2 O 2 0 rpm O 2 300 rpm O 2 600 rpm O 2 900 rpm O 2 1200 rpm O 2 1800 rpm O 2 2400 rpm O 2 3000 rpm Rux. Sey
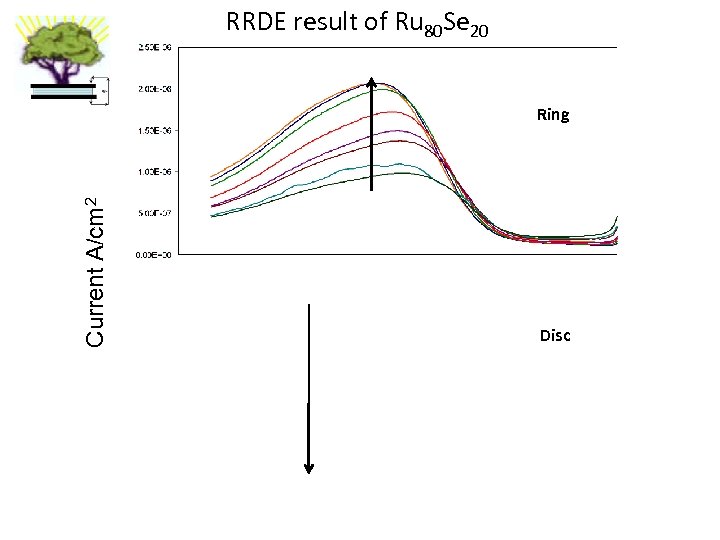
RRDE result of Ru 80 Se 20 Current A/cm 2 Ring Disc

Tafel plots of O 2 reduction on Ru 2 Se and Pt RDE electrodes in 0. 5 M H 2 SO 4 solution. Scan rate=2 m. V/sec, ω=1800 rpm.
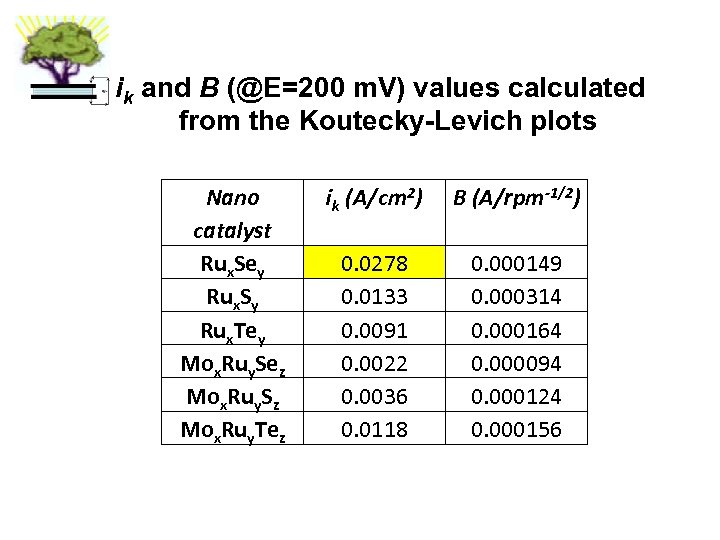
ik and B (@E=200 m. V) values calculated from the Koutecky-Levich plots Nano catalyst Rux. Sey Rux. Sy Rux. Tey Mox. Ruy. Sez Mox. Ruy. Sz Mox. Ruy. Tez ik (A/cm 2) B (A/rpm-1/2) 0. 0278 0. 0133 0. 0091 0. 0022 0. 0036 0. 0118 0. 000149 0. 000314 0. 000164 0. 000094 0. 000124 0. 000156
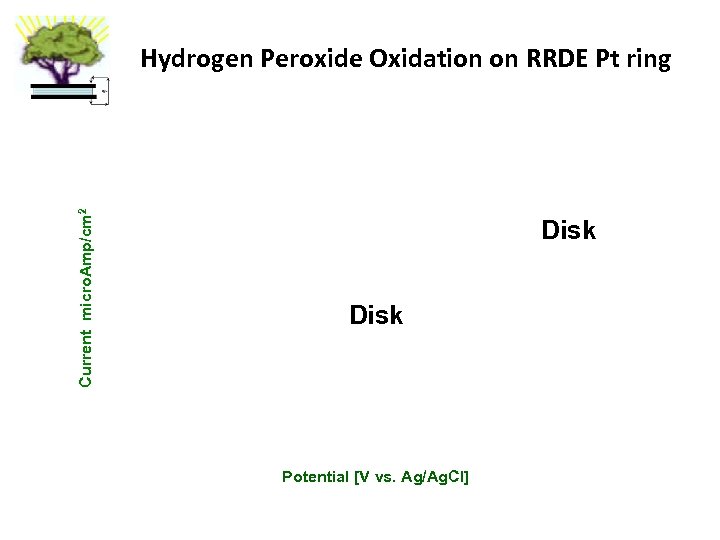
Current micro. Amp/cm 2 Hydrogen Peroxide Oxidation on RRDE Pt ring Disk Potential [V vs. Ag/Ag. Cl]
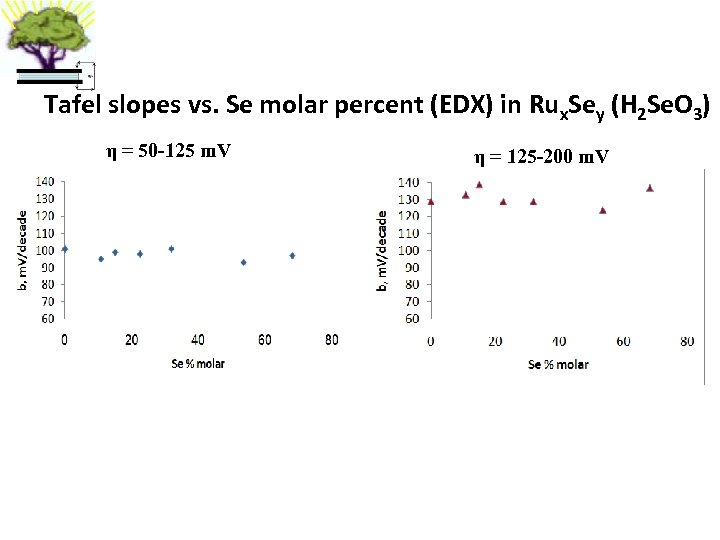
Tafel slopes vs. Se molar percent (EDX) in Rux. Sey (H 2 Se. O 3) η = 50 -125 m. V η = 125 -200 m. V
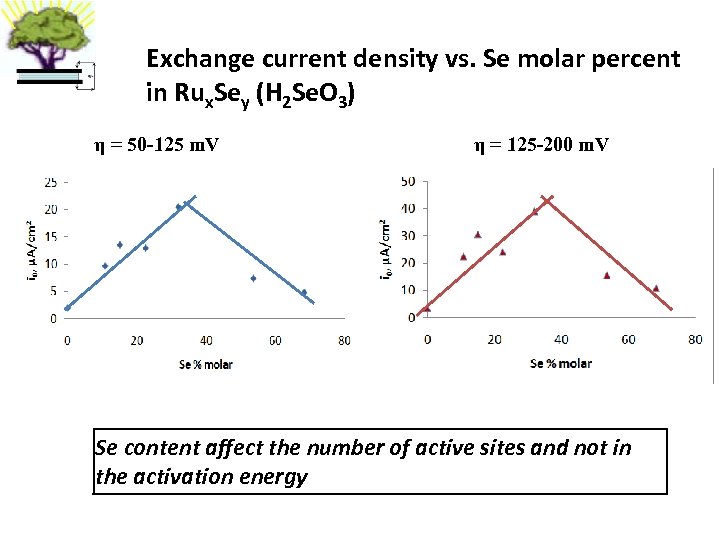
Exchange current density vs. Se molar percent in Rux. Sey (H 2 Se. O 3) η = 50 -125 m. V η = 125 -200 m. V Se content affect the number of active sites and not in the activation energy
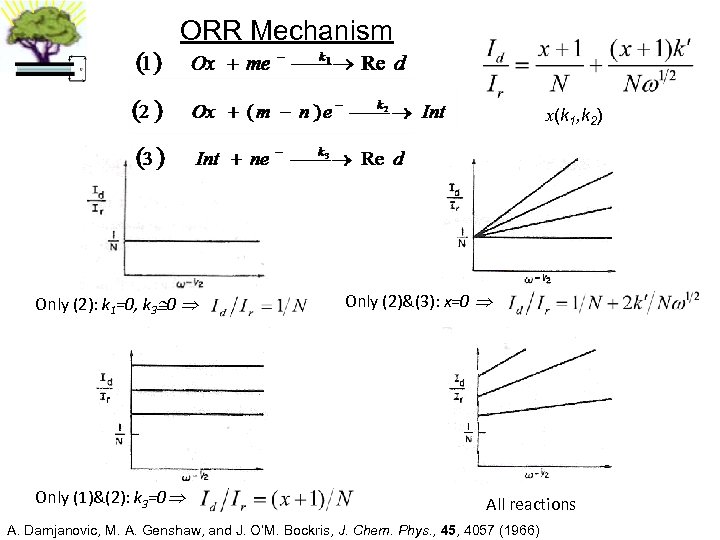
ORR Mechanism x(k 1, k 2) Only (2): k 1=0, k 3 0 Only (1)&(2): k 3=0 Only (2)&(3): x=0 All reactions A. Damjanovic, M. A. Genshaw, and J. O’M. Bockris, J. Chem. Phys. , 45, 4057 (1966)
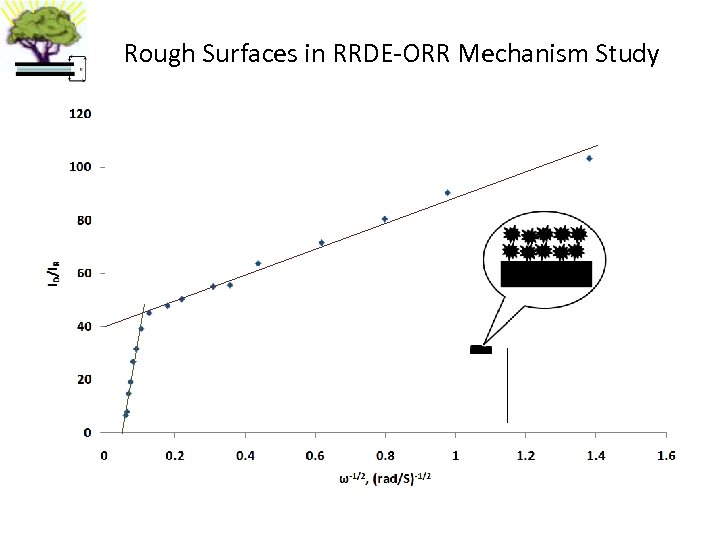
Rough Surfaces in RRDE-ORR Mechanism Study
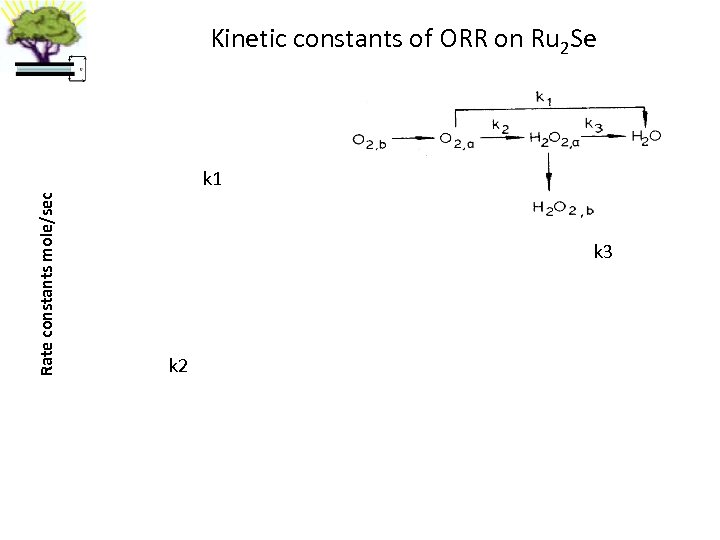
Kinetic constants of ORR on Ru 2 Se Rate constants mole/sec k 1 k 3 k 2

oxygen reduction on Ru 2 Se versus Pt in the Presence of methanol @0. 4 V 1 Pt/C 0. 8 Ru 2 Se/C Oxygen Reduction 0. 6 Disk Current, m. A/cm 2 0. 4 0. 2 0 -0. 2 Methanol Oxidation -0. 4 0 0. 5 1 1. 5 2 2. 5 Methanol Concentration, mol/l 3 3. 5 4

Current Amp/cm 2 Ru 2 Se/C Electrode in 1 M Me. OH/5 M H 3 PO 4 at 60°C 1 st day 4 th day 7 th day

Stability of ORR Activity of Ru 2 Se Catalyst Pt Ru 2 Se (powder Se) Measured at 0. 3 V , during storage in 5 M H 3 PO 4 solution @ 60 C Se. O 3) Ru 2 Se (H 2

Pt Fuel cell Testing in DMFC: Pt versus Rux. Sey Pt Rux. Sey • Conditions: T= 25 o. C, 1 M CH 3 OH, air 150 ml/min

State of the art comparison Power Per Gram of Cathode Catalyst Pt Rux. Sey

Summary Ø Rux. Sey synthesis can be controlled by microwave Ø Optimum ORR kinetics is seen in Ru 2 Se (~35% Se) Ø Mostly 4 e- oxygen reaction occur, distinctly at high over potential Ø Unlike previous reports – Ru. Se presents high stability and excellent methanol tolerance Ø Further inmprovment of catalytic performance is required to compete with Pt.

Acknowledgments ØDr. Hanan Teller ØDr. Oleg Stanevsky ØDr. Maria Rylov ØMr. Phillip Hoffhimer ØMr. Avinoam Burnstien ØMrs. Mietal Gor ØMr. Victor Moltenan ØMr. Rami Kriger ØFunding: Israeli Ministry of National Infrastructures

Thank You
bfc3706f55d30981a05eab611bb3aa6c.ppt