295a56b47316c71c7dfea23650553cb7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 RURAL MARKETING STRATEGIES
RURAL MARKETING STRATEGIES
 RURAL MARKETING STRATEGIES Product Price Promotion Physical
RURAL MARKETING STRATEGIES Product Price Promotion Physical
 Marketing Mix n Is a crucial element of any marketing plan as it offers marketers a mix of product, services and prices, utilizes a promotion mix of advertising, sales promotion, direct marketing and personal selling to reach the target customers through distribution of channels
Marketing Mix n Is a crucial element of any marketing plan as it offers marketers a mix of product, services and prices, utilizes a promotion mix of advertising, sales promotion, direct marketing and personal selling to reach the target customers through distribution of channels
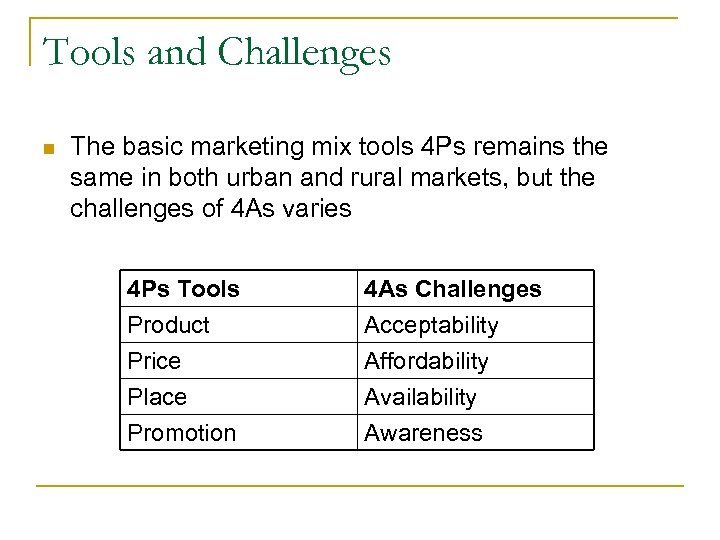 Tools and Challenges n The basic marketing mix tools 4 Ps remains the same in both urban and rural markets, but the challenges of 4 As varies 4 Ps Tools Product Price Place 4 As Challenges Acceptability Affordability Availability Promotion Awareness
Tools and Challenges n The basic marketing mix tools 4 Ps remains the same in both urban and rural markets, but the challenges of 4 As varies 4 Ps Tools Product Price Place 4 As Challenges Acceptability Affordability Availability Promotion Awareness
 Contd… n Availability : availability of products Eg: FMCG Company HLL (Coca- Cola) has a strong distribution system, auto rickshaw, bullock carts. LG- company depot supplies, twice a week to distributors –has 45 area offices and 59 rural office n Affordability : with low disposable income , products need to be affordable. Eg: Godrej – Cinthol, Fairglow. Videocon’s washer without dryer launched specifically for the rural market, Cost Rs 3000/-
Contd… n Availability : availability of products Eg: FMCG Company HLL (Coca- Cola) has a strong distribution system, auto rickshaw, bullock carts. LG- company depot supplies, twice a week to distributors –has 45 area offices and 59 rural office n Affordability : with low disposable income , products need to be affordable. Eg: Godrej – Cinthol, Fairglow. Videocon’s washer without dryer launched specifically for the rural market, Cost Rs 3000/-
 Contd… n Acceptability : Gain acceptability for the product. Need to offer products that suit the rural market. LG Electronics – Sampoorna sold 100, 000 sets in the first year. Coca cola provides low cost ice boxes, that is a tin box for new outlets and a thermo Cole box for seasonal outlets. n Awareness : advertising media- television, movies, music. HLL relies on companies media Godrej for soap products
Contd… n Acceptability : Gain acceptability for the product. Need to offer products that suit the rural market. LG Electronics – Sampoorna sold 100, 000 sets in the first year. Coca cola provides low cost ice boxes, that is a tin box for new outlets and a thermo Cole box for seasonal outlets. n Awareness : advertising media- television, movies, music. HLL relies on companies media Godrej for soap products
 Product Strategies
Product Strategies
 PRODUCT STRATEGIES a company plan for marketing its products Product Strategies • New Product Designs • Sturdy Products • Brand Name • Small Unit Packing • Low Priced Packing
PRODUCT STRATEGIES a company plan for marketing its products Product Strategies • New Product Designs • Sturdy Products • Brand Name • Small Unit Packing • Low Priced Packing
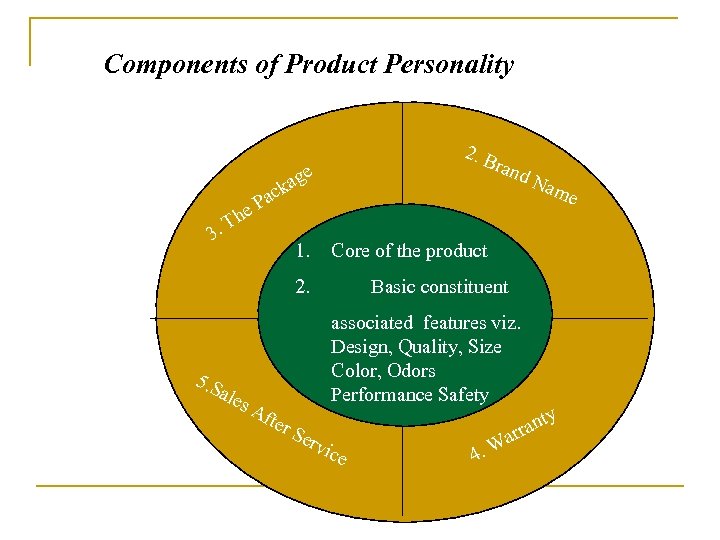 Components of Product Personality 2. B ran ge a ck a d N P e Th. 3 les Core of the product 2. 5. S a 1. ame Basic constituent Af associated features viz. Design, Quality, Size Color, Odors Performance Safety ter Se rvi c e 4. W a nt rra y
Components of Product Personality 2. B ran ge a ck a d N P e Th. 3 les Core of the product 2. 5. S a 1. ame Basic constituent Af associated features viz. Design, Quality, Size Color, Odors Performance Safety ter Se rvi c e 4. W a nt rra y
 1. The core of the Product: Mysore Sandal Soap – combination of luxury & tradition 2. Brand name: Name, Term, Symbol or Design or a combination of them which is intended to identify goods and services of seller and to differentiate with competitors.
1. The core of the Product: Mysore Sandal Soap – combination of luxury & tradition 2. Brand name: Name, Term, Symbol or Design or a combination of them which is intended to identify goods and services of seller and to differentiate with competitors.
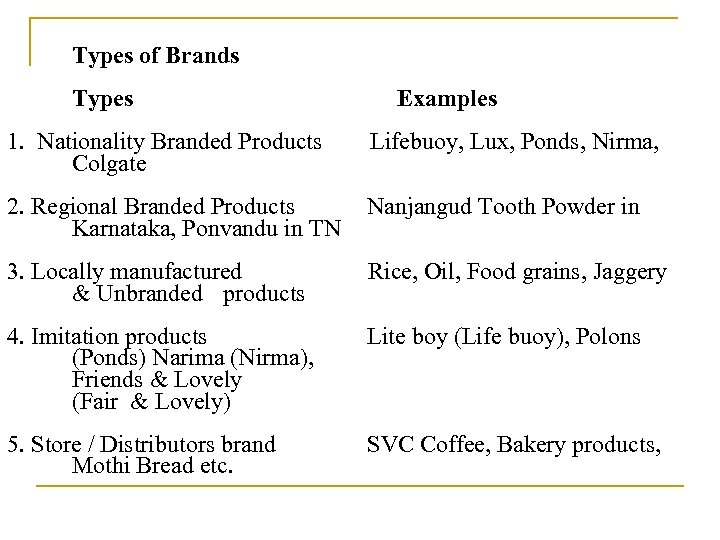 Types of Brands Types Examples 1. Nationality Branded Products Lifebuoy, Lux, Ponds, Nirma, Colgate 2. Regional Branded Products Nanjangud Tooth Powder in Karnataka, Ponvandu in TN 3. Locally manufactured Rice, Oil, Food grains, Jaggery & Unbranded products 4. Imitation products (Ponds) Narima (Nirma), Friends & Lovely (Fair & Lovely) Lite boy (Life buoy), Polons 5. Store / Distributors brand Mothi Bread etc. SVC Coffee, Bakery products,
Types of Brands Types Examples 1. Nationality Branded Products Lifebuoy, Lux, Ponds, Nirma, Colgate 2. Regional Branded Products Nanjangud Tooth Powder in Karnataka, Ponvandu in TN 3. Locally manufactured Rice, Oil, Food grains, Jaggery & Unbranded products 4. Imitation products (Ponds) Narima (Nirma), Friends & Lovely (Fair & Lovely) Lite boy (Life buoy), Polons 5. Store / Distributors brand Mothi Bread etc. SVC Coffee, Bakery products,
 3. The Package: General group of activities in the planning of a product. These activities concentrate on formulating a design of the package and producing an appropriate and attractive container or wrapper for a product. 4. Product Warranty: An obligation of the producer and seller to stand behind the product and assure the buyer that he will derive certain services and satisfaction from the product. An assurance of the Quality, Service and Performance.
3. The Package: General group of activities in the planning of a product. These activities concentrate on formulating a design of the package and producing an appropriate and attractive container or wrapper for a product. 4. Product Warranty: An obligation of the producer and seller to stand behind the product and assure the buyer that he will derive certain services and satisfaction from the product. An assurance of the Quality, Service and Performance.
 5. Service after sales : • For smooth maintenance and repairs at low charges as well as quick availability of spare parts and accessories at reasonable rates. • Important selling point helping the customer to take a quick decision to purchase costly durable goods.
5. Service after sales : • For smooth maintenance and repairs at low charges as well as quick availability of spare parts and accessories at reasonable rates. • Important selling point helping the customer to take a quick decision to purchase costly durable goods.
 Issues to be resolved in Product plan n n n Product line Product mix Packaging Labeling Branding Service after Sales
Issues to be resolved in Product plan n n n Product line Product mix Packaging Labeling Branding Service after Sales
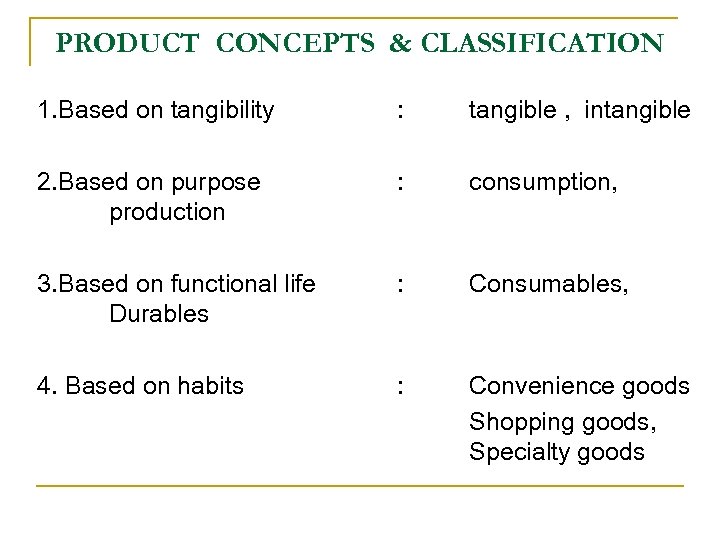 PRODUCT CONCEPTS & CLASSIFICATION 1. Based on tangibility : tangible , intangible 2. Based on purpose production : consumption, 3. Based on functional life Durables : Consumables, 4. Based on habits : Convenience goods Shopping goods, Specialty goods
PRODUCT CONCEPTS & CLASSIFICATION 1. Based on tangibility : tangible , intangible 2. Based on purpose production : consumption, 3. Based on functional life Durables : Consumables, 4. Based on habits : Convenience goods Shopping goods, Specialty goods
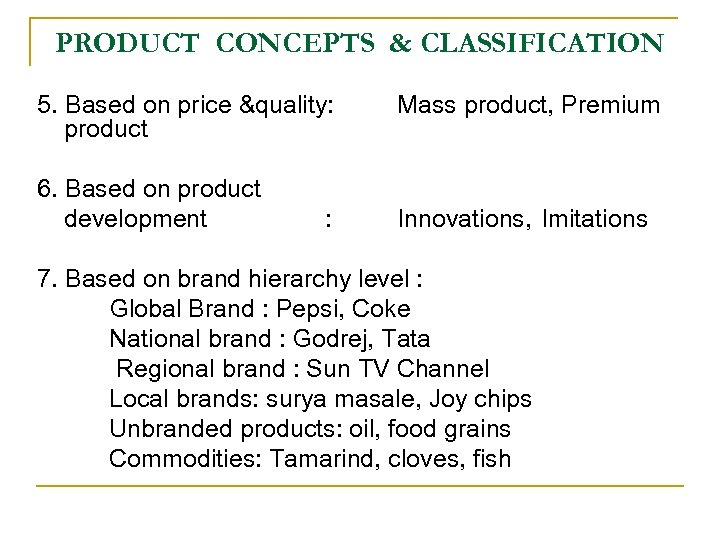 PRODUCT CONCEPTS & CLASSIFICATION 5. Based on price &quality: product 6. Based on product development : Mass product, Premium Innovations, Imitations 7. Based on brand hierarchy level : Global Brand : Pepsi, Coke National brand : Godrej, Tata Regional brand : Sun TV Channel Local brands: surya masale, Joy chips Unbranded products: oil, food grains Commodities: Tamarind, cloves, fish
PRODUCT CONCEPTS & CLASSIFICATION 5. Based on price &quality: product 6. Based on product development : Mass product, Premium Innovations, Imitations 7. Based on brand hierarchy level : Global Brand : Pepsi, Coke National brand : Godrej, Tata Regional brand : Sun TV Channel Local brands: surya masale, Joy chips Unbranded products: oil, food grains Commodities: Tamarind, cloves, fish
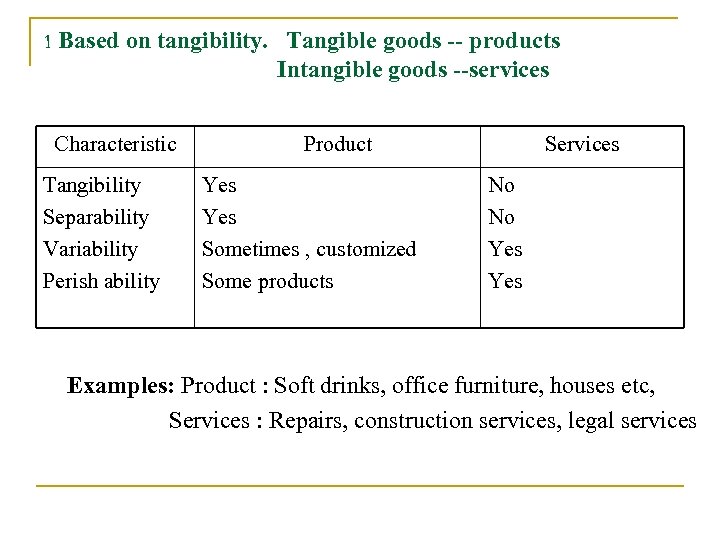 1 Based on tangibility. Tangible goods -- products Intangible goods --services Characteristic Tangibility Separability Variability Perish ability Product Yes Sometimes , customized Some products Services No No Yes Examples: Product : Soft drinks, office furniture, houses etc, Services : Repairs, construction services, legal services
1 Based on tangibility. Tangible goods -- products Intangible goods --services Characteristic Tangibility Separability Variability Perish ability Product Yes Sometimes , customized Some products Services No No Yes Examples: Product : Soft drinks, office furniture, houses etc, Services : Repairs, construction services, legal services
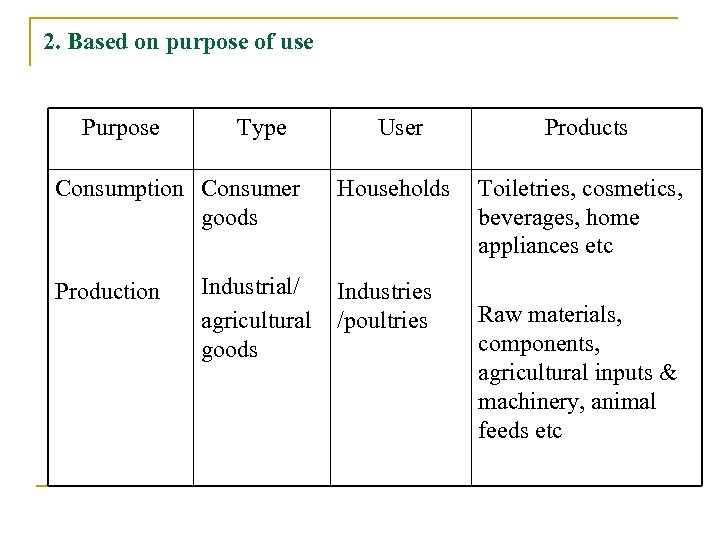 2. Based on purpose of use Purpose Type Consumption Consumer goods Production User Products Households Toiletries, cosmetics, beverages, home appliances etc Raw materials, components, agricultural inputs & machinery, animal feeds etc Industrial/ Industries agricultural /poultries goods
2. Based on purpose of use Purpose Type Consumption Consumer goods Production User Products Households Toiletries, cosmetics, beverages, home appliances etc Raw materials, components, agricultural inputs & machinery, animal feeds etc Industrial/ Industries agricultural /poultries goods
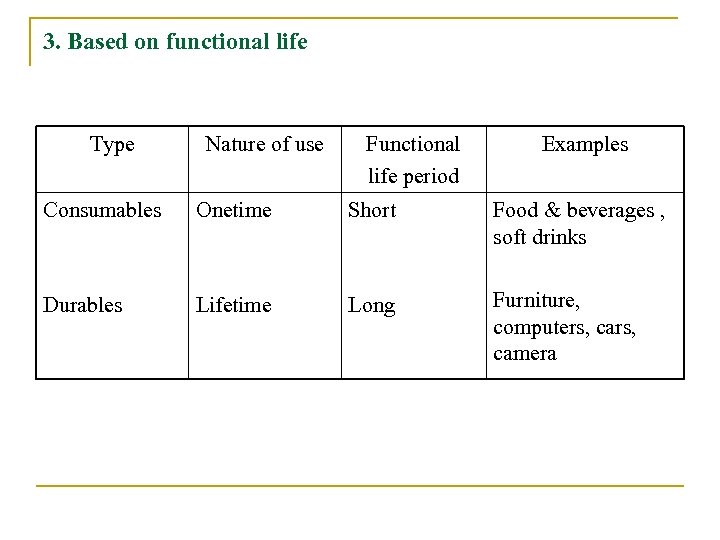 3. Based on functional life Type Nature of use Functional life period Examples Consumables Onetime Short Food & beverages , soft drinks Durables Lifetime Long Furniture, computers, cars, camera
3. Based on functional life Type Nature of use Functional life period Examples Consumables Onetime Short Food & beverages , soft drinks Durables Lifetime Long Furniture, computers, cars, camera
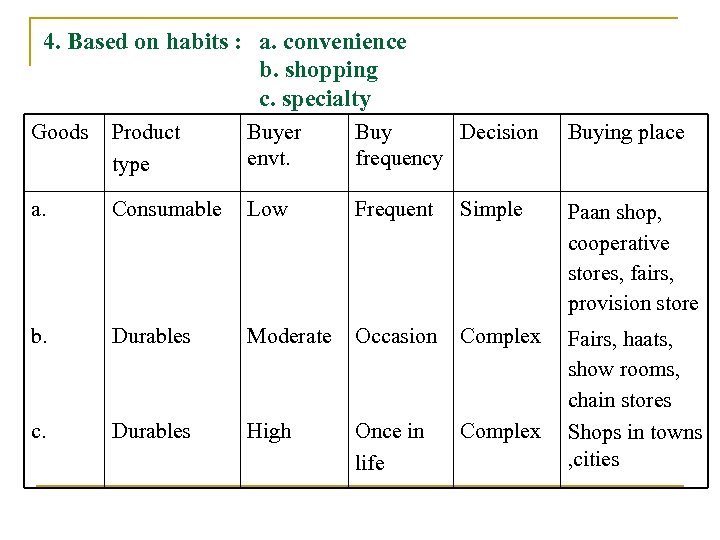 4. Based on habits : a. convenience b. shopping c. specialty Goods Product type Buyer envt. Buy Decision frequency Buying place a. Consumable Low Frequent Simple Paan shop, cooperative stores, fairs, provision store b. Durables Moderate Occasion Complex c. Durables High Once in life Complex Fairs, haats, show rooms, chain stores Shops in towns , cities
4. Based on habits : a. convenience b. shopping c. specialty Goods Product type Buyer envt. Buy Decision frequency Buying place a. Consumable Low Frequent Simple Paan shop, cooperative stores, fairs, provision store b. Durables Moderate Occasion Complex c. Durables High Once in life Complex Fairs, haats, show rooms, chain stores Shops in towns , cities
 Concept of Product strategy Long range competitive plan involving decisions on products, product line and product mix to make proper utilization of resources and achieve marketing goals
Concept of Product strategy Long range competitive plan involving decisions on products, product line and product mix to make proper utilization of resources and achieve marketing goals
 Significance n n Achieves product- market fit Encourages innovativeness Provides competitive edge Makes better use of resources
Significance n n Achieves product- market fit Encourages innovativeness Provides competitive edge Makes better use of resources
 Scope n Decisions at three levels 1. Level Product mix Strategy Width extension- new product line Length extension – new product items Depth extension – new product variants 2. Product line Stretching – upward, downward Line pruning –line modernization 3. Product item Quality, features, design, brand Augmentations
Scope n Decisions at three levels 1. Level Product mix Strategy Width extension- new product line Length extension – new product items Depth extension – new product variants 2. Product line Stretching – upward, downward Line pruning –line modernization 3. Product item Quality, features, design, brand Augmentations
 Contd… 2. Product line Line pruning : product lines lend to lengthen over time like rational grounds or emotional reasons. Both case dead wood will accumulate. It has to be taken out at periodical reviews. Pruning may be done when • • It is identified that dead wood is depressing profits It is found that the production capacity is limited and cannot handle all the existing products
Contd… 2. Product line Line pruning : product lines lend to lengthen over time like rational grounds or emotional reasons. Both case dead wood will accumulate. It has to be taken out at periodical reviews. Pruning may be done when • • It is identified that dead wood is depressing profits It is found that the production capacity is limited and cannot handle all the existing products
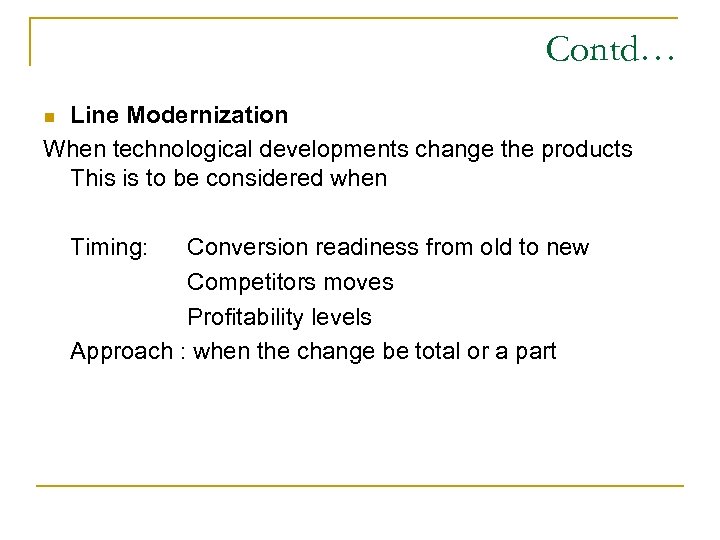 Contd… Line Modernization When technological developments change the products This is to be considered when n Timing: Conversion readiness from old to new Competitors moves Profitability levels Approach : when the change be total or a part
Contd… Line Modernization When technological developments change the products This is to be considered when n Timing: Conversion readiness from old to new Competitors moves Profitability levels Approach : when the change be total or a part
 Contd… 3. Product Item q q q Core product development (need product relationships) Tangible product development Quality- durability, capacity, efficiency, economy, reliability Features – rational, problem solving, fancy, emotional Design - arrangements of parts Style - appearance and function Packaging Branding Augmented product development
Contd… 3. Product Item q q q Core product development (need product relationships) Tangible product development Quality- durability, capacity, efficiency, economy, reliability Features – rational, problem solving, fancy, emotional Design - arrangements of parts Style - appearance and function Packaging Branding Augmented product development
 Contd… n Packaging Primary package : to hold the product Secondary package : to hold the primary package : cardboard box Shipping package : carry the products from one place to another
Contd… n Packaging Primary package : to hold the product Secondary package : to hold the primary package : cardboard box Shipping package : carry the products from one place to another
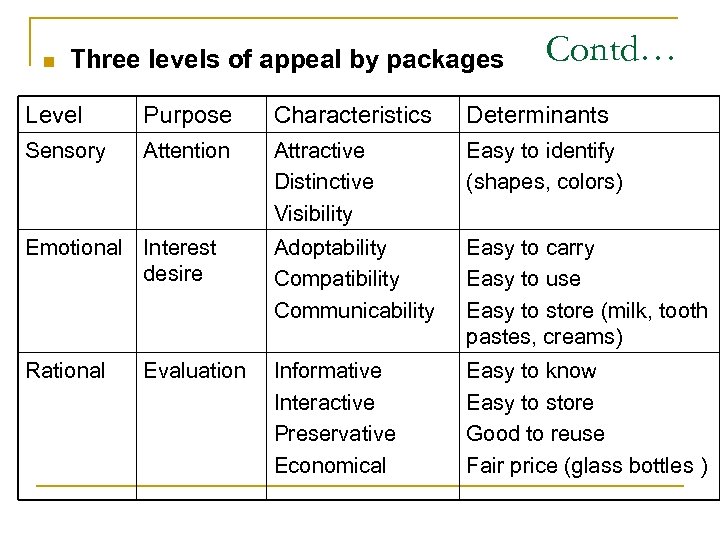 n Three levels of appeal by packages Contd… Level Purpose Characteristics Determinants Sensory Attention Attractive Distinctive Visibility Easy to identify (shapes, colors) Emotional Interest desire Adoptability Compatibility Communicability Easy to carry Easy to use Easy to store (milk, tooth pastes, creams) Rational Informative Interactive Preservative Economical Easy to know Easy to store Good to reuse Fair price (glass bottles ) Evaluation
n Three levels of appeal by packages Contd… Level Purpose Characteristics Determinants Sensory Attention Attractive Distinctive Visibility Easy to identify (shapes, colors) Emotional Interest desire Adoptability Compatibility Communicability Easy to carry Easy to use Easy to store (milk, tooth pastes, creams) Rational Informative Interactive Preservative Economical Easy to know Easy to store Good to reuse Fair price (glass bottles ) Evaluation
 Contd… n Branding q q q Brand concept Branding policy: To brand or not to brand Sponsorship Naming Branding the need
Contd… n Branding q q q Brand concept Branding policy: To brand or not to brand Sponsorship Naming Branding the need
 Contd… q q q Branding arguments for and against For : q Identify helps processing q Image gives competitive advantage q Personality convinces consumers q Equity enhances value Against Investment- returns doubtful Image and personality an emotional nonsense Brand equity- sensible but not new
Contd… q q q Branding arguments for and against For : q Identify helps processing q Image gives competitive advantage q Personality convinces consumers q Equity enhances value Against Investment- returns doubtful Image and personality an emotional nonsense Brand equity- sensible but not new
 Contd… n Brand sponsoring q q n Manufacturer brand Distributor band Brand identity Name what q Each product to give brand name individuals with company name: Ponda dream flower talc individuals without company name: Cinthol, Lifebuoy q Family brand name: Raymonds - Raymonds for textiles and Park avenue for shirts, shoes q Associated brand name Usha - fans, sewing machine Name how? q Easy to use, understand, distinguish
Contd… n Brand sponsoring q q n Manufacturer brand Distributor band Brand identity Name what q Each product to give brand name individuals with company name: Ponda dream flower talc individuals without company name: Cinthol, Lifebuoy q Family brand name: Raymonds - Raymonds for textiles and Park avenue for shirts, shoes q Associated brand name Usha - fans, sewing machine Name how? q Easy to use, understand, distinguish
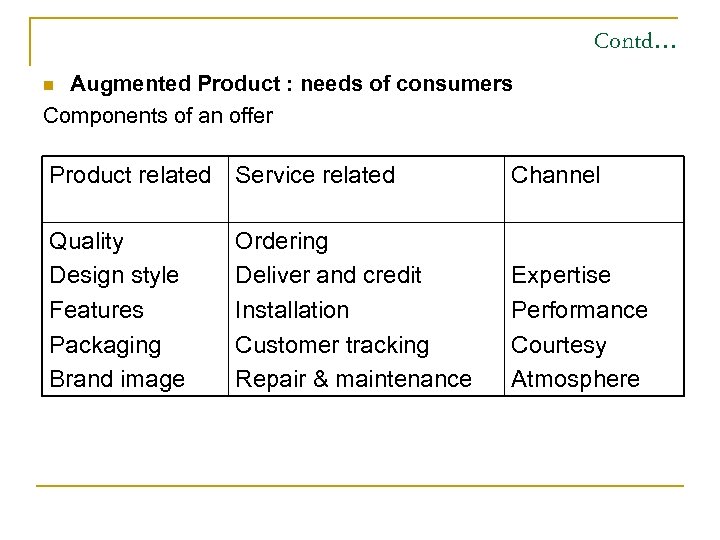 Contd… Augmented Product : needs of consumers Components of an offer n Product related Service related Channel Quality Design style Features Packaging Brand image Expertise Performance Courtesy Atmosphere Ordering Deliver and credit Installation Customer tracking Repair & maintenance
Contd… Augmented Product : needs of consumers Components of an offer n Product related Service related Channel Quality Design style Features Packaging Brand image Expertise Performance Courtesy Atmosphere Ordering Deliver and credit Installation Customer tracking Repair & maintenance
 Strategies for marketers n Identity strategies q q n Customer value strategies q q n Commodity strategies vegetables, oil, steels Branding strategies brook bond’s red label tea, LG Sampoorna Mass product strategies – Maharaja appliances Ltd, Rajdoot 223 Premium product strategies – Fair &Lovely, Surf Innovation strategies q q Rural urban strategies - Bajar electricals, Appollo hospital servicing in rural Special for rural – Nyle Shampoo, Titan watches
Strategies for marketers n Identity strategies q q n Customer value strategies q q n Commodity strategies vegetables, oil, steels Branding strategies brook bond’s red label tea, LG Sampoorna Mass product strategies – Maharaja appliances Ltd, Rajdoot 223 Premium product strategies – Fair &Lovely, Surf Innovation strategies q q Rural urban strategies - Bajar electricals, Appollo hospital servicing in rural Special for rural – Nyle Shampoo, Titan watches
 Strategies for marketers n Quality strategies q q n Quality improvement strategies –TVS 50 48 cc to 49. 9 cc Spurious goods strategies – Lifebuoy-Love boy Packaging strategies – Affordability, usage, storability, small, combi packs n Brand strategies q q Brand extension strategies – New Cinthol Multi band strategy – HLL Soaps- Lifebuoy, Lux Co-branding strategy – IBM and Compaq buys Intel chip and advertise as ‘Intel’ inside Brand image/ equity management – Onida, Lux
Strategies for marketers n Quality strategies q q n Quality improvement strategies –TVS 50 48 cc to 49. 9 cc Spurious goods strategies – Lifebuoy-Love boy Packaging strategies – Affordability, usage, storability, small, combi packs n Brand strategies q q Brand extension strategies – New Cinthol Multi band strategy – HLL Soaps- Lifebuoy, Lux Co-branding strategy – IBM and Compaq buys Intel chip and advertise as ‘Intel’ inside Brand image/ equity management – Onida, Lux
 Class discussion Critically examine the product strategy of the two regional washing soap brands, in comparison to one local brand, in rural markets Use 4 As for analysis Identify the success and failures of brands in general.
Class discussion Critically examine the product strategy of the two regional washing soap brands, in comparison to one local brand, in rural markets Use 4 As for analysis Identify the success and failures of brands in general.
 Class discussion n Explain brand image strategies of any two companies operating in rural areas
Class discussion n Explain brand image strategies of any two companies operating in rural areas


