 Running example ¤ The 4 -houses puzzle: ¤ 4 families A, B, C and D live next to each other in houses numbered 1, 2, 3 and 4. è D lives in a house with lower number than B, è B lives next to A in a house with higher number, è There is at least one house between B and C, è D does not live in the house with number 2, è C does not live in the house with number 4. ¤ Which family lives in which house ? 1
Running example ¤ The 4 -houses puzzle: ¤ 4 families A, B, C and D live next to each other in houses numbered 1, 2, 3 and 4. è D lives in a house with lower number than B, è B lives next to A in a house with higher number, è There is at least one house between B and C, è D does not live in the house with number 2, è C does not live in the house with number 4. ¤ Which family lives in which house ? 1
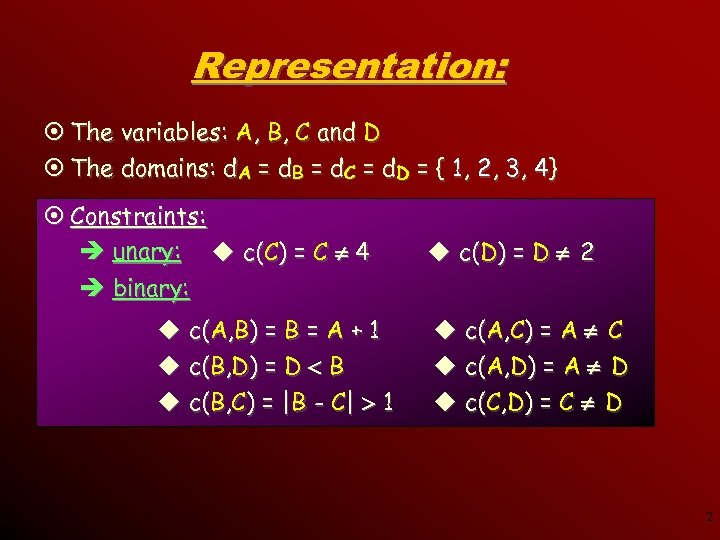 Representation: ¤ The variables: A, B, C and D ¤ The domains: d. A = d. B = d. C = d. D = { 1, 2, 3, 4} ¤ Constraints: è unary: u c(C) = C 4 è binary: u c(A, B) = B = A + 1 u c(B, D) = D B u c(B, C) = |B - C| 1 u c(D) = D 2 u c(A, C) = A C u c(A, D) = A D u c(C, D) = C D 2
Representation: ¤ The variables: A, B, C and D ¤ The domains: d. A = d. B = d. C = d. D = { 1, 2, 3, 4} ¤ Constraints: è unary: u c(C) = C 4 è binary: u c(A, B) = B = A + 1 u c(B, D) = D B u c(B, C) = |B - C| 1 u c(D) = D 2 u c(A, C) = A C u c(A, D) = A D u c(C, D) = C D 2
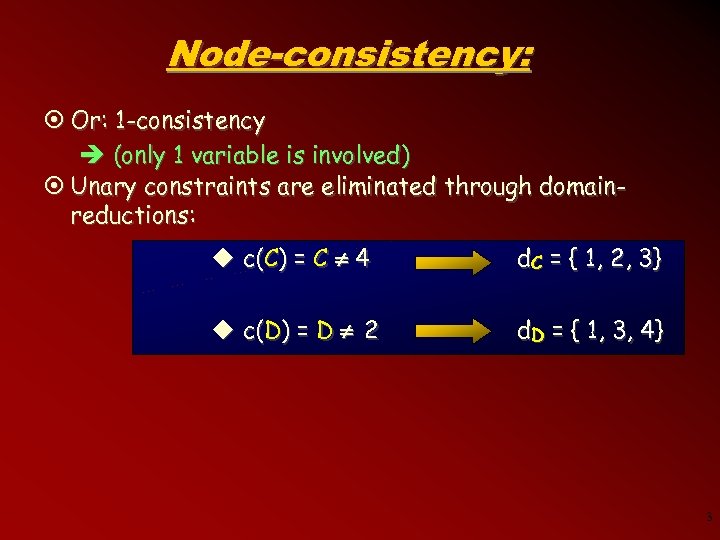 Node-consistency: ¤ Or: 1 -consistency è (only 1 variable is involved) ¤ Unary constraints are eliminated through domainreductions: u c(C) = C 4 d C = { 1, 2 , 3 } u c(D) = D 2 d D = { 1, 3 , 4 } 3
Node-consistency: ¤ Or: 1 -consistency è (only 1 variable is involved) ¤ Unary constraints are eliminated through domainreductions: u c(C) = C 4 d C = { 1, 2 , 3 } u c(D) = D 2 d D = { 1, 3 , 4 } 3
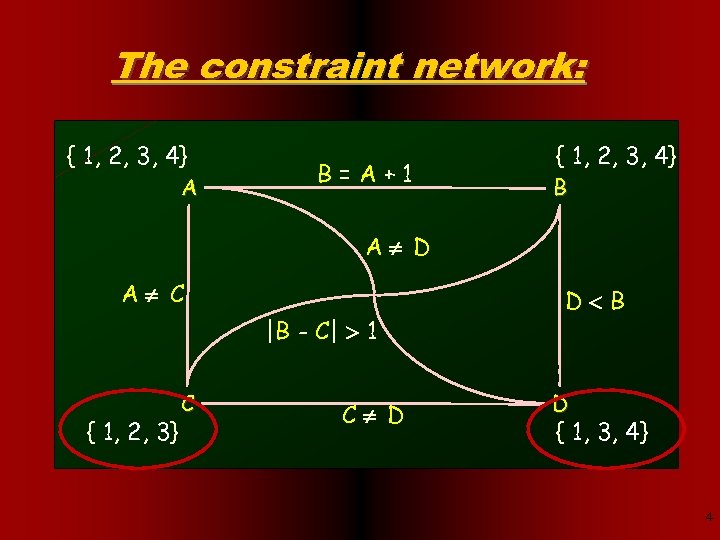 The constraint network: { 1, 2, 3, 4} A B=A+1 { 1, 2, 3, 4} B A D A C |B - C| 1 { 1, 2, 3} C C D D B D { 1, 3, 4} 4
The constraint network: { 1, 2, 3, 4} A B=A+1 { 1, 2, 3, 4} B A D A C |B - C| 1 { 1, 2, 3} C C D D B D { 1, 3, 4} 4
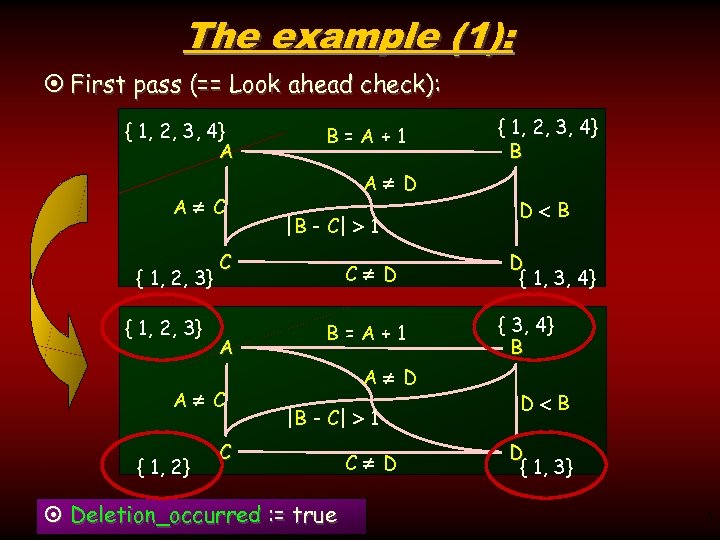 The example (1): ¤ First pass (== Look ahead check): { 1, 2, 3, 4} A A C { 1, 2, 3} A D |B - C| 1 C A A C { 1, 2} B=A+1 C D B=A+1 A D |B - C| 1 C ¤ Deletion_occurred : = true C D { 1, 2, 3, 4} B D { 1, 3, 4} { 3, 4} B D { 1, 3} 5
The example (1): ¤ First pass (== Look ahead check): { 1, 2, 3, 4} A A C { 1, 2, 3} A D |B - C| 1 C A A C { 1, 2} B=A+1 C D B=A+1 A D |B - C| 1 C ¤ Deletion_occurred : = true C D { 1, 2, 3, 4} B D { 1, 3, 4} { 3, 4} B D { 1, 3} 5
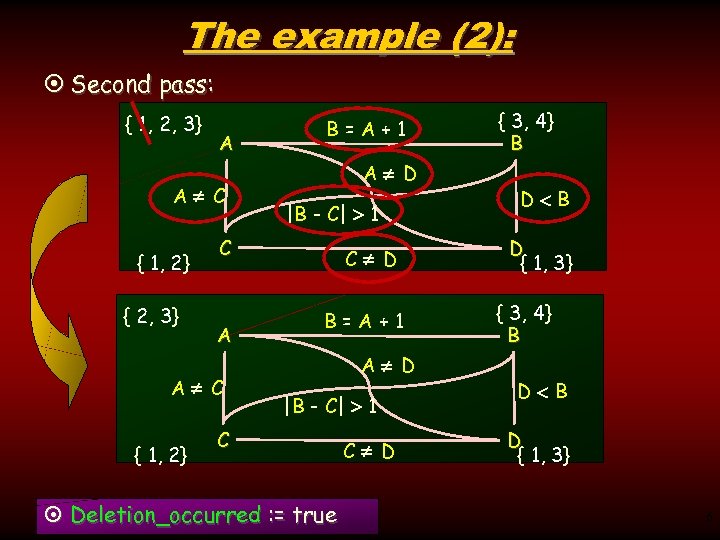 The example (2): ¤ Second pass: { 1, 2, 3} A A C { 1, 2} { 2, 3} A D |B - C| 1 C A A C { 1, 2} B=A+1 C D B=A+1 A D |B - C| 1 C ¤ Deletion_occurred : = true C D { 3, 4} B D B D { 1, 3} 6
The example (2): ¤ Second pass: { 1, 2, 3} A A C { 1, 2} { 2, 3} A D |B - C| 1 C A A C { 1, 2} B=A+1 C D B=A+1 A D |B - C| 1 C ¤ Deletion_occurred : = true C D { 3, 4} B D B D { 1, 3} 6
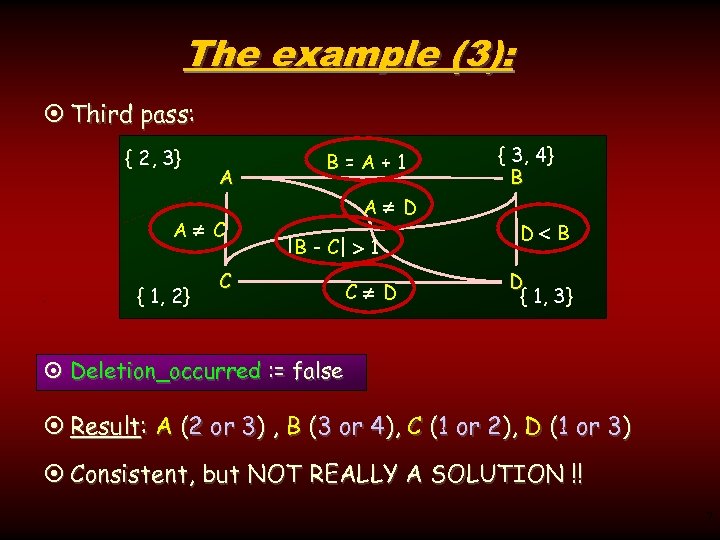 The example (3): ¤ Third pass: { 2, 3} A A C { 1, 2} B=A+1 A D |B - C| 1 C C D { 3, 4} B D { 1, 3} ¤ Deletion_occurred : = false ¤ Result: A (2 or 3) , B (3 or 4), C (1 or 2), D (1 or 3) ¤ Consistent, but NOT REALLY A SOLUTION !! 7
The example (3): ¤ Third pass: { 2, 3} A A C { 1, 2} B=A+1 A D |B - C| 1 C C D { 3, 4} B D { 1, 3} ¤ Deletion_occurred : = false ¤ Result: A (2 or 3) , B (3 or 4), C (1 or 2), D (1 or 3) ¤ Consistent, but NOT REALLY A SOLUTION !! 7
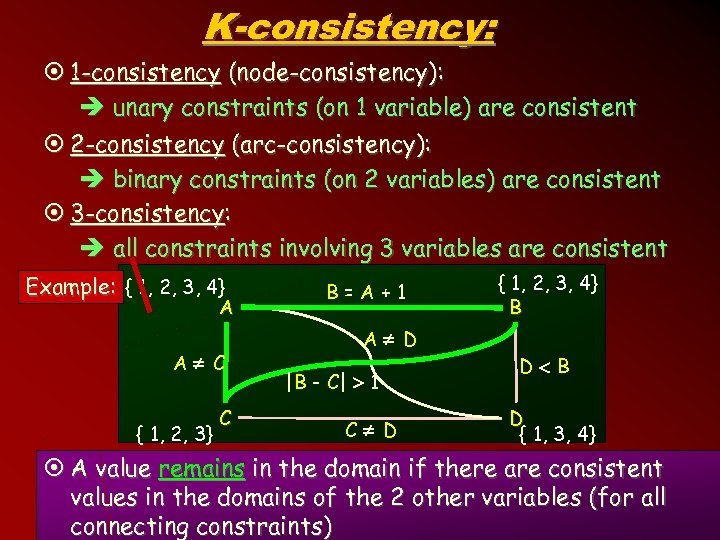 K-consistency: ¤ 1 -consistency (node-consistency): è unary constraints (on 1 variable) are consistent ¤ 2 -consistency (arc-consistency): è binary constraints (on 2 variables) are consistent ¤ 3 -consistency: è all constraints involving 3 variables are consistent Example: { 1, 2, 3, 4} A A C { 1, 2, 3} C B=A+1 A D |B - C| 1 C D { 1, 2, 3, 4} B D { 1, 3, 4} ¤ A value remains in the domain if there are consistent values in the domains of the 2 other variables (for all connecting constraints) 8
K-consistency: ¤ 1 -consistency (node-consistency): è unary constraints (on 1 variable) are consistent ¤ 2 -consistency (arc-consistency): è binary constraints (on 2 variables) are consistent ¤ 3 -consistency: è all constraints involving 3 variables are consistent Example: { 1, 2, 3, 4} A A C { 1, 2, 3} C B=A+1 A D |B - C| 1 C D { 1, 2, 3, 4} B D { 1, 3, 4} ¤ A value remains in the domain if there are consistent values in the domains of the 2 other variables (for all connecting constraints) 8
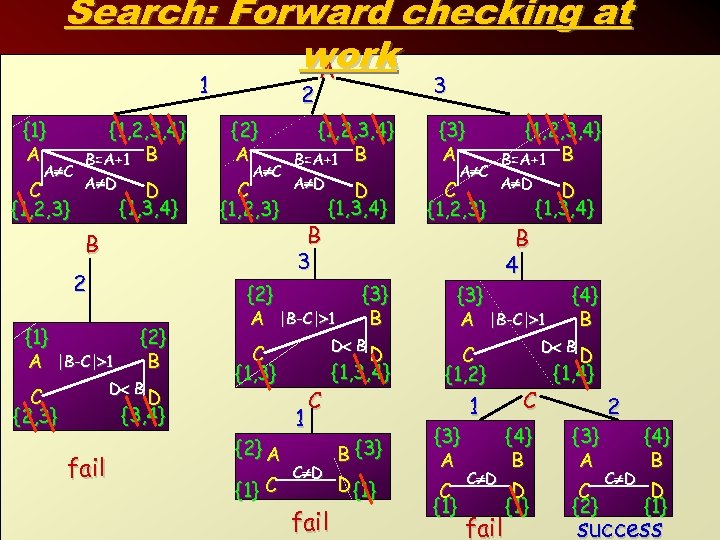 Search: Forward checking at work A 1 {1} A A C C {1, 2, 3} {1, 2, 3, 4} B=A+1 B A D D {1, 3, 4} {2} A A C C {1, 2, 3} B 2 {1} A |B-C| 1 {2} B D B C {2, 3} D {3, 4} fail 3 2 {1, 2, 3, 4} B=A+1 B A D B 3 D {1, 3, 4} {2} A |B-C| 1 D B C {1, 3} {2} A {1} C {3} B 1 C C D fail D {1, 3, 4} B {3} D {1} {3} A A C C {1, 2, 3} {1, 2, 3, 4} B=A+1 B A D D {1, 3, 4} B 4 {3} A |B-C| 1 C {1, 2} {3} A C {1} 1 C D fail {4} B D B C {4} B D {1} D {1, 4} {3} A C {2} 2 C D {4} B D {1} success 9
Search: Forward checking at work A 1 {1} A A C C {1, 2, 3} {1, 2, 3, 4} B=A+1 B A D D {1, 3, 4} {2} A A C C {1, 2, 3} B 2 {1} A |B-C| 1 {2} B D B C {2, 3} D {3, 4} fail 3 2 {1, 2, 3, 4} B=A+1 B A D B 3 D {1, 3, 4} {2} A |B-C| 1 D B C {1, 3} {2} A {1} C {3} B 1 C C D fail D {1, 3, 4} B {3} D {1} {3} A A C C {1, 2, 3} {1, 2, 3, 4} B=A+1 B A D D {1, 3, 4} B 4 {3} A |B-C| 1 C {1, 2} {3} A C {1} 1 C D fail {4} B D B C {4} B D {1} D {1, 4} {3} A C {2} 2 C D {4} B D {1} success 9
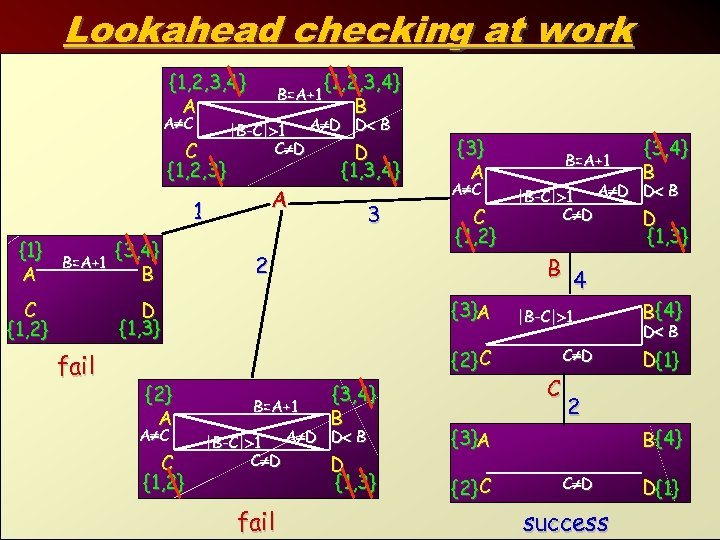 Lookahead checking at work {1, 2, 3, 4} A A C C {1, 2, 3} B=A+1 |B-C| 1 A D D B C D D A 1 {1} A B=A+1 C {1, 2} {3, 4} B {1, 2, 3, 4} B {1, 3, 4} 3 2 D {1, 3} fail {3} A A C C {1, 2} {3}A {2} C {2} A A C C {1, 2} B=A+1 {3, 4} B |B-C| 1 A D D B C D D {1, 3} fail B=A+1 |B-C| 1 A D D B C D D {1, 3} B 4 |B-C| 1 C D C B {4} D B D{1} 2 {3}A {2} C {3, 4} B B {4} C D success D{1} 10
Lookahead checking at work {1, 2, 3, 4} A A C C {1, 2, 3} B=A+1 |B-C| 1 A D D B C D D A 1 {1} A B=A+1 C {1, 2} {3, 4} B {1, 2, 3, 4} B {1, 3, 4} 3 2 D {1, 3} fail {3} A A C C {1, 2} {3}A {2} C {2} A A C C {1, 2} B=A+1 {3, 4} B |B-C| 1 A D D B C D D {1, 3} fail B=A+1 |B-C| 1 A D D B C D D {1, 3} B 4 |B-C| 1 C D C B {4} D B D{1} 2 {3}A {2} C {3, 4} B B {4} C D success D{1} 10