7599aab4b6a46ae929d5df6356fba12d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
![Run Time: [01: 41: 52] This riveting two-hour special investigates a new image of Run Time: [01: 41: 52] This riveting two-hour special investigates a new image of](https://present5.com/presentation/7599aab4b6a46ae929d5df6356fba12d/image-1.jpg) Run Time: [01: 41: 52] This riveting two-hour special investigates a new image of the Vikings that goes far deeper than their savage 1 stereotype as raiding marauders. Faithful replicas of their magnificent ships, life-like computer animation and fascinating recreations reveal the Vikings as canny merchants, expert shipbuilders, superb artisans, and bold colonizers of lands that lay beyond the edge of the known world.
Run Time: [01: 41: 52] This riveting two-hour special investigates a new image of the Vikings that goes far deeper than their savage 1 stereotype as raiding marauders. Faithful replicas of their magnificent ships, life-like computer animation and fascinating recreations reveal the Vikings as canny merchants, expert shipbuilders, superb artisans, and bold colonizers of lands that lay beyond the edge of the known world.
 Viking 2
Viking 2
 Chapter 20 The Vikings Words, Terms and People to Know ►Vinland ►Jutland ►Erik ►Leif the Red ►Ethelred ►Rurik ►Fjord ►Jarl ►Norselaw ►Rollo Eriksson ►Berserkers ►Sagas ►Eddas ►Varangian Route ►Canute 3
Chapter 20 The Vikings Words, Terms and People to Know ►Vinland ►Jutland ►Erik ►Leif the Red ►Ethelred ►Rurik ►Fjord ►Jarl ►Norselaw ►Rollo Eriksson ►Berserkers ►Sagas ►Eddas ►Varangian Route ►Canute 3
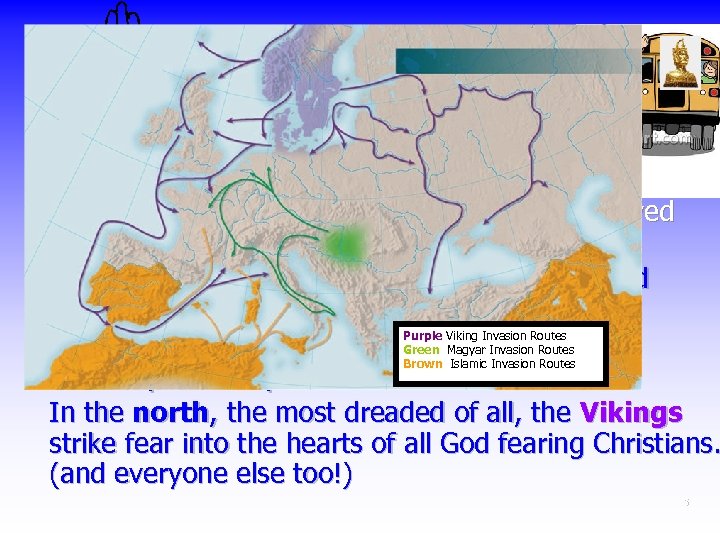 Chapter 20 The Vikings 800 A. D. — 1035 A. D. Good Bye Charlemagne Between 800 -1000 invasions completely destroyed the Carolingian Empire Muslim invaders from the south seized Sicily and raided Italy Purple Viking Invasion Routes Green Magyar terrorize In the east the Magyars invade and Invasion Routes Brown Islamic Invasion Routes Germany and Italy In the north, the most dreaded of all, the Vikings strike fear into the hearts of all God fearing Christians. (and everyone else too!) 5
Chapter 20 The Vikings 800 A. D. — 1035 A. D. Good Bye Charlemagne Between 800 -1000 invasions completely destroyed the Carolingian Empire Muslim invaders from the south seized Sicily and raided Italy Purple Viking Invasion Routes Green Magyar terrorize In the east the Magyars invade and Invasion Routes Brown Islamic Invasion Routes Germany and Italy In the north, the most dreaded of all, the Vikings strike fear into the hearts of all God fearing Christians. (and everyone else too!) 5
 The raids of the Vikings can be considered the last phase of the Germanic invasions begun in the 4 th century ► Reasons It has been estimated that about 17% of the population died in infancy, before reaching five years of age. About 16% did not survive to around 20 years of age. In all, more than 33% of the population did not reach adulthood. for the Viking Invasions § Climate would not support a large and growing Viking population § Constant warfare where a and 30 years of age and this may would As this chart shows, 50% of adult men died between 21 defeated chief be because of warfare and turbulent times. rather and childbirththe generally them than For women, theyears. were in go elsewhere did not survive beyond 30 risks accept vassalage. Life pregnancy and 35% of tended to olds were the 'middle-aged' people of the Viking Age and 50 years of age The 31 to 40 year be short and brutal. (chart) would be thought of as 'old'. Women seem to have had an especially high death rate in the age group 41 to 50 when compared with the men, but this is because about eight out of ten of the adult men had already died at an earlier age. It was exceptional for anyone to reach what we would today call 'old age'. § Skilled and versatile seamen whose ships allowed them to go any where including areas with a very 6 shallow draught.
The raids of the Vikings can be considered the last phase of the Germanic invasions begun in the 4 th century ► Reasons It has been estimated that about 17% of the population died in infancy, before reaching five years of age. About 16% did not survive to around 20 years of age. In all, more than 33% of the population did not reach adulthood. for the Viking Invasions § Climate would not support a large and growing Viking population § Constant warfare where a and 30 years of age and this may would As this chart shows, 50% of adult men died between 21 defeated chief be because of warfare and turbulent times. rather and childbirththe generally them than For women, theyears. were in go elsewhere did not survive beyond 30 risks accept vassalage. Life pregnancy and 35% of tended to olds were the 'middle-aged' people of the Viking Age and 50 years of age The 31 to 40 year be short and brutal. (chart) would be thought of as 'old'. Women seem to have had an especially high death rate in the age group 41 to 50 when compared with the men, but this is because about eight out of ten of the adult men had already died at an earlier age. It was exceptional for anyone to reach what we would today call 'old age'. § Skilled and versatile seamen whose ships allowed them to go any where including areas with a very 6 shallow draught.
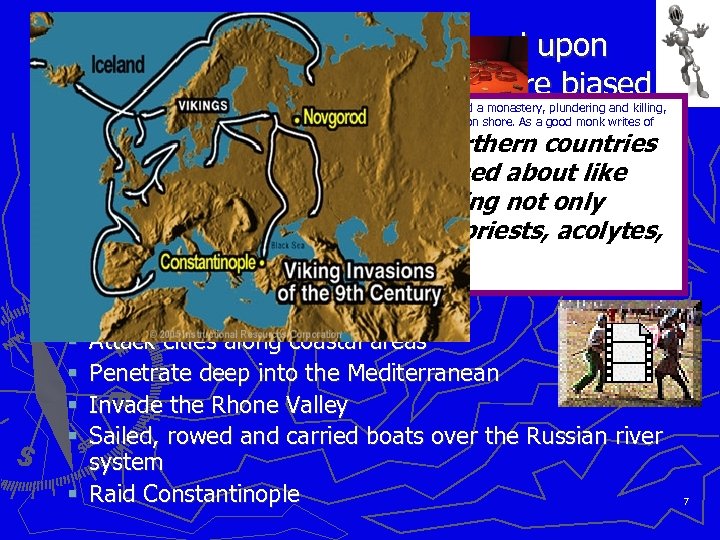 Most accounts of Vikings are based upon recollections of victims and therefore biased In 794 came another flock of these vultures of the sea, who robbed a church and a monastery, plundering and killing, and being killed in their turn when a storm wrecked their ships and threw them on shore. As a good monk writes of them: "The heathen ► Typically Vikingcame from the northern countries to§Britain like stinging wasps, roamed deliver us!" Trade ”From the fury of the Northmen, Good Lord about like savage wolves, robbing, people joined fervently in the prayed the priests, and the biting, killing not only § Raid horses, sheep, and cattle, but also priests, acolytes, prayer § Settlement monks, and nuns. " ► Join the Vikings! Meet strange peoples…and kill them! Attack cities along coastal areas Penetrate deep into the Mediterranean Invade the Rhone Valley Sailed, rowed and carried boats over the Russian river system § Raid Constantinople § § 7
Most accounts of Vikings are based upon recollections of victims and therefore biased In 794 came another flock of these vultures of the sea, who robbed a church and a monastery, plundering and killing, and being killed in their turn when a storm wrecked their ships and threw them on shore. As a good monk writes of them: "The heathen ► Typically Vikingcame from the northern countries to§Britain like stinging wasps, roamed deliver us!" Trade ”From the fury of the Northmen, Good Lord about like savage wolves, robbing, people joined fervently in the prayed the priests, and the biting, killing not only § Raid horses, sheep, and cattle, but also priests, acolytes, prayer § Settlement monks, and nuns. " ► Join the Vikings! Meet strange peoples…and kill them! Attack cities along coastal areas Penetrate deep into the Mediterranean Invade the Rhone Valley Sailed, rowed and carried boats over the Russian river system § Raid Constantinople § § 7
 What were their goals? • Raids and loot were not the whole story of the Vikings. Land to farm was also a commodity. There were limited sources of food. • They received influences from Europe that they saw as technologically and politically superior to their culture. Unlike many other invaders in history, the vikings weren’t trying to spread their religion that was paganism, rather gain new resources and new connections. They wanted political and economical advantage. • They had to find food, live off the land, and set up shop. They drove people out and took their money and other valuables they had. Vikings targeted the church and monasteries, which were the major sources of wealth at the time. An accurate depiction of what a Viking looked like. 8
What were their goals? • Raids and loot were not the whole story of the Vikings. Land to farm was also a commodity. There were limited sources of food. • They received influences from Europe that they saw as technologically and politically superior to their culture. Unlike many other invaders in history, the vikings weren’t trying to spread their religion that was paganism, rather gain new resources and new connections. They wanted political and economical advantage. • They had to find food, live off the land, and set up shop. They drove people out and took their money and other valuables they had. Vikings targeted the church and monasteries, which were the major sources of wealth at the time. An accurate depiction of what a Viking looked like. 8
 Gone in a ► The most amazing thing about Norse emigrations was the ephemeral nature of their settlements and kingdoms. ► The Norse quickly incorporated themselves into the existing populations and institutions and discard most distinctly “Viking” characteristics. ► We know most about their world view from Icelandic literature—especially the edda of Snorri Sturlusonan Icelandic historian, poet and politician. (1178 -1241? ) 9
Gone in a ► The most amazing thing about Norse emigrations was the ephemeral nature of their settlements and kingdoms. ► The Norse quickly incorporated themselves into the existing populations and institutions and discard most distinctly “Viking” characteristics. ► We know most about their world view from Icelandic literature—especially the edda of Snorri Sturlusonan Icelandic historian, poet and politician. (1178 -1241? ) 9
 How do we know about the Vikings? Sources and Contemporary Accounts • Vikings left many traces of their settlements that are still visible today. Archaeology provides physical evidence of their conquests, settlements, and daily life. • Not a lot of evidence survives, and much of what we have is either uninformative or unreliable. Many popular ideas of Vikings are 19 th century inventions, such as horns on helmets. Few historical records and contemporary written sources exist anymore. • Surviving accounts of Viking activity was almost exclusively written by churchmen. These included monastic chronicles such as the Anglo Saxon chronicle, Frankish, and Irish Annals. The chronicles reflect the fact that Vikings attacked these monasteries for their wealth and the accounts had a hostile tone to give a popular image of Viking atrocities. The Vikings were considered heathens for their invasions in monasteries and as a result were portrayed in the worst possible way. One of the earliest Icelandic Manuscripts in Old Norse, the Viking language. 10
How do we know about the Vikings? Sources and Contemporary Accounts • Vikings left many traces of their settlements that are still visible today. Archaeology provides physical evidence of their conquests, settlements, and daily life. • Not a lot of evidence survives, and much of what we have is either uninformative or unreliable. Many popular ideas of Vikings are 19 th century inventions, such as horns on helmets. Few historical records and contemporary written sources exist anymore. • Surviving accounts of Viking activity was almost exclusively written by churchmen. These included monastic chronicles such as the Anglo Saxon chronicle, Frankish, and Irish Annals. The chronicles reflect the fact that Vikings attacked these monasteries for their wealth and the accounts had a hostile tone to give a popular image of Viking atrocities. The Vikings were considered heathens for their invasions in monasteries and as a result were portrayed in the worst possible way. One of the earliest Icelandic Manuscripts in Old Norse, the Viking language. 10
 Samples of Viking language 8 year old Gisli from Reykjavik, Iceland talks to you in his native language, the genuine language Listen to what he says: of the Vikings. I'm a Viking from Iceland Ég er víkingur frá Íslandi. WAV AU Iceland is an island Ísland er eyja. WAV AU WAV AU The vikings travelled a lot Víkingar ferðuðust mikið. Greetings from Iceland Kveða frá Íslandi. One, two, three, four Einn, tveir, Þrír, fjórir. Good night Góða nótt. 11
Samples of Viking language 8 year old Gisli from Reykjavik, Iceland talks to you in his native language, the genuine language Listen to what he says: of the Vikings. I'm a Viking from Iceland Ég er víkingur frá Íslandi. WAV AU Iceland is an island Ísland er eyja. WAV AU WAV AU The vikings travelled a lot Víkingar ferðuðust mikið. Greetings from Iceland Kveða frá Íslandi. One, two, three, four Einn, tveir, Þrír, fjórir. Good night Góða nótt. 11
![Run Time: [13: 56] The authority of chieftains was dependent upon their ability to Run Time: [13: 56] The authority of chieftains was dependent upon their ability to](https://present5.com/presentation/7599aab4b6a46ae929d5df6356fba12d/image-11.jpg) Run Time: [13: 56] The authority of chieftains was dependent upon their ability to provide for their followers. In the early years of the Viking Age, the population of Scandinavia was on the rise, and so was the number of chieftains. 12
Run Time: [13: 56] The authority of chieftains was dependent upon their ability to provide for their followers. In the early years of the Viking Age, the population of Scandinavia was on the rise, and so was the number of chieftains. 12
 Chapter 20 The Vikings 800 A. D. — 1035 A. D. Did Vikings really wear horns on their helmets? ► Section One: discusses the effects of geography on the development of the Vikings as seafaring people Extra Credit: view this 1958 spectacular and write a 250 word synopsis of the movie and earn points. 13
Chapter 20 The Vikings 800 A. D. — 1035 A. D. Did Vikings really wear horns on their helmets? ► Section One: discusses the effects of geography on the development of the Vikings as seafaring people Extra Credit: view this 1958 spectacular and write a 250 word synopsis of the movie and earn points. 13
 I. The Land ast Greenland coast A. forests, ruggedeastern Greenland, The coastline of coastlines, with its many fjords. At the bottom is natural harbors fjord in the world, Scoresby the longest called fjords, the Sund. southern part called Jutland, or Denmark, was well suited for farming ► B. Most of Scandinavia not suited to farming with rocky soil and a short growing season ► 14 The Hardangerfjord in Hordaland, Norway.
I. The Land ast Greenland coast A. forests, ruggedeastern Greenland, The coastline of coastlines, with its many fjords. At the bottom is natural harbors fjord in the world, Scoresby the longest called fjords, the Sund. southern part called Jutland, or Denmark, was well suited for farming ► B. Most of Scandinavia not suited to farming with rocky soil and a short growing season ► 14 The Hardangerfjord in Hordaland, Norway.
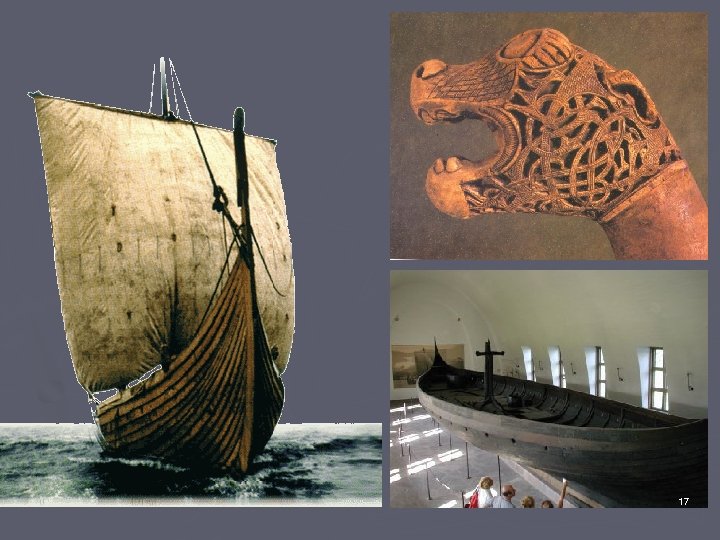
 ► C. Ships and Trade ► 1. Viking long ships (see handout) ► 2. tall bows carved with shapes meant to frighten enemies and evil spirits of the ocean. ► 3. awning to protect from weather ► 4. slept in sleeping bags and carried bronze pots ► 5. plotted course from positions of sun and stars ► 6. traded furs, hides, fish and slaves for silk, wine, wheat and silver 15
► C. Ships and Trade ► 1. Viking long ships (see handout) ► 2. tall bows carved with shapes meant to frighten enemies and evil spirits of the ocean. ► 3. awning to protect from weather ► 4. slept in sleeping bags and carried bronze pots ► 5. plotted course from positions of sun and stars ► 6. traded furs, hides, fish and slaves for silk, wine, wheat and silver 15
 Ships and Navigation • We know what their ships looked like because many vikings were buried with their goods that sometimes included their boats. • They had swift wooden long ships, equipped with sails and oars. • Shallow drought of these ships meant they were able to reach far inland by river or stream to strike and move before local forces could assemble. • Ships had overlapping planks, and measured between 17. 5 m and 36 m in length. They were steered by a single oar mounted on the starboard side. Figureheads would be raised at stem and stern as a sign of war. • Reached an average speed of 10 to 11 knots • Crews of 25 to 60 men would be common, but larger ships could carry over a hundred people. • Sea battles were rare. They fought close to shore. Ships were roped together in lines to face an enemy fleet. 16
Ships and Navigation • We know what their ships looked like because many vikings were buried with their goods that sometimes included their boats. • They had swift wooden long ships, equipped with sails and oars. • Shallow drought of these ships meant they were able to reach far inland by river or stream to strike and move before local forces could assemble. • Ships had overlapping planks, and measured between 17. 5 m and 36 m in length. They were steered by a single oar mounted on the starboard side. Figureheads would be raised at stem and stern as a sign of war. • Reached an average speed of 10 to 11 knots • Crews of 25 to 60 men would be common, but larger ships could carry over a hundred people. • Sea battles were rare. They fought close to shore. Ships were roped together in lines to face an enemy fleet. 16
 17
17
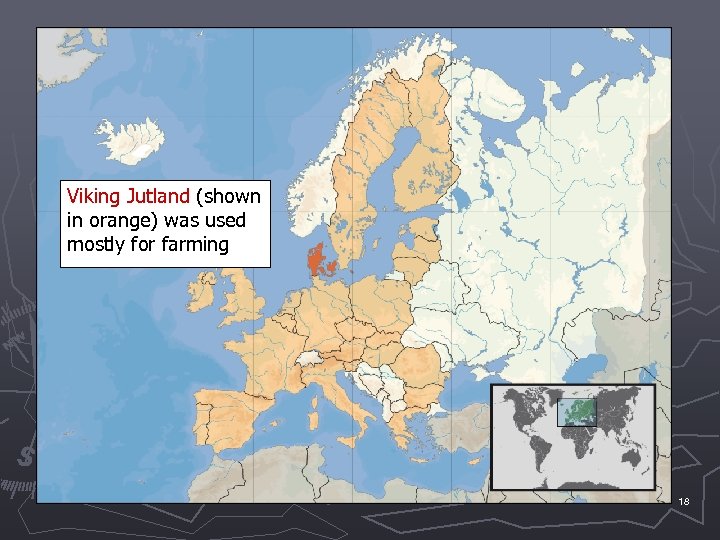 Viking Jutland (shown in orange) was used mostly for farming 18
Viking Jutland (shown in orange) was used mostly for farming 18
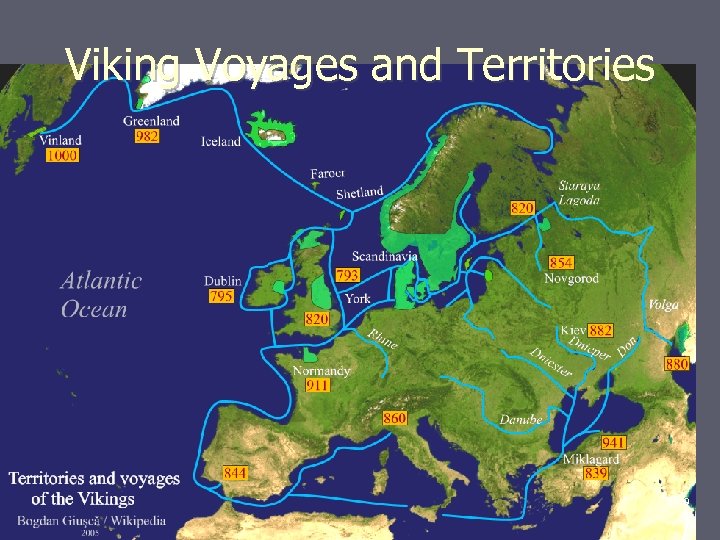 Viking Voyages and Territories 19
Viking Voyages and Territories 19
 I. cont. Viking women wore a long linen dress. It could be Viking men first put on a long woolen shirt and either plain probably had decorative wall Houses of wealthy familiesor pleated. Over the dress they wore a long cloth trousers which were held up by a sash woolen tunic, little like an apron. It hangings, § D. On top of orlong up worn pair ofaon. Jarls tapestries hung was Villages, a andbrooches, sometimes joined or a drawstring. Towns, carvings, or possibly paintings. The sagas tell of this was held elaborately decorated by a shields hung the and to sleeved jerkin or a three-quarter coat with a belt. hall chain or ► 1. decorate theby afor feasts. string of beads. Over the tunic she trade led to market towns On his feet he would wear socks and soft leather shawl. § (a. ) two might wear awould Her legs and feet were shoes or long leather boots. main streets with booths In battle he covered with thick woolly socks and soft leather § (b. ) towns protected by mounds of earth, wooden wear an iron helmet and a mail-chain to protect shoes. walls and towers; houses had steep roofs and himself. Both men and women wore fur or woolen hats porches and cloaks in cold weather. The cloaks were § (c. ) most Vikingsat the shoulder with villages or a pin. fastened lived in scattered a brooch § (d. ) no central govt. , people divided into groups ruled by military chiefs called jarls. § (e. ) Some jarls become strong enough to be declared kings § (f. ) Warriors preferred to die by their own hand rather than give their enemies the satisfaction of capturing or killing them § (g. ) Women given great respect § (h. ) Men took great pride in their mustaches and beards p. 303 20
I. cont. Viking women wore a long linen dress. It could be Viking men first put on a long woolen shirt and either plain probably had decorative wall Houses of wealthy familiesor pleated. Over the dress they wore a long cloth trousers which were held up by a sash woolen tunic, little like an apron. It hangings, § D. On top of orlong up worn pair ofaon. Jarls tapestries hung was Villages, a andbrooches, sometimes joined or a drawstring. Towns, carvings, or possibly paintings. The sagas tell of this was held elaborately decorated by a shields hung the and to sleeved jerkin or a three-quarter coat with a belt. hall chain or ► 1. decorate theby afor feasts. string of beads. Over the tunic she trade led to market towns On his feet he would wear socks and soft leather shawl. § (a. ) two might wear awould Her legs and feet were shoes or long leather boots. main streets with booths In battle he covered with thick woolly socks and soft leather § (b. ) towns protected by mounds of earth, wooden wear an iron helmet and a mail-chain to protect shoes. walls and towers; houses had steep roofs and himself. Both men and women wore fur or woolen hats porches and cloaks in cold weather. The cloaks were § (c. ) most Vikingsat the shoulder with villages or a pin. fastened lived in scattered a brooch § (d. ) no central govt. , people divided into groups ruled by military chiefs called jarls. § (e. ) Some jarls become strong enough to be declared kings § (f. ) Warriors preferred to die by their own hand rather than give their enemies the satisfaction of capturing or killing them § (g. ) Women given great respect § (h. ) Men took great pride in their mustaches and beards p. 303 20
 What people ate and drank What did the population of a Viking town eat and drink? The evidence is that the people in one town, Jorvik, (present day York England) ate well and were not, in normal times, likely to have experienced much of a 'hungry gap' towards the end of winter. The main meat in the diet came from the domesticated animals - beef, pork, mutton and lamb, chicken and goose. Sometimes the meat of hunted animals and birds (especially deer, hares, moorland birds, woodland birds and waterfowl) was eaten. Fish also featured in the diet of the townspeople of Jorvik, both from the rivers and from the sea, though sea fish became more important in the eleventh century. Shellfish were eaten. Bread was made from wheat, barley and rye. Oats were grown and made into bread or cakes. Oatcakes were still made and called 'havercakes' or 'haverbread' in Yorkshire right up to the early twentieth century, from the Old Norse word for oats, 'hafre'. Sometimes the cereal grains would be steeped (or 'creed') in milk, or milk and water, to soften them; the mixture would then be cooked as porridge. Nuts such as hazelnuts and walnuts were eaten. Viking House Some of the vegetables we are familiar with today would have been available, including leeks, carrots, peas, field beans, parsnips, beet and the cabbage family. A variety of fruits and berries were eaten, amongst them plums, cherries, sloes, apples, blackberries, raspberries, dewberries, elderberries, hawthorn berries and rowanberries. Honey was used Reconstruction make mead. for sweetening and was also fermented toof housing Hop remains have been found in the Jorvik excavations, showing that beer brewing went on. Birka listen (help·info) (Birca in medieval sources), As with any town, most of the Björkö (literally: "Birchfrom the surrounding countryside. on the island of food would have come Island") in Sweden, Though the townspeople may have kept a few poultry - and sometimes perhaps a pig they were generally too busy and had too little room to produce much of their own food. They would have relied mainly on produce from the rich farmlands of the Vale of York. The town would have provided a steady, rich market for the people round about who worked the land could produce more than they needed for themselves. http: //www. viking. no/e/england/york/life_expectancy_in_jorvik. html 21
What people ate and drank What did the population of a Viking town eat and drink? The evidence is that the people in one town, Jorvik, (present day York England) ate well and were not, in normal times, likely to have experienced much of a 'hungry gap' towards the end of winter. The main meat in the diet came from the domesticated animals - beef, pork, mutton and lamb, chicken and goose. Sometimes the meat of hunted animals and birds (especially deer, hares, moorland birds, woodland birds and waterfowl) was eaten. Fish also featured in the diet of the townspeople of Jorvik, both from the rivers and from the sea, though sea fish became more important in the eleventh century. Shellfish were eaten. Bread was made from wheat, barley and rye. Oats were grown and made into bread or cakes. Oatcakes were still made and called 'havercakes' or 'haverbread' in Yorkshire right up to the early twentieth century, from the Old Norse word for oats, 'hafre'. Sometimes the cereal grains would be steeped (or 'creed') in milk, or milk and water, to soften them; the mixture would then be cooked as porridge. Nuts such as hazelnuts and walnuts were eaten. Viking House Some of the vegetables we are familiar with today would have been available, including leeks, carrots, peas, field beans, parsnips, beet and the cabbage family. A variety of fruits and berries were eaten, amongst them plums, cherries, sloes, apples, blackberries, raspberries, dewberries, elderberries, hawthorn berries and rowanberries. Honey was used Reconstruction make mead. for sweetening and was also fermented toof housing Hop remains have been found in the Jorvik excavations, showing that beer brewing went on. Birka listen (help·info) (Birca in medieval sources), As with any town, most of the Björkö (literally: "Birchfrom the surrounding countryside. on the island of food would have come Island") in Sweden, Though the townspeople may have kept a few poultry - and sometimes perhaps a pig they were generally too busy and had too little room to produce much of their own food. They would have relied mainly on produce from the rich farmlands of the Vale of York. The town would have provided a steady, rich market for the people round about who worked the land could produce more than they needed for themselves. http: //www. viking. no/e/england/york/life_expectancy_in_jorvik. html 21
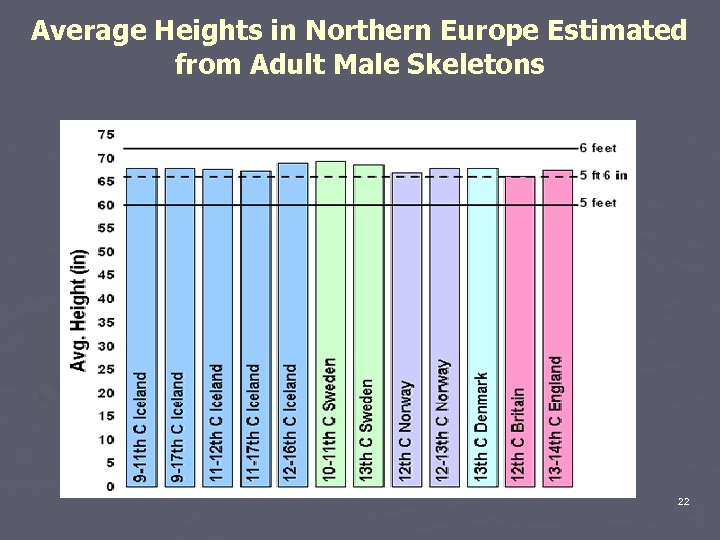 Average Heights in Northern Europe Estimated from Adult Male Skeletons 22
Average Heights in Northern Europe Estimated from Adult Male Skeletons 22
 Section Two: describes the culture of the Viking people II. Daily Life ► A. The People ► ► Death of Balder B. Viking Warriors were called berserkers ► Terms to Learn: Eddas ► C. Religion § 1. Viking gods variations of Germanic gods § 2. Viking practices sacrifices to bargain with their gods The Tollund Man is the naturally mummified corpse of a man who lived during the 4 th century BC, during the time period characterzsed in Scandinavia as the Pre -Roman Iron Age. [1] He was found in 1950 buried in a peat bog on the Jutland Peninsula in Denmark, which preserved his body. This is a historically important area inhabited by the Germanic peoples. His corpse is one of several well preserved bog bodies from written down after 1100 the Pre-Roman Iron Age. § 3. stories of the gods great deeds called “eddas” § 4. sagas kept Viking traditions in the oral tradition ► (a. ) sagas ► § 5. Vikings spoke one of for languages: Danish, Swedish, Norwegian, or Icelandic—all closely related to Germanic languages ► (a. ) languages written in runes 23
Section Two: describes the culture of the Viking people II. Daily Life ► A. The People ► ► Death of Balder B. Viking Warriors were called berserkers ► Terms to Learn: Eddas ► C. Religion § 1. Viking gods variations of Germanic gods § 2. Viking practices sacrifices to bargain with their gods The Tollund Man is the naturally mummified corpse of a man who lived during the 4 th century BC, during the time period characterzsed in Scandinavia as the Pre -Roman Iron Age. [1] He was found in 1950 buried in a peat bog on the Jutland Peninsula in Denmark, which preserved his body. This is a historically important area inhabited by the Germanic peoples. His corpse is one of several well preserved bog bodies from written down after 1100 the Pre-Roman Iron Age. § 3. stories of the gods great deeds called “eddas” § 4. sagas kept Viking traditions in the oral tradition ► (a. ) sagas ► § 5. Vikings spoke one of for languages: Danish, Swedish, Norwegian, or Icelandic—all closely related to Germanic languages ► (a. ) languages written in runes 23
 Offensive Weapons • The main offensive weapons were the spear, sword, and battle-axe. • They carried weapons not just for battle but also as a symbol of their owners’ class and wealth. Weapons were decorated with inlays, twisted wire and other accessories in silver, copper, and bronze. • The spear was the common weapon with an iron blade 2 m to 3 m in length. • Swords were a sign of high status because they were costly to make. The blades were usually double edged and up to 90 cm. Many swords were given names. 25
Offensive Weapons • The main offensive weapons were the spear, sword, and battle-axe. • They carried weapons not just for battle but also as a symbol of their owners’ class and wealth. Weapons were decorated with inlays, twisted wire and other accessories in silver, copper, and bronze. • The spear was the common weapon with an iron blade 2 m to 3 m in length. • Swords were a sign of high status because they were costly to make. The blades were usually double edged and up to 90 cm. Many swords were given names. 25
 Defensive Weapons • There were circular shields up to one meter across that were carried. The shield may have been leather covered. Around 1000, the kite shaped shield was introduced to the Vikings to provide more protection for the legs. • It was essential to wear thick padding underneath to absorb the force of blows or arrow strikes. Reindeer hide was used as armor. • They used long tunics of mail armor reaching below the waist. They were not very protective. It took many hours to produce a shirt, making it very expensive. It’s likely they were worn more by leaders. • Helmets were probably worn by leaders as well. Horned helmets also took great skill to produce. An accurate viking helmet left. The mail armor shown right. A modern myth!!! 26
Defensive Weapons • There were circular shields up to one meter across that were carried. The shield may have been leather covered. Around 1000, the kite shaped shield was introduced to the Vikings to provide more protection for the legs. • It was essential to wear thick padding underneath to absorb the force of blows or arrow strikes. Reindeer hide was used as armor. • They used long tunics of mail armor reaching below the waist. They were not very protective. It took many hours to produce a shirt, making it very expensive. It’s likely they were worn more by leaders. • Helmets were probably worn by leaders as well. Horned helmets also took great skill to produce. An accurate viking helmet left. The mail armor shown right. A modern myth!!! 26
 The Sword and Ideology By Karl N E ► As early as the Bronze Age, was the sword the most important hand-weapon for the free Germanic warrior. They had an onion shape, and polished to shine like gold. In early times the swords was short, as the Roman ”gladius”, blade and handle was made from one cast. During the pre-Roman Iron Age, the handles were given the Gaulish ”ardennes”. Later, during the Migrationperiod the swords grew larger and were made an artwork in itself. Animals appeared on the grip which in many times were made from gold, magical figures, signs and runes began to spring forth. 27
The Sword and Ideology By Karl N E ► As early as the Bronze Age, was the sword the most important hand-weapon for the free Germanic warrior. They had an onion shape, and polished to shine like gold. In early times the swords was short, as the Roman ”gladius”, blade and handle was made from one cast. During the pre-Roman Iron Age, the handles were given the Gaulish ”ardennes”. Later, during the Migrationperiod the swords grew larger and were made an artwork in itself. Animals appeared on the grip which in many times were made from gold, magical figures, signs and runes began to spring forth. 27
 ►The swords of Viking Age were more efficient, but also longer and heavier, the longest being around forty inches, but more normal at a length of two and one-half feet. The blade was called ”brand” and the grip ”hjalt”, connecting the grip was the upper and lower hjalt, protecting the hand from enemy cuts. 28
►The swords of Viking Age were more efficient, but also longer and heavier, the longest being around forty inches, but more normal at a length of two and one-half feet. The blade was called ”brand” and the grip ”hjalt”, connecting the grip was the upper and lower hjalt, protecting the hand from enemy cuts. 28
 ► Some of the best blades were imported from the Frankish region. These swords were often damascened, a technique where iron and steel layers are repeatedly folded and hammered together, producing a hard but flexible blade. The grips were provided by Nordic craftsmen. The best swords were said to have been made by dwarves. These special swords had names, like Sigurd Fafnisbane had a sword named Gram, the Gothic royal sword´s name was Tyrfing. Fafnirs and later Olav Haraldssons swords were both named Hrotte. The sword of Odin was named Mimung. 29
► Some of the best blades were imported from the Frankish region. These swords were often damascened, a technique where iron and steel layers are repeatedly folded and hammered together, producing a hard but flexible blade. The grips were provided by Nordic craftsmen. The best swords were said to have been made by dwarves. These special swords had names, like Sigurd Fafnisbane had a sword named Gram, the Gothic royal sword´s name was Tyrfing. Fafnirs and later Olav Haraldssons swords were both named Hrotte. The sword of Odin was named Mimung. 29
 ►The swords were often given names of the smith, owner or its self-name in runes. This could also hold some sort of magical curse or ”mal”. Along the swordblade there was a shallow channel or a bloodgroove, in which the sword could hold a serpent image that was visible when blood covered the blade. At the sheath end there was often placed metal holding runes and there was also often a container holding magical items, often stones, that protected the blade. 30
►The swords were often given names of the smith, owner or its self-name in runes. This could also hold some sort of magical curse or ”mal”. Along the swordblade there was a shallow channel or a bloodgroove, in which the sword could hold a serpent image that was visible when blood covered the blade. At the sheath end there was often placed metal holding runes and there was also often a container holding magical items, often stones, that protected the blade. 30
 ► From early times, the swords were often destroyed, bent or broken in an attempt to ”kill” the sword, or sacrifice it to the gods as a spoil of war. At burials, swords were often destroyed this way. They were laid down in the urne after it had been burnt on the funeral pyre with its owner. But swords could be powerful even after its owners death. From Snorri´s Heimskringla, there is witness of the importance of the sword, and how grave-mounds of former kings are opened by their successors. 31
► From early times, the swords were often destroyed, bent or broken in an attempt to ”kill” the sword, or sacrifice it to the gods as a spoil of war. At burials, swords were often destroyed this way. They were laid down in the urne after it had been burnt on the funeral pyre with its owner. But swords could be powerful even after its owners death. From Snorri´s Heimskringla, there is witness of the importance of the sword, and how grave-mounds of former kings are opened by their successors. 31
 ► This is the case with Olav Haraldsson, the The murderer Gamla Uppsal in Christian martyr and Royal mounds ofof heathens, Sweden from the 5 th and the 6 th centuries. who takes up the sword from the pagan Olav Digerbein´s grave-mound. Olav also bears his name, and both the power of the sword and of the name is passed down. There was in the Viking Age and in the early Middle Age, a fear of the living dead within the mounds. Sometimes these mounds were opened and the inside of the tomb were desecrated, and the bones scattered. The sword would disappear in this sort of ”grave-robbery”. 32
► This is the case with Olav Haraldsson, the The murderer Gamla Uppsal in Christian martyr and Royal mounds ofof heathens, Sweden from the 5 th and the 6 th centuries. who takes up the sword from the pagan Olav Digerbein´s grave-mound. Olav also bears his name, and both the power of the sword and of the name is passed down. There was in the Viking Age and in the early Middle Age, a fear of the living dead within the mounds. Sometimes these mounds were opened and the inside of the tomb were desecrated, and the bones scattered. The sword would disappear in this sort of ”grave-robbery”. 32
 ► Swords were sometimes made of different magical materials. When being made, the smith, could pour bonepowder from a dead person or from a powerful animal, making the sword invincible and connected to the persons’ strength or the character of the animal. The maker was considered a magician in his craft. It was him who controlled the fire and the secrets of iron and steel. It is easy to understand what power he held, as he was the creator of powerful weapons leading to the death of many great men. 33
► Swords were sometimes made of different magical materials. When being made, the smith, could pour bonepowder from a dead person or from a powerful animal, making the sword invincible and connected to the persons’ strength or the character of the animal. The maker was considered a magician in his craft. It was him who controlled the fire and the secrets of iron and steel. It is easy to understand what power he held, as he was the creator of powerful weapons leading to the death of many great men. 33
 ► In ways, the sword in Viking Age could be looked upon as an ideology, similar to the emerging warrior codex, which had a long past in Scandinavian pre-history. In the location of the former city of Birka near Stockholm Viking Age a class of warriors distant to civil society becomes clearly visible. This is for example the case in Swedish Birka, where there was a garrison containing the warriors of the town. This part of the town was dedicated to the arts of war. In the Middle Ages, this warrior-class grew to be the future aristocracy of knighthood, and the sword remained their closest companion 34
► In ways, the sword in Viking Age could be looked upon as an ideology, similar to the emerging warrior codex, which had a long past in Scandinavian pre-history. In the location of the former city of Birka near Stockholm Viking Age a class of warriors distant to civil society becomes clearly visible. This is for example the case in Swedish Birka, where there was a garrison containing the warriors of the town. This part of the town was dedicated to the arts of war. In the Middle Ages, this warrior-class grew to be the future aristocracy of knighthood, and the sword remained their closest companion 34
 The Eddas • There also Norse oral religious traditions written as poems that are collectively named as Eddas. • They are folktales. • Eddas and Sagas weren’t written on paper. Instead on vellumsheepskin or calf skin. Vellum is more resistant to rot and preserves much better than paper does. Thank god they used vellum!! 35
The Eddas • There also Norse oral religious traditions written as poems that are collectively named as Eddas. • They are folktales. • Eddas and Sagas weren’t written on paper. Instead on vellumsheepskin or calf skin. Vellum is more resistant to rot and preserves much better than paper does. Thank god they used vellum!! 35
 The Sagas • “Saga” is a Norse word meaning tales. These writings provide almost all of the knowledge we have of the Vikings. • There about forty sagas that include descriptions of historical events in Iceland voyages across the North Atlantic from Norway, Greenland Vinland (Newfoundland). The sagas also have records of family history such as Erik the Red who founded Greenland, and his son Leif Erickson who discovered North America. • The Sagas were compiled in the 13 th and 14 th century, and later based on stories that originated as early as 400 and 500 years before that. • Archaeology is providing that a lot of these stories have a good basis of fact; in fact the Icelandic sagas were used to help find what might be the site of Vinland. 36
The Sagas • “Saga” is a Norse word meaning tales. These writings provide almost all of the knowledge we have of the Vikings. • There about forty sagas that include descriptions of historical events in Iceland voyages across the North Atlantic from Norway, Greenland Vinland (Newfoundland). The sagas also have records of family history such as Erik the Red who founded Greenland, and his son Leif Erickson who discovered North America. • The Sagas were compiled in the 13 th and 14 th century, and later based on stories that originated as early as 400 and 500 years before that. • Archaeology is providing that a lot of these stories have a good basis of fact; in fact the Icelandic sagas were used to help find what might be the site of Vinland. 36
 Write your name in Runes! ► http: //www. pbs. org/wgbh/nova/vikings/runes. html Runes Through Time by Nicole Sanderson The Vikings are often portrayed as illiterate, uncultured barbarians who evinced more interest in plunder than in poetry. In fact, the Vikings left behind a great number of documents in stone, wood and metal, all written in the enigmatic symbols known as runes. They relied on these symbols not only for writing but also to tell fortunes, cast spells, and provide protection. Early Germanic tribes of northern Europe were first to develop runes, but the Scandinavians soon adopted the symbols for their own use. When the seafaring Vikings traveled to faraway lands, they brought their system of writing with them, leaving runic inscriptions in places as distant as Greenland. 37
Write your name in Runes! ► http: //www. pbs. org/wgbh/nova/vikings/runes. html Runes Through Time by Nicole Sanderson The Vikings are often portrayed as illiterate, uncultured barbarians who evinced more interest in plunder than in poetry. In fact, the Vikings left behind a great number of documents in stone, wood and metal, all written in the enigmatic symbols known as runes. They relied on these symbols not only for writing but also to tell fortunes, cast spells, and provide protection. Early Germanic tribes of northern Europe were first to develop runes, but the Scandinavians soon adopted the symbols for their own use. When the seafaring Vikings traveled to faraway lands, they brought their system of writing with them, leaving runic inscriptions in places as distant as Greenland. 37
 Early Germanic tribes of northern Europe were first to develop runes, but the Scandinavians soon adopted the symbols for their own use. When the seafaring Vikings traveled to faraway lands, they brought their system of writing withrune characters were also Viking them, leaving inscribed on Greenland. runic inscriptions in places as distant as thumb-sized stones. They were placed in bags and removed one by to ► Wherever they went, Vikings turned to runes Viking fortunetellers and magicians to tell express both the poetic ("Listen, the future, heal the sick, banish evil, ring-bearers, while or bless people, places, I speak/Of the glories in war of Harald, most and things. wealthy") and the prosaic ("Rannvieg owns this box"), inscribing them on everything from great stone monuments to common household items. ► § Runes used as magic charms § When Vikings accepted Christianity began writing in Roman letters 38
Early Germanic tribes of northern Europe were first to develop runes, but the Scandinavians soon adopted the symbols for their own use. When the seafaring Vikings traveled to faraway lands, they brought their system of writing withrune characters were also Viking them, leaving inscribed on Greenland. runic inscriptions in places as distant as thumb-sized stones. They were placed in bags and removed one by to ► Wherever they went, Vikings turned to runes Viking fortunetellers and magicians to tell express both the poetic ("Listen, the future, heal the sick, banish evil, ring-bearers, while or bless people, places, I speak/Of the glories in war of Harald, most and things. wealthy") and the prosaic ("Rannvieg owns this box"), inscribing them on everything from great stone monuments to common household items. ► § Runes used as magic charms § When Vikings accepted Christianity began writing in Roman letters 38
 Section Three: discusses Viking influences in England, France, Russia and the North Atlantic III. Raiders and Adventurers ► A. By 800, due to population increases, Vikings began to seek their fortunes in other lands B. From east Europe to North § § Americahttp: //www. histori. ca/minutes/minute. do? id=10121 ► ► ► 1. establish trade routes from the Baltic to the Black Sea and on to Byzantium. Water route known as Varangian Route. 2. 862 Swedish chief Rurik founded settlement that became Kievan Rus state in Russia 3. Norwegian Vikings set up trading towns in Ireland 4. Erik the Red founds a colony on Greenland in 986 5. Leif Eriksson lands on northeast coast of North America 1000 A. D. and founds a colony they called Vinland. 39 6. Europe feared the Vikings
Section Three: discusses Viking influences in England, France, Russia and the North Atlantic III. Raiders and Adventurers ► A. By 800, due to population increases, Vikings began to seek their fortunes in other lands B. From east Europe to North § § Americahttp: //www. histori. ca/minutes/minute. do? id=10121 ► ► ► 1. establish trade routes from the Baltic to the Black Sea and on to Byzantium. Water route known as Varangian Route. 2. 862 Swedish chief Rurik founded settlement that became Kievan Rus state in Russia 3. Norwegian Vikings set up trading towns in Ireland 4. Erik the Red founds a colony on Greenland in 986 5. Leif Eriksson lands on northeast coast of North America 1000 A. D. and founds a colony they called Vinland. 39 6. Europe feared the Vikings
 § C. The Danes King Canute on the Seashore Book of Virtues § 1. Viking raiders of western and southern Long ago, England was ruled by a king named Canute. Like many Europe leaders and men of power, Canute was surrounded by people who were always praising him. Every time he walked into a room, the § 2. set up settlements in the Danelaw flattery began. regon—eventually become known as "You are the greatest man that ever lived, " one would say. Normans "O king, there can never heir of Alfred the Great forces them as you, " § 3. 954 be another as mightychest of Canute another The mortuary the Great (? 994 would insist. 1035). Canute was King of England from 1016 to to leave. 1035, King of Denmark from 1018 to 1035, and Norway from 1028 to 1035. As a Danish prince, "Your highness, there is nothing you cannot do, " someone would ► (a. ) Ethelred, King of England Canute won the alliance of Danes who had settled smile. in England, and he conquered the in 1018. nicknamed the Unready, Harold histhatisland Canute When his brother by died year, added the crown of Denmark and sing. "Great Canute, you weakness encouraged Danish attacks are the monarch of all, " another wouldrepelled an invasion fleet from Sweden and Norway. By 1026, "Nothing in this world dares to disobey you. " driven King Olaf the Stout from Canute had Norway, and in England § 4. 1016 Danish king Denmarkhe ruled there as well as. This chest Canute conquered and until his hearing such death in 1035. The king was a man of sense, and he grew tired of containing the bones of Canute and his wife England foolish speeches. Emma is one of several mortuary receptacles that are to Christianity (a. ) Canute convertsatop the choir screen of Winchester Cathedral at London. One day he was walking by the seashore, and his officers and ► courtiers were with (b. ) In 1035 after Canute dies the Danes lose 40 him, praising him as usual. Canute decided to control of England teach them a lesson. ►
§ C. The Danes King Canute on the Seashore Book of Virtues § 1. Viking raiders of western and southern Long ago, England was ruled by a king named Canute. Like many Europe leaders and men of power, Canute was surrounded by people who were always praising him. Every time he walked into a room, the § 2. set up settlements in the Danelaw flattery began. regon—eventually become known as "You are the greatest man that ever lived, " one would say. Normans "O king, there can never heir of Alfred the Great forces them as you, " § 3. 954 be another as mightychest of Canute another The mortuary the Great (? 994 would insist. 1035). Canute was King of England from 1016 to to leave. 1035, King of Denmark from 1018 to 1035, and Norway from 1028 to 1035. As a Danish prince, "Your highness, there is nothing you cannot do, " someone would ► (a. ) Ethelred, King of England Canute won the alliance of Danes who had settled smile. in England, and he conquered the in 1018. nicknamed the Unready, Harold histhatisland Canute When his brother by died year, added the crown of Denmark and sing. "Great Canute, you weakness encouraged Danish attacks are the monarch of all, " another wouldrepelled an invasion fleet from Sweden and Norway. By 1026, "Nothing in this world dares to disobey you. " driven King Olaf the Stout from Canute had Norway, and in England § 4. 1016 Danish king Denmarkhe ruled there as well as. This chest Canute conquered and until his hearing such death in 1035. The king was a man of sense, and he grew tired of containing the bones of Canute and his wife England foolish speeches. Emma is one of several mortuary receptacles that are to Christianity (a. ) Canute convertsatop the choir screen of Winchester Cathedral at London. One day he was walking by the seashore, and his officers and ► courtiers were with (b. ) In 1035 after Canute dies the Danes lose 40 him, praising him as usual. Canute decided to control of England teach them a lesson. ►
 Lion of Rollo, Ruler of Normandy § (b. ) In 1035 after Canute dies the Danes lose control of England ► 5. Danes attack the French in 885 led by Rollo Photo of Rollo statue depicted among the 6 § (a. ) 911 square of Falaise dukes of Normandy in the town French king signs treaty with Rollo § (b. ) Danes become Christian and promised loyalty to French king § (c. ) Region of Danish settlement under Rollo's grave at the cathedral of Rouen Norselaw becomes known as Normandy. Rouen Cathedral was the The Danes living on the coast of France world's become known as Normanstallest building from 1876 to 1880. * 41
Lion of Rollo, Ruler of Normandy § (b. ) In 1035 after Canute dies the Danes lose control of England ► 5. Danes attack the French in 885 led by Rollo Photo of Rollo statue depicted among the 6 § (a. ) 911 square of Falaise dukes of Normandy in the town French king signs treaty with Rollo § (b. ) Danes become Christian and promised loyalty to French king § (c. ) Region of Danish settlement under Rollo's grave at the cathedral of Rouen Norselaw becomes known as Normandy. Rouen Cathedral was the The Danes living on the coast of France world's become known as Normanstallest building from 1876 to 1880. * 41
 Pick one of the following essay questions to prepare for the chapter 20 test. ► 1. How do you think life in the United States might be different today if the Vikings had established colonies where they landed in North America before the year 1000? ► 2. What effect did Vikings have on the development of Europe during the Middle Ages? ► 3. Write an essay explaining the effect Christianity had on Viking Life? 42
Pick one of the following essay questions to prepare for the chapter 20 test. ► 1. How do you think life in the United States might be different today if the Vikings had established colonies where they landed in North America before the year 1000? ► 2. What effect did Vikings have on the development of Europe during the Middle Ages? ► 3. Write an essay explaining the effect Christianity had on Viking Life? 42


