c04dae829d07e45e11470beec1504e5a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 83

Rule-based approach in Arabic NLP: Tools, Systems and Resources Dr Khaled Shaalan Professor, Faculty of Computers & Information, Cairo University On Secondment to BUi. D, UAE Khaled. shaalan@{buid. ac. ae, gmail. com} CITALA 2009 - Morroco

Agenda n n n n Objective Language Tasks NLP Approaches Rule-based Arabic Analysis and generation tools Rule-based Arabic NLP applications Some Arabic NLP Free Resources Major and Arabic mailing lists Conclusion

Objective n To show rule-based approach has successfully used to develop Arabic natural language processing tools and applications.

Separating Language Tasks n n n n English vs. French vs. Arabic vs. . . spoken language (dialogue) vs written test vs hand written script Genuine Script vs transliterated (Romanized) script Vocalized (vowelized) vs non-vocalized Understanding vs. generation First language learner vs second language learner Classical or Qur’anical Arabic vs Modern Standard Arabic vs colloquial (dialects) Stem-based vs root-based

Rules n Situation/Action n n If match(stem. prefix, def_article) then romve(stem. prefix, Stem_FS) If match(stem. definitness, indefinite) then morph_gen(stem. definitness, Stem_FS)

Common Mistake n n n Rule-based approach is not a rule-based expert systems !!!!!!! Both consist of rules. Rule-based expert systems solves the problem by Recognize-Act Cycle n n Loop Conflict resolution strategy
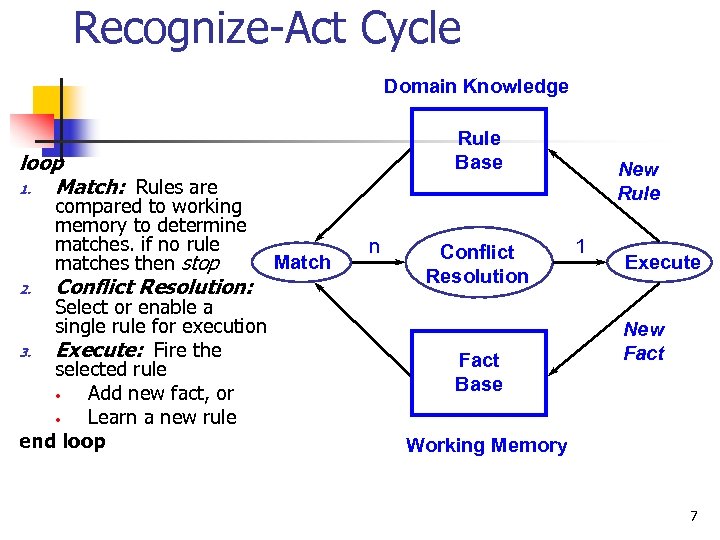
Recognize-Act Cycle Domain Knowledge Rule Base loop 1. Match: Rules are compared to working memory to determine matches. if no rule matches then stop 2. Conflict Resolution: Select or enable a single rule for execution 3. Execute: Fire the selected rule • Add new fact, or • Learn a new rule end loop Match n Conflict Resolution Fact Base New Rule 1 Execute New Fact Working Memory 7

NLP Approaches n n Rule-based Statistical-based
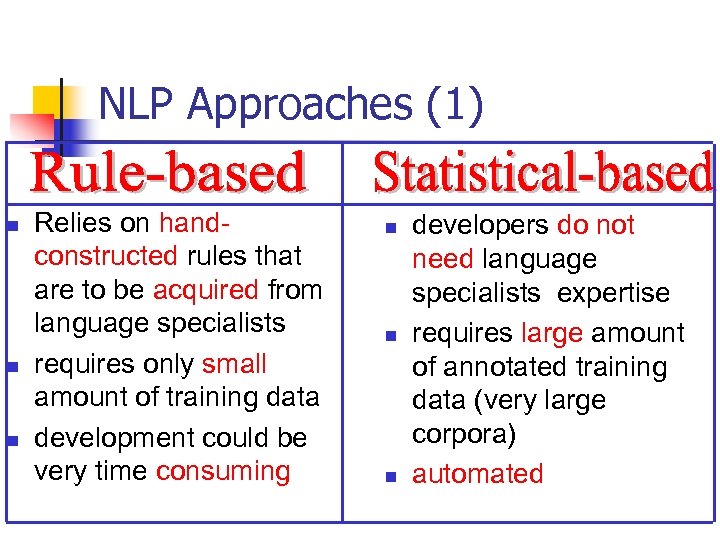
NLP Approaches (1) n n n Relies on handconstructed rules that are to be acquired from language specialists requires only small amount of training data development could be very time consuming n n n developers do not need language specialists expertise requires large amount of annotated training data (very large corpora) automated
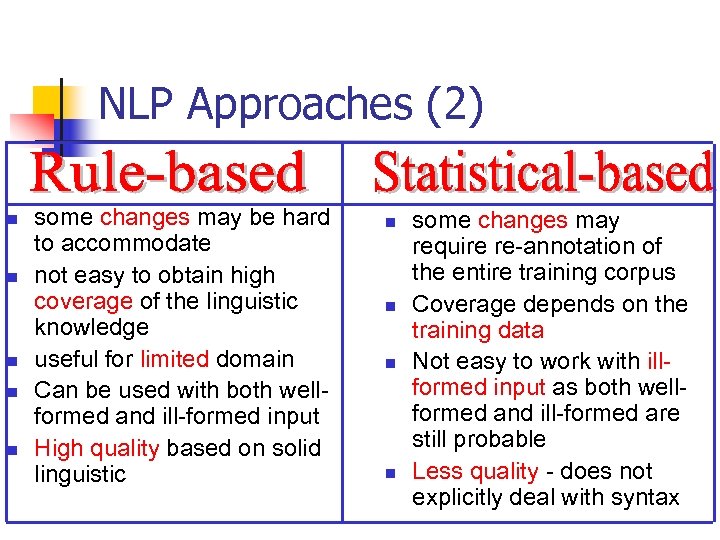
NLP Approaches (2) n n n some changes may be hard to accommodate not easy to obtain high coverage of the linguistic knowledge useful for limited domain Can be used with both wellformed and ill-formed input High quality based on solid linguistic n n some changes may require re-annotation of the entire training corpus Coverage depends on the training data Not easy to work with illformed input as both wellformed and ill-formed are still probable Less quality - does not explicitly deal with syntax

Rule-based Arabic NLP tools n n Morphological Analyzers Morphological Generators Syntactic Analyzers Syntactic Generators

Rule-based Arabic Morphological Analyzer
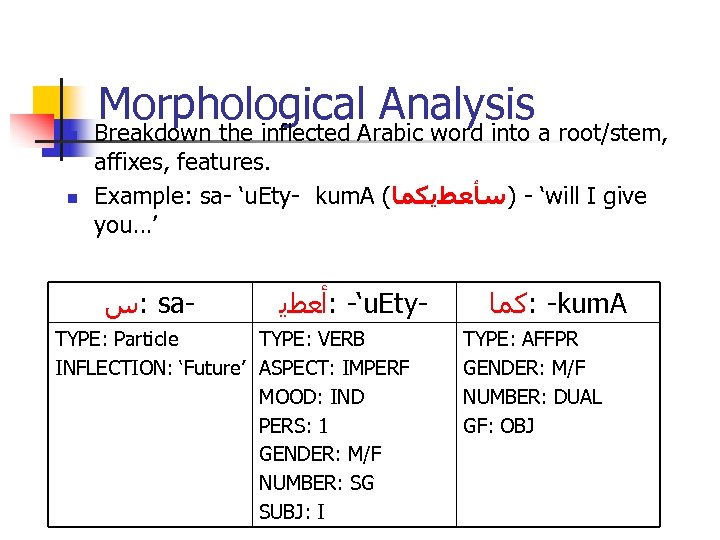
n n Morphological. Arabic word into a root/stem, Analysis Breakdown the inflected affixes, features. Example: sa- ‘u. Ety- kum. A ( ‘ - )ﺳﺄﻌﻄﯾﻜﻤﺎ will I give you…’ : ﺱ sa- ‘- : ﺃﻌﻄﯾ u. Ety- TYPE: Particle TYPE: VERB INFLECTION: ‘Future’ ASPECT: IMPERF MOOD: IND PERS: 1 GENDER: M/F NUMBER: SG SUBJ: I - : ﻛﻤﺎ kum. A TYPE: AFFPR GENDER: M/F NUMBER: DUAL GF: OBJ
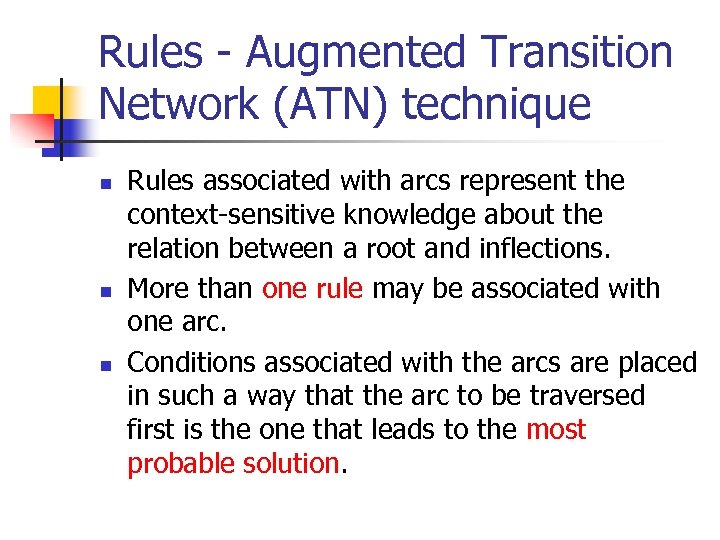
Rules - Augmented Transition Network (ATN) technique n n n Rules associated with arcs represent the context-sensitive knowledge about the relation between a root and inflections. More than one rule may be associated with one arc. Conditions associated with the arcs are placed in such a way that the arc to be traversed first is the one that leads to the most probable solution.
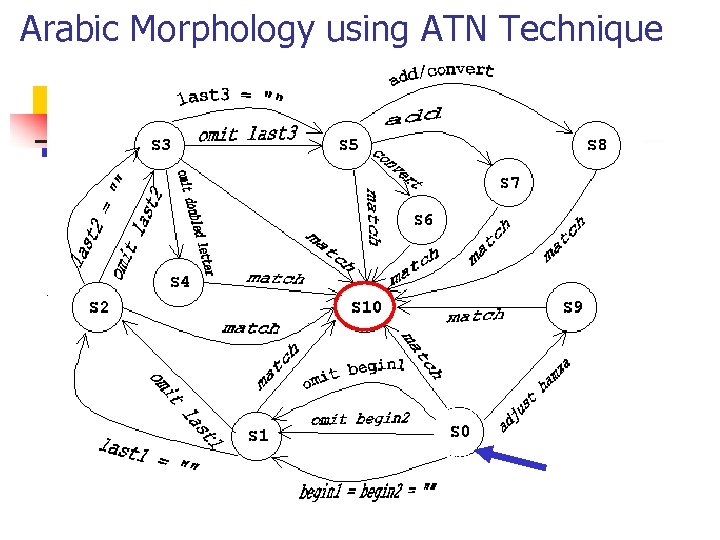
Arabic Morphology using ATN Technique

Types of Rules n n Remove Prefix or Suffix Remove doubled letter Add/change Hamza, Weak letter, … …
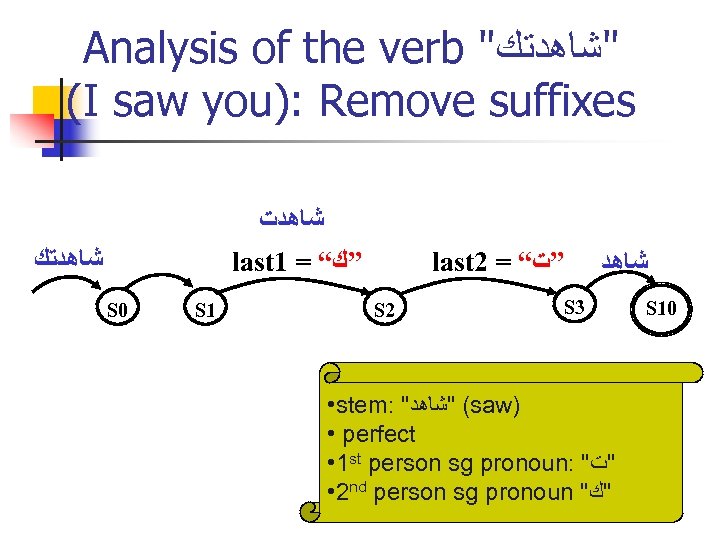
Analysis of the verb " "ﺷﺎﻫﺪﺗﻚ (I saw you): Remove suffixes ﺷﺎﻫﺪﺕ ﺷﺎﻫﺪﺗﻚ last 1 = “ ”ﻙ S 0 S 1 last 2 = “ ”ﺕ S 2 ﺷﺎﻫﺪ S 3 • stem: " ( "ﺷﺎﻫﺪ saw) • perfect • 1 st person sg pronoun: " "ﺕ • 2 nd person sg pronoun " "ﻙ S 10
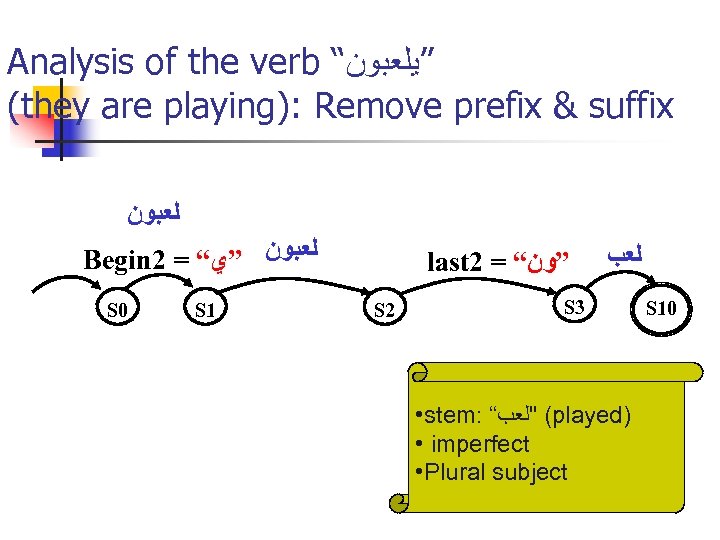
Analysis of the verb “ ”ﻳﻠﻌﺒﻮﻥ (they are playing): Remove prefix & suffix ﻟﻌﺒﻮﻥ Begin 2 = “ ﻟﻌﺒﻮﻥ ”ﻱ S 0 S 1 last 2 = “ ”ﻭﻥ S 2 ﻟﻌﺐ S 3 • stem: “ ( "ﻟﻌﺐ played) • imperfect • Plural subject S 10

Issues in the morphological analysis n n n n Overgeneration (too many output) Ambiguity Reconstruction of vowels Multi. Word/compound Expressions Out-of-Vocabulary (OOV) Handling ill-formed input n Detection (spell checking) n Correction- relaxation “ ”ﻩ instead of “ ”ﺓ Prevent ill-formed output n Check the compatibility (the prefix “ ”ﻑ cannot come after the prefix “ ( ”ﺏ or “. ))”ﻙ

Rule-based Arabic Morphological Generator

Morphological generation n Synthesis of an inflected Arabic word from a given root/stem according to a combination of morphological properties that include: n n n definiteness (definite article “ , )”ﺍﻝ gender (masculine, feminine), number (singular, dual, plural), case (nominative, genitive, accusative, …), person (first, second, third) …

Types of Rules n synthesis of inflected n n n Noun Verb particle

Synthesis of inflected Nouns n n n n definite noun feminine noun pluralize noun dual noun attach a prefix preposition attach a suffix pronoun end case ….

Synthesis of feminine noun n n If noun. gender = masculine Then attach suffix feminine letter Example: n “ ( ”ﺯﻭﺝ husband) “ ( ”ﺯﻭﺟﺔ wife)

Synthesis of suffix pronoun n n If pronoun. person = first and pronoun. number = singular Then attach first person singular suffix pronoun Example: n “ ( ”ﺯﻭﺟﺔ wife) “ ( ”ﺯﻭﺟﺘﻲ my wife)

Synthesis of inflected Verbs (very complex-rich in form and meaning) n n n conjugate …. a a verb with tense number prefix pronoun suffix pronoun

Rule: synthesize first person plural of assimilated verbs Input: first person singular past verb Output: inflected verb Example: ﻧﺼﻞ- ﺳﻨﺼﻞ - ﻭﺻﻠﻨﺎ If verb. tense = future then remove first weak & attach_prefix(" )"ﺳﻦ else if verb. tense = present then remove first weak & attach_prefix(" )"ﻥ else attach_suffix(verb. stem, " )"ﻧﺎ

Issues in the morphological generation n Multi. Word/compound Expressions Out-of-Vocabulary (OOV) Some forms need special handling: n n n Substitution: This man – ﻫﺬﺍ ﺍﻟﺮﺟﻞ literal numbers (complex nouns) Arabic script n n n ‘ ’ﺍﻝ‘ + ’ﻝ ‘ ’ﻟﻠـ “ ”ﺯﻣﻼﺀ“ + ”ﻱ ‘ ’ﺯﻣﻼﺀﻱ ‘ ’ﺯﻣﻼﺋﻲ “ ”ﻏﺮﻓﺔ “ ”ﻏﺮﻓﺘﺎﻥ

Rule-based Arabic Syntactic Analyzer

Types of Rules n Grammatical rules: n n Describe sentence and phrase structures, and ensure the agreement relations between various elements in the sentence. Parsing n Accepts the input and generates the sentence structure (parse tree)
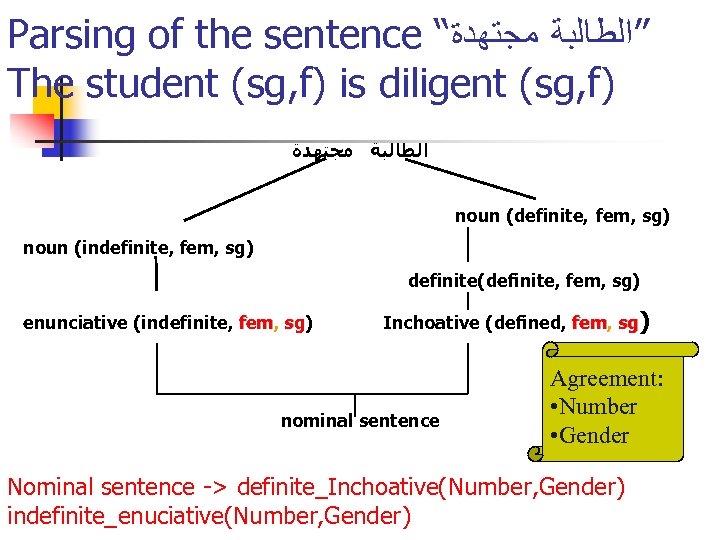
Parsing of the sentence “ ”ﺍﻟﻄﺎﻟﺒﺔ ﻣﺠﺘﻬﺪﺓ The student (sg, f) is diligent (sg, f) ﺍﻟﻄﺎﻟﺒﺔ ﻣﺠﺘﻬﺪﺓ noun (definite, fem, sg) noun (indefinite, fem, sg) definite(definite, fem, sg) enunciative (indefinite, fem, sg) fem sg Inchoative (defined, fem, sg) fem nominal sentence Agreement: • Number • Gender Nominal sentence -> definite_Inchoative(Number, Gender) indefinite_enuciative(Number, Gender)
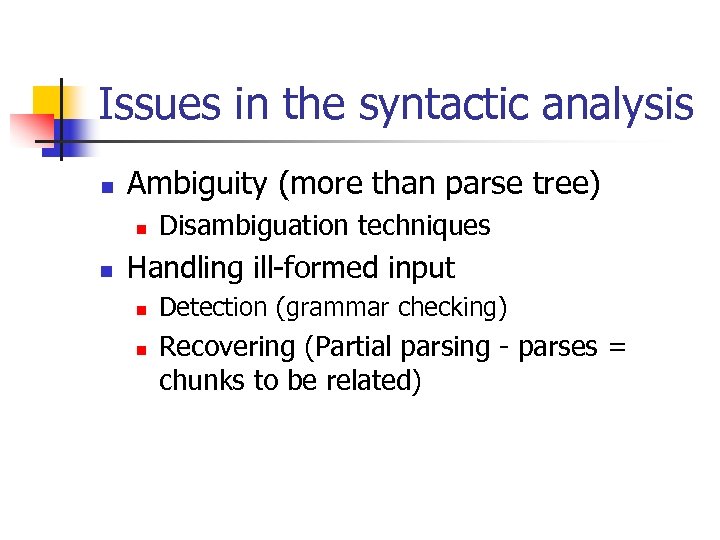
Issues in the syntactic analysis n Ambiguity (more than parse tree) n n Disambiguation techniques Handling ill-formed input n n Detection (grammar checking) Recovering (Partial parsing - parses = chunks to be related)

Rule-based Arabic Syntactic Generator

Types of Rules n n n Determine phrase structures Determine syntactic structure Ensure the agreement relations between various elements in the sentence.

Rule: verb-subject agreement Input: verb and inflected subject (a preverbal NP ) Output: inflected verb agreed with its inflected subject synthesize_verb(Subject. number, verb. stem) synthesize_verb(Subject. gender, verb. stem)

An agreement example: ﺍﻷﻮﻻﺩ ﺯﺍﺭﻭﺍ ﺧﻤﺲ ﻣﺘﺎﺣﻒ ﻗﺪﻳﻤﺔ the-boys visited-they five museum old The boys visited five old museums ﻗﺪﻳﻤﺔ Adj-noun (G) ﻣﺘﺎﺣﻒ ﺧﻤﺲ counted-Num (G) ﺯﺍﺭﻭﺍ ﺍﻷﻮﻻﺩ verb-Subject (N, G)

Issues in the syntactic generation n n Word order (VSO, SVO, etc. ) Agreement (full/partial) dropping the subject pronoun (called Pro-drop), i. e. , to have a null subject, when the inflected verb includes subject affixes. Syntax that captures the source/intended meaning n n My son is 8 = ﺃﺒﻨﻲ ﻋﻤﺮﻩ ﺛﻤﺎﻧﻲ ﺳﻨﻮﺍﺕ I did not understand the last sentence = ﺃﻨﺎ ﻟﻢ ﺃﻔﻬﻢ ﺍﻟﺠﻤﻠﺔ ﺍﻷﺨﻴﺮﺓ

A Rule-based Arabic NLP applications n n n Named Entity Recognition Machine translation Transferring Egyptian Colloquial Dialect into Modern Standard Arabic

What is entity recognition? n n Identifying, extracting, and normalizing entities from documents such as names of people, locations, or companies. Makes unstructured data more structured
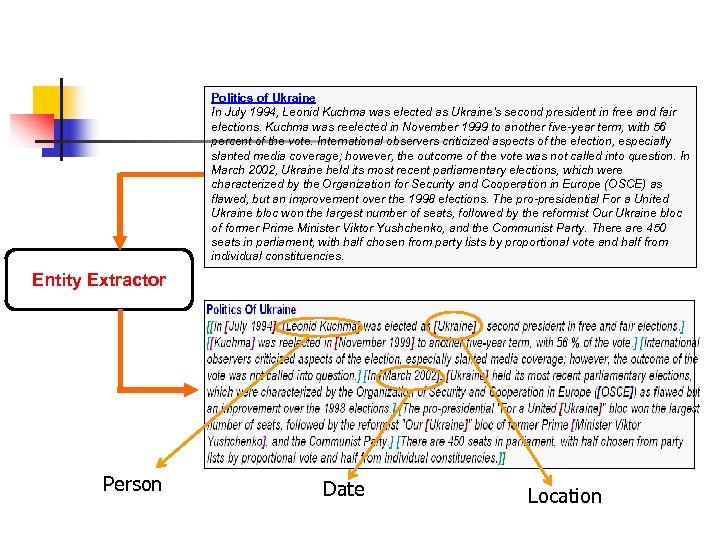
Politics of Ukraine In July 1994, Leonid Kuchma was elected as Ukraine's second president in free and fair elections. Kuchma was reelected in November 1999 to another five-year term, with 56 percent of the vote. International observers criticized aspects of the election, especially slanted media coverage; however, the outcome of the vote was not called into question. In March 2002, Ukraine held its most recent parliamentary elections, which were characterized by the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) as flawed, but an improvement over the 1998 elections. The pro-presidential For a United Ukraine bloc won the largest number of seats, followed by the reformist Our Ukraine bloc of former Prime Minister Viktor Yushchenko, and the Communist Party. There are 450 seats in parliament, with half chosen from party lists by proportional vote and half from individual constituencies. Entity Extractor Person Date Location

Person Entity Recognition (1) Example: ‘ ﺍﻷﺮﺩﻧﻲ ﻋﺒﺪ ﺍﻟﻠﻪ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻧﻲ ’ﺍﻟﻤﻠﻚ The Jordanian king Abdullah II n We want to have a rule that recognizes a person name composed of a first name followed by optional last names, based on a preceding person indicator pattern.
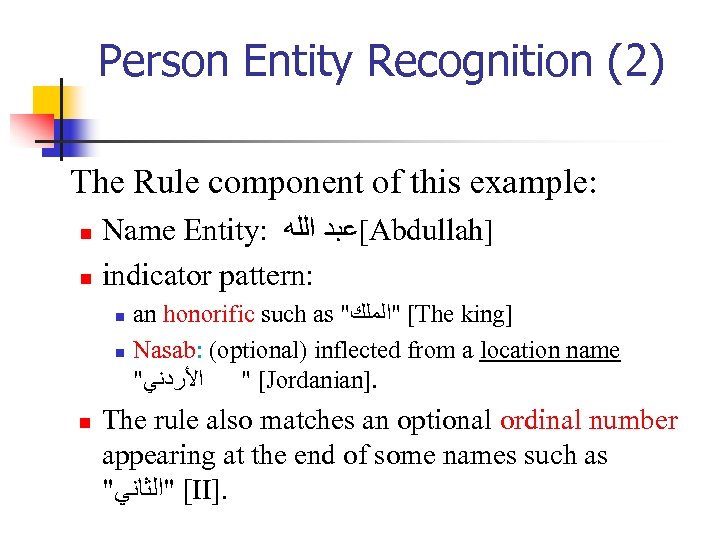
Person Entity Recognition (2) The Rule component of this example: n n Name Entity: [ﻋﺒﺪ ﺍﻟﻠﻪ Abdullah] indicator pattern: n n n an honorific such as " [ "ﺍﻟﻤﻠﻚ The king] Nasab: (optional) inflected from a location name " ﺍﻷﺮﺩﻧﻲ " [Jordanian]. The rule also matches an optional ordinal number appearing at the end of some names such as " [ "ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻧﻲ II].

Person Entity Recognition (3) ((honorfic+(location( +)? ))ﻱ|ﻳﺔ first_Name(last_Name)? +(number)? ) n This (Regular Expression) rule can recognize: n ﺍﻟﻤﻠﻚ ﻋﺒﺪ ﺍﻟﻠﻪ n ﺍﻷﺮﺩﻧﻲ ﻋﺒﺪ ﺍﻟﻠﻪ ﺍﻟﻤﻠﻚ n ﺍﻷﺮﺩﻧﻲ ﻋﺒﺪ ﺍﻟﻠﻪ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻧﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﻠﻚ n ﺍﻷﺮﺩﻧﻴﺔ ﺭﺍﻧﻴﺎ ﺍﻟﻤﻠﻜﺔ n …

Issues in the Arabic NER n n Complex Morphological System (inflections) Non-casing language (No initial capital for proper nouns) Non-standardization and inconsistency in Arabic written text (typos, and spelling variants) Ambiguity
Machine Translation n Direct Transfer Interlingua
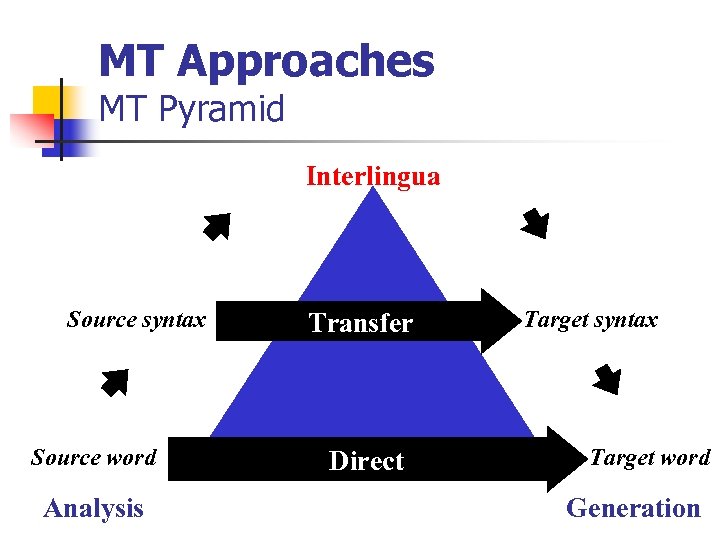
MT Approaches MT Pyramid Interlingua Source syntax Source word Analysis Transfer Direct Target syntax Target word Generation
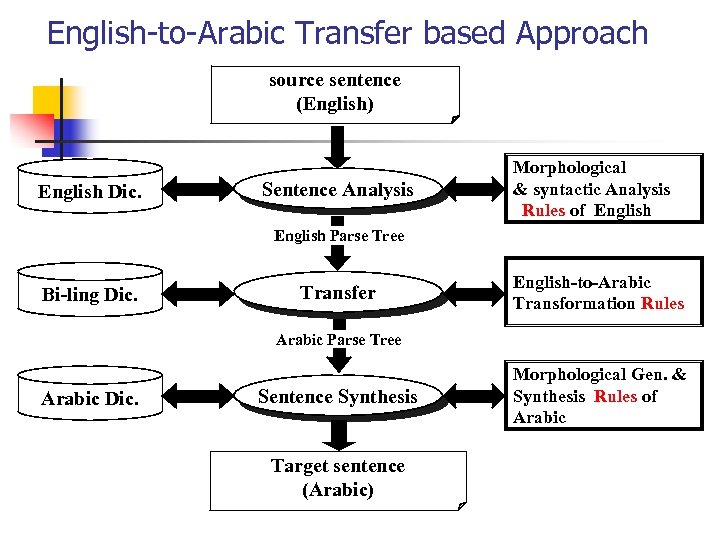
English-to-Arabic Transfer based Approach source sentence (English) English Dic. Sentence Analysis Morphological & syntactic Analysis Rules of English Parse Tree Bi-ling Dic. Transfer English-to-Arabic Transformation Rules Arabic Parse Tree Arabic Dic. Sentence Synthesis Target sentence (Arabic) Morphological Gen. & Synthesis Rules of Arabic

Transfer approach n n Involves analysis, transfer, and generation components If you have an Arabic parser & Arabic syntactic generator, All you need is to acquire the transfer rules and build the transfer component
![Simple Transfer (1) [wi: $1, wi+1: $2, …, wk: $k] (1 i k) [wk: Simple Transfer (1) [wi: $1, wi+1: $2, …, wk: $k] (1 i k) [wk:](https://present5.com/presentation/c04dae829d07e45e11470beec1504e5a/image-49.jpg)
Simple Transfer (1) [wi: $1, wi+1: $2, …, wk: $k] (1 i k) [wk: $k, wk-1: $k-1, …, wi: $i] (1 i k)
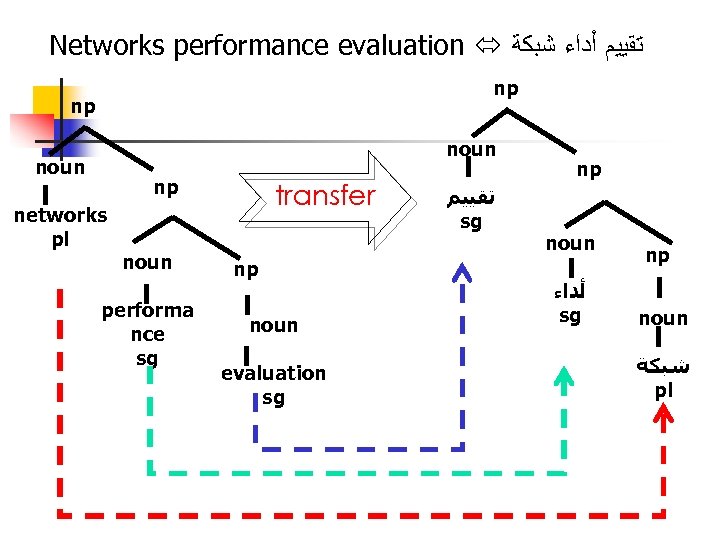
Networks performance evaluation ﺗﻘﻴﻴﻢ ﺃﺪﺍﺀ ﺷﺒﻜﺔ np np noun np networks pl noun performa nce sg transfer np noun evaluation sg ﺗﻘﻴﻴﻢ sg np noun ﺃﺪﺍﺀ sg np noun ﺷﺒﻜﺔ pl

Issues in the Transfer-based MT approach n Synonyms of a word n n Agreement n n Acquisition “ ”ﺍﻛﺘﺴﺎﺏ or “. ”ﺍﺳﺘﺨﻼﺹ intelligent tutoring systems “ ﻧﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻴﻢ ”ﺍﻟﺬﻛﻴﺔ or “ ”ﻧﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻴﻢ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﻲ Problems with prepositions did you do fungal analysis? “ ”ﻫﻞ ﻗﻤﺖ ﺑـﺘﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻔﻄﺮ؟ n n …
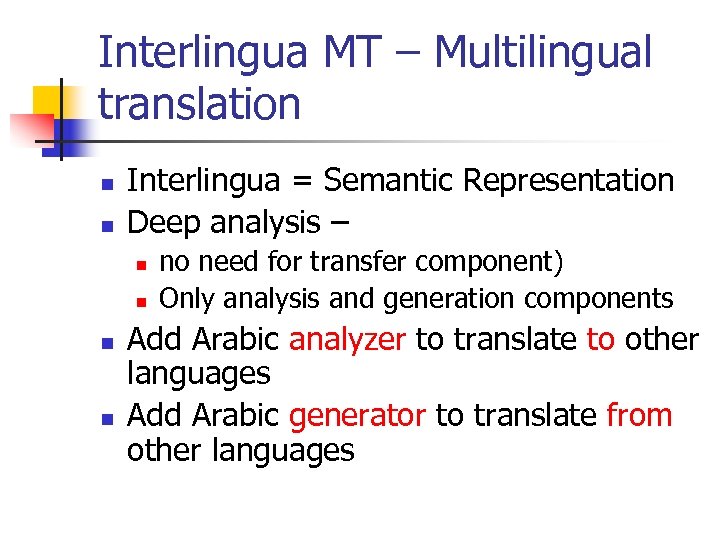
Interlingua MT – Multilingual translation n n Interlingua = Semantic Representation Deep analysis – n n no need for transfer component) Only analysis and generation components Add Arabic analyzer to translate to other languages Add Arabic generator to translate from other languages
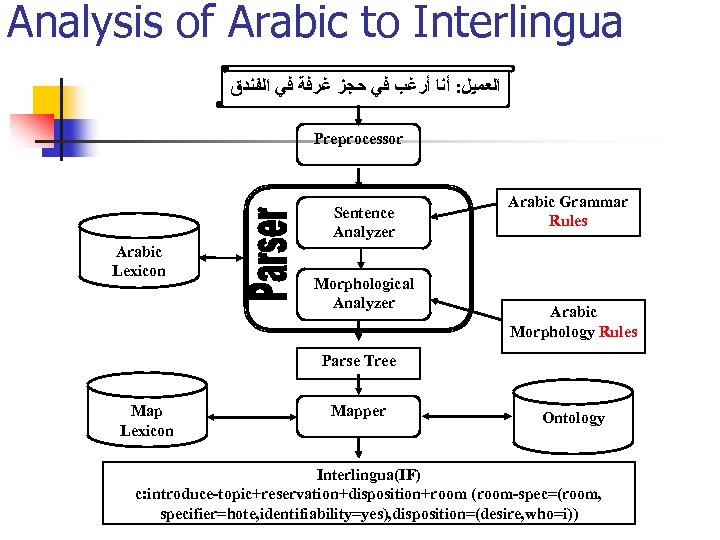
Analysis of Arabic to Interlingua ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻴﻞ: ﺃﻨﺎ ﺃﺮﻏﺐ ﻓﻲ ﺣﺠﺰ ﻏﺮﻓﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻔﻨﺪﻕ Preprocessor Sentence Analyzer Arabic Lexicon Morphological Analyzer Arabic Grammar Rules Arabic Morphology Rules Parse Tree Map Lexicon Mapper Ontology Interlingua(IF) c: introduce-topic+reservation+disposition+room (room-spec=(room, specifier=hote, identifiability=yes), disposition=(desire, who=i))
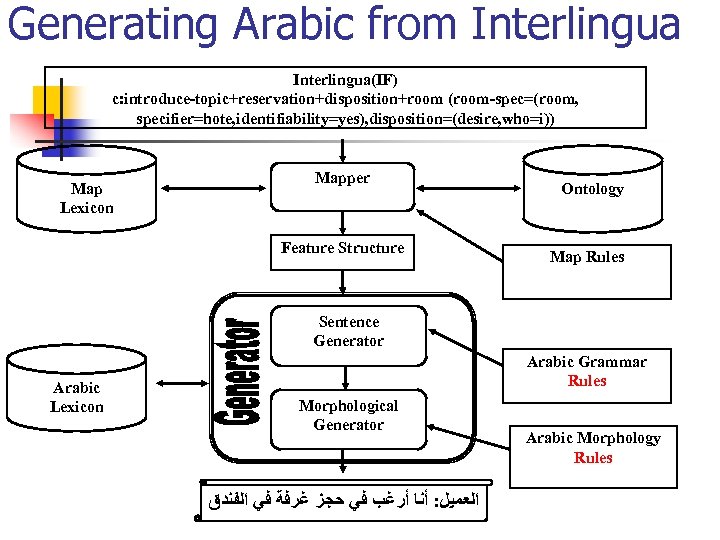
Generating Arabic from Interlingua(IF) c: introduce-topic+reservation+disposition+room (room-spec=(room, specifier=hote, identifiability=yes), disposition=(desire, who=i)) Map Lexicon Mapper Feature Structure Ontology Map Rules Sentence Generator Arabic Lexicon Arabic Grammar Rules Morphological Generator ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻴﻞ: ﺃﻨﺎ ﺃﺮﻏﺐ ﻓﻲ ﺣﺠﺰ ﻏﺮﻓﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻔﻨﺪﻕ Arabic Morphology Rules

Issues in the interlingua approach n Interlingua: n n n language-neutral representation captures the intended meaning of the source sentence Requires a fully-disambiguating parser

Transferring Egyptian Colloquial Dialect into Modern Standard Arabic n n n Be able to reuse MSA processing tools with colloquial Arabic by transferring colloquial Arabic words into their corresponding MSA words. Facilitate the communication with colloquial Arabic speakers Restore the Arabic dialect to the standard language in use nowadays.
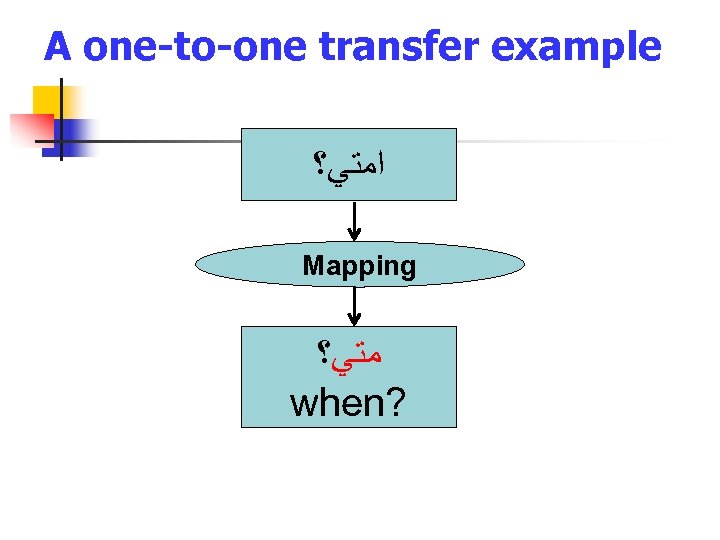
A one-to-one transfer example ﺍﻣﺘﻲ؟ Mapping ﻣﺘﻲ؟ when?
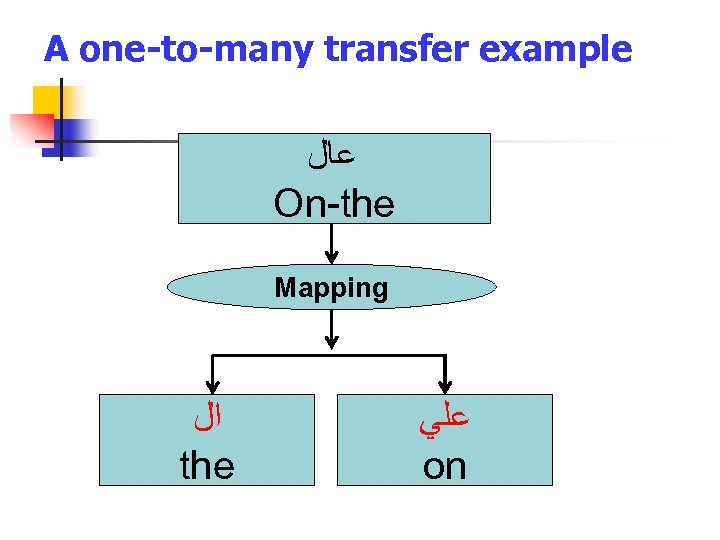
A one-to-many transfer example ﻋﺎﻝ On-the Mapping ﺍﻝ the ﻋﻠﻲ on
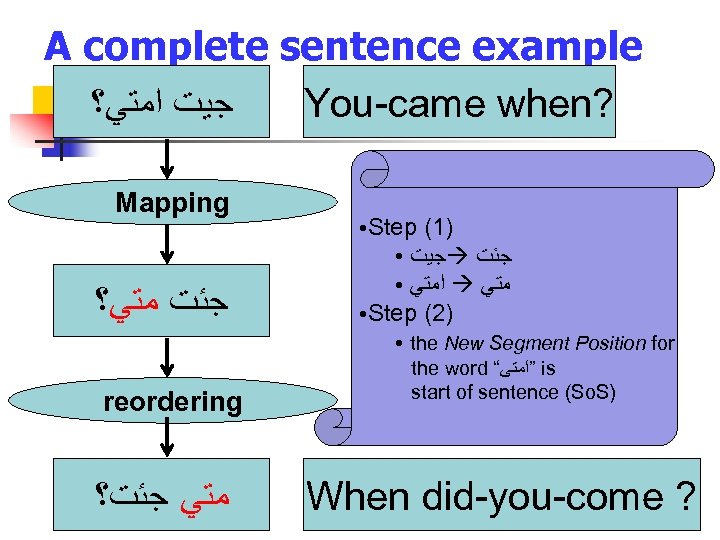
A complete sentence example ﺟﻴﺖ ﺍﻣﺘﻲ؟ You-came when? Mapping Step (1) ● ﺟﻴﺖ ﺟﺌﺖ ● ﺍﻣﺘﻲ ●Step (2) ● ﺟﺌﺖ ﻣﺘﻲ؟ ● reordering ﻣﺘﻲ ﺟﺌﺖ؟ the New Segment Position for the word “ ”ﺍﻣﺘﻰ is start of sentence (So. S) When did-you-come ?

Issues in the transfer to MSA n More investigations are needed

Arabic NLP Free Resources

Arabic Morphological Analyzers n Tim Buckwalter Morphological http: //www. qamus. org/ n http: //www. ldc. upenn. edu/Catalog. E ntry. jsp? catalog. Id=LDC 2002 L 49 n n Xerox n http: //www. cis. upenn. edu/~cis 639/a rabic/input/keyboard_input. html

Arabic Morphological Analyzers n Aramorph n http: //www. nongnu. org/aramorph/englis h/index. html

Arabic spell checker n Aspell http: //aspell. net/ n http: //www. freshports. org/arabic/aspell n

Arabic Morphological Generation n Sarf n http: //sourceforge. net/projects/sarf

Tokenization & POS tagging n Arabic. SVMTools: The tools utilize the Yamcha SVM tools to tokenize, POS tag and Base Phrase Chunk Arabic text http: //www 1. cs. columbia. edu/~mdiab/ n http: //www 1. cs. columbia. edu/~mdiab/softw are/AMIRA-1. 0. tar. gz n

Tokenization & POS tagging n MADA: a full morphological tagger for Modern Standard Arabic. n http: //www 1. cs. columbia. edu/~rambow/sof tware-downloads/MADA_Distribution. html
POS tagging n Stanford Log-linear Part-Of-Speech Tagger http: //nlp. stanford. edu/software/tagger. sht ml n http: //nlp. stanford. edu/software/stanfordarabic-tagger-2008 -09 -28. tar. gz n

Tokenization & POS tagging n Attia's Finite State Tools for Modern Standard Arabic n http: //www. attiaspace. com/getrec. asp? rec= htm. Files/fsttools

Arabic Parsers n Dan Bikel’s Parser n http: //www. cis. upenn. edu/~dbikel/software. html n Attia Arabic Parser n http: //www. attiaspace. com/ n http: //decentius. aksis. uib. no/logon/xle. xml n
Arabic wordnet n Arabic Word. Net http: //www. globalwordnet. org/AWN/ n http: //personalpages. manchester. ac. uk/staff /paul. thompson/AWNBrowser. zip n

Translation resources n Tools: GIZA++, MOSES, Pharaoh, Rewrite and BLEU n n http: //www. statmt. org/ APIs: http: //code. google. com/apis/ajax/playgroun d/#translate n http: //code. google. com/apis/ajax/playgroun d/#batch_translate n

Transliterate n http: //code. google. com/apis/ajax/playgroun d/#transliterate_arabic

Mailing Lists – just to be connected to the NLP community n corpora@uib. no n n linguist@LINGUISTLIST. ORG n n http: //www. linguistlist. org/ semitic@cs. haifa. ac. il n n http: //mailman. uib. no/listinfo/corpora http: //www. semitic. tk/ caasl-list@arabicscript. org n http: //www. arabicscript. org/CAASL 3/index. html

Conclusion (1) n n Arabic requires the treatment of the language constituents at all levels: morphology, syntax, and semantics. Most of the researches in Arabic NLP are mainly concentrated on the analysis part aiming at automated understanding of Arabic language.

Conclusion (2) n n Arabic NLP in general is significantly under developed. In order to bridge this gab and help Arabic NLP research to catch up with the many recent advances of Latin languages, we need collaborative efforts from the Arabic research community.

Conclusion (3) n We need Public Domain (in Electronic Form) for: n n n Linguistic resources such as large Arabic (bilingual) Corpora and treebanks. Machine readable (bilingual) dictionaries Morphological Analyzers Parsers …

Conclusion (4) n We need to secure fund for: n n n Exchanging visits (experience Expert Network) Buy software Secure dedicated RA’s and/or Ph. D students for the NLP task.

References (1) - Journals n n n Khaled Shaalan, Hafsa Raza, NERA: Named Entity Recognition for Arabic, the Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology (JASIST), John Wiley & Sons, Inc. , NJ, USA, 60(7): 1– 12, July 2009. Shaalan, K. , Monem, A. A. , Rafea, A. , Arabic Morphological Generation from Interlingua: A Rule-based Approach, in IFIP International Federation for Information Processing, Vol. 228, Intelligent Information Processing III, eds. Z. Shi, Shimohara K. , Feng D. , (Boston: Springer), PP. 441 -451, 2006. Shaalan, K. , Talhami H. , and Kamel I. , Morphological Generation for Indexing Arabic Speech Recordings, The International Journal of Computer Processing of Oriental Languages (IJCPOL), World Scientific Publishing Company, 20(1)1: 14, 2007.

References (2) - Journals n n n Shaalan K. An Intelligent Computer Assisted Language Learning System for Arabic Learners, Computer Assisted Language Learning: An International Journal, Taylor & Francis Group Ltd. , 18(1 & 2): 81 -108, February 2005. Shaalan K. Arabic Gram. Check: A Grammar Checker for Arabic, Software Practice and Experience, John Wiley & sons Ltd. , UK, 35(7): 643 -665, June 2005. Shaalan K. , Rafea, A. , Abdel Monem, A. , Baraka, H. , Machine Translation of English Noun Phrases into Arabic, The International Journal of Computer Processing of Oriental Languages (IJCPOL), World Scientific Publishing Company, n 17(2): 121 -134, 2004. Rafea A. , Shaalan K. , Lexical Analysis of Inflected Arabic words using Exhaustive Search of an Augmented Transition Network, Software Practice and Experience, John Wiley & sons Ltd. , UK, 23(6): 567 -588, June 1993.

References (3) – workshops & conferences n Hosny, A. , Shaalan, K. , Fahmy, A. , Automatic Morphological Rule Induction for Arabic, In the Proceedings of The LREC'08 workshop on HLT & NLP within the Arabic world: Arabic Language and local languages processing: Status Updates and Prospects, 31 st May, PP. 97 -101, 2008. n Shaalan, K. , Abo Bakr, H. , Ziedan, I. , Transferring Egyptian Colloquial into Modern Standard Arabic, International Conference on Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing (RANLP – 2007) , Borovets, Bulgaria, PP. 525 n 529, September 27 -29, 2007. Shaalan, K. , Abdel Monem, A. , Rafea, A. , Baraka, H. , Generating Arabic Text from Interlingua, In the Proceedings of the 2 nd Workshop on Computational Approaches to Arabic Script-based Languages, CAASL-2, Linguistic Institute, Stanford, California, USA, PP. 137 -144, July 21 -22, 2007.

References (4) – workshops & conferences n Othman E. , Shaalan K. , and Rafea A. , Towards Resolving Ambiguity in Understanding Arabic Sentence, In the Proceedings of the International Conference on Arabic Language Resources and Tools, n NEMLAR, PP. 118 -122, 22 nd– 23 rd Sept. , Egypt, , 2004. Othman E. , Shaalan K. , and Rafea A. A Chart Parser for Analyzing Modern Standard Arabic Sentence, In proceedings of the MT Summit IX Workshop on Machine Translation for Semitic Languages: Issues and Approaches, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA. , September, 2003.
Thank you! Merci! Shukran! ﺷﻜﺮﺍ
c04dae829d07e45e11470beec1504e5a.ppt