602ff4594b886f5dce9b476a078f51a5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50

RTI International Designing a metabolomics experiment Grier P Page Ph. D. Senior Statistical Geneticist RTI International Atlanta Office gpage@rti. org 770 -407 -4907 RTI International is a trade name of Research Triangle Institute. www. rti. org
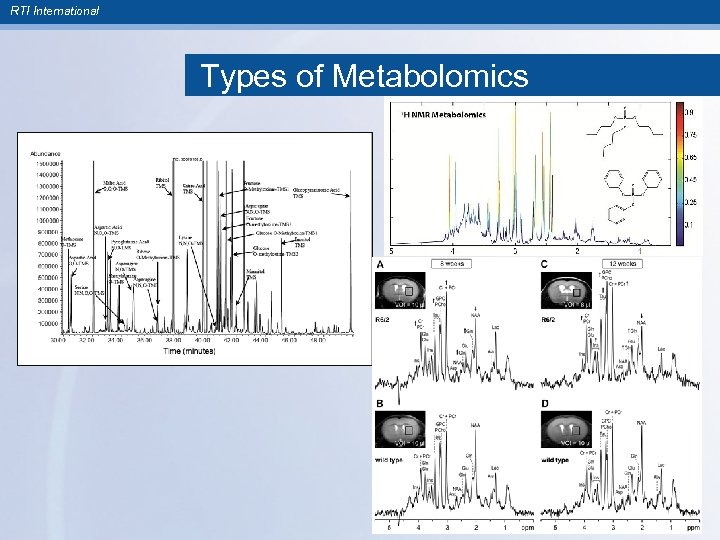
RTI International Types of Metabolomics

RTI International Designing a good study

RTI International Primary consideration of good experimental design Understand the strengths and weaknesses of each step of the experiments. § Take these strengths and weaknesses into account in your design. §
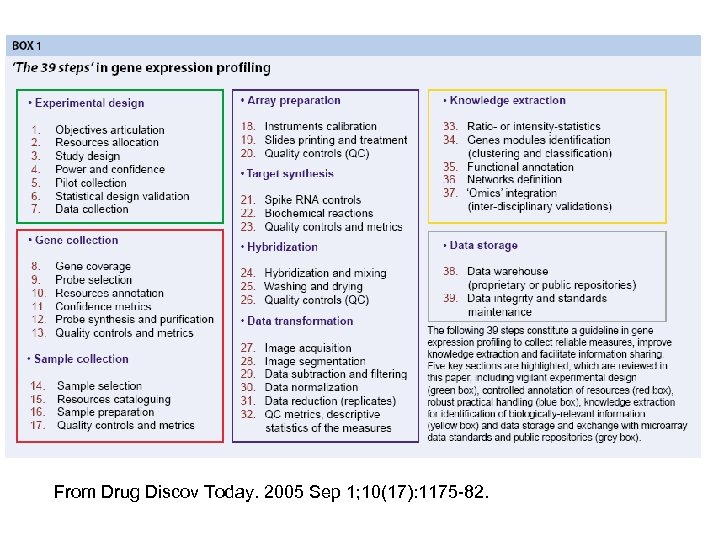
From Drug Discov Today. 2005 Sep 1; 10(17): 1175 -82.

RTI International State the Question and Articulate the Goals

RTI International The Myth That Data Mining has No Hypothesis There always needs to be a biological question in the experiment. If there is not even a question don’t bother. § The question could be nebulous: What happens to the gene expression of this tissue when I apply Drug A. § The purpose of the question is to drive the experimental design. § Make sure the samples answer the question: Cause vs. effect. §

RTI International Experimental Design
RTI International Biological replication is essential. Two types of replication – Biological replication – samples from different individuals are analyzed – Technical replication – same sample measured repeatedly § Technical replicates allow only the effects of measurement variability to be estimated and reduced, whereas biological replicates allow this to be done for both measurement variability and biological differences between cases. Almost all experiments that use statistical inference require biological replication, §
RTI International Statistical analyses Supervised analyses – linear models etc – Using fold change alone as a differential expression test is not valid. – ‘Shrinkage’ and or use of Bayes can be a good thing. § False-discovery rate is a good alternative to conventional multiple-testing approaches. § Data is not missing at random § Pathway testing is desirable. §
RTI International Classification Supervised classification – Supervised-classification procedures require independent cross-validation. – See MAQC-II recommendations Nat Biotechnol. 2010 August ; 28(8): 827– 838. doi: 10. 1038/nbt. 1665. § Wholly separate model building and validation stages. Can be 3 stage with multiple models tested § Unsupervised classification – Unsupervised classification should be validated using resampling-based procedures. §

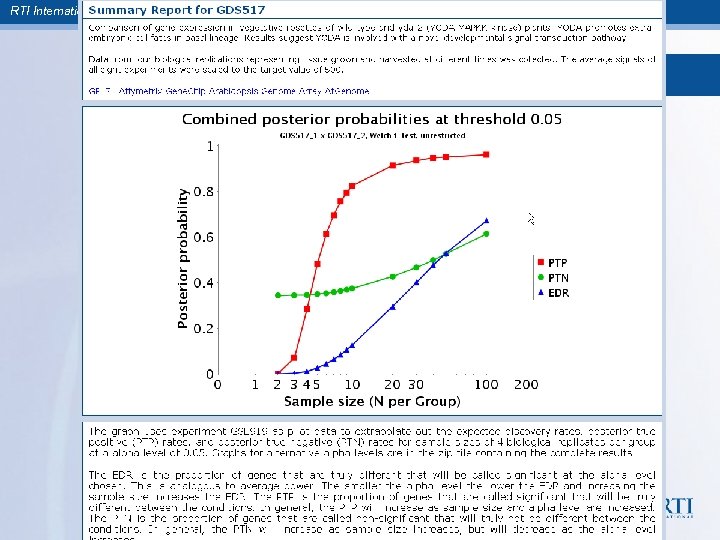
RTI International Sample size estimation for metabolomics studies
RTI International There is strength in numbers — power and sample size. § Unsupervised analyses Principal components, clustering, heat maps and variants – These are actually data transformations or data display rather than hypothesis testing, thus unclear if sample size estimation is appropriate or even possible. – Stability of clustering may be appropriate to think about. Garge et al 2005 suggested 50+ samples for any stability. –

RTI International Sample size in supervised experiments § Supervised analyses – – Linear models and variants Methods are still evolving, but we suggest the approach we developed for microarrays may be appropriate for metabolomics (being evaluated)
RTI International
RTI International

RTI International Experimental Conduct All experiments are subject to nonbiological variability that can confound any study
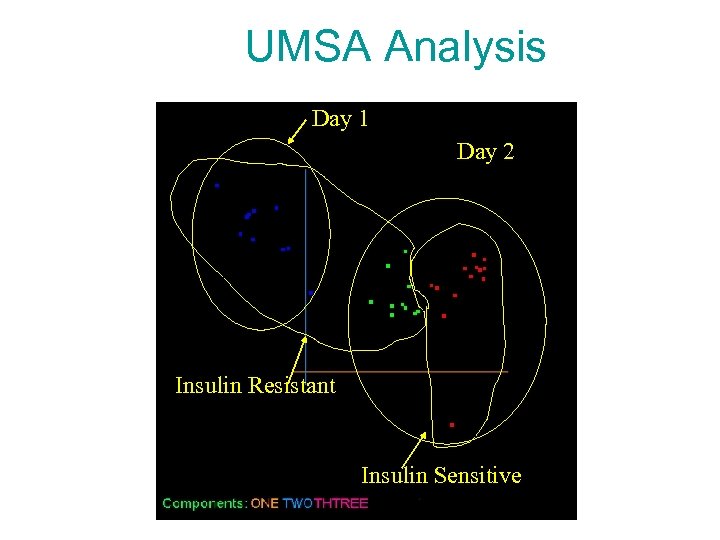
UMSA Analysis Day 1 Day 2 Insulin Resistant Insulin Sensitive

RTI International Design Issues § Known sources of non-biological error (not exhaustive) that must be addressed – – – – Technician / post-doc Reagent lot Temperature Protocol Date Location Cage/ Field positions

RTI International Control Everything! § Know what you are doing § Practice!

RTI International Metabolite quality § Still evolving field, few good metrics such as RIN score or A 260/A 280 ratios to assess contamination and quality of extraction.
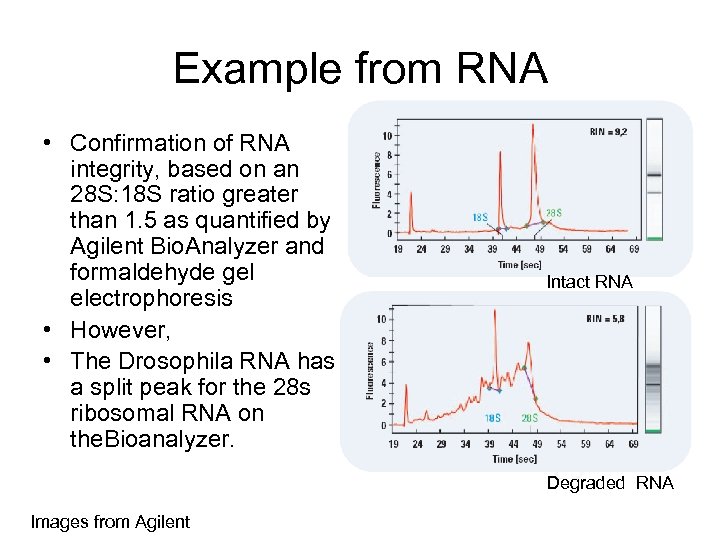
Example from RNA • Confirmation of RNA integrity, based on an 28 S: 18 S ratio greater than 1. 5 as quantified by Agilent Bio. Analyzer and formaldehyde gel electrophoresis • However, • The Drosophila RNA has a split peak for the 28 s ribosomal RNA on the. Bioanalyzer. Intact RNA Degraded RNA Images from Agilent
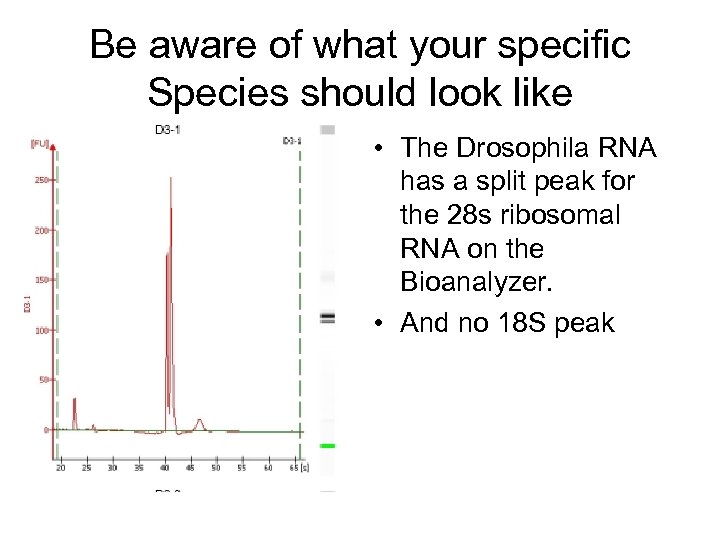
Be aware of what your specific Species should look like • The Drosophila RNA has a split peak for the 28 s ribosomal RNA on the Bioanalyzer. • And no 18 S peak

RTI International What if you can’t control or make all things uniform Randomize § Orthogonalize §

What are Orthogonalization and Randomization ? • Orthogonalization- spreading the biological sources of error evenly across the nonbiological sources of error. – Maximally powerful for known sources of error. • Randomization – spear the biological sources of error at random across the nonbiological sources of error. – Useful for controlling for unknown sources of error
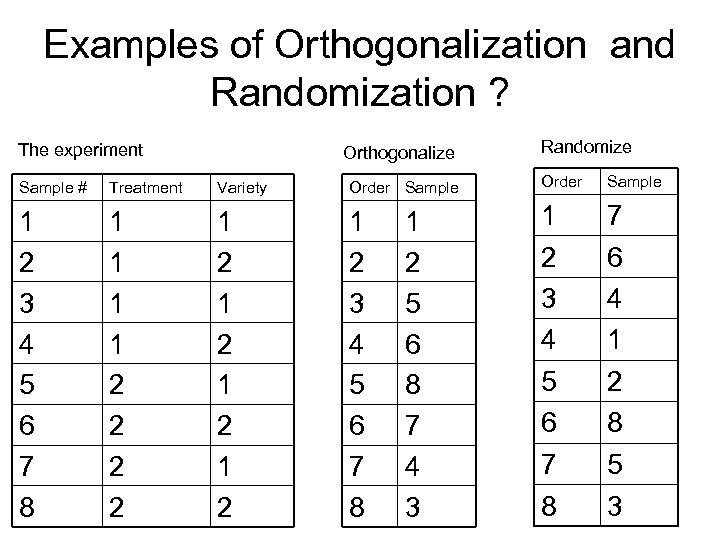
Examples of Orthogonalization and Randomization ? The experiment Orthogonalize Randomize Sample # Treatment Variety Order Sample 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 1 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 7 6 4 1 2 8 5 3 1 2 5 6 8 7 4 3
RTI International Know your data - What should it look like
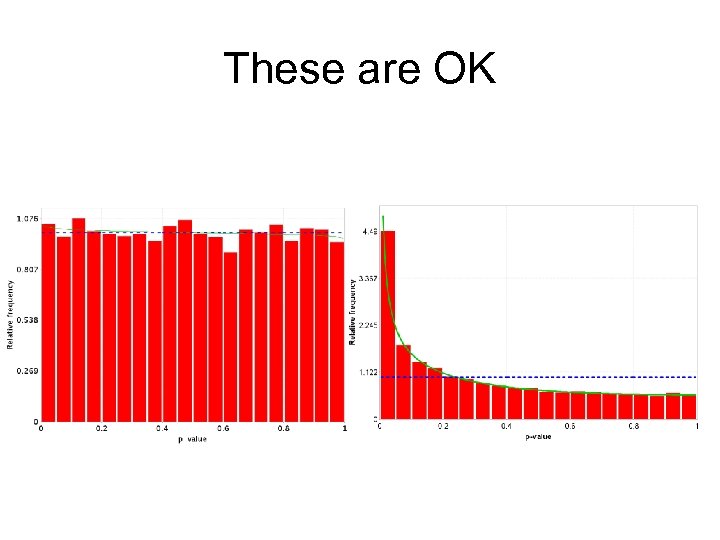
These are OK
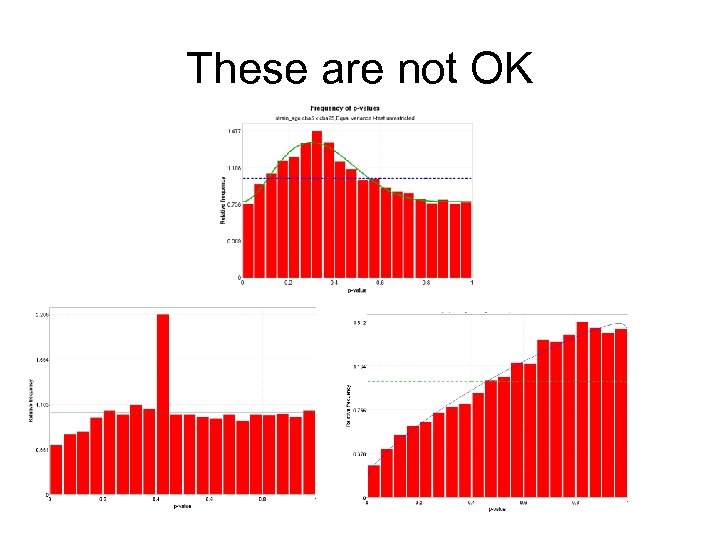
These are not OK

RTI International One bad sample can contaminate an experiment
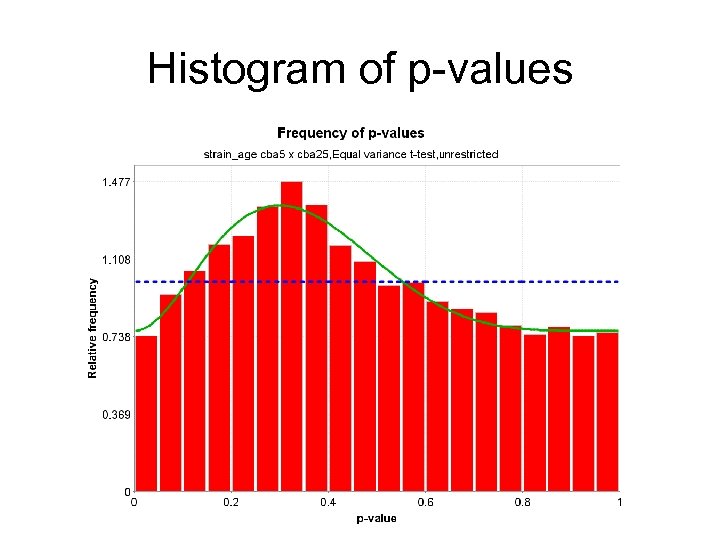
Histogram of p-values
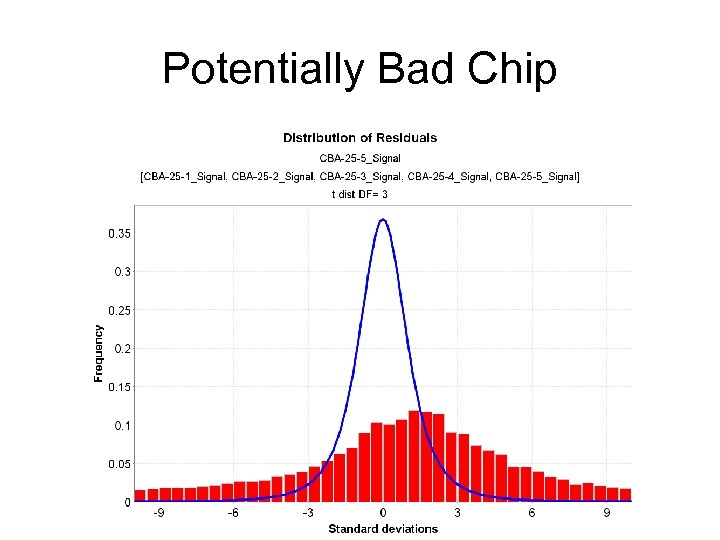
Potentially Bad Chip
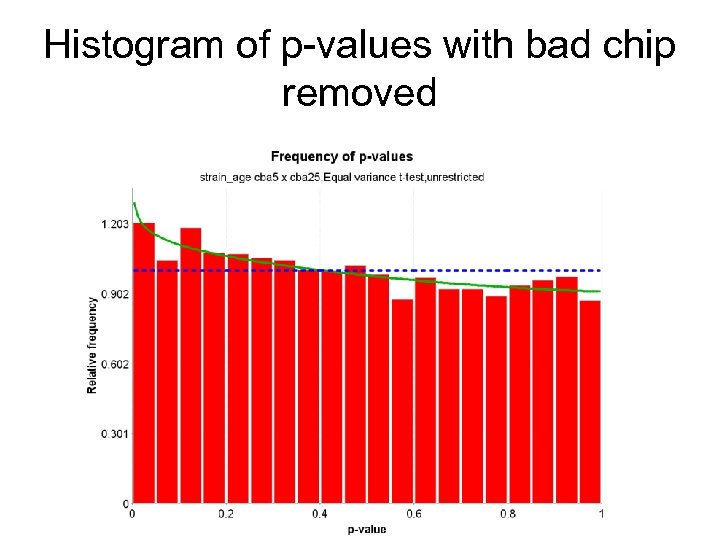
Histogram of p-values with bad chip removed

RTI International Quality of Database, Bioinformatics and Interpretative tools

RTI International Understand what databases include, don’t include, and assumptions § § § Just because a database says something does not mean it is right. Read the evidence. Databases are biased. Databases are incomplete Databases have lots of data Understand data before you use it Database are useful!

RTI International Issues in the Annotation of Genes RTI International is a trade name of Research Triangle Institute. www. rti. org
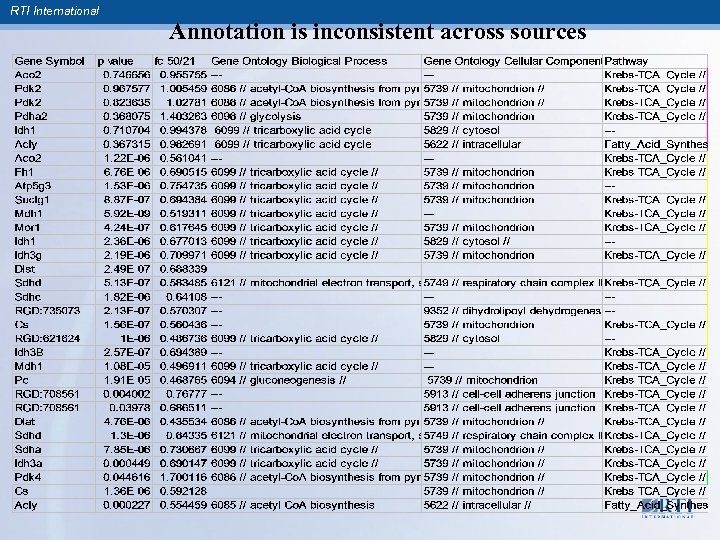
RTI International Annotation is inconsistent across sources

RTI International Issues with pathway data RTI International is a trade name of Research Triangle Institute. www. rti. org
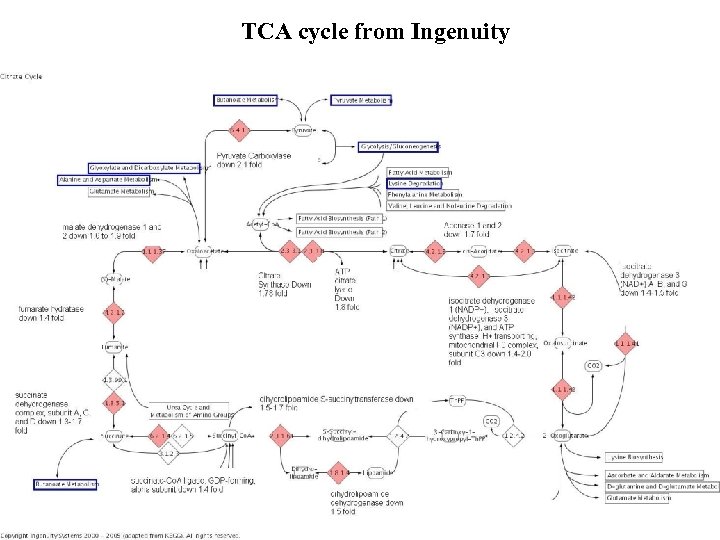
TCA cycle from Ingenuity
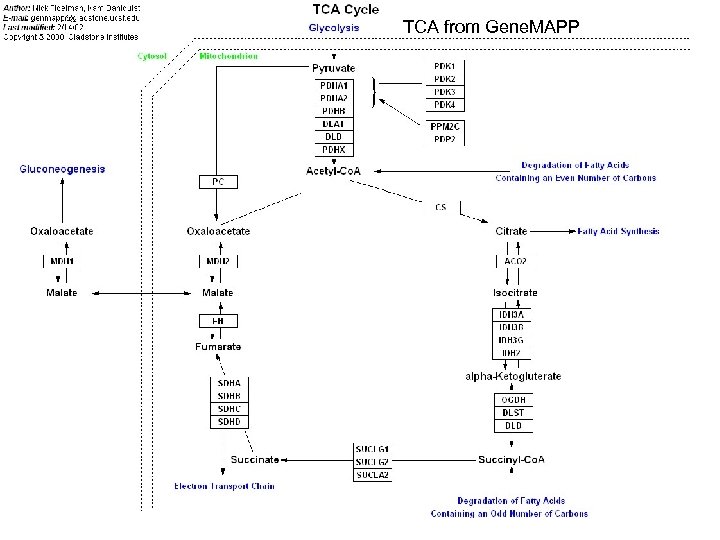
TCA from Gene. MAPP
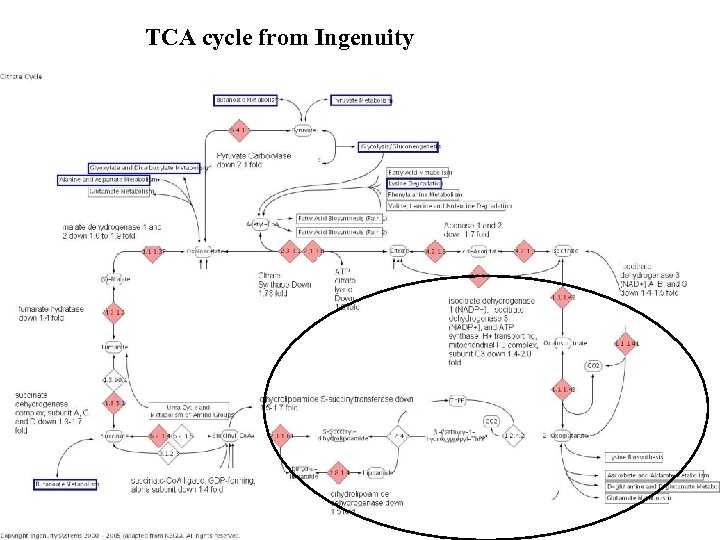
TCA cycle from Ingenuity

RTI International Summary § § § Design your experiment well Conduct your experiment well Control for non-biological sources of error Know what is good and bad quality data at each stage including metabolite, image, data, and annotation If you are aware of these issues and control for them highly powerful and reproducible metabolite experimentation is possible. Else you get garbage

RTI International Overshare your data and show work Practice compendium research – to allow others to replicate your work § Many high profile omic studies are not even technically reproducible §

RTI International References § § § The Micro. Array Quality Control (MAQC)-II study of common practices for the development and validation of microarray based predictive models. Nat Biotechnol. 2010 August ; 28(8): 827– 838. Microarray data analysis: from disarray to consolidation and consensus. Nat Rev Genet. 2006 Jan; 7(1): 55 -65. Reproducible clusters from microarray research: whither? BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Jul 15; 6 Suppl 2: S 10. Baggerly K. "Disclose all data in publications. " Nature. 2010 Sep 23; 467(7314): 401. PMID: 20864982 Repeatability of published microarray gene expression analyses. Nat Genet. 2009 Feb; 41(2): 149 -55 A design and statistical perspective on microarray gene expression studies in nutrition: the need for playful creativity and scientific hard-mindedness. Nutrition. 2003 Nov-Dec; 19(11 -12): 9971000.

If time allows

RTI International RTI Regional Comprehensive Metabolomics Resource Core (RTI RCMRC) Susan Sumner, Ph. D Director RTI RCMRC Discovery Sciences Proteomics and Metabolomics Programs RTI International is a trade name of Research Triangle Institute. www. rti. org

RTI International Contact Information for the RTI RCMRC Susan C. J. Sumner, Ph. D Director RTI RCMRC Senior Scientist nano. Safety RTI International Discovery Sciences 3040 Cornwallis Drive Research Triangle Park North Carolina 27709 ssumner@rti. org 919 -541 -7479 (office) 919 -622 -4456 (cell) Jason P. Burgess, Ph. D Program Coordinator, RTI RCMRC Associate Director, Discovery Sciences RTI International 3040 Cornwallis Drive Research Triangle Park North Carolina 27709 jpb@rti. org 919 -541 -6700 (office)
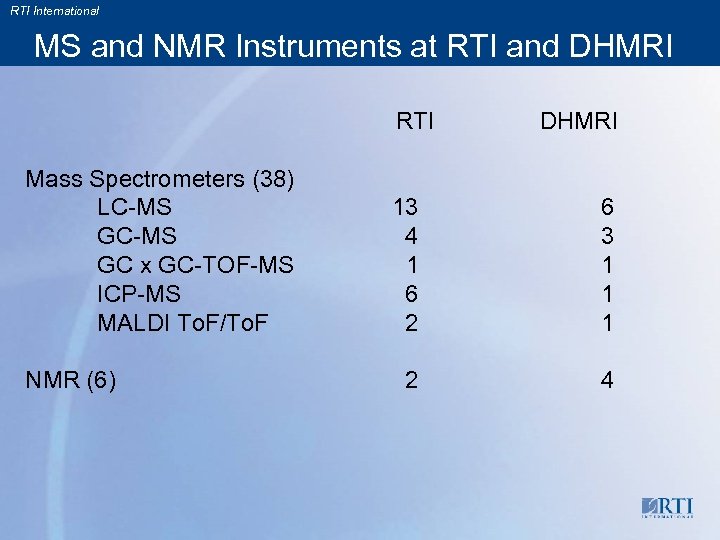
RTI International MS and NMR Instruments at RTI and DHMRI RTI Mass Spectrometers (38) LC-MS GC x GC-TOF-MS ICP-MS MALDI To. F/To. F NMR (6) DHMRI 13 4 1 6 2 6 3 1 1 1 2 4

RTI International Some RTI Metabolomics Applications and Pilots Experience with adolescent and adult human subject research, animal model and cell based research, e. g. , §Apoptosis- cells §Drug induced liver injury- animal models §in utero exposure to chemicals and fetal imprinting- animal models §Dietary exposure and imprinting- animal models §NAFLD - pediatric obesity; microbiome §Weight Loss- pediatric obesity §Preterm delivery- human subjects §Response to vaccine- human subjects §Nicotine withdrawal- human subjects §Colon cancer- human subjects

RTI International Pilot and Feasibility Studies § The aim of the pilot and feasibility program is to foster collaborations and promote the use of metabolomics. § Studies will be selected through an application process. – Application involves abstract, description of samples available (matrix type, volume, type and duration of storage, sample processing, freeze thaws, etc), description of phenotypes, and plan for subsequent grant/contract submissions for metabolomics analysis beyond initial pilot study. § Applications may also include technology development. § Applications must agree to deposit data in DRCC, coauthor publications, and submit joint grant/contract proposals. § Deadlines being defined
602ff4594b886f5dce9b476a078f51a5.ppt