L3_2013.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Routing protocols. Static routing. Lecture 3
Routing protocols. Static routing. Lecture 3
 Routing (маршрутизація) • The primary function of a router is to forward a packet toward its destination network, which is the destination IP address of the packet. • To do this, a router needs to search the routing information stored in its routing table. • A routing table (таблиця маршрутизації) is a data file in RAM that is used to store route information about directly connected and remote networks. • To check a routing table use show ip route command in privileged EXEC mode of a router. 2
Routing (маршрутизація) • The primary function of a router is to forward a packet toward its destination network, which is the destination IP address of the packet. • To do this, a router needs to search the routing information stored in its routing table. • A routing table (таблиця маршрутизації) is a data file in RAM that is used to store route information about directly connected and remote networks. • To check a routing table use show ip route command in privileged EXEC mode of a router. 2
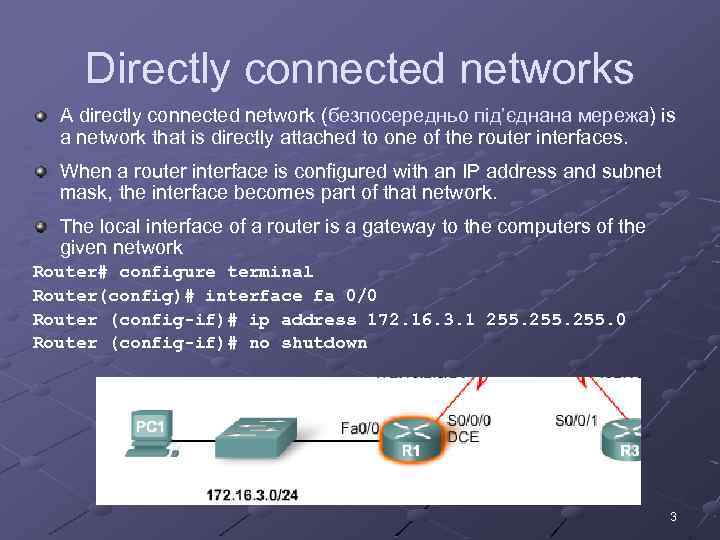 Directly connected networks A directly connected network (безпосередньо під’єднана мережа) is a network that is directly attached to one of the router interfaces. When a router interface is configured with an IP address and subnet mask, the interface becomes part of that network. The local interface of a router is a gateway to the computers of the given network Router# configure terminal Router(config)# interface fa 0/0 Router (config-if)# ip address 172. 16. 3. 1 255. 0 Router (config-if)# no shutdown 3
Directly connected networks A directly connected network (безпосередньо під’єднана мережа) is a network that is directly attached to one of the router interfaces. When a router interface is configured with an IP address and subnet mask, the interface becomes part of that network. The local interface of a router is a gateway to the computers of the given network Router# configure terminal Router(config)# interface fa 0/0 Router (config-if)# ip address 172. 16. 3. 1 255. 0 Router (config-if)# no shutdown 3
 Directly connected networks Once interface is up, the network it belongs to is added to the routing table, denoted with a “C” character. 4
Directly connected networks Once interface is up, the network it belongs to is added to the routing table, denoted with a “C” character. 4
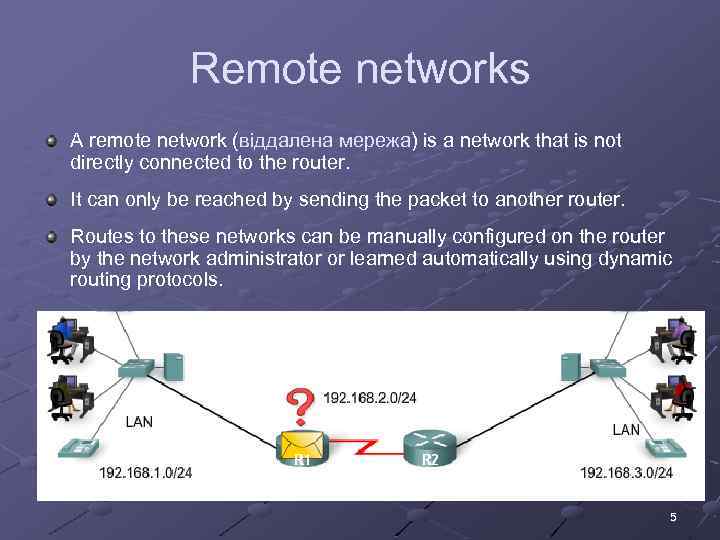 Remote networks A remote network (віддалена мережа) is a network that is not directly connected to the router. It can only be reached by sending the packet to another router. Routes to these networks can be manually configured on the router by the network administrator or learned automatically using dynamic routing protocols. 5
Remote networks A remote network (віддалена мережа) is a network that is not directly connected to the router. It can only be reached by sending the packet to another router. Routes to these networks can be manually configured on the router by the network administrator or learned automatically using dynamic routing protocols. 5
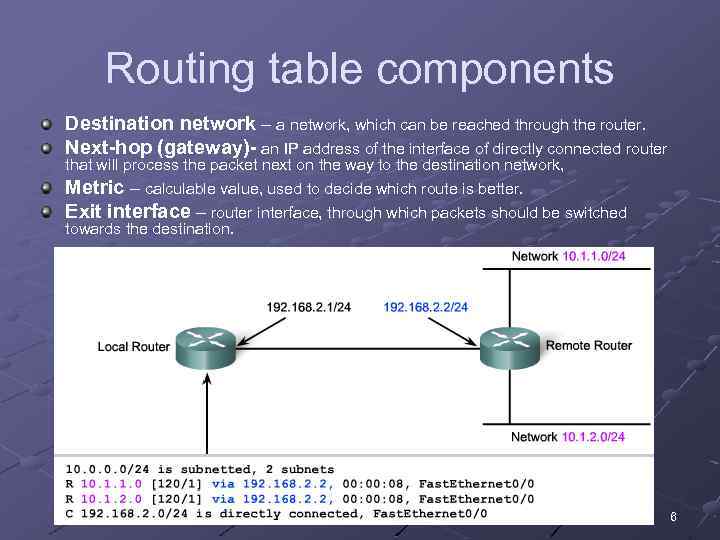 Routing table components Destination network – a network, which can be reached through the router. Next-hop (gateway)- an IP address of the interface of directly connected router that will process the packet next on the way to the destination network, Metric – calculable value, used to decide which route is better. Exit interface – router interface, through which packets should be switched towards the destination. 6
Routing table components Destination network – a network, which can be reached through the router. Next-hop (gateway)- an IP address of the interface of directly connected router that will process the packet next on the way to the destination network, Metric – calculable value, used to decide which route is better. Exit interface – router interface, through which packets should be switched towards the destination. 6
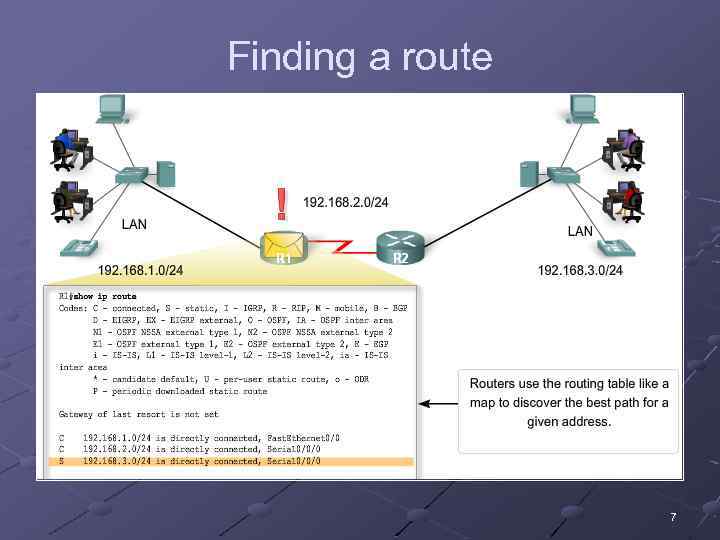 Finding a route 7
Finding a route 7
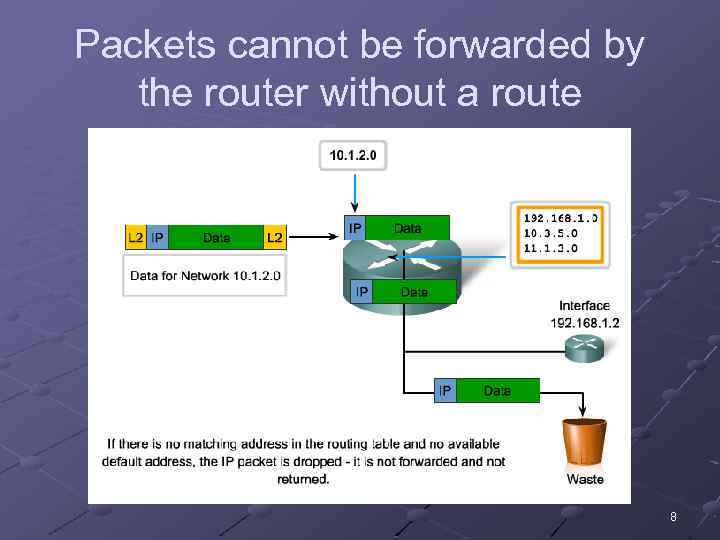 Packets cannot be forwarded by the router without a route 8
Packets cannot be forwarded by the router without a route 8
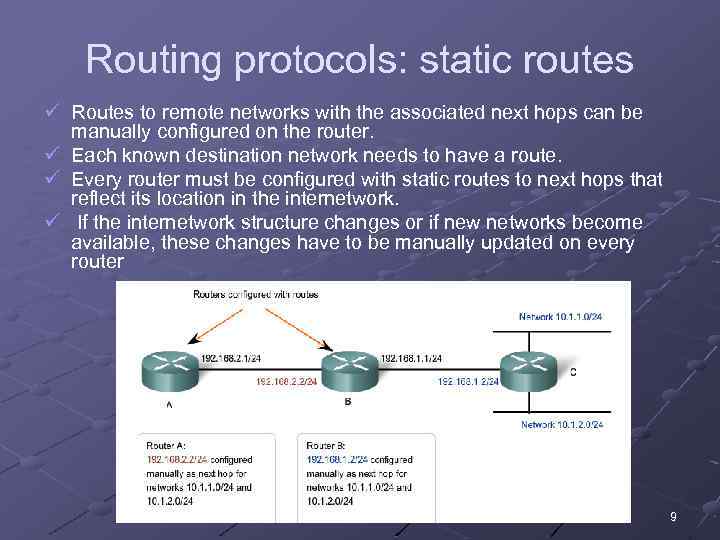 Routing protocols: static routes ü Routes to remote networks with the associated next hops can be manually configured on the router. ü Each known destination network needs to have a route. ü Every router must be configured with static routes to next hops that reflect its location in the internetwork. ü If the internetwork structure changes or if new networks become available, these changes have to be manually updated on every router 9
Routing protocols: static routes ü Routes to remote networks with the associated next hops can be manually configured on the router. ü Each known destination network needs to have a route. ü Every router must be configured with static routes to next hops that reflect its location in the internetwork. ü If the internetwork structure changes or if new networks become available, these changes have to be manually updated on every router 9
 Static routes should be used in the following cases: A network consists of only a few routers and is not expected to grow significantly. A network is connected to the Internet only through a single ISP. A large network is configured in a hub-and-spoke topology. A hub-and-spoke topology consists of a central location (the hub) and multiple branch locations (spokes), with each spoke having only one connection to the hub. 10
Static routes should be used in the following cases: A network consists of only a few routers and is not expected to grow significantly. A network is connected to the Internet only through a single ISP. A large network is configured in a hub-and-spoke topology. A hub-and-spoke topology consists of a central location (the hub) and multiple branch locations (spokes), with each spoke having only one connection to the hub. 10
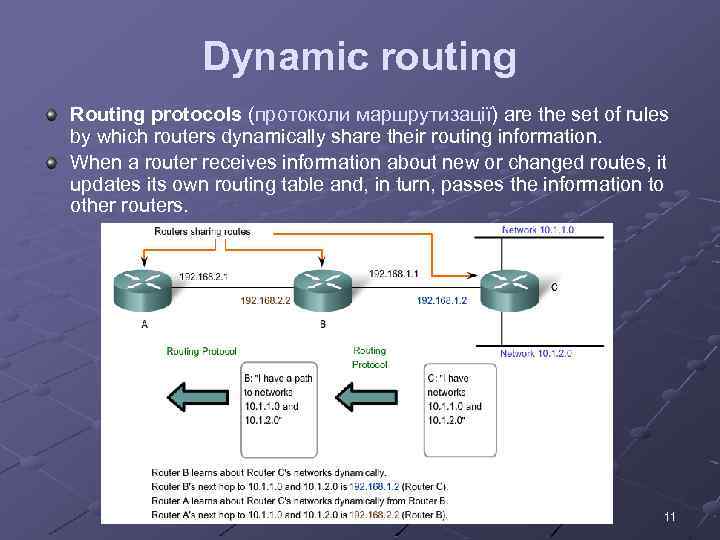 Dynamic routing Routing protocols (протоколи маршрутизації) are the set of rules by which routers dynamically share their routing information. When a router receives information about new or changed routes, it updates its own routing table and, in turn, passes the information to other routers. 11
Dynamic routing Routing protocols (протоколи маршрутизації) are the set of rules by which routers dynamically share their routing information. When a router receives information about new or changed routes, it updates its own routing table and, in turn, passes the information to other routers. 11
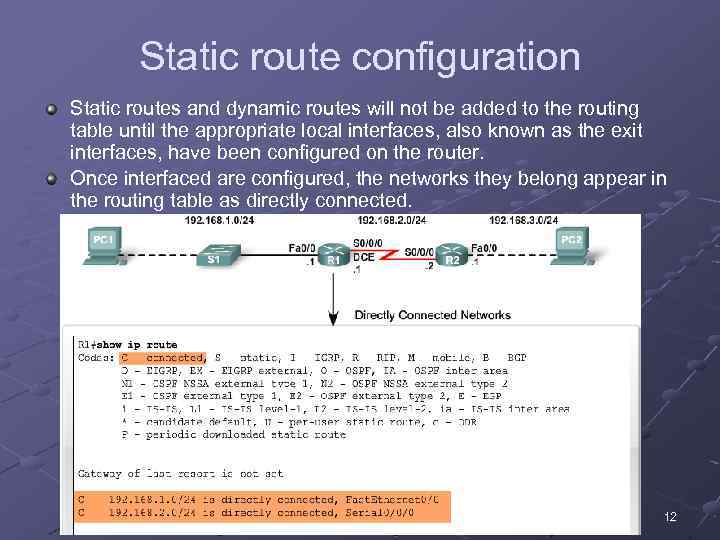 Static route configuration Static routes and dynamic routes will not be added to the routing table until the appropriate local interfaces, also known as the exit interfaces, have been configured on the router. Once interfaced are configured, the networks they belong appear in the routing table as directly connected. 12
Static route configuration Static routes and dynamic routes will not be added to the routing table until the appropriate local interfaces, also known as the exit interfaces, have been configured on the router. Once interfaced are configured, the networks they belong appear in the routing table as directly connected. 12
 Static routing configuration The command for configuring a static route is ip route: Router(config)# ip route ip-address mask {exit-interface/ next hop ip-address) [administrative distance] The following parameters are used: network-address - Destination network address of the remote network to be added to the routing table mask - Subnet mask of the remote network to be added to the routing table. The subnet mask can be modified to summarize a group of networks. exit-interface - Outgoing interface type and interface number (e. g. s 0/3/0) that would be used in forwarding packets to the destination network next hop ip-address - Commonly referred to as the next-hop router's IP address Administrative distance -Optional parameter, that defines the preference of a routing source, equals 1 by default. 13
Static routing configuration The command for configuring a static route is ip route: Router(config)# ip route ip-address mask {exit-interface/ next hop ip-address) [administrative distance] The following parameters are used: network-address - Destination network address of the remote network to be added to the routing table mask - Subnet mask of the remote network to be added to the routing table. The subnet mask can be modified to summarize a group of networks. exit-interface - Outgoing interface type and interface number (e. g. s 0/3/0) that would be used in forwarding packets to the destination network next hop ip-address - Commonly referred to as the next-hop router's IP address Administrative distance -Optional parameter, that defines the preference of a routing source, equals 1 by default. 13
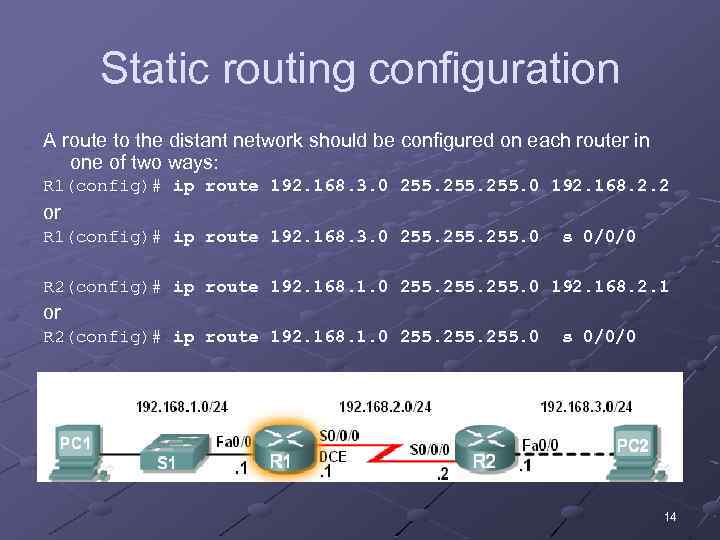 Static routing configuration A route to the distant network should be configured on each router in one of two ways: R 1(config)# ip route 192. 168. 3. 0 255. 0 192. 168. 2. 2 or R 1(config)# ip route 192. 168. 3. 0 255. 0 s 0/0/0 R 2(config)# ip route 192. 168. 1. 0 255. 0 192. 168. 2. 1 or R 2(config)# ip route 192. 168. 1. 0 255. 0 s 0/0/0 14
Static routing configuration A route to the distant network should be configured on each router in one of two ways: R 1(config)# ip route 192. 168. 3. 0 255. 0 192. 168. 2. 2 or R 1(config)# ip route 192. 168. 3. 0 255. 0 s 0/0/0 R 2(config)# ip route 192. 168. 1. 0 255. 0 192. 168. 2. 1 or R 2(config)# ip route 192. 168. 1. 0 255. 0 s 0/0/0 14
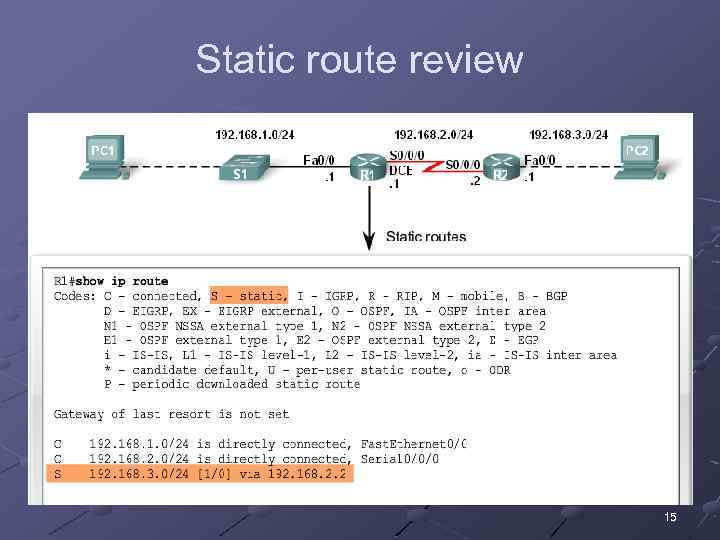 Static route review 15
Static route review 15
 Default route (маршрут за замовчуванням) Instead of routers having to store routes for all of the networks in the Internet, they can store a single default route to represent any network that is not in the routing table. A default static route is a route that will match all packets. The syntax for a default static route is similar to any other static route, except that the network address is 0. 0 and the subnet mask is 0. 0: Router(config)#ip route 0. 0 [exitinterface | ip-address ] 16
Default route (маршрут за замовчуванням) Instead of routers having to store routes for all of the networks in the Internet, they can store a single default route to represent any network that is not in the routing table. A default static route is a route that will match all packets. The syntax for a default static route is similar to any other static route, except that the network address is 0. 0 and the subnet mask is 0. 0: Router(config)#ip route 0. 0 [exitinterface | ip-address ] 16
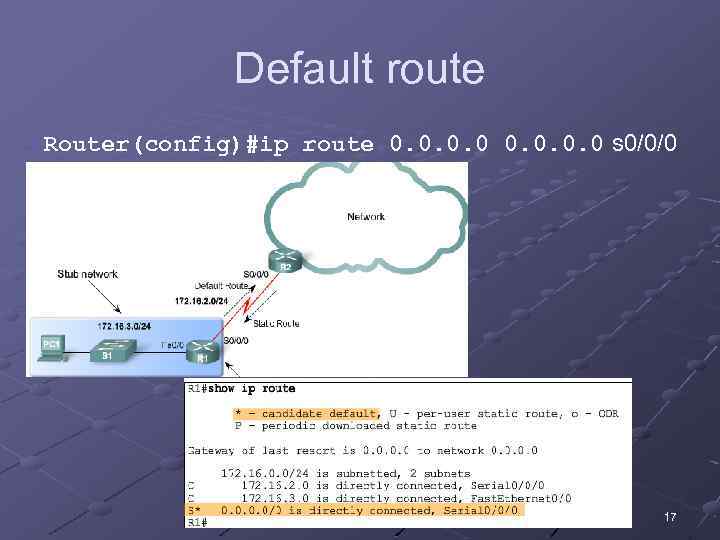 Default route Router(config)#ip route 0. 0 s 0/0/0 17
Default route Router(config)#ip route 0. 0 s 0/0/0 17
 Static route check & troubleshooting Route configuration and usage are subject to many faults, such as: § § An interface fails. A service provider drops a connection. There is an over-saturation of links. An administrator enters a wrong configuration. To monitor and troubleshoot the routes the following tools can be used: ü ü ping traceroute show ip route show running-config 18
Static route check & troubleshooting Route configuration and usage are subject to many faults, such as: § § An interface fails. A service provider drops a connection. There is an over-saturation of links. An administrator enters a wrong configuration. To monitor and troubleshoot the routes the following tools can be used: ü ü ping traceroute show ip route show running-config 18
 Static Routing Advantages and Disadvantages Static routing advantages (переваги): Minimal CPU processing. Easier for administrator to understand. Easy to configure. Enhanced security. The path of packet transition is predetermined (no calculations and decision making needed). Static routing disadvantages (недоліки): Configuration and maintenance is time-consuming. Configuration is error-prone, especially in large networks. Administrator intervention is required to maintain changing route information. Does not scale well with growing networks; maintenance becomes cumbersome. Requires complete knowledge of the whole network for proper implementation. No adjustment to any topology changes. 19
Static Routing Advantages and Disadvantages Static routing advantages (переваги): Minimal CPU processing. Easier for administrator to understand. Easy to configure. Enhanced security. The path of packet transition is predetermined (no calculations and decision making needed). Static routing disadvantages (недоліки): Configuration and maintenance is time-consuming. Configuration is error-prone, especially in large networks. Administrator intervention is required to maintain changing route information. Does not scale well with growing networks; maintenance becomes cumbersome. Requires complete knowledge of the whole network for proper implementation. No adjustment to any topology changes. 19
 20
20


