59a4ced1563e03b21aaec2b044eeb9ba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Rotifer resting eggs Nadav Y. Denekamp National Institute of Oceanography Israel Oceanographic & Limnological Research 1
Rotifer resting eggs Nadav Y. Denekamp National Institute of Oceanography Israel Oceanographic & Limnological Research 1
 Outline § § Participation in workpackages Previous meeting report summary Current report in detail Future directions 2
Outline § § Participation in workpackages Previous meeting report summary Current report in detail Future directions 2
 Workpackages § The NIO research group participates in workpackages: WP 1, WP 2, WP 4, WP 5 and WP 6. § WP 1 deliverables: D 4: Optimal conditions for the indcution of asexually and sexually reproducing rotifers and their resting eggs (M 9) D 5: c. DNA libraries, EST sequencing and database construction (M 16) D 6 -D 8: Scheduled for M 30 -M 36 § WP 2, WP 4, WP 5 and WP 6 are scheduled to M 30 -M 36 3
Workpackages § The NIO research group participates in workpackages: WP 1, WP 2, WP 4, WP 5 and WP 6. § WP 1 deliverables: D 4: Optimal conditions for the indcution of asexually and sexually reproducing rotifers and their resting eggs (M 9) D 5: c. DNA libraries, EST sequencing and database construction (M 16) D 6 -D 8: Scheduled for M 30 -M 36 § WP 2, WP 4, WP 5 and WP 6 are scheduled to M 30 -M 36 3
 Last meeting report § Setting up asexually reproducing rotifer cultures (high salinity media) § Setting up sexually reproducing rotifer cultures (low salinity media) § Hatching experiments § Development of an RNA extraction method for rotifers. 4
Last meeting report § Setting up asexually reproducing rotifer cultures (high salinity media) § Setting up sexually reproducing rotifer cultures (low salinity media) § Hatching experiments § Development of an RNA extraction method for rotifers. 4
 The current report § Collection of samples for c. DNA libraries from rotifer cultures § Collection of sample for c. DNA libraries from resting eggs and various stages of hatching § Future experiments 5
The current report § Collection of samples for c. DNA libraries from rotifer cultures § Collection of sample for c. DNA libraries from resting eggs and various stages of hatching § Future experiments 5
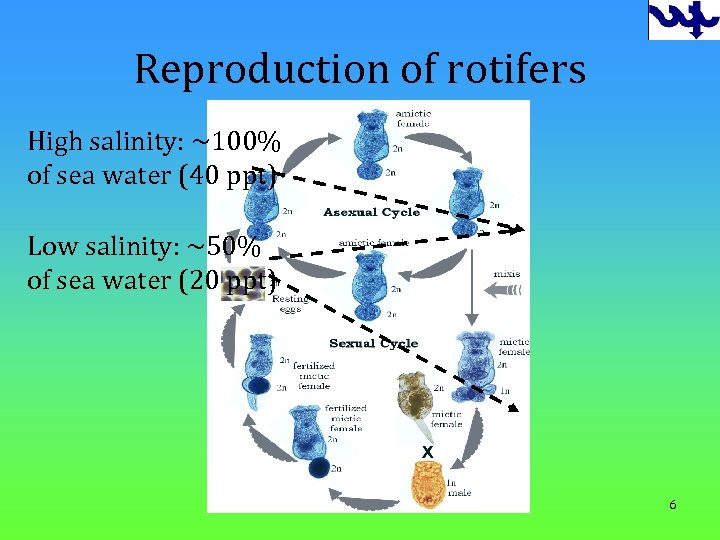 Reproduction of rotifers High salinity: ~100% of sea water (40 ppt) Low salinity: ~50% of sea water (20 ppt) 6
Reproduction of rotifers High salinity: ~100% of sea water (40 ppt) Low salinity: ~50% of sea water (20 ppt) 6
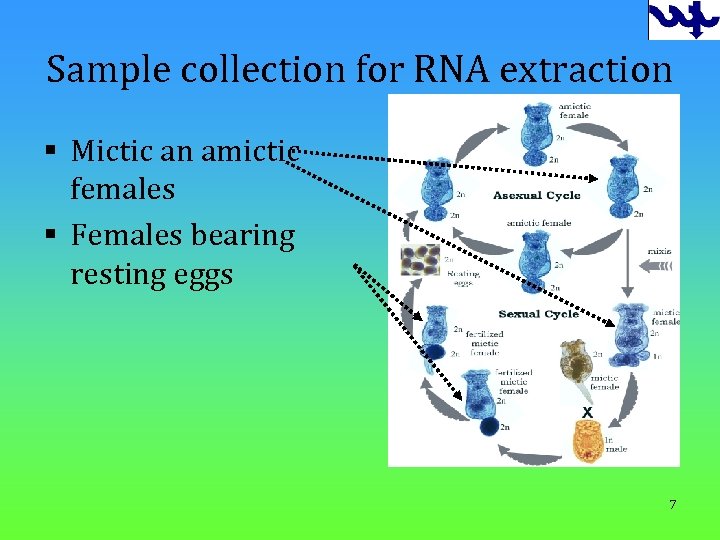 Sample collection for RNA extraction § Mictic an amictic females § Females bearing resting eggs 7
Sample collection for RNA extraction § Mictic an amictic females § Females bearing resting eggs 7
 Picking females bearing resting eggs one by one… 8
Picking females bearing resting eggs one by one… 8
 Samples collection From RE toward hatching Dormant stage 10 hr 20 hr 30 hr 9
Samples collection From RE toward hatching Dormant stage 10 hr 20 hr 30 hr 9
 RNA amounts obtained from rotifers and RE § 12 -32 mg RNA were extracted from 10002000 rotifers (300 -800 ng/ml at 40 ml) § 4 -12 mg RNA were extracted from 20003000 RE (100 -300 ng/ml at 40 ml) § The amount of m. RNA in RE is not known. § Large amounts of RE are needed for the extraction of RNA from different stages toward hatching 10
RNA amounts obtained from rotifers and RE § 12 -32 mg RNA were extracted from 10002000 rotifers (300 -800 ng/ml at 40 ml) § 4 -12 mg RNA were extracted from 20003000 RE (100 -300 ng/ml at 40 ml) § The amount of m. RNA in RE is not known. § Large amounts of RE are needed for the extraction of RNA from different stages toward hatching 10
 Production of RE § Non clonal rotifer cultures were set up in low salinity media (~10 ppt) § Cultures were fed with Nannochloropsis § Females bearing RE appeared after 5 days § RE were collected after 11 -12 days. § 30, 000 RE were collected from 6 liter cultures. § RE were divided in to batches of 2000 -3000 RE and were stored for 84 days at 25 o. C in 11
Production of RE § Non clonal rotifer cultures were set up in low salinity media (~10 ppt) § Cultures were fed with Nannochloropsis § Females bearing RE appeared after 5 days § RE were collected after 11 -12 days. § 30, 000 RE were collected from 6 liter cultures. § RE were divided in to batches of 2000 -3000 RE and were stored for 84 days at 25 o. C in 11
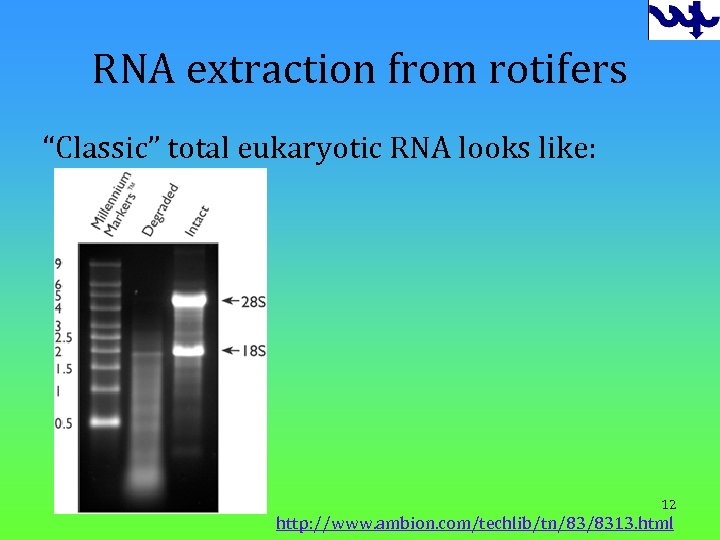 RNA extraction from rotifers “Classic” total eukaryotic RNA looks like: 12 http: //www. ambion. com/techlib/tn/83/8313. html
RNA extraction from rotifers “Classic” total eukaryotic RNA looks like: 12 http: //www. ambion. com/techlib/tn/83/8313. html
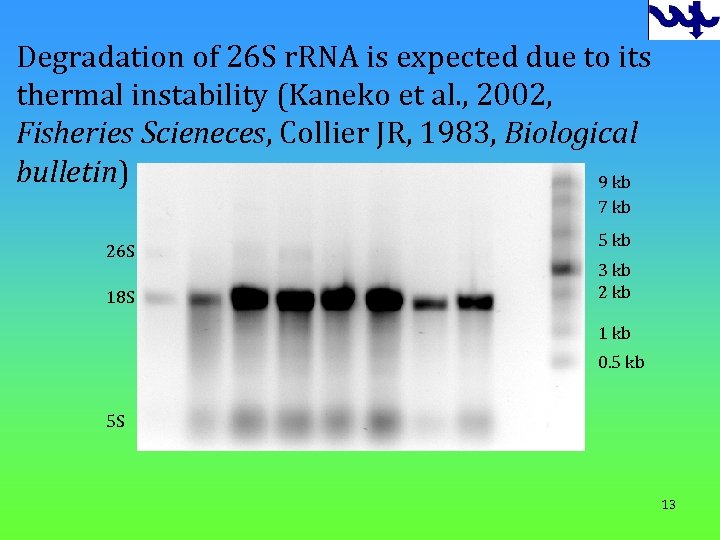 Degradation of 26 S r. RNA is expected due to its thermal instability (Kaneko et al. , 2002, Fisheries Scieneces, Collier JR, 1983, Biological bulletin) 9 kb 7 kb 26 S 18 S 5 kb 3 kb 2 kb 1 kb 0. 5 kb 5 S 13
Degradation of 26 S r. RNA is expected due to its thermal instability (Kaneko et al. , 2002, Fisheries Scieneces, Collier JR, 1983, Biological bulletin) 9 kb 7 kb 26 S 18 S 5 kb 3 kb 2 kb 1 kb 0. 5 kb 5 S 13
 PCR experiments § In order to evaluate the m. RNA quality PCR experiments were performed for expression of actin and eft 1 a. § The sequence of actin for B. plicatilis is known (AB 111352) § The sequence of eft 1 a for B. plicatilis had to be found 14
PCR experiments § In order to evaluate the m. RNA quality PCR experiments were performed for expression of actin and eft 1 a. § The sequence of actin for B. plicatilis is known (AB 111352) § The sequence of eft 1 a for B. plicatilis had to be found 14
 Degenerated primers were designed by MSA of eft 1 a genes from: C. elegans, Nereis, S. cerevisiae and Human. 15
Degenerated primers were designed by MSA of eft 1 a genes from: C. elegans, Nereis, S. cerevisiae and Human. 15
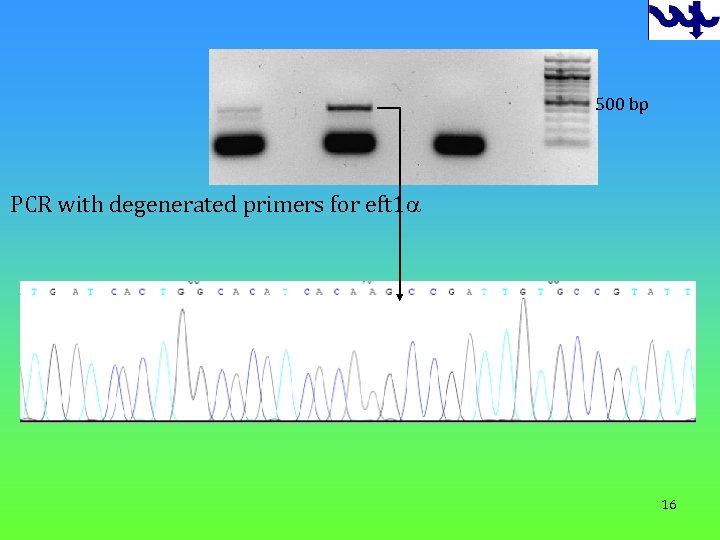 500 bp PCR with degenerated primers for eft 1 a 16
500 bp PCR with degenerated primers for eft 1 a 16
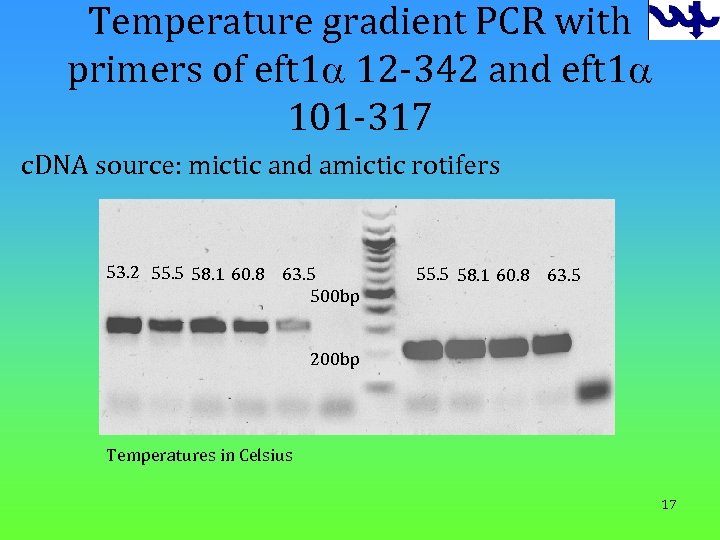 Temperature gradient PCR with primers of eft 1 a 12 -342 and eft 1 a 101 -317 c. DNA source: mictic and amictic rotifers 53. 2 55. 5 58. 1 60. 8 63. 5 500 bp 55. 5 58. 1 60. 8 63. 5 200 bp Temperatures in Celsius 17
Temperature gradient PCR with primers of eft 1 a 12 -342 and eft 1 a 101 -317 c. DNA source: mictic and amictic rotifers 53. 2 55. 5 58. 1 60. 8 63. 5 500 bp 55. 5 58. 1 60. 8 63. 5 200 bp Temperatures in Celsius 17
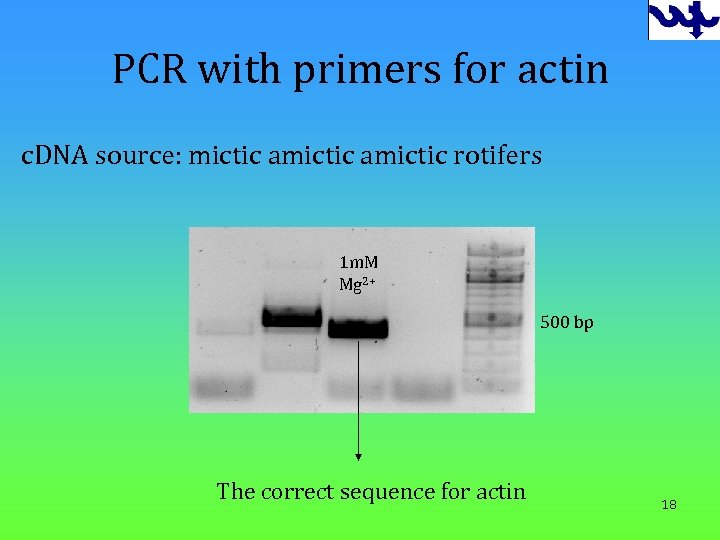 PCR with primers for actin c. DNA source: mictic amictic rotifers 1 m. M Mg 2+ 500 bp The correct sequence for actin 18
PCR with primers for actin c. DNA source: mictic amictic rotifers 1 m. M Mg 2+ 500 bp The correct sequence for actin 18
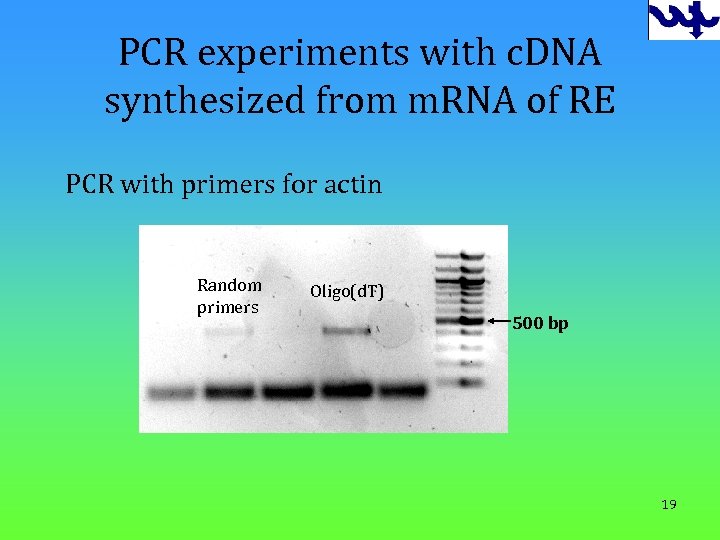 PCR experiments with c. DNA synthesized from m. RNA of RE PCR with primers for actin Random primers Oligo(d. T) 500 bp 19
PCR experiments with c. DNA synthesized from m. RNA of RE PCR with primers for actin Random primers Oligo(d. T) 500 bp 19
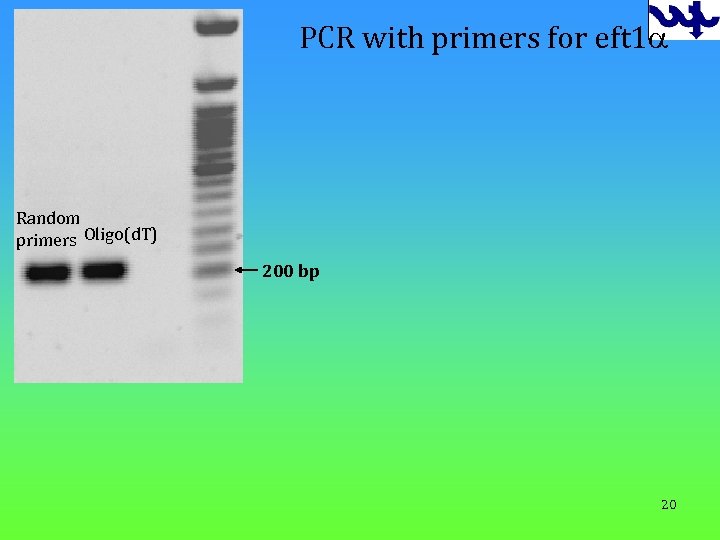 PCR with primers for eft 1 a Random primers Oligo(d. T) 200 bp 20
PCR with primers for eft 1 a Random primers Oligo(d. T) 200 bp 20
 Proposed c. DNA libraries to be constructed from the RNA samples (A) Normalized library of sexual and asexual reproducing rotifers (Clonal and no clonal cultures) (B) Normalized library of RE in dormant stage (C) Non-normalized library of RE in dormant stage (D) Normalized library of RE 20 and 30 hours after hatching initiation. (E) Subtractive library of female bearing RE against sexual+asexual reproducing rotifers, 21 both from the same clone.
Proposed c. DNA libraries to be constructed from the RNA samples (A) Normalized library of sexual and asexual reproducing rotifers (Clonal and no clonal cultures) (B) Normalized library of RE in dormant stage (C) Non-normalized library of RE in dormant stage (D) Normalized library of RE 20 and 30 hours after hatching initiation. (E) Subtractive library of female bearing RE against sexual+asexual reproducing rotifers, 21 both from the same clone.
 Future experiments § Gene expression analysis toward production of resting eggs – HSP 70: May stabilize proteins structure during dormancy. Its sequence in B. plicatilis is known. – Mn SOD: Antioxidant enzyme. Oxidative stress may cause damage during hatching. Sequence in B. plicatilis is known – TPS 1: Trehalose phosphate synthase. Sequence in B. plicatilis is not known 22
Future experiments § Gene expression analysis toward production of resting eggs – HSP 70: May stabilize proteins structure during dormancy. Its sequence in B. plicatilis is known. – Mn SOD: Antioxidant enzyme. Oxidative stress may cause damage during hatching. Sequence in B. plicatilis is known – TPS 1: Trehalose phosphate synthase. Sequence in B. plicatilis is not known 22
 Role of trehalose in RE survival § Trehalose enhances survival during anhydrobiosis in other organisms such as yeasts and artemia. § Cloning of trehalose producing genes resulted in desiccation tolerance in mammalian cells (Crowe and Crowe, 2000, Nature). § Trehalose was not found in desiccated Bdelloid rotifers (Tunnacliffe and Lapinski, 2002, R. SOC. , Caprioli et al. , 2004, CBP). § Very little ammount of trehalose was found in B. plicatilis RE (Caprioli et al. , 2004, CBP) 23
Role of trehalose in RE survival § Trehalose enhances survival during anhydrobiosis in other organisms such as yeasts and artemia. § Cloning of trehalose producing genes resulted in desiccation tolerance in mammalian cells (Crowe and Crowe, 2000, Nature). § Trehalose was not found in desiccated Bdelloid rotifers (Tunnacliffe and Lapinski, 2002, R. SOC. , Caprioli et al. , 2004, CBP). § Very little ammount of trehalose was found in B. plicatilis RE (Caprioli et al. , 2004, CBP) 23
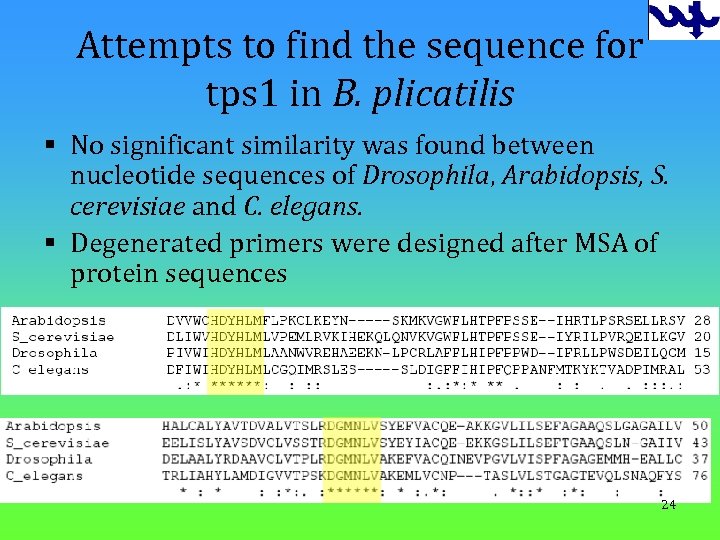 Attempts to find the sequence for tps 1 in B. plicatilis § No significant similarity was found between nucleotide sequences of Drosophila, Arabidopsis, S. cerevisiae and C. elegans. § Degenerated primers were designed after MSA of protein sequences 24
Attempts to find the sequence for tps 1 in B. plicatilis § No significant similarity was found between nucleotide sequences of Drosophila, Arabidopsis, S. cerevisiae and C. elegans. § Degenerated primers were designed after MSA of protein sequences 24
 § The sequence of the PCR products did not match any known tps 1 genes. § Further trials will be done using the AUAP primer and one of the degenerated primers. 25
§ The sequence of the PCR products did not match any known tps 1 genes. § Further trials will be done using the AUAP primer and one of the degenerated primers. 25
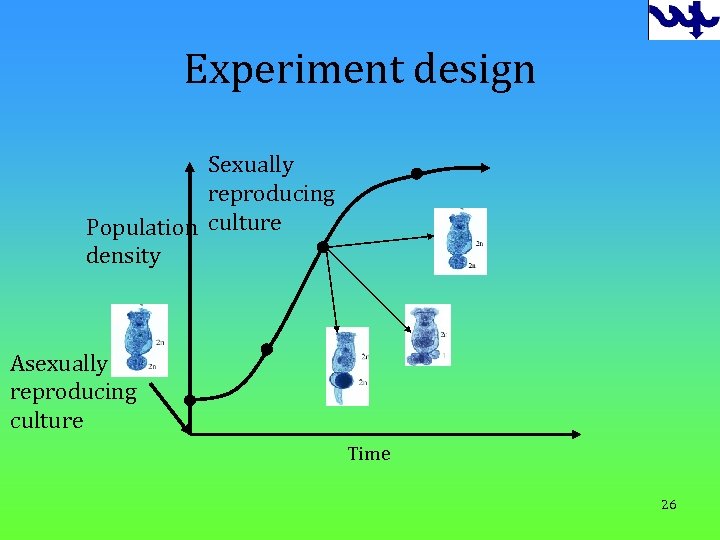 Experiment design Sexually reproducing Population culture density Asexually reproducing culture Time 26
Experiment design Sexually reproducing Population culture density Asexually reproducing culture Time 26


