 ROLL RPL Security IETF 77 status draft-sdt-roll-rpl-security Kris Pister, pister@eecs. berkeley. edu Security Design Team Slide #1 IETF 77 – Roll WG – March 2010
ROLL RPL Security IETF 77 status draft-sdt-roll-rpl-security Kris Pister, pister@eecs. berkeley. edu Security Design Team Slide #1 IETF 77 – Roll WG – March 2010
 Status • Drafts: – draft-tsao-roll-security-framework-02 – draft-sdt-roll-rpl-security-00 – draft-struik-roll-rpl-security-design-00 • Related: – Draft-oflynn-6 lowapp-bootstrapping-00 Slide #2 IETF 77 – Roll WG – March 2010
Status • Drafts: – draft-tsao-roll-security-framework-02 – draft-sdt-roll-rpl-security-00 – draft-struik-roll-rpl-security-design-00 • Related: – Draft-oflynn-6 lowapp-bootstrapping-00 Slide #2 IETF 77 – Roll WG – March 2010
 Scope • Routing Security – Provide mechanisms to protect RPL {DIS, DIO, DAO, “flow label”} from outsider attack • Later or out of scope – Policy – Key distribution – Insider attack – Relationship to other security (L 2, L 4, …)
Scope • Routing Security – Provide mechanisms to protect RPL {DIS, DIO, DAO, “flow label”} from outsider attack • Later or out of scope – Policy – Key distribution – Insider attack – Relationship to other security (L 2, L 4, …)
 Range of RPL Applications • Toys – No security ok? • Consumer/commercial – Perception of risk varies widely • Enterprise-critical – Appropriate paranoia • Need to satisfy “enterprise-critical” without driving away “consumer/commercial”
Range of RPL Applications • Toys – No security ok? • Consumer/commercial – Perception of risk varies widely • Enterprise-critical – Appropriate paranoia • Need to satisfy “enterprise-critical” without driving away “consumer/commercial”
 “Protect” • DIO, DIS, DAO, flow label – Packets are not modified during transport – Participant IDs are authentic – Retransmissions are detected – Content optionally encrypted
“Protect” • DIO, DIS, DAO, flow label – Packets are not modified during transport – Participant IDs are authentic – Retransmissions are detected – Content optionally encrypted
 Mechanisms • AES 128 CCM* • Where to draw the “MUST support” line? – 1) no security – 2) shared instance-wide key – 3) shared pair-wise keys – 4) digital signatures
Mechanisms • AES 128 CCM* • Where to draw the “MUST support” line? – 1) no security – 2) shared instance-wide key – 3) shared pair-wise keys – 4) digital signatures
 Authentication Proposed 4 levels • No authentication • Pre-configured, instance-wide join key • Pre-configured join key(s) with access control list at LBR • Public key certificate
Authentication Proposed 4 levels • No authentication • Pre-configured, instance-wide join key • Pre-configured join key(s) with access control list at LBR • Public key certificate
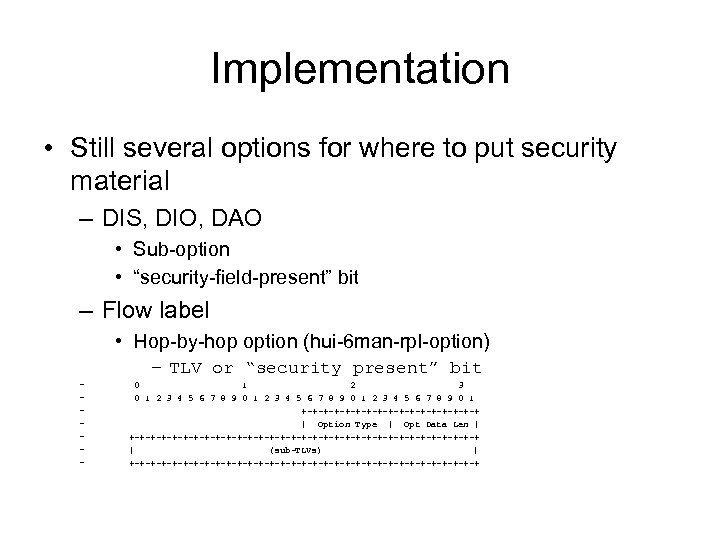 Implementation • Still several options for where to put security material – DIS, DIO, DAO • Sub-option • “security-field-present” bit – Flow label • Hop-by-hop option (hui-6 man-rpl-option) – TLV or “security present” bit – – – – 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | Option Type | Opt Data Len | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | (sub-TLVs) | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
Implementation • Still several options for where to put security material – DIS, DIO, DAO • Sub-option • “security-field-present” bit – Flow label • Hop-by-hop option (hui-6 man-rpl-option) – TLV or “security present” bit – – – – 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | Option Type | Opt Data Len | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | (sub-TLVs) | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
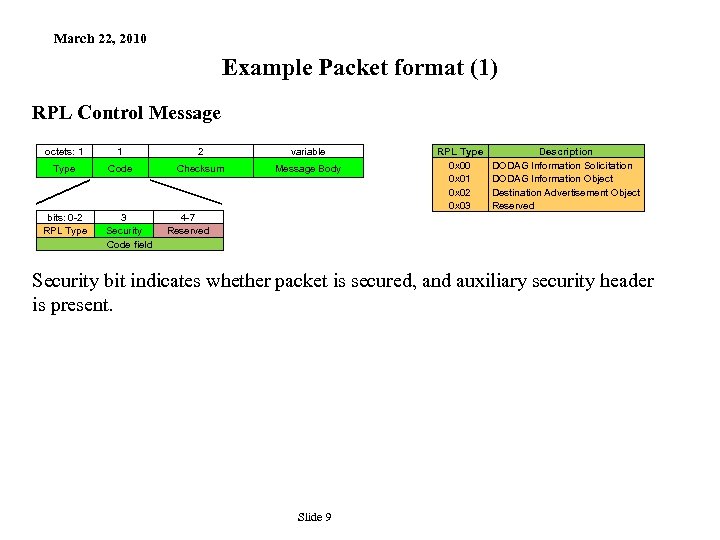 March 22, 2010 Example Packet format (1) RPL Control Message octets: 1 1 2 variable Type Code Checksum Message Body bits: 0 -2 RPL Type 3 Security Code field RPL Type 0 x 00 0 x 01 0 x 02 0 x 03 Description DODAG Information Solicitation DODAG Information Object Destination Advertisement Object Reserved 4 -7 Reserved Security bit indicates whether packet is secured, and auxiliary security header is present. Slide 9
March 22, 2010 Example Packet format (1) RPL Control Message octets: 1 1 2 variable Type Code Checksum Message Body bits: 0 -2 RPL Type 3 Security Code field RPL Type 0 x 00 0 x 01 0 x 02 0 x 03 Description DODAG Information Solicitation DODAG Information Object Destination Advertisement Object Reserved 4 -7 Reserved Security bit indicates whether packet is secured, and auxiliary security header is present. Slide 9
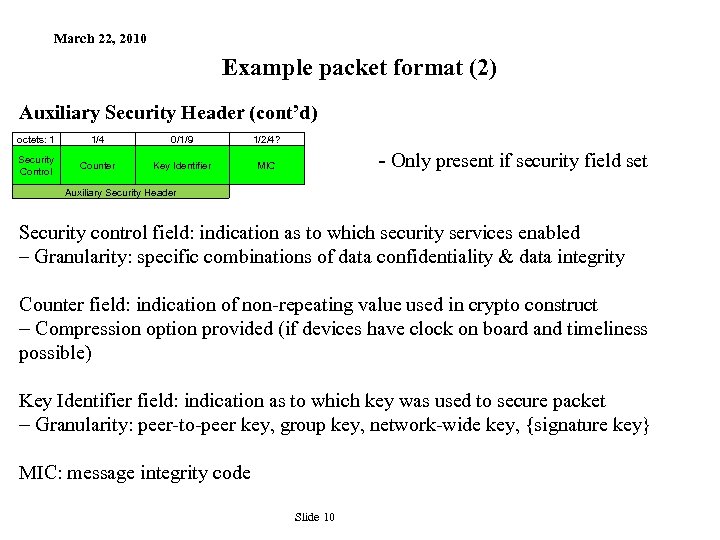 March 22, 2010 Example packet format (2) Auxiliary Security Header (cont’d) octets: 1 1/4 0/1/9 1/2/4? Security Control Counter Key Identifier MIC - Only present if security field set Auxiliary Security Header Security control field: indication as to which security services enabled – Granularity: specific combinations of data confidentiality & data integrity Counter field: indication of non-repeating value used in crypto construct - Compression option provided (if devices have clock on board and timeliness possible) Key Identifier field: indication as to which key was used to secure packet - Granularity: peer-to-peer key, group key, network-wide key, {signature key} MIC: message integrity code Slide 10
March 22, 2010 Example packet format (2) Auxiliary Security Header (cont’d) octets: 1 1/4 0/1/9 1/2/4? Security Control Counter Key Identifier MIC - Only present if security field set Auxiliary Security Header Security control field: indication as to which security services enabled – Granularity: specific combinations of data confidentiality & data integrity Counter field: indication of non-repeating value used in crypto construct - Compression option provided (if devices have clock on board and timeliness possible) Key Identifier field: indication as to which key was used to secure packet - Granularity: peer-to-peer key, group key, network-wide key, {signature key} MIC: message integrity code Slide 10
 Summary • Can provide simple, standard, lightweight mechanisms to protect routing information – Min 2 B? per data packet (flow label) – Typ 5 B? per DIS/DIO/DAO • Still lots of detail work to do • Open issues – Insider attack: LBR consistency checking? – Error/alarm messages
Summary • Can provide simple, standard, lightweight mechanisms to protect routing information – Min 2 B? per data packet (flow label) – Typ 5 B? per DIS/DIO/DAO • Still lots of detail work to do • Open issues – Insider attack: LBR consistency checking? – Error/alarm messages