215f417c456417039f1444ca3f6c63c4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53

Rockets How to go fast Blow things up Go to Space
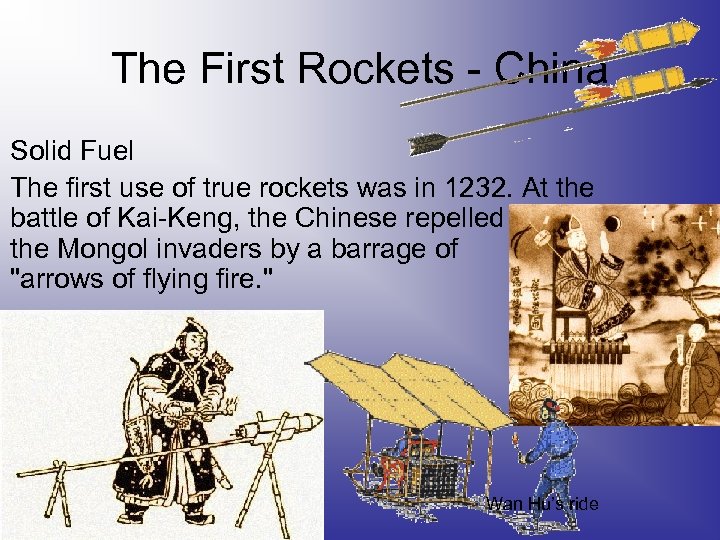
The First Rockets - China Solid Fuel The first use of true rockets was in 1232. At the battle of Kai-Keng, the Chinese repelled the Mongol invaders by a barrage of "arrows of flying fire. " Wan Hu’s ride

The Rockets Red Glare • Skyrockets for Light

Robert Goddard • The man who wants to go to Mars – but moves to Roswell to test Liquid Fueled Rockets
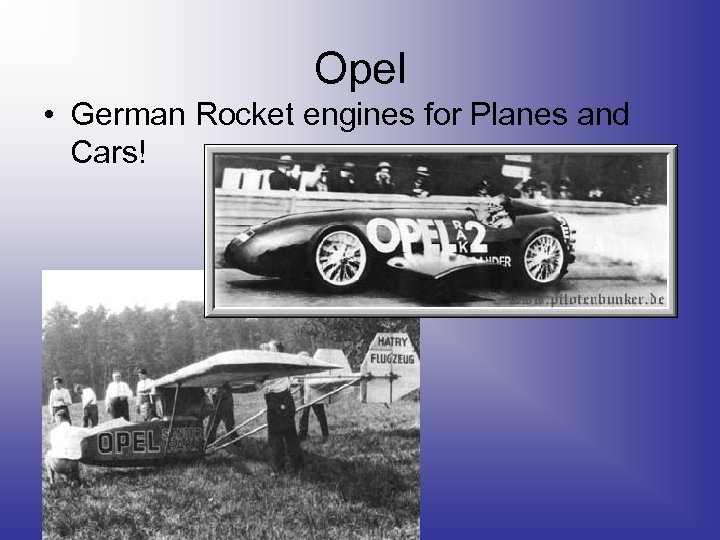
Opel • German Rocket engines for Planes and Cars!

Vf. R Verein fuer for Space Travel Raumschiffahrt The Society Hermann Oberth L to R: Rudolf Nebel, Franz Ritter, Unknown, Kurt Heinisch. I, Unknown, Hermann Oberth, Unknown, Klaus Riedel, Wernher Von Braun, Unknown, Klaus Riedel Holds Early Version of 'MIRAK'.

Rockets for War (USSR) • Katyusha • “Stalin Organs”

Recent Katyushas Katyusha in 2 nd Chechen war Syrian Katyusha Lebanese Katyusha

Rockets for War (Japan) • Baka – suicide rocket glider

Me-163 The WW 2 German Rocket “fighter” that occasionally dissolved its pilot on landing

Rockets for War (Germany) • The V-2

Rockets for Exploration

Werner von Braun Germany WW 2 USA after

Sergey Pavlovich Korolev Сергей Павлович Королев (1907 -1966) “The Chief Designer” • • • R-1 to R-7 Sputnik 1, 2, 3 Luna 1, 2, 3 Vostok 1 – 6 Voskhod Designed N-1 and Soyuz Kapustin Yar 1953

Rockets of the CCCP / Rossiya • Many are launched from Kazakstan • Ukraine also launches it’s own rockets

Sputnik • Sputnik, launched October 4, 1957 • First satellite in orbit

• Vostok

• Bottom end of a Soyuz, being transported to the launch area via train

• Soyuz

• Proton

• Proton-Zvesda

• Buran – made one flight, un-manned

Russian Launch Sites • Космодром Байконур, Kosmodrom Baykonur (Now a part of Kazakhstan) • Капустин Яр Kapustin Yar • Плесе цк, Plesetsk • Свобо дный, Svobodny • Yasny Cosmodrome - Dombarovskiy

Rockets of the USA
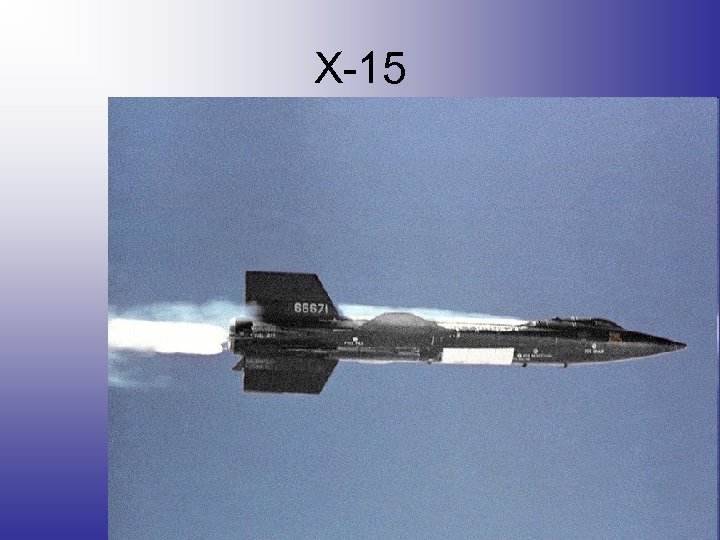

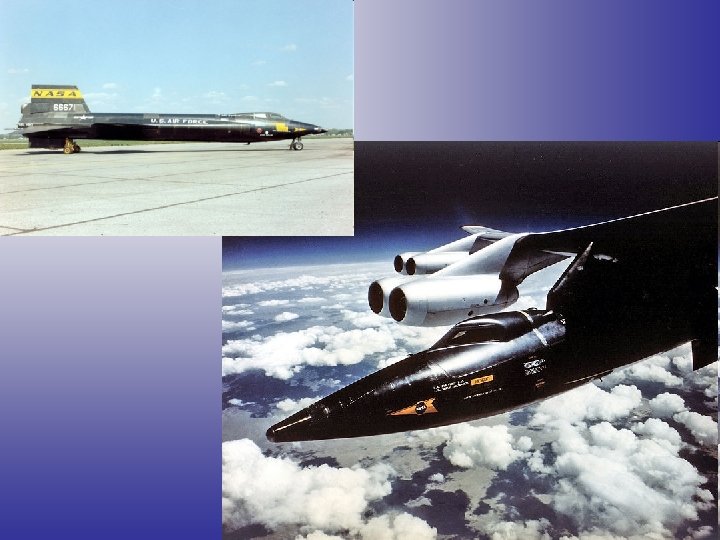
X-15


• Mercury. Redstone Alan Shepard

• Mercury Atlas John Glenn

• Gemini - Titan

• Titan - Centaur

• Apollo 11 – Saturn V Michael Collins Neil Armstrong Buzz Aldrin

• Space Shuttle Columbia

• STS 45 Atlantis

US Launch Sites • Kennedy Space Center – Cape Canaveral, Florida • Vandenburg Air Force Base – California • Kodiak, Alaska • Wallops Island, Virginia

Rocket of the PRC Yáng Lìwěi 楊利偉
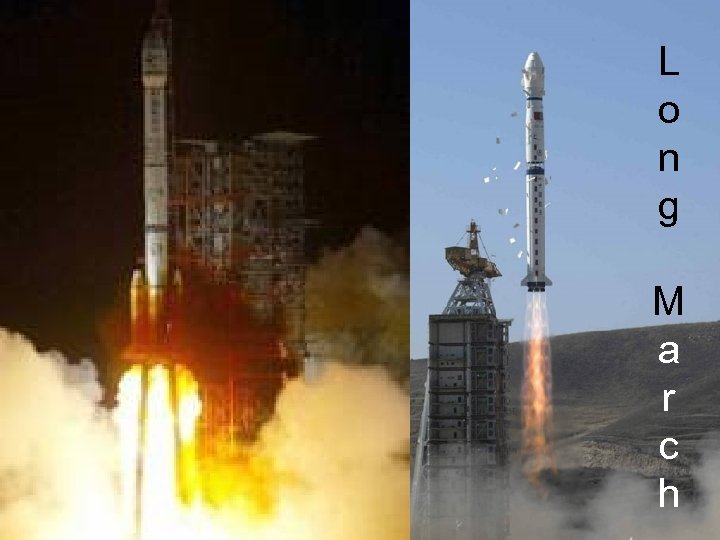

L o n g M a r c h

Chinese Launch Sites • 酒泉 , Jiuquan • 西昌 , Xichang

Rocket of Japan • H-2 • Launch Site: 種子島 , Tanegashima © JAXA

Rocket of India • PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle • Launch Site: Sriharikota

• GSLV – Geosynchronus Satellite Vehicle • Launch Site: Sriharikota

Rocket of Israel Shavit Launch site: פלמחים Palmachim

Non-National Rockets • Rockets made by individuals or companies for themselves, for profit, for fun, and not necessarily for a “national” purpose.

Space. X Falcon 1 Launch Site: Kwajalein Atoll From - www. spacex. com

Rockets for Fun “Bugs in It”

White Knight and Space Ship One To win the X-Prize challlenge – get to “space” twice in a week with room for pilot and 2 passengers

Space Ship One – Boost Phase Mike Melville


Fuels!!! • Other than the law of “Action-Reaction” (“For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction” Newton’s 3 rd Law) reaction – what really makes the rockets work? • You have to throw something out the back of the rocket really fast to make m 1 v 1 = m 2 v 2 • The three choices are – Solid – Liquid and Hybrid (solid + gas. . . )

Solid Fuel • The earliest rockets were created hundreds of years ago by the Chinese and fueled with black powder, consisting of a mixture of Charcoal, Sulfur and Potassium nitrate (saltpeter). • All rocket fuels) consist of an Oxidizer and a Fuel. For gunpowder, the fuel is charcoal, the catalyst is sulfur and the oxidizer is the potassium nitrate. During the 1950 s and 60 s researchers in the United States developed a fuel made of a mixture of Ammonium perchlorate powder (an oxidizer), with fine Aluminum powder (a fuel), held together in a base of rubber-like fuel. The mixture is formed as a liquid, and then cast into the correct shape and forms a rubbery solid. • Solid fueled rockets are much easier to store and handle than liquid fueled rockets. Adapted from - http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Rocket_fuel

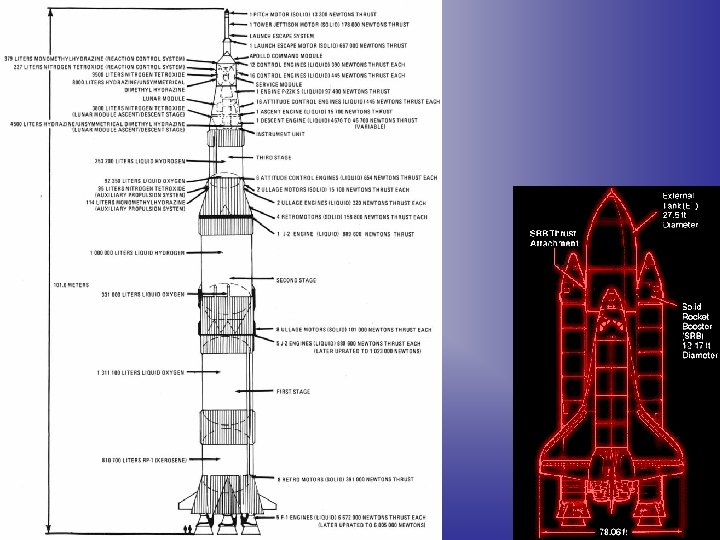
Liquid Fuel • Liquid propellants have much better specific impulse than solid fuels and are safer, because you can turn them off. • The main difficulties are with the oxidizers. They are difficult to store and handle, due to extreme toxicity (nitric acids), extreme cold (liquid oxygen - LOX), or both (liquid fluorine). • The common liquid propellant combinations in use today are: – LOX and Kerosene (RP-1). Used in most Russian and Chinese boosters, and the first stage of the Saturn 5. This combination is regarded as the most practical for civilian orbital launchers. – LOX and Liquid Hydrogen (LHx), used in the Space Shuttle, the Centaur upper stage, the Delta IV, and most stages of the European Ariane rockets. – Nitrogen tetroxide (N 2 O 4) and hydrazine (N 2 H 4). Used in military, orbital and deep space rockets, because both liquids are storable for long periods at reasonable temperatures and pressures. This combination is hypergolic for simple ignition sequences. The major inconvenience is that these propellants are highly toxic. Adapted from - http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Rocket_fuel
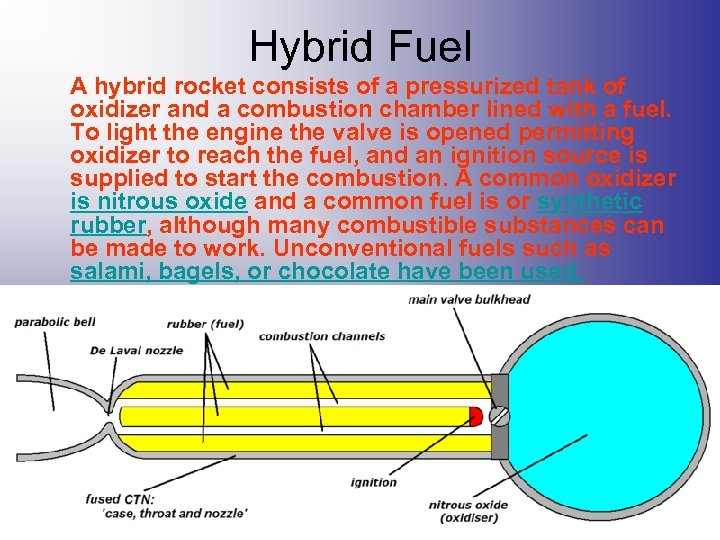
Hybrid Fuel A hybrid rocket consists of a pressurized tank of oxidizer and a combustion chamber lined with a fuel. To light the engine the valve is opened permitting oxidizer to reach the fuel, and an ignition source is supplied to start the combustion. A common oxidizer is nitrous oxide and a common fuel is or synthetic rubber, although many combustible substances can be made to work. Unconventional fuels such as salami, bagels, or chocolate have been used.

Disclaimer Aloha I put together these power points for use in my science classes. You may use them in your classes. Some images are public domain, some are used under the fair-use provisions of the copyright law, some are mine. Copyright is retained by the owners! Ted Brattstrom
215f417c456417039f1444ca3f6c63c4.ppt