af0db1e59903c0726e02ccb07ef8db47.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44


‘Rock-A-Bye Baby’— Implementing CDI in Women’s and Children’s Units Linda Rhodes, RN, BSN, CCDS Manager, Clinical Documentation Improvement Program New Hanover Regional Medical Center, Wilmington, NC Monique Halyard, RN, CNOR Clinical Documentation Specialist New Hanover Regional Medical Center, Wilmington, NC

New Hanover Regional Medical Center, Wilmington, NC • • Licensed for 760 beds Teaching hospital Level II trauma center Full cardiology service— Cardiac Center of Excellence by BC/BS of NC • NHRMC Rehab Hospital • NHRMC Behavioral Health Hospital • Orthopedic specialty hospital

Betty H. Cameron Women’s and Children’s Hospital • • • 45 -bed Level III NICU 6 -bed pediatric ICU 17 -bed pediatric unit 13 -bed antepartum unit 35 -bed mother/baby unit 20 -bed women’s unit

Goals • Share the NHRMC implementation of a CDI • • • program in women’s and children’s units Describe benefits/challenges of NICU/pediatric/OB/GYN reviews Present methods for physician/staff engagement and education Discuss various CDIS staffing model options Identify pediatric/OB/GYN documentation opportunities Demonstrate program metrics for success
Why? • • • Quality Opportunity Education Relationships Program growth
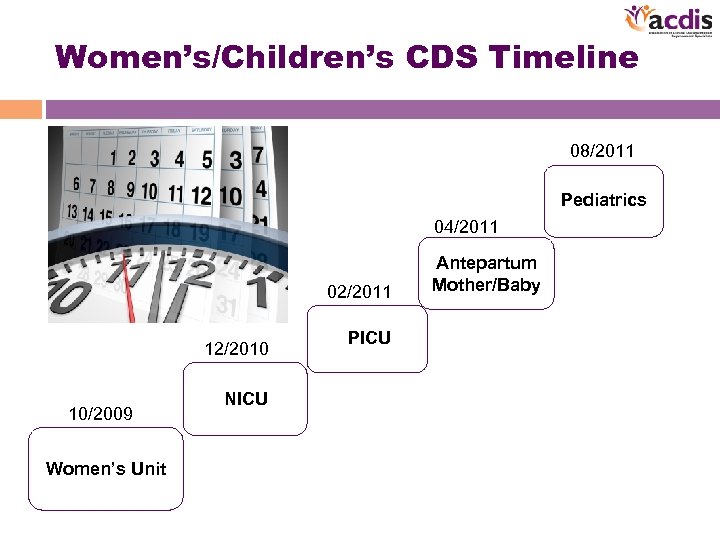
Women’s/Children’s CDS Timeline 08/2011 Pediatrics 04/2011 02/2011 12/2010 10/2009 Women’s Unit NICU PICU Antepartum Mother/Baby

Getting Started: Women’s Unit • Payer source—DRG system – Medicare – Medicaid – TRICARE – Self-insured UHC

Women’s Unit • Diagnoses/procedures – Cervical, ovarian, and uterine malignancy – Hysterectomy, pelvic evisceration – Pelvic peritonitis, inflammatory dx, abscess – Sepsis, wound infection – Pelvic organ prolapse – Incontinence – Sling/suspension procedures – Bariatric procedures – Medical overflow
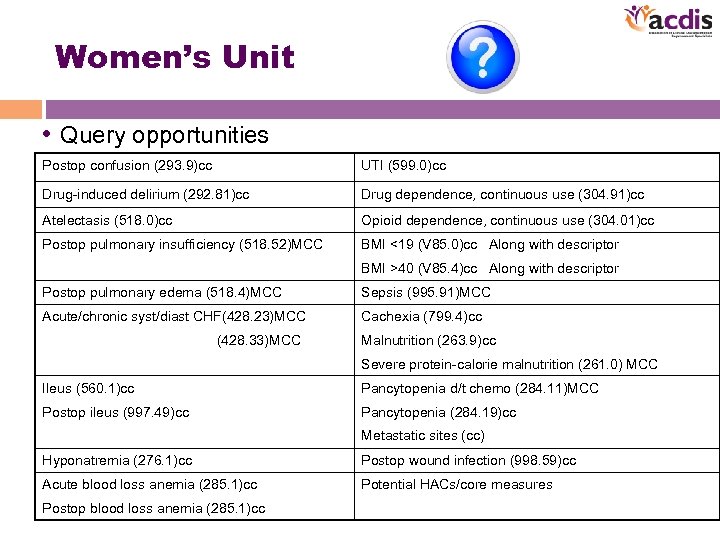
Women’s Unit • Query opportunities Postop confusion (293. 9)cc UTI (599. 0)cc Drug-induced delirium (292. 81)cc Drug dependence, continuous use (304. 91)cc Atelectasis (518. 0)cc Opioid dependence, continuous use (304. 01)cc Postop pulmonary insufficiency (518. 52)MCC BMI <19 (V 85. 0)cc Along with descriptor BMI >40 (V 85. 4)cc Along with descriptor Postop pulmonary edema (518. 4)MCC Sepsis (995. 91)MCC Acute/chronic syst/diast CHF(428. 23)MCC Cachexia (799. 4)cc (428. 33)MCC Malnutrition (263. 9)cc Severe protein-calorie malnutrition (261. 0) MCC Ileus (560. 1)cc Pancytopenia d/t chemo (284. 11)MCC Postop ileus (997. 49)cc Pancytopenia (284. 19)cc Metastatic sites (cc) Hyponatremia (276. 1)cc Postop wound infection (998. 59)cc Acute blood loss anemia (285. 1)cc Potential HACs/core measures Postop blood loss anemia (285. 1)cc

Women’s Unit • CDIS staffing – Utilized current CDS from surgical floor to cover women’s unit – No additional training required CDS
Women’s Unit • Physician/staff engagement and education – Presentation by CDI physician advisor/CDS team – Case scenarios – One-on-one MD education by CDS – Physician education posters/lounge – Laminated documentation hint pocket cards – CDI presentation to women’s unit management
Moving on Up: NICU • Payer source—DRG system – Medicaid 70% – TRICARE 10% – Self-insured UHC • MD electronic documentation (Neo. Data) – Diagnosis dropdowns

NICU • Neonatal DRGs—a different animal – DRG 790 Extreme immaturity or RDS • <1499 grams • <26 weeks gestation • Extreme fetal immaturity • Respiratory distress syndrome (769) – respiratory signs/symptoms – CXR-ground glass opacities – mechanical ventilation, CPAP, HFNC >24 hrs, reintubation – surfactant administration

NICU – DRGs 791– 794 • Determined by weight (fetal immaturity) and diagnosis of prematurity (weeks of gestation) • Require a principal or secondary diagnosis with/without major problems • Challenging to designate DRG without encoder • Focus on documentation of all diagnoses/problems
NICU • NICU documentation tips – Perinatal period is birth through 28 th day – Differentiate between RDS and TTN (transitory tachypnea of newborn) – Specificity of acute and congenital – Documentation of all congenital anomalies – Review pregnancy and labor history for maternal conditions affecting newborn (codes 760– 763) • 763. 4 Newborn affected by C-section

NICU • Major problems (principal or secondary diagnoses) – (747. 83) Persistent fetal circulation, persistent /primary pulmonary hypertension – (756. 71 -. 73) Prune belly, omphalocele, gastroschisis – (768*) Severe birth asphyxia, moderate/severe HIE (hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy) – (770*) Congenital pneumonia, fetal/newborn aspiration, meconium aspiration, aspiration of amniotic fluid, blood, stomach contents, pneumothorax, pulmonary immaturity, pulmonary hemorrhage, respiratory failure – (771. 81) Sepsis of newborn – (772*) Fetal blood loss, IVH/grade, SAH, GI hemorrhage

NICU – (775*) Neonatal diabetes, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, hypoglycemia, late metabolic acidosis – (776. 1) Neonatal thrombocytopenia (transient) – (776. 6) Anemia of prematurity – (777. 5*) Necrotizing enterocolitis – (779) Convulsions – (779. 85) Cardiac arrest – (285. 1) Acute blood loss anemia – (292) Drug withdrawal – (377*) Papilledema complications – (530. 84) TE fistula
NICU • CDIS staffing – 2 NICU case managers – 1. 8 FTE – Rotate CDI workload – Training—documentation software—Midas CDI module • MDC 15 only • Query process • DRG reconciliation process • Coding summaries • Frequency of reviews CDS
NICU • Physician/staff engagement/education – CDI presentation to neonatology – Case scenarios – Review of charts – Physician education posters/lounge – Laminated documentation hints pocket cards – CDI presentation to NICU nursing management/staff – CDI rounding

We’re Growing Up: PICU/Pediatrics • Payer source—DRG system – Medicaid – TRICARE – Self-insured UHC

PICU/Pediatrics • Top 5 MDCs – 1 Nervous system—seizures, meningitis, migraines – 4 Respiratory—pneumonia, asthma, respiratory arrest, cystic fibrosis, reactive airway disease, bronchiolitis, bronchitis – 9 Skin—cellulitis, impetigo – 10 Endocrine/nutritional/metabolic —diabetes, DKA, hypoglycemia – 16 Blood—Sickle-cell anemia/crisis
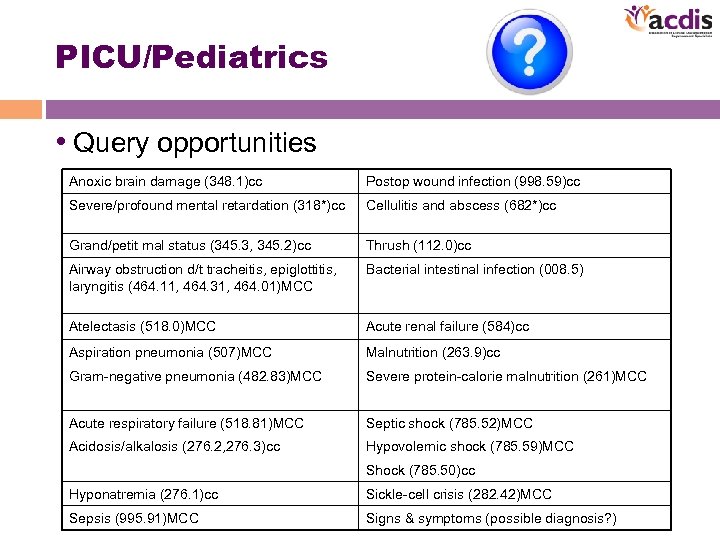
PICU/Pediatrics • Query opportunities Anoxic brain damage (348. 1)cc Postop wound infection (998. 59)cc Severe/profound mental retardation (318*)cc Cellulitis and abscess (682*)cc Grand/petit mal status (345. 3, 345. 2)cc Thrush (112. 0)cc Airway obstruction d/t tracheitis, epiglottitis, laryngitis (464. 11, 464. 31, 464. 01)MCC Bacterial intestinal infection (008. 5) Atelectasis (518. 0)MCC Acute renal failure (584)cc Aspiration pneumonia (507)MCC Malnutrition (263. 9)cc Gram-negative pneumonia (482. 83)MCC Severe protein-calorie malnutrition (261)MCC Acute respiratory failure (518. 81)MCC Septic shock (785. 52)MCC Acidosis/alkalosis (276. 2, 276. 3)cc Hypovolemic shock (785. 59)MCC Shock (785. 50)cc Hyponatremia (276. 1)cc Sickle-cell crisis (282. 42)MCC Sepsis (995. 91)MCC Signs & symptoms (possible diagnosis? )
PICU/Pediatrics • CDIS staffing – Different combinations of staff – NICU case managers/CDS— trained on top 5 MDCs, then … – OB case manager/CDS—trained on CDI and pregnancy DRGs, then … – CDS (0. 8 FTE)—experienced CDS trained on both neonatal and pregnancy DRGs • WHEW! CDS

PICU/Pediatrics • Physician/staff engagement and education – CDI presentation to pediatricians – Case scenarios – Review of charts – Physician education posters/lounge – Laminated documentation hints pocket cards – CDI presentation to PICU/pediatrics nursing management/staff – Documentation tips for nursing staff
We’re Having a Baby! Antepartum/Postpartum • Payer source—DRG system – Medicaid 70% – TRICARE 10% – Self-insured UHC
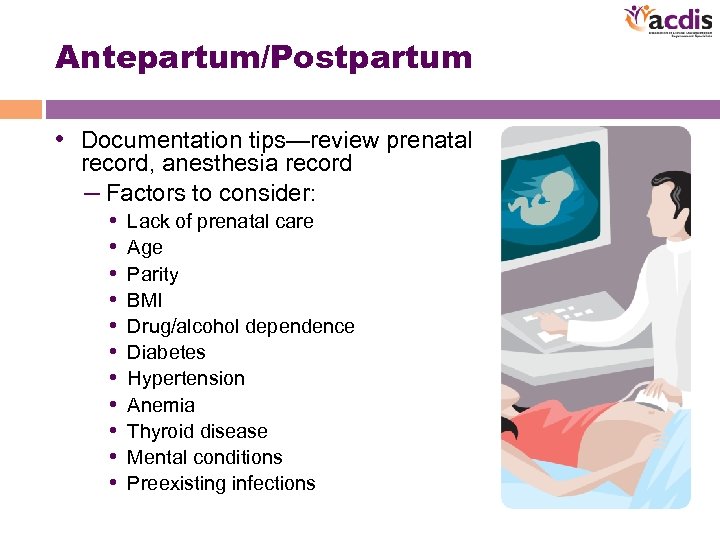
Antepartum/Postpartum • Documentation tips—review prenatal record, anesthesia record – Factors to consider: • Lack of prenatal care • Age • Parity • BMI • Drug/alcohol dependence • Diabetes • Hypertension • Anemia • Thyroid disease • Mental conditions • Preexisting infections
Antepartum/Postpartum • Other considerations: - Pt admitted pregnant with ANY diagnosis codes to complication of pregnancy UNLESS provider documents that the pregnancy is incidental to the encounter!

Antepartum/Postpartum • Preterm labor – Before 22 wks = threatened abortion – After 22 wks but before 37 wks = threatened premature labor • 5 th digit codes • Postpartum period = delivery to 6 weeks • Postpartum complication = any complication during 6 -week time frame

Antepartum • DRG 781/782 Principal and secondary diagnoses – (641*) Placenta previa w/w/o hemorrhage, hemorrhage – (642*) Severe pre-eclampsia, Pre. E, PIH, other HTN – (643*) Hyperemesis, vomiting – (644. 2) Premature labor before 37 weeks – (646. 63) GI infections – (648*) Maternal DM, thyroid, anemia, drug dependence – (657. 03) Polyhydramnios – (658. 03) Oligohydramnios – (658. 13) PROM

Antepartum – (647*) Syphilis, gonorrhea, STDs, HIV, hep B/C – (648. 63) Other maternal CV (MI) – (648. 93) Other conditions (pneumothorax, asthma, etc. ) • Once delivery occurs, some secondary diagnoses will not move the DRG!
Postpartum • DRG—Vaginal or C-section delivery – Principal and/or secondary diagnosis (In addition to the antepartum diagnoses) • (641. 21) Abruptio • (648. 24) Acute blood loss anemia • (659. 21) Maternal fever during labor, delivered • (659. 31) Generalized infection (sepsis) during labor • (666*) Postpartum hemorrhage • (667. 02) Retained placenta
Postpartum – (668*) Complications of anesthesia – (669*) Maternal shock, hypotension, ARF – (670*) Major puerperal infections, sepsis, peritonitis – (671*) DVTs – (673*) Pulmonary air embolism, amniotic and blood clot embolism – (674*) CVA – (675*) Nipple infections, nonpurulent mastitis

Antepartum/Postpartum • CDIS staffing – OB case manager/CDS— trained on CDI and pregnancy DRGs, then … – CDS (0. 8 FTE)— experienced CDS trained on both neonatal and pregnancy DRGs CDS
Antepartum/Postpartum • Physician/staff engagement and education – CDI presentation to OB department – Case scenarios – Review of charts – Physician education posters/lounge – Laminated documentation hints pocket cards – CDI presentation to OB nursing management/staff – Documentation tips for nursing staff
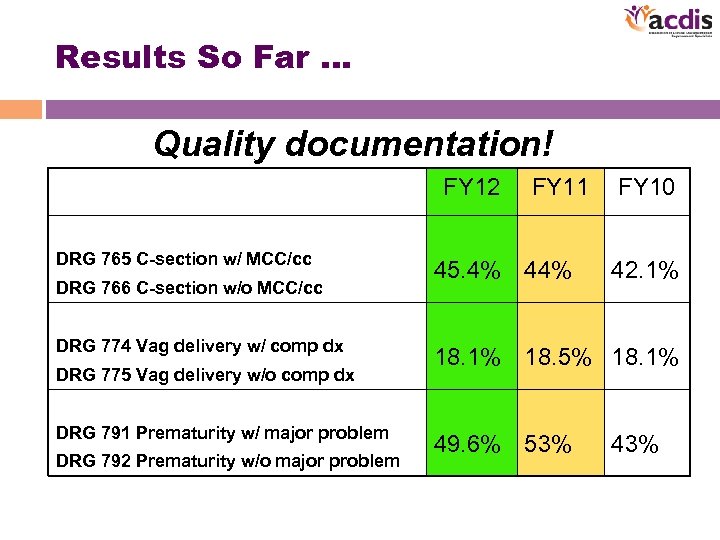
Results So Far … Quality documentation! FY 12 DRG 765 C-section w/ MCC/cc DRG 766 C-section w/o MCC/cc DRG 774 Vag delivery w/ comp dx DRG 775 Vag delivery w/o comp dx DRG 791 Prematurity w/ major problem DRG 792 Prematurity w/o major problem FY 11 45. 4% 44% FY 10 42. 1% 18. 5% 18. 1% 49. 6% 53% 43%

Next Steps … • • SOI/ROM Continued physician education Train additional CDS staff Prepare for ICD-10
ICD-10 -CM Considerations • Pregnancy—categories O 00 -O 9 a – O = Obstetrics – O 80 = full-term uncomplicated delivery – New codes identify trimester when condition occurs – New codes identify # fetuses when condition occurs – Category Z 37. x- Outcome of delivery – New codes for multiple births beyond twins

ICD-10 -CM Considerations • Diabetes in pregnancy – Type 1 diabetes – Type 2 diabetes & identify when patient is on long-term insulin – Diabetes secondary to another condition & name the condition • Gestational diabetes • Identify peripheral manifestations of diabetes (e. g. , retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy) • Clarify trimester of each visit
ICD-10 -CM Considerations • Obstetrical embolism – Identify source – Venous from leg vs. from pelvic veins – Amniotic fluid embolism – Septic embolism – Air embolism – Specify trimester that it occurred or childbirth – Identify severity – Acute respiratory failure – ARDS when it occurs – Identify when saddle embolism

ICD-10 -CM Considerations • Newborns—category Z 38 – Identifies # births—single, twin, triplet – Born in/outside of hospital – Vaginal/C-section
ICD-10 -CM Considerations • Newborn aspiration – Clarify the substance aspirated: • Meconium • Blood • Gastric content • Amniotic fluid – Clarify manifestations: • w/o respiratory manifestations • w/ hypoxia • w/ atelectasis • w/ acute respiratory failure • w/ ARDS

ICD-10 -PCS Considerations • Obstetrics—Section 1 – Procedures performed on “products of conception” – Procedures performed on mother—med-surg – Body system = pregnancy – Root operation • Abortion: artificially terminating pregnancy • Extraction: C-section • Delivery: manual & vaginal delivery – Body part—products of conception

Questions? In order to receive your continuing education certificate for this program, you must complete the online evaluation which can be found in the continuing education section at the front of the workbook.
af0db1e59903c0726e02ccb07ef8db47.ppt