1aca1b8b5b691e420f1a4f0cecd8f0ac.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Rochester HCAL CMS Experiment CMS Hadron Calorimeter - Arie Bodek University of Rochester Do. E Review (15 min Talk) - Wednesday, July 23, 2003 I will only talk about Rochester contributions We==Rochester CDF Plug Upgrade/CMS-HCAL Task D Group) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Brief History - Rochester CDF-Plug Upgrade Group We invented Megatile-Tile-Fiber Technology for CDF We built the CDF-Plug HCAL We tested and calibrated CDF-Plug Upgrade Calorimeter in test beam We developed very large Megatile technology for CMS-Barrel HCAL We are building all the HCAL Megatiles. Optical Cables, Optical Decoders/Photodetector Boxes for CMS -HCAL We installed all the Megatiles into CMS-HCAL at CERN We have built an ECAL module for the CERN test beam Rochester (Slattery-Lobkowicz-Ginther) built the massive test beam table We have led and are leading test beam efforts and analyses at CERN We are now in charge of all of US-CMS installation at CERN University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 1
Rochester HCAL CMS Experiment CMS Hadron Calorimeter - Arie Bodek University of Rochester Do. E Review (15 min Talk) - Wednesday, July 23, 2003 I will only talk about Rochester contributions We==Rochester CDF Plug Upgrade/CMS-HCAL Task D Group) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Brief History - Rochester CDF-Plug Upgrade Group We invented Megatile-Tile-Fiber Technology for CDF We built the CDF-Plug HCAL We tested and calibrated CDF-Plug Upgrade Calorimeter in test beam We developed very large Megatile technology for CMS-Barrel HCAL We are building all the HCAL Megatiles. Optical Cables, Optical Decoders/Photodetector Boxes for CMS -HCAL We installed all the Megatiles into CMS-HCAL at CERN We have built an ECAL module for the CERN test beam Rochester (Slattery-Lobkowicz-Ginther) built the massive test beam table We have led and are leading test beam efforts and analyses at CERN We are now in charge of all of US-CMS installation at CERN University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 1
 Rochester • HCAL Outline Overview • CMS-HCAL Rochester Group • Past CMS HCAL Activities at U of R • Test Beam Motion Table (Slattery/Ginther) • 1995 and 1996 HCAL Test Beam at CERN (data taking, analysis, NIM article) • Design of the HCAL Optics System • Construction of Scintillator Megatiles for Hadron Barrel Calorimeter • Rochester L 3 Management Responsibilities, Fermilab FY 98 -F 03 • Present CMS HCAL Activities • HCAL Installation and Commissioning, CERN FY 03 -07 • Test. Beam Activities, 2002, 2003, 2004 • Summary University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 2
Rochester • HCAL Outline Overview • CMS-HCAL Rochester Group • Past CMS HCAL Activities at U of R • Test Beam Motion Table (Slattery/Ginther) • 1995 and 1996 HCAL Test Beam at CERN (data taking, analysis, NIM article) • Design of the HCAL Optics System • Construction of Scintillator Megatiles for Hadron Barrel Calorimeter • Rochester L 3 Management Responsibilities, Fermilab FY 98 -F 03 • Present CMS HCAL Activities • HCAL Installation and Commissioning, CERN FY 03 -07 • Test. Beam Activities, 2002, 2003, 2004 • Summary University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 2
 Rochester HCAL Rochester CMS HCAL Group • Physicists ( at Rochester, FNAL, CERN) Prof. Arie Bodek (25% CMS, 25% Neutrino, 50% CDF) - current effort Prof. Paul Slattery (mostly Dzero now) Pawel de Barbaro (Senior RA) At CERN - 90% CMS (rest CDF) Howard Budd (Senior RA) At FNAL - 30% CMS (rest CDF, Neutrino) George Ginther (Senior RA) At FNAL - 5% CMS (rest Dzero) Willis Sakumoto (Senior RA) At FNAL - 5% CMS (rest CDF) Y, S. Chung (RA) at FNAL - 5% CMS (rest CDF) • Technical Staff (we had 6 techs, now down to 4) Dan Ruggiero (lab engineer) - 100% CMS Project Funds (At FNAL) Janina Gielata (technician) - 100% CMS Project Funds (At FNAL)->TOB Agnieszka Sanocka (technician) -100% CMS Projectd Funds (At FNAL)->TOB Heng Bao Zeng (technician) - 100% CMS Project Funds (AT FNAL) Tom Haelen (Engineer) - At Rochester • Summer Students Matthias Imboden (Bern U. , 2002 -US citizen NSF-REU) - at CERN summer Pawel Sopicki (Jagellonian U. , 2003) - at CERN summer • Administrative Staff Sue Brightman and Judy Mack University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 3
Rochester HCAL Rochester CMS HCAL Group • Physicists ( at Rochester, FNAL, CERN) Prof. Arie Bodek (25% CMS, 25% Neutrino, 50% CDF) - current effort Prof. Paul Slattery (mostly Dzero now) Pawel de Barbaro (Senior RA) At CERN - 90% CMS (rest CDF) Howard Budd (Senior RA) At FNAL - 30% CMS (rest CDF, Neutrino) George Ginther (Senior RA) At FNAL - 5% CMS (rest Dzero) Willis Sakumoto (Senior RA) At FNAL - 5% CMS (rest CDF) Y, S. Chung (RA) at FNAL - 5% CMS (rest CDF) • Technical Staff (we had 6 techs, now down to 4) Dan Ruggiero (lab engineer) - 100% CMS Project Funds (At FNAL) Janina Gielata (technician) - 100% CMS Project Funds (At FNAL)->TOB Agnieszka Sanocka (technician) -100% CMS Projectd Funds (At FNAL)->TOB Heng Bao Zeng (technician) - 100% CMS Project Funds (AT FNAL) Tom Haelen (Engineer) - At Rochester • Summer Students Matthias Imboden (Bern U. , 2002 -US citizen NSF-REU) - at CERN summer Pawel Sopicki (Jagellonian U. , 2003) - at CERN summer • Administrative Staff Sue Brightman and Judy Mack University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 3
 Rochester HCAL Installing Megatiles at CERN Rochester CDF Plug Group was in charge of CMS HCAL megatile construction at Fermilab and installation at CERN. Rochester technical staff flew to CERN. University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 Megatile design made this a rather simple job. 4
Rochester HCAL Installing Megatiles at CERN Rochester CDF Plug Group was in charge of CMS HCAL megatile construction at Fermilab and installation at CERN. Rochester technical staff flew to CERN. University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 Megatile design made this a rather simple job. 4
 Rochester HCAL Status of HCAL detectors, May 2003 HE University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 HB 5
Rochester HCAL Status of HCAL detectors, May 2003 HE University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 HB 5
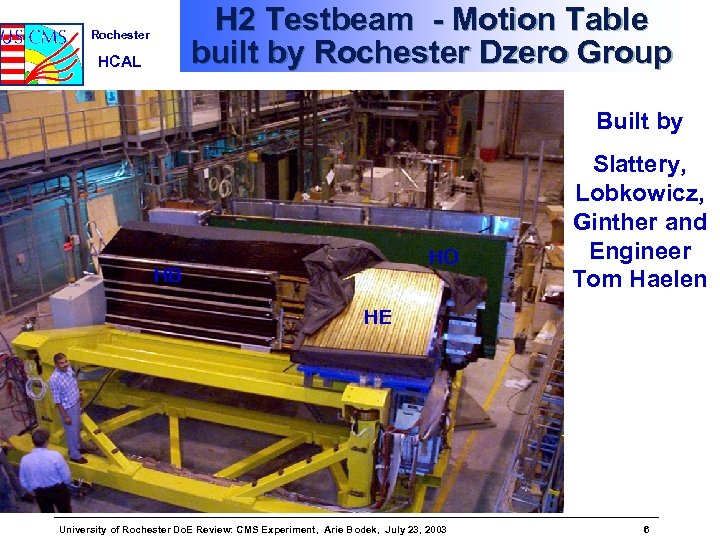 H 2 Testbeam - Motion Table built by Rochester Dzero Group Rochester HCAL Built by HO HB Slattery, Lobkowicz, Ginther and Engineer Tom Haelen HE University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 6
H 2 Testbeam - Motion Table built by Rochester Dzero Group Rochester HCAL Built by HO HB Slattery, Lobkowicz, Ginther and Engineer Tom Haelen HE University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 6
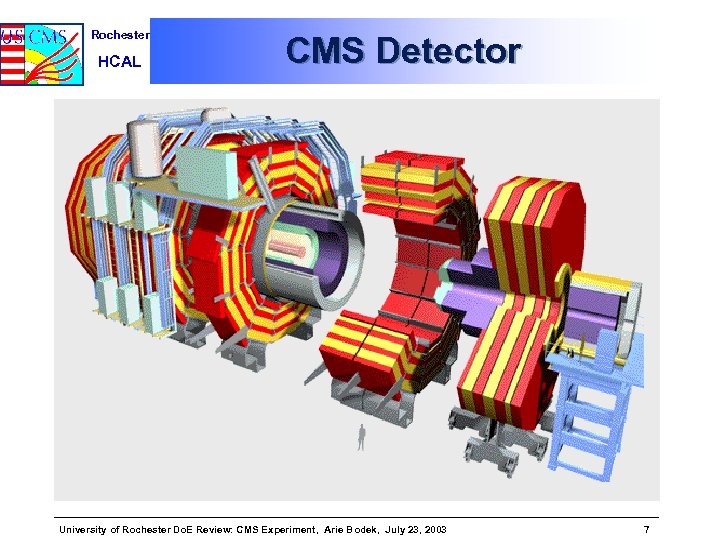 Rochester HCAL CMS Detector University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 7
Rochester HCAL CMS Detector University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 7
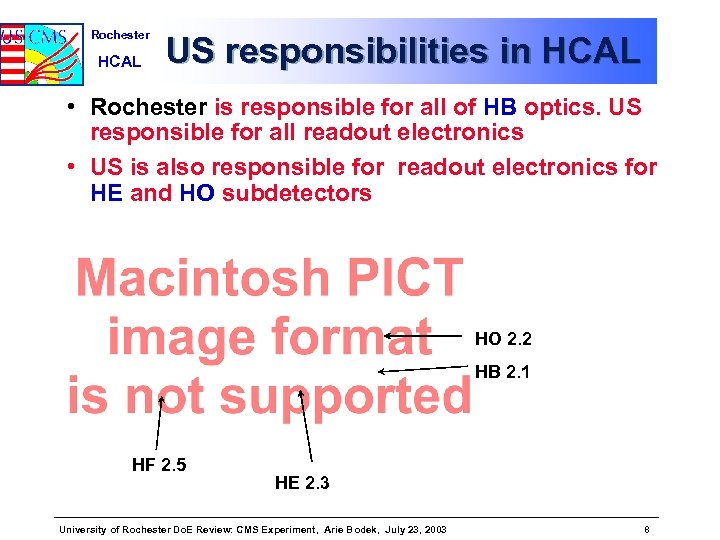 Rochester HCAL US responsibilities in HCAL • Rochester is responsible for all of HB optics. US responsible for all readout electronics • US is also responsible for readout electronics for HE and HO subdetectors HO 2. 2 HB 2. 1 HF 2. 5 HE 2. 3 University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 8
Rochester HCAL US responsibilities in HCAL • Rochester is responsible for all of HB optics. US responsible for all readout electronics • US is also responsible for readout electronics for HE and HO subdetectors HO 2. 2 HB 2. 1 HF 2. 5 HE 2. 3 University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 8
 Rochester HCAL Design of Optical System • Scintillation light is collected by wavelength shifting (WLS) fibers embedded in the tiles • Outside the tile, WLS fibers are spliced to clear fibers • Clear optical fiber cables with mass terminated connectors carry light to the outside of the detector ----> UNIT IS A MEGATILE read by Optical Cables with Connectors • Decoder boxes re-group fibers from layer-wise to tower-wise scheme and house photodetectors • CMS HCAL HB, HE and HO have adopted most of design features of the CDF End Plug Upgrade University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 9
Rochester HCAL Design of Optical System • Scintillation light is collected by wavelength shifting (WLS) fibers embedded in the tiles • Outside the tile, WLS fibers are spliced to clear fibers • Clear optical fiber cables with mass terminated connectors carry light to the outside of the detector ----> UNIT IS A MEGATILE read by Optical Cables with Connectors • Decoder boxes re-group fibers from layer-wise to tower-wise scheme and house photodetectors • CMS HCAL HB, HE and HO have adopted most of design features of the CDF End Plug Upgrade University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 9
 Rochester HCAL Techical issues specific to CMS • Calorimeter Performance in 4 Tesla Magnetic field magnetic field has two-fold effect on the response of the calorimeter. First it changes light yield of the scintillator and secondly, it affects the particle shower development. The second effect depends on the field orientation. • HCAL resolution with and w/o crystal ECAL presence of highly non-compensating lead tungstate crystal electromagnetic calorimeter (ECAL) degrades the overall response of the combined ECAL+HCAL calorimeter to hadrons. • Radiation damage of clear and WLS fibers assuming int. luminosity of 5 x 10**5 pb-1 for first ten years of LHC operations, radiation dose will reach 30 k. Rads for HB (eta=1. 1). Radiation dose scales with 1/theta**3, so that high eta region (eta ~2. 8, HE) is affected most (2. 4 Mrads). University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 10
Rochester HCAL Techical issues specific to CMS • Calorimeter Performance in 4 Tesla Magnetic field magnetic field has two-fold effect on the response of the calorimeter. First it changes light yield of the scintillator and secondly, it affects the particle shower development. The second effect depends on the field orientation. • HCAL resolution with and w/o crystal ECAL presence of highly non-compensating lead tungstate crystal electromagnetic calorimeter (ECAL) degrades the overall response of the combined ECAL+HCAL calorimeter to hadrons. • Radiation damage of clear and WLS fibers assuming int. luminosity of 5 x 10**5 pb-1 for first ten years of LHC operations, radiation dose will reach 30 k. Rads for HB (eta=1. 1). Radiation dose scales with 1/theta**3, so that high eta region (eta ~2. 8, HE) is affected most (2. 4 Mrads). University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 10
 Rochester HCAL • • • Rochester Management Responsibilities P. de Barbaro was L 3 manager responsible for HCAL Optics Rochester managed the production of megatiles for Hadron Barrel Calorimeter: Purchasing of materials (over $2 M) Organization of production (14 technicians, 3 years) Quality control (light yield, uniformity) L 3 manager responsibilities included supervision of several institutes working on the HCAL Optics Production of scintillator megatiles and optical cables has been completed on time All HB scintillators have been installed into the absorber in 2002 University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 11
Rochester HCAL • • • Rochester Management Responsibilities P. de Barbaro was L 3 manager responsible for HCAL Optics Rochester managed the production of megatiles for Hadron Barrel Calorimeter: Purchasing of materials (over $2 M) Organization of production (14 technicians, 3 years) Quality control (light yield, uniformity) L 3 manager responsibilities included supervision of several institutes working on the HCAL Optics Production of scintillator megatiles and optical cables has been completed on time All HB scintillators have been installed into the absorber in 2002 University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 11
 Rochester HCAL Calibration Goal: Calibrate from test beam to 3%. Time in HCAL electronics. Monitor performance, including radiation damage. Tools: 1. Nitrogen laser distributed to each sub-detector. Excites scintillator 2. Laser injects light to photo-detectors. 3. LEDs (fast) inject light to photodetector. Programmable pulser. 4. Moving wire radioactive source for long term calibration. 5. Charge injection to ADC’s (QIE). Specialized calibration modules designed and built to achieve goals. University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 12
Rochester HCAL Calibration Goal: Calibrate from test beam to 3%. Time in HCAL electronics. Monitor performance, including radiation damage. Tools: 1. Nitrogen laser distributed to each sub-detector. Excites scintillator 2. Laser injects light to photo-detectors. 3. LEDs (fast) inject light to photodetector. Programmable pulser. 4. Moving wire radioactive source for long term calibration. 5. Charge injection to ADC’s (QIE). Specialized calibration modules designed and built to achieve goals. University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 12
 Rochester HCAL Test Beam activities • HCAL had a major test beam effort in 1995 and 1996 • The focus of these test beams were to resolve some technical issues prior to completing the design of optics • UR played a major role in these test beams: ØLobkowicz/Slattery/Ginther/Haelen have designed and constructed HCAL Motion table, able to carry over 100 t of detectors ØP. de Barbaro was the corresponding author of NIM article sumarizing these test beam results - analysis done by Rochester University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 13
Rochester HCAL Test Beam activities • HCAL had a major test beam effort in 1995 and 1996 • The focus of these test beams were to resolve some technical issues prior to completing the design of optics • UR played a major role in these test beams: ØLobkowicz/Slattery/Ginther/Haelen have designed and constructed HCAL Motion table, able to carry over 100 t of detectors ØP. de Barbaro was the corresponding author of NIM article sumarizing these test beam results - analysis done by Rochester University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 13
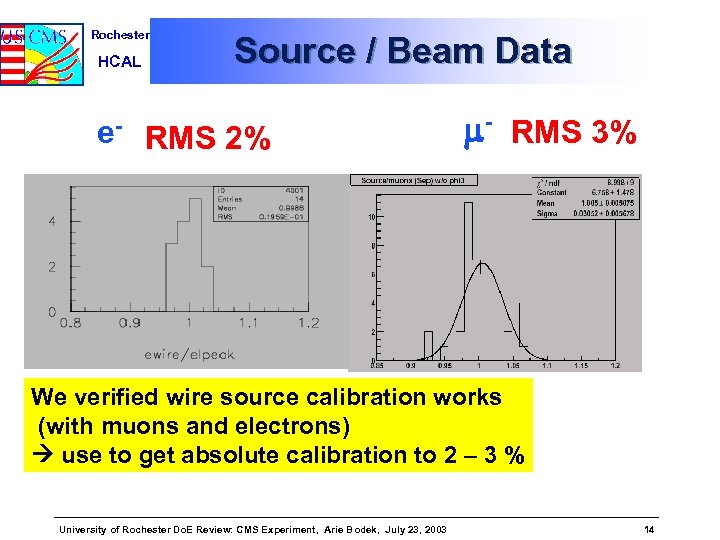 Rochester HCAL Source / Beam Data e- RMS 2% m- RMS 3% We verified wire source calibration works (with muons and electrons) use to get absolute calibration to 2 – 3 % University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 14
Rochester HCAL Source / Beam Data e- RMS 2% m- RMS 3% We verified wire source calibration works (with muons and electrons) use to get absolute calibration to 2 – 3 % University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 14
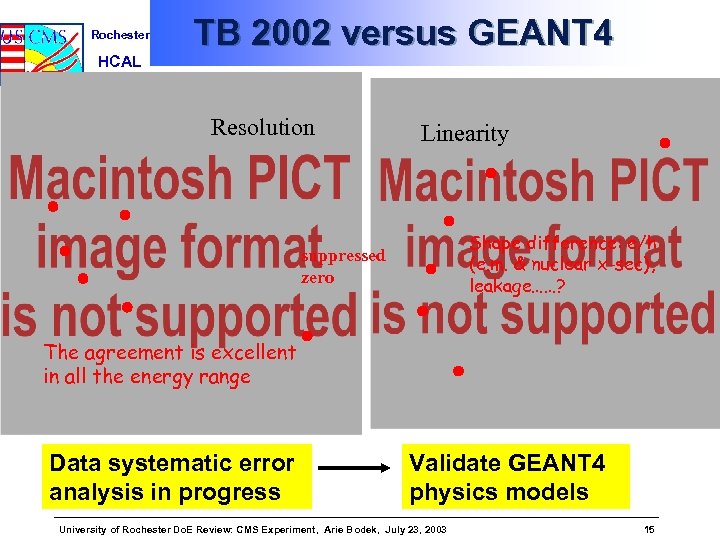 Rochester HCAL TB 2002 versus GEANT 4 Resolution Linearity Shape difference: e/h (e. m. & nuclear x-sec), leakage……? suppressed zero The agreement is excellent in all the energy range Data systematic error analysis in progress Validate GEANT 4 physics models University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 15
Rochester HCAL TB 2002 versus GEANT 4 Resolution Linearity Shape difference: e/h (e. m. & nuclear x-sec), leakage……? suppressed zero The agreement is excellent in all the energy range Data systematic error analysis in progress Validate GEANT 4 physics models University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 15
 Rochester HCAL Test Beam in 2003 • Present test beam runs focus on verification of electronics: • We are testing two 20 deg HB wedges, 20 deg of HE module, and 30 deg of HO • 40 MHz Charge Integrators (QIE) send data to HCAL Trigger Cards (HTR) via 1. 6 GHz link • For each channel, we collect 20 time slices, each time slice is 25 ns wide • In addition, we have ECAL module (100 Pb. WO 4 crystals with PMT readout, module designed/built/tested by UR) to study response of the combined ECAL+HCAL, especially in the 53 deg crack region. University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 16
Rochester HCAL Test Beam in 2003 • Present test beam runs focus on verification of electronics: • We are testing two 20 deg HB wedges, 20 deg of HE module, and 30 deg of HO • 40 MHz Charge Integrators (QIE) send data to HCAL Trigger Cards (HTR) via 1. 6 GHz link • For each channel, we collect 20 time slices, each time slice is 25 ns wide • In addition, we have ECAL module (100 Pb. WO 4 crystals with PMT readout, module designed/built/tested by UR) to study response of the combined ECAL+HCAL, especially in the 53 deg crack region. University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 16
 Rochester HCAL Rochester Responsibilities at CERN • P. de Barbaro has assumed responsibilities of Installation and Commissioning Coordinator for HCAL at CERN • Rochester responsibilities cover installation of scintillators, optical cables, radioactive source tubes, readout electronics, cooling. • Testing of entire chain (scintillator, photodetector, QIE, DAQ) – vertical slice test University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 17
Rochester HCAL Rochester Responsibilities at CERN • P. de Barbaro has assumed responsibilities of Installation and Commissioning Coordinator for HCAL at CERN • Rochester responsibilities cover installation of scintillators, optical cables, radioactive source tubes, readout electronics, cooling. • Testing of entire chain (scintillator, photodetector, QIE, DAQ) – vertical slice test University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 17
 Rochester HCAL • • 1. 2. 3. 4. Rochester CMS HCAL task summary Rochester lead the design, management and production of the optics system for the HCAL Barrel and corresponding test beam activities, Production of scintillator megatiles and optical cables has been completed. Several test beam runs completed - First NIM article published Rochester is now responsible for installation and commissioning of HCAL detector at CERN Rochester Major Tasks in 2003 -2004: installation of HB, HE and HO scintillators, optical cables and readout electronics at CERN Test and integration of full HCAL readout and DAQ with other sub-detectors (vertical slice test) at CERN At Fermilab, continue construction of Optical Decoder Boxes and Electronics. Provide Root Support and Test Beam Analysis - CMS supplemental request for a postdoc to be at CERN. University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 18
Rochester HCAL • • 1. 2. 3. 4. Rochester CMS HCAL task summary Rochester lead the design, management and production of the optics system for the HCAL Barrel and corresponding test beam activities, Production of scintillator megatiles and optical cables has been completed. Several test beam runs completed - First NIM article published Rochester is now responsible for installation and commissioning of HCAL detector at CERN Rochester Major Tasks in 2003 -2004: installation of HB, HE and HO scintillators, optical cables and readout electronics at CERN Test and integration of full HCAL readout and DAQ with other sub-detectors (vertical slice test) at CERN At Fermilab, continue construction of Optical Decoder Boxes and Electronics. Provide Root Support and Test Beam Analysis - CMS supplemental request for a postdoc to be at CERN. University of Rochester Do. E Review: CMS Experiment, Arie Bodek, July 23, 2003 18


