16760c83c2a10a207cca16ac4e50aa2e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Robust Technologies for Automated Ingestion and Long-Term Preservation of Digital Information Principal Investigator: Joseph Ja. Ja Lead Programmers: Mike Smorul and Mike Mc. Gann Graduate Students: Sang Song and Muluwork Geremew Institute for Advanced Computer Studies University of Maryland, College Park

Research Objectives n n n Development of tools and technologies for automated ingestion and for managing preservation processes. Evaluation and demonstration of tools on widely different collections. Framework: • • Overall layered architecture based on distributed repositories using open standards, web and data grid technologies Overall approach is consistent with the Open Archival Information System (OAIS) Reference Framework.

Recent Accomplishments n n Development of the PAWN software environment that enables reliable, scalable, and secure distributed ingestion of remote data. Development of a Global Digital Format Registry prototype – FOCUS (FOrmat CUration Service). Automated ingestion tools and testing on the ICDL collection – ICDL Book Builder. Preliminary design of policy driven integrity auditing of archived data.

Rest of Presentation n Brief Overview of PAWN and the ICDL Book Builder. n Overview of FOCUS n Overview of Integrity Auditing Service

Producer – Archive Workflow Network (PAWN) n n n Distributed and secure ingestion of digital objects into the archive. flexible environment for setting up and managing interactions between producers and the archive Definable roles that can be flexibly combined and assigned to accounts Interfaces for designing package builders and archival resource gateways Currently being used to ingest SLAC data into the National Archives.
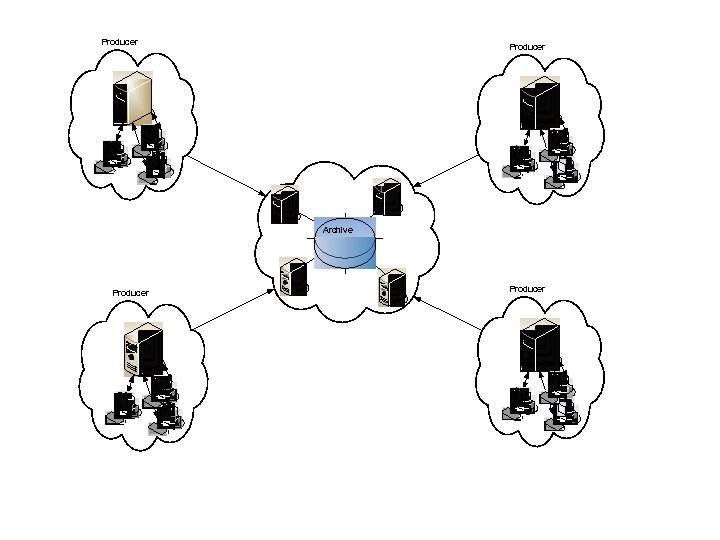
Producer ` ` ` Archive Producer ` ` `
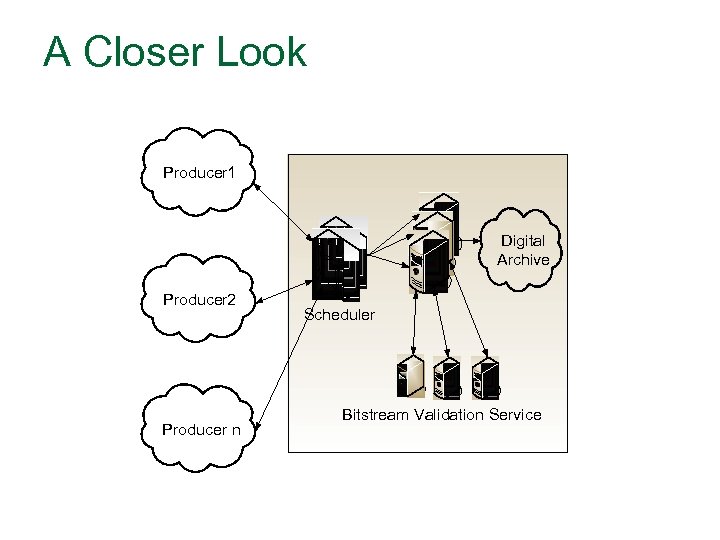
A Closer Look Producer 1 Digital Archive Producer 2 Producer n Scheduler Bitstream Validation Service

Overall Organization n Producers organized into domains, each domain containing a record schedule negotiated with the archive. Each domain contains a hierarchy of the types of data and record sets (convenient groupings from the record schedule). An end-user operates within a domain with record sets associated with the account.

International Children’s Digital Library (ICDL) n n Joint project between UMD and the Internet Archive funded by NSF and IMLS (Allison Druin). Goal: efficient search, browsing, and reading of a collection of 10, 000 books in 100 languages. Current holdings almost 1000 books in over 30 languages, with innovative book readers and browsing tools. Books are digitized in TIFF format, and processed in 6 sizes of JPEG 2000 for each page of each book.

ICDL Book Builder n Purpose: archive digital book collection of ICDL (International Children’s Digital Library). • Builder allows users to: n n n Select books from ICDL Map metadata from ICDL database Create Submission Information Packets(SIP) and transfer into PAWN
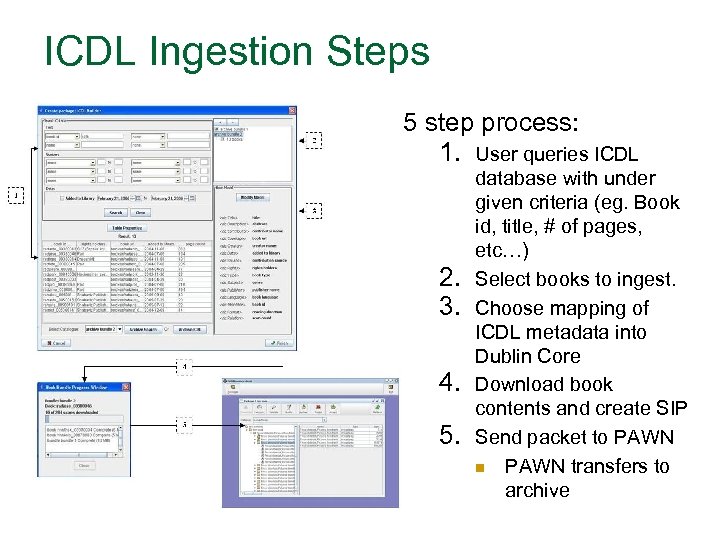
ICDL Ingestion Steps 5 step process: 1. User queries ICDL 2. 3. 4. 5. database with under given criteria (eg. Book id, title, # of pages, etc…) Select books to ingest. Choose mapping of ICDL metadata into Dublin Core Download book contents and create SIP Send packet to PAWN n PAWN transfers to archive
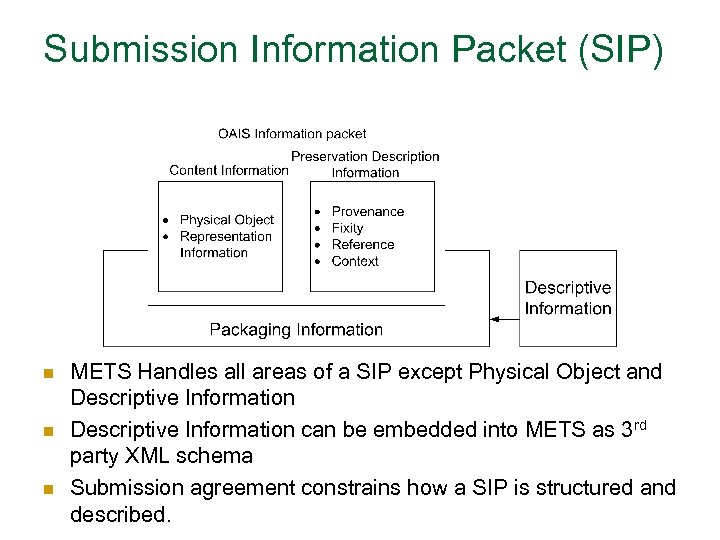
Submission Information Packet (SIP) n n n METS Handles all areas of a SIP except Physical Object and Descriptive Information can be embedded into METS as 3 rd party XML schema Submission agreement constrains how a SIP is structured and described.

Rest of Presentation n n Overview of FOCUS (Format CUration Service) Integrity Auditing Service

Format Obsolescence n n n Handling of digital formats is an essential part of long-term preservation Preservation of any object must include ways to render and transform the object if necessary. Needs to preserve • • Different essential aspects of objects. Tools for capturing the essential format characteristics of information stored as digital objects.
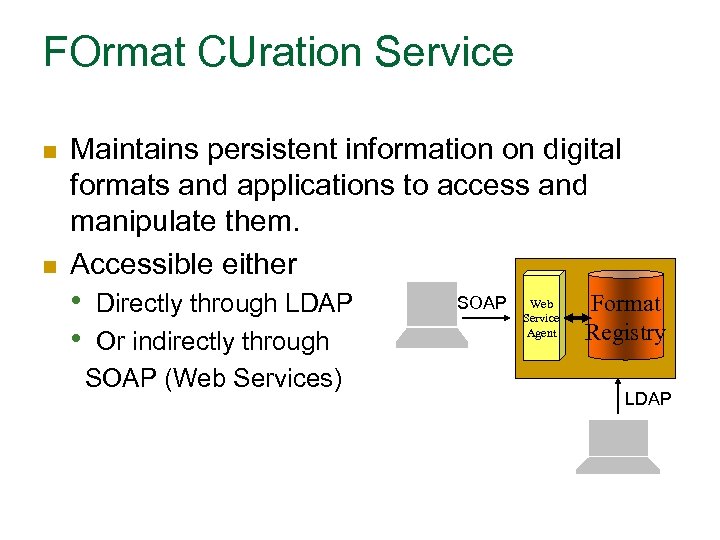
FOrmat CUration Service n n Maintains persistent information on digital formats and applications to access and manipulate them. Accessible either • • Directly through LDAP Or indirectly through SOAP (Web Services) SOAP Web Service Agent Format Registry LDAP

FOCUS on LDAP/SOAP n n Interoperability • Scalability • • • n LDAP and SOAP provide the standard models and protocols, being platform independent. LDAP is a proven scalable technology. LDAP schema can be extended and server can be replicated with ease. SOAP server side can be extended without affecting client sides. Security • • SOAP can be on top of SSL (https). LDAP also provides its own secure authentication and authorization methods.
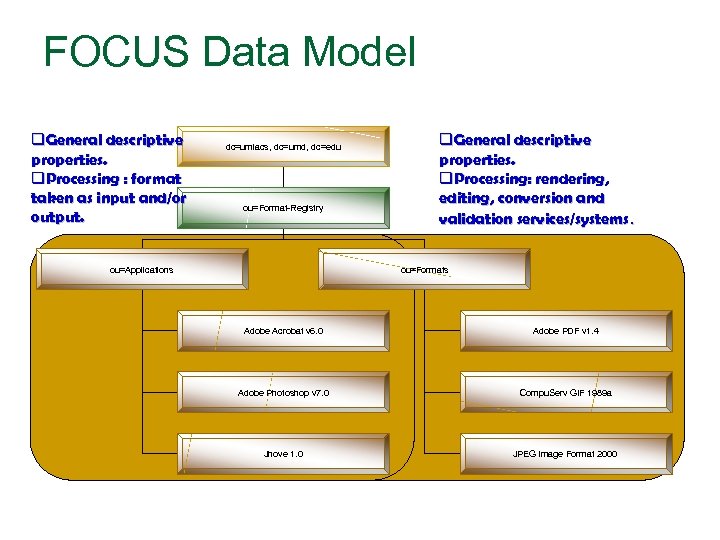
FOCUS Data Model q. General descriptive properties. q. Processing : format taken as input and/or output. dc=umiacs, dc=umd, dc=edu ou=Format-Registry ou=Applications q. General descriptive properties. q. Processing: rendering, editing, conversion and validation services/systems. ou=Formats Adobe Acrobat v 6. 0 Adobe PDF v 1. 4 Adobe Photoshop v 7. 0 Compu. Serv GIF 1989 a Jhove 1. 0 JPEG Image Format 2000
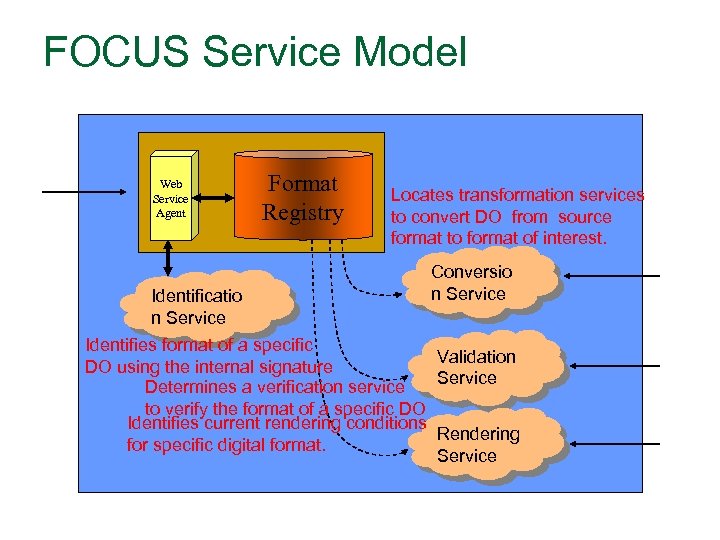
FOCUS Service Model Web Service Agent Identificatio n Service Format Registry Locates transformation services to convert DO from source format to format of interest. Conversio n Service Identifies format of a specific Validation DO using the internal signature Service Determines a verification service to verify the format of a specific DO Identifies current rendering conditions Rendering for specific digital format. Service

Rest of Presentation n Integrity Auditing Service

Integrity Auditing Service n Many types of errors: • • • n Media or hardware degradation Technology evolution/upgrades Operational errors Malicious alterations Hardware/software malfunctions …. Digital objects are subject to transformations and changing standards/protocols.

Basic Ideas n n Auditing service is managed and run independently of the archiving system. Active and user-triggered auditing. Time-stamped certificates that enable the verification of the integrity of the object throughout its lifetime – auditable record of every transformation. Highly available and secure service with the ability to detect and correct errors.

Auditing Service - Certificates n n Time-stamped certificate that includes the hash of the object, hash algorithm identifier, time, owner id, version #, and old certificate if any. Certificates are managed by a persistent, distributed environment based on erasure codes and Merckle hash trees, and only visible to trusted archive repositories.
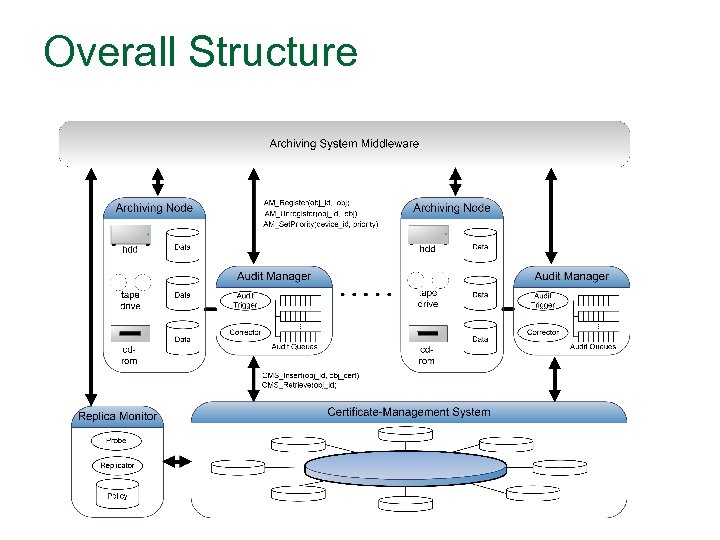
Overall Structure

Software Components n n n Audit Manager: registers objects to be audited, and performs auditing either actively or as triggered by user/archive. Certificate Management System: An independent, highly available, and highly secure environment for preserving and ensuring the integrity of the certificates. Object Monitor: Verifies the availability of the data in the archive using the object ids in the CMS.

Conclusion n Research program focusing on tools and environments for ingestion, management of preservation processes, and in the near future access for long term digital archives. Software prototyping and testing on a wide variety of collections that are available locally. Tools to be used by the Chronopolis Consortium, NARA, and NDIIPP partners.
16760c83c2a10a207cca16ac4e50aa2e.ppt