8c947632efdbe6b1d2ec2e5559f4bc6d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Road to Revolution 1754 - 1776
Road to Revolution 1754 - 1776
 After the French & Indian War… British Goals: Keep the Colonist out of Indian Territory to avoid spending money on protection and increasing the already doubled debt. Conflict with Indians = Military Protection = Increased Spending $$$
After the French & Indian War… British Goals: Keep the Colonist out of Indian Territory to avoid spending money on protection and increasing the already doubled debt. Conflict with Indians = Military Protection = Increased Spending $$$
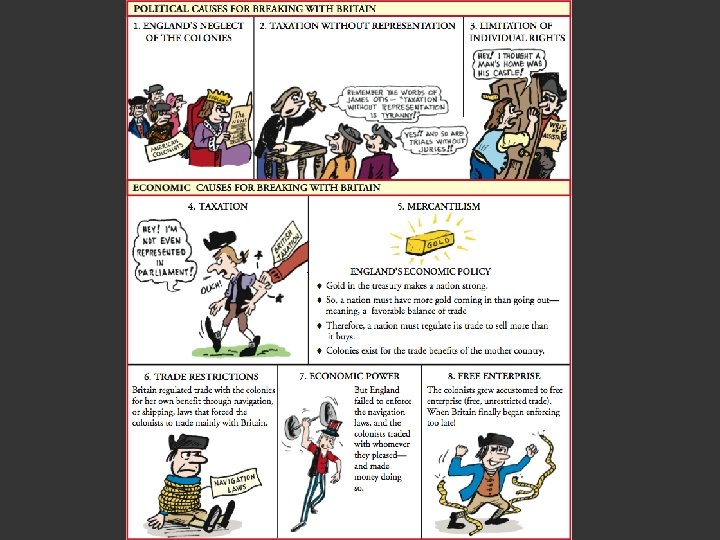
 How will England Pay its Debts? ? ? ANSWER • Tax the American colonists. • England believes that since colonies are responsible for debt, they should help pay
How will England Pay its Debts? ? ? ANSWER • Tax the American colonists. • England believes that since colonies are responsible for debt, they should help pay
 Taxing the Colonies Action Reaction Sugar Act (1764) – tax Colonist are ANGRY!!! placed on sugar and molasses Mercantilist Policy Smugglers would be tried in courts without juries Taxing them without their consent is wrong Trials without juries are unfair
Taxing the Colonies Action Reaction Sugar Act (1764) – tax Colonist are ANGRY!!! placed on sugar and molasses Mercantilist Policy Smugglers would be tried in courts without juries Taxing them without their consent is wrong Trials without juries are unfair
 Taxation Without Representation is Tyranny Colonists thought of themselves as English citizens with the same rights as those living in Britain. Colonists had no representatives/ members in Parliament to voice their concerns. Tax laws were being passed without the colonists having a say so. They did not want to be taxed without consent/ permission.
Taxation Without Representation is Tyranny Colonists thought of themselves as English citizens with the same rights as those living in Britain. Colonists had no representatives/ members in Parliament to voice their concerns. Tax laws were being passed without the colonists having a say so. They did not want to be taxed without consent/ permission.
 John Locke and William Blackstone John Locke – wrote that government was a “Social Contract” Government has contract/obligation to protect individual freedom and property If they fail to do this, citizens have the right to overthrow it William Blackstone – defined the rights of individuals in English law as well as property rights that could not be violated even by the king.
John Locke and William Blackstone John Locke – wrote that government was a “Social Contract” Government has contract/obligation to protect individual freedom and property If they fail to do this, citizens have the right to overthrow it William Blackstone – defined the rights of individuals in English law as well as property rights that could not be violated even by the king.
 Patriots were American Colonists who wanted to be free and independent of British rule. Also called Whigs and Rebels. John Adams Ben Franklin Alexander Hamilton Sam Adams Paul Revere Thomas Paine George Washington
Patriots were American Colonists who wanted to be free and independent of British rule. Also called Whigs and Rebels. John Adams Ben Franklin Alexander Hamilton Sam Adams Paul Revere Thomas Paine George Washington
 Loyalist were colonists who were loyal to the King of Great Britain. Also called Tories and Redcoats.
Loyalist were colonists who were loyal to the King of Great Britain. Also called Tories and Redcoats.
 Taxing Continues Action Stamp Act (1765) – tax on all printed material (printed publications and official documents) Reaction Colonist protest Colonist begin Boycotts (refuse to buy) on British goods Sons of Liberty formed by Sam Adams
Taxing Continues Action Stamp Act (1765) – tax on all printed material (printed publications and official documents) Reaction Colonist protest Colonist begin Boycotts (refuse to buy) on British goods Sons of Liberty formed by Sam Adams
 Taxing Continues Action Quartering Act (1765)Required the colonists to quarter (house and feed) British troops in America. Reaction Colonist protest Colonists were upset that they were forced to house British soldiers. Colonists were expected to pay the expenses for British soldiers.
Taxing Continues Action Quartering Act (1765)Required the colonists to quarter (house and feed) British troops in America. Reaction Colonist protest Colonists were upset that they were forced to house British soldiers. Colonists were expected to pay the expenses for British soldiers.
 Opposition Grows – Townshend Acts Action Stamp Act Repealed – Repeal means to revoke, takeback, officially withdraw Townshend Acts (1767) - tax on lead, glass, paper, paint, and tea Use Writs of Assistance to enforce tax - Writs of assistance were court orders that authorized British customs officers to conduct general (non-specific) searches of premises for illegal imports or exports. Sent more British soldiers to keep order Reaction Boycotts continued Colonial governments oppose them Sons of Liberty take action – attack customs officials
Opposition Grows – Townshend Acts Action Stamp Act Repealed – Repeal means to revoke, takeback, officially withdraw Townshend Acts (1767) - tax on lead, glass, paper, paint, and tea Use Writs of Assistance to enforce tax - Writs of assistance were court orders that authorized British customs officers to conduct general (non-specific) searches of premises for illegal imports or exports. Sent more British soldiers to keep order Reaction Boycotts continued Colonial governments oppose them Sons of Liberty take action – attack customs officials
 Colonial Leaders Samuel Adams • Helped organize the first Committee of Correspondence, Sons of Liberty and the Boston Tea Party.
Colonial Leaders Samuel Adams • Helped organize the first Committee of Correspondence, Sons of Liberty and the Boston Tea Party.
 Committees of Correspondence Mercy Otis Warren Helped organize the Committee of Correspondence Wrote pamphlets and stories against the British as a form of protest Mercy wrote the first history of the American Revolutionary War using her notes from meetings and conversations. Mercy’s ideas and writing convinced many people in the colonies to take up the Patriot cause.
Committees of Correspondence Mercy Otis Warren Helped organize the Committee of Correspondence Wrote pamphlets and stories against the British as a form of protest Mercy wrote the first history of the American Revolutionary War using her notes from meetings and conversations. Mercy’s ideas and writing convinced many people in the colonies to take up the Patriot cause.
 Colonial Anger Reaches Boiling Point: Boston Massacre, 1770 v The group of colonist in Boston taunted the soldiers and threw snowballs. By accident, the soldiers fired, and several protestors were killed. v Crispus Attacks, a man of mixed African and Native American Indian ancestry, was the first colonist killed. v There were 8 British soldiers, and they killed 5 colonists. v Samuel Adams called it the “Boston Massacre”.
Colonial Anger Reaches Boiling Point: Boston Massacre, 1770 v The group of colonist in Boston taunted the soldiers and threw snowballs. By accident, the soldiers fired, and several protestors were killed. v Crispus Attacks, a man of mixed African and Native American Indian ancestry, was the first colonist killed. v There were 8 British soldiers, and they killed 5 colonists. v Samuel Adams called it the “Boston Massacre”.
 Propaganda – information giving only one side of the story in order to influence the audience Samuel Adams referred to the event as the Boston Massacre, despite the fact that only 5 of the 400 colonists present were killed Adams asked Paul Revere to make an engraving of the event. This image was circulated in newspapers all throughout the colonies in order to win public support against the British.
Propaganda – information giving only one side of the story in order to influence the audience Samuel Adams referred to the event as the Boston Massacre, despite the fact that only 5 of the 400 colonists present were killed Adams asked Paul Revere to make an engraving of the event. This image was circulated in newspapers all throughout the colonies in order to win public support against the British.
 Boston Massacre Image Analysis
Boston Massacre Image Analysis
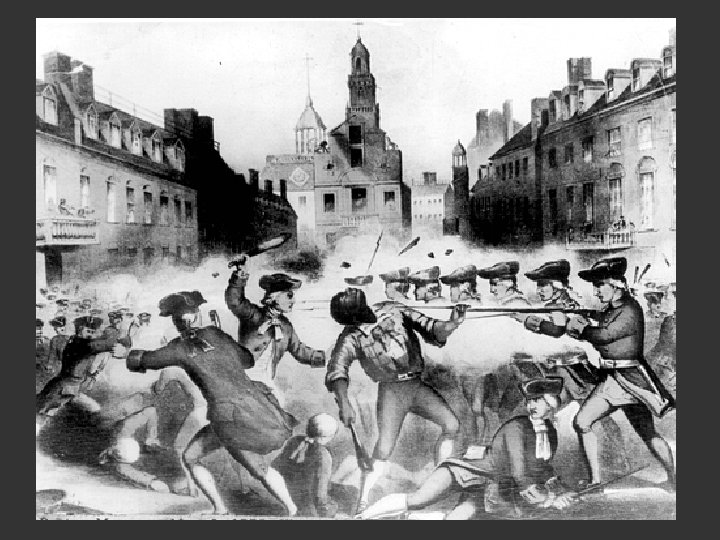
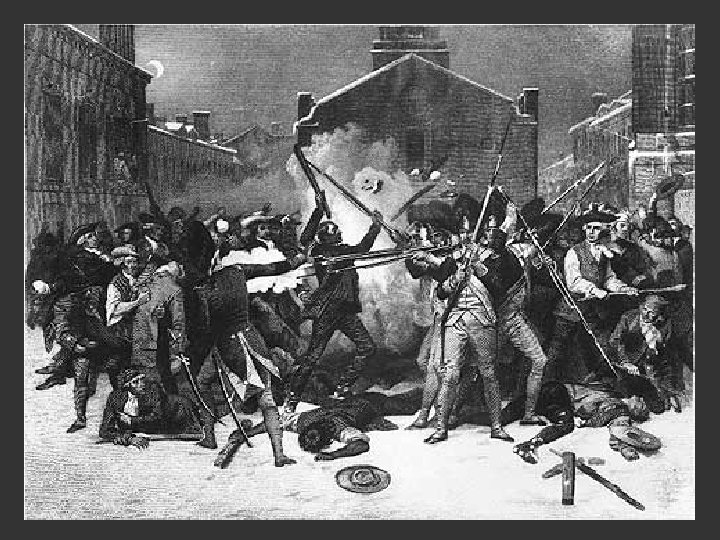





 New Trouble – Tea Action Parliament repeals the Townshend Acts, except for a tax on tea Tea Act (1773) – tax on tea, East India Company monopolizes tea business Reaction Colonist protest Boston Tea Party (1773) – colonist led by Sons of Liberty, dump 45 tons of tea into Boston Harbor
New Trouble – Tea Action Parliament repeals the Townshend Acts, except for a tax on tea Tea Act (1773) – tax on tea, East India Company monopolizes tea business Reaction Colonist protest Boston Tea Party (1773) – colonist led by Sons of Liberty, dump 45 tons of tea into Boston Harbor
 England is Outraged !!!!!! Coercive Acts Passed Action Coercive Acts (1774) – called Intolerable Acts by colonists Closed Boston Harbor Quartering Act was back Eliminated elected gov’t council British officials charged with major crimes were to be tried in England Reaction Tension escalates to an all time high First Continental Congress is called
England is Outraged !!!!!! Coercive Acts Passed Action Coercive Acts (1774) – called Intolerable Acts by colonists Closed Boston Harbor Quartering Act was back Eliminated elected gov’t council British officials charged with major crimes were to be tried in England Reaction Tension escalates to an all time high First Continental Congress is called