5103c44244475ffb6a2f7d8df79f5dc5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Road to Independence 1763 -1776 Chapter 5
Road to Independence 1763 -1776 Chapter 5
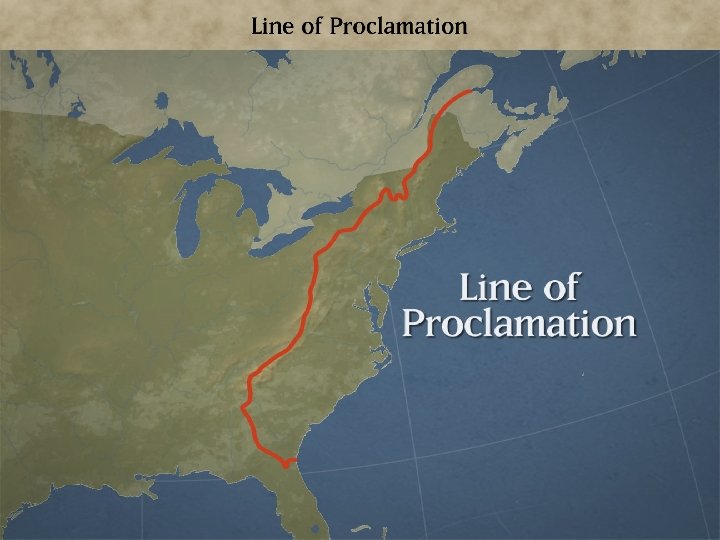
 Relations with Britain • 1763—Great Britain tries to end troubles with the Native Americans by issuing the Proclamation of 1763 • Prohibited colonist from moving west of the Appalachian Mountains • Colonist feared that a large number of British troops in North America might be used to interfere with their liberties • Distrust was growing between Britain and the colonies
Relations with Britain • 1763—Great Britain tries to end troubles with the Native Americans by issuing the Proclamation of 1763 • Prohibited colonist from moving west of the Appalachian Mountains • Colonist feared that a large number of British troops in North America might be used to interfere with their liberties • Distrust was growing between Britain and the colonies
 Financial Troubles • Great Britain had a huge debt after the French and Indian War. • Desperate for new revenue (incoming money) the King and Parliament decide to tax the colonies their fair share
Financial Troubles • Great Britain had a huge debt after the French and Indian War. • Desperate for new revenue (incoming money) the King and Parliament decide to tax the colonies their fair share
 Britain’s Trade Laws • George Grenville becomes prime minister of Britain • Grenville decides to stop illegal smuggling of goods. • Smugglers to be sent to vice-admiralty courts • Writs of assistance – legal document allowing custom agents to enter ANY location to search for smuggled goods
Britain’s Trade Laws • George Grenville becomes prime minister of Britain • Grenville decides to stop illegal smuggling of goods. • Smugglers to be sent to vice-admiralty courts • Writs of assistance – legal document allowing custom agents to enter ANY location to search for smuggled goods
 The Sugar Act • 1764 Parliament passes the Sugar Act • Was used to try to increase tax revenue • If caught smuggling officers are permitted to seize goods without going to court • Writs of Assistance—violated their right to be secure in their home • Vice-admiralty court---violated their right to trial by jury “Guilty to Proven Innocent” • James Otis—Boston Lawyer argued for colonial rights
The Sugar Act • 1764 Parliament passes the Sugar Act • Was used to try to increase tax revenue • If caught smuggling officers are permitted to seize goods without going to court • Writs of Assistance—violated their right to be secure in their home • Vice-admiralty court---violated their right to trial by jury “Guilty to Proven Innocent” • James Otis—Boston Lawyer argued for colonial rights
 The Stamp Act • 1765 Tax on almost all printed material in the colonies (newspapers, playing cards, wills) • Opposition to Stamp Act focuses on 2 issues – Parliament interfered in colonial affairs by taxing the colonies without consent – Parliament ignored the colonial tradition of self-government
The Stamp Act • 1765 Tax on almost all printed material in the colonies (newspapers, playing cards, wills) • Opposition to Stamp Act focuses on 2 issues – Parliament interfered in colonial affairs by taxing the colonies without consent – Parliament ignored the colonial tradition of self-government
 Protesting the Stamp Act • Patrick Henry—young member of the Virginia House of Burgesses – Persuaded the burgesses to take action – Virginia assembly passes a resolution declaring it had the exclusive right and power to tax its citizens • Samuel Adams in Boston forms the Sons of Liberty—protest the Stamp Act--1765 • 1765—Protesters burn effigies of tax collectors, also raided and destroyed houses
Protesting the Stamp Act • Patrick Henry—young member of the Virginia House of Burgesses – Persuaded the burgesses to take action – Virginia assembly passes a resolution declaring it had the exclusive right and power to tax its citizens • Samuel Adams in Boston forms the Sons of Liberty—protest the Stamp Act--1765 • 1765—Protesters burn effigies of tax collectors, also raided and destroyed houses

 Stamp Act Congress • 1765 Delegates from 9 Colonies meet in NY • Declare they cant be taxed by Britain • Urged merchants, artisans, and farmers to boycott goods from Britain • Non-importation Agreements—farmers promised not to buy from Britain • March 1766 Parliament repeals the Stamp Act • Same day Parliament passes the Declaratory Act —stated that Parliament had the right to tax and make decisions for the colonies
Stamp Act Congress • 1765 Delegates from 9 Colonies meet in NY • Declare they cant be taxed by Britain • Urged merchants, artisans, and farmers to boycott goods from Britain • Non-importation Agreements—farmers promised not to buy from Britain • March 1766 Parliament repeals the Stamp Act • Same day Parliament passes the Declaratory Act —stated that Parliament had the right to tax and make decisions for the colonies
 New Taxes • Parliament passes the Townshend Act in 1767 • Tax on imported goods such as glass, tea, paper, and lead • Again, colonist boycott • Women take active role—Daughters of Liberty – Urged colonist to wear homemade fabrics
New Taxes • Parliament passes the Townshend Act in 1767 • Tax on imported goods such as glass, tea, paper, and lead • Again, colonist boycott • Women take active role—Daughters of Liberty – Urged colonist to wear homemade fabrics
 Writs of assistance enabled British customs officers to search A. Foreigners B. Foreign goods C. People for contraband D. Homes for smuggled goods [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
Writs of assistance enabled British customs officers to search A. Foreigners B. Foreign goods C. People for contraband D. Homes for smuggled goods [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
 The colonist paid lower taxes on molasses because of the A. Sugar Act B. Stamp Act C. Proclamation of 1763 D. Writ of assistance [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
The colonist paid lower taxes on molasses because of the A. Sugar Act B. Stamp Act C. Proclamation of 1763 D. Writ of assistance [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
 Which act ignored the colonial tradition of self-government? A. Townshend Act B. Sugar Act C. Stamp Act D. Declaratory Act [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
Which act ignored the colonial tradition of self-government? A. Townshend Act B. Sugar Act C. Stamp Act D. Declaratory Act [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
 Good being imported to the colonist were taxed by the A. Stamp Act B. Declaratory Act C. Sugar Act D. Townshend Acts [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
Good being imported to the colonist were taxed by the A. Stamp Act B. Declaratory Act C. Sugar Act D. Townshend Acts [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
 Which act did the Daughters of Liberty protest? A. Stamp Act B. Townshend Act C. Declaratory Act D. Sugar Act [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
Which act did the Daughters of Liberty protest? A. Stamp Act B. Townshend Act C. Declaratory Act D. Sugar Act [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
 What do we call a refusal to buy a good boycott
What do we call a refusal to buy a good boycott
 Who organized the Sons of Liberty? A. John Adams B. Abigail Adams C. Samuel Adams D. Adam Brown [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
Who organized the Sons of Liberty? A. John Adams B. Abigail Adams C. Samuel Adams D. Adam Brown [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
![A formal expression of opinion A. effigies B. boycott C. resolution D. revenue [Default] A formal expression of opinion A. effigies B. boycott C. resolution D. revenue [Default]](https://present5.com/presentation/5103c44244475ffb6a2f7d8df79f5dc5/image-19.jpg) A formal expression of opinion A. effigies B. boycott C. resolution D. revenue [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
A formal expression of opinion A. effigies B. boycott C. resolution D. revenue [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
![Incoming money A. effigies B. boycott C. resolution D. revenue [Default] [MC Any] [MC Incoming money A. effigies B. boycott C. resolution D. revenue [Default] [MC Any] [MC](https://present5.com/presentation/5103c44244475ffb6a2f7d8df79f5dc5/image-20.jpg) Incoming money A. effigies B. boycott C. resolution D. revenue [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
Incoming money A. effigies B. boycott C. resolution D. revenue [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
![Rag figures A. effigies B. boycott C. resolution D. revenue [Default] [MC Any] [MC Rag figures A. effigies B. boycott C. resolution D. revenue [Default] [MC Any] [MC](https://present5.com/presentation/5103c44244475ffb6a2f7d8df79f5dc5/image-21.jpg) Rag figures A. effigies B. boycott C. resolution D. revenue [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]
Rag figures A. effigies B. boycott C. resolution D. revenue [Default] [MC Any] [MC All]


