5f95012cc97f601dd101b22f53be3d24.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Ro. A and So. A Integration for Message Brokers Group Name: WG 2 -ARC Source: ALU Meeting Date: 2013 -10 -21 Agenda Item:
Ro. A and So. A Integration for Message Brokers Group Name: WG 2 -ARC Source: ALU Meeting Date: 2013 -10 -21 Agenda Item:
 Outline • Specifying Services in one. M 2 M • Integration scenarios of message brokers (e. g. MQTT) • Management considerations © 2013 one. M 2 M Partners one. M 2 M-ARC-2013 -xxxx 2
Outline • Specifying Services in one. M 2 M • Integration scenarios of message brokers (e. g. MQTT) • Management considerations © 2013 one. M 2 M Partners one. M 2 M-ARC-2013 -xxxx 2
 Specifying Services in one. M 2 M
Specifying Services in one. M 2 M
 Outline • Specifying Services in one. M 2 M • Integration scenarios of message brokers (e. g. MQTT) • Management considerations © 2013 one. M 2 M Partners one. M 2 M-ARC-2013 -xxxx 4
Outline • Specifying Services in one. M 2 M • Integration scenarios of message brokers (e. g. MQTT) • Management considerations © 2013 one. M 2 M Partners one. M 2 M-ARC-2013 -xxxx 4
 What does So. A do for Us? • So. A allows for modular software component design – Allows possible pluggable components to existing M 2 M systems (MQTT, XMPP solutions) – Allows for rapid extensions of additional features (easy add -ons) – Allows for deployed software components to be rapidly enhanced – Allows for easy penetration into existing Enterprise systems (e. g. , ERP, CRM) © 2013 one. M 2 M Partners one. M 2 M-ARC-2013 -xxxx 5
What does So. A do for Us? • So. A allows for modular software component design – Allows possible pluggable components to existing M 2 M systems (MQTT, XMPP solutions) – Allows for rapid extensions of additional features (easy add -ons) – Allows for deployed software components to be rapidly enhanced – Allows for easy penetration into existing Enterprise systems (e. g. , ERP, CRM) © 2013 one. M 2 M Partners one. M 2 M-ARC-2013 -xxxx 5
 What do we have to specify for So. A • Services – These are the set of messages that comprise the inter-component and external interfaces) • Components for the services – these are those deployable pluggable implementations of the service • Unified interfaces that permit communication between Components by simply specifying the message without the need for a specific protocol. – Unified in the sense that we do not have to specify messages for point to point flows between components and worry about their representations in a protocol because most implementations will use an Enterprise Service Bus and the ESB mediates the protocol. © 2013 one. M 2 M Partners one. M 2 M-ARC-2013 -xxxx 6
What do we have to specify for So. A • Services – These are the set of messages that comprise the inter-component and external interfaces) • Components for the services – these are those deployable pluggable implementations of the service • Unified interfaces that permit communication between Components by simply specifying the message without the need for a specific protocol. – Unified in the sense that we do not have to specify messages for point to point flows between components and worry about their representations in a protocol because most implementations will use an Enterprise Service Bus and the ESB mediates the protocol. © 2013 one. M 2 M Partners one. M 2 M-ARC-2013 -xxxx 6
 Integrating Ro. A and So. A From a specification viewpoint integrating Ro. A and So. A would require: • Resources operations and associated procedures to be defined such that they can be encapsulated as a Service to be used as a service building block and placed in a Service component. • Define and document specific Services within the CSFs to be used as a service building block and placed in a Service component Note: These 2 principles would say that a Resource is owned by a CSF by the fact that the Resource is encapsulated by Service and the Services are documented within the CSFs. © 2013 one. M 2 M Partners one. M 2 M-ARC-2013 -xxxx 7
Integrating Ro. A and So. A From a specification viewpoint integrating Ro. A and So. A would require: • Resources operations and associated procedures to be defined such that they can be encapsulated as a Service to be used as a service building block and placed in a Service component. • Define and document specific Services within the CSFs to be used as a service building block and placed in a Service component Note: These 2 principles would say that a Resource is owned by a CSF by the fact that the Resource is encapsulated by Service and the Services are documented within the CSFs. © 2013 one. M 2 M Partners one. M 2 M-ARC-2013 -xxxx 7
 Services – The Minimium • • • Define the subset of services necessary to get the device communicating with applications this would be at a minimum: – M 2 M Business service subscription – Device/Application Provisioning and Registration with onboarding – Device/Application (CSE) to Server (CSE) protocol negotiation (XMPP, MQTT) – Network service exposure for triggering, M 2 M Business service subscription – Data Exchange for oversight and monitoring of the M 2 M traffic between endpoints – Device Management – Security Other services Data Repository, Policy Management would be commodity services that a SP could just buy off-the-shelf and plug into the ESB. Note that Device and Application registration would most likely require a minimalist protocol (possibly IP/UDP based) so that correct Service plugins can be used (open up the transport protocols) © 2013 one. M 2 M Partners one. M 2 M-ARC-2013 -xxxx 8
Services – The Minimium • • • Define the subset of services necessary to get the device communicating with applications this would be at a minimum: – M 2 M Business service subscription – Device/Application Provisioning and Registration with onboarding – Device/Application (CSE) to Server (CSE) protocol negotiation (XMPP, MQTT) – Network service exposure for triggering, M 2 M Business service subscription – Data Exchange for oversight and monitoring of the M 2 M traffic between endpoints – Device Management – Security Other services Data Repository, Policy Management would be commodity services that a SP could just buy off-the-shelf and plug into the ESB. Note that Device and Application registration would most likely require a minimalist protocol (possibly IP/UDP based) so that correct Service plugins can be used (open up the transport protocols) © 2013 one. M 2 M Partners one. M 2 M-ARC-2013 -xxxx 8
 Integration of Message Brokers Group Name: WG 2 -ARC Source: ALU Meeting Date: 2013 -10 -21 Agenda Item:
Integration of Message Brokers Group Name: WG 2 -ARC Source: ALU Meeting Date: 2013 -10 -21 Agenda Item:
 Ro. A Integration
Ro. A Integration
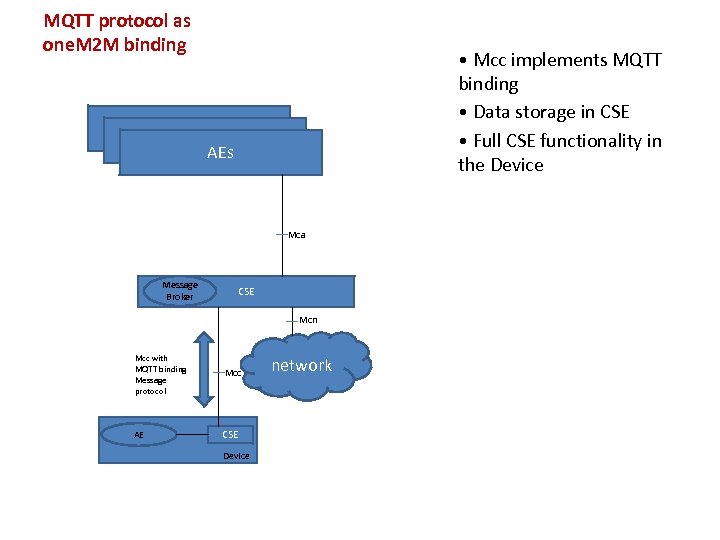 MQTT protocol as one. M 2 M binding • Mcc implements MQTT binding • Data storage in CSE • Full CSE functionality in the Device AEs Mca Message Broker CSE Mcn Mcc with MQTT binding Message protocol Mcc AE CSE Device network
MQTT protocol as one. M 2 M binding • Mcc implements MQTT binding • Data storage in CSE • Full CSE functionality in the Device AEs Mca Message Broker CSE Mcn Mcc with MQTT binding Message protocol Mcc AE CSE Device network
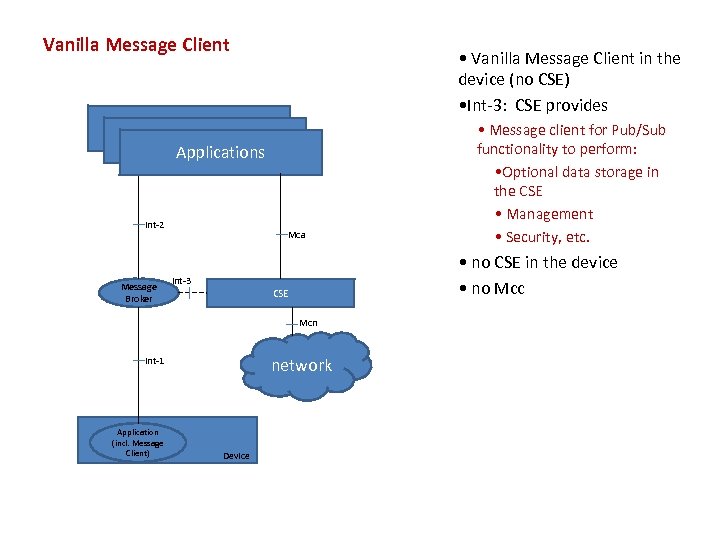 Vanilla Message Client • Vanilla Message Client in the device (no CSE) • Int-3: CSE provides Applications Int-2 Message Broker Mca Int-3 • no CSE in the device • no Mcc CSE Mcn network Int-1 Application (incl. Message Client) Device • Message client for Pub/Sub functionality to perform: • Optional data storage in the CSE • Management • Security, etc.
Vanilla Message Client • Vanilla Message Client in the device (no CSE) • Int-3: CSE provides Applications Int-2 Message Broker Mca Int-3 • no CSE in the device • no Mcc CSE Mcn network Int-1 Application (incl. Message Client) Device • Message client for Pub/Sub functionality to perform: • Optional data storage in the CSE • Management • Security, etc.
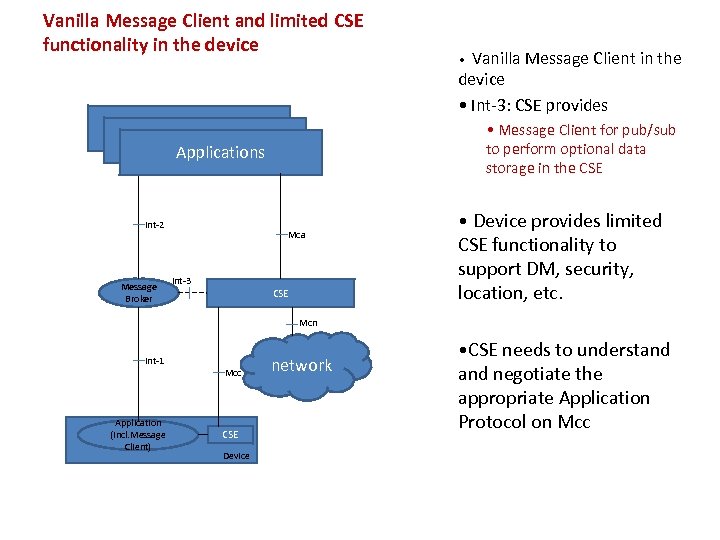 Vanilla Message Client and limited CSE functionality in the device • Message Client for pub/sub to perform optional data storage in the CSE Applications Int-2 Message Broker Mca Int-3 Vanilla Message Client in the device • Int-3: CSE provides • CSE • Device provides limited CSE functionality to support DM, security, location, etc. Mcn Int-1 Application (incl. Message Client) Mcc CSE Device network • CSE needs to understand negotiate the appropriate Application Protocol on Mcc
Vanilla Message Client and limited CSE functionality in the device • Message Client for pub/sub to perform optional data storage in the CSE Applications Int-2 Message Broker Mca Int-3 Vanilla Message Client in the device • Int-3: CSE provides • CSE • Device provides limited CSE functionality to support DM, security, location, etc. Mcn Int-1 Application (incl. Message Client) Mcc CSE Device network • CSE needs to understand negotiate the appropriate Application Protocol on Mcc
 So. A Integration
So. A Integration
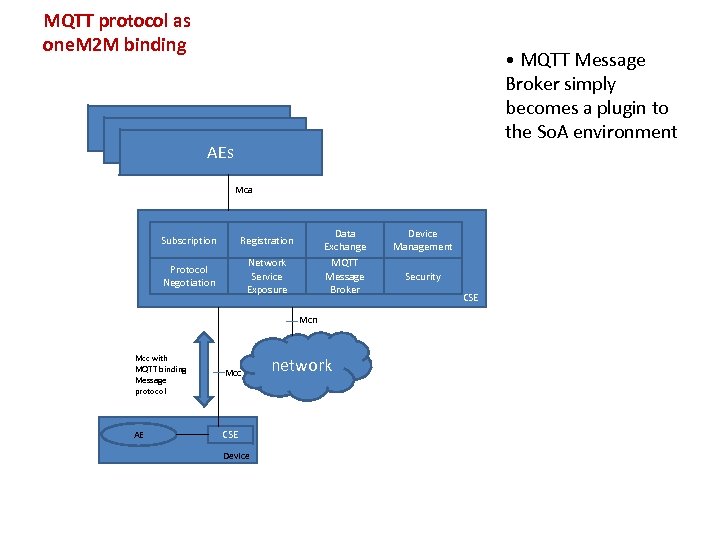 MQTT protocol as one. M 2 M binding • MQTT Message Broker simply becomes a plugin to the So. A environment AEs Mca Subscription Protocol Negotiation Data Exchange MQTT Message Broker Registration Network Service Exposure Mcn Mcc with MQTT binding Message protocol Mcc AE CSE Device network Device Management Security CSE
MQTT protocol as one. M 2 M binding • MQTT Message Broker simply becomes a plugin to the So. A environment AEs Mca Subscription Protocol Negotiation Data Exchange MQTT Message Broker Registration Network Service Exposure Mcn Mcc with MQTT binding Message protocol Mcc AE CSE Device network Device Management Security CSE
 Management considerations
Management considerations
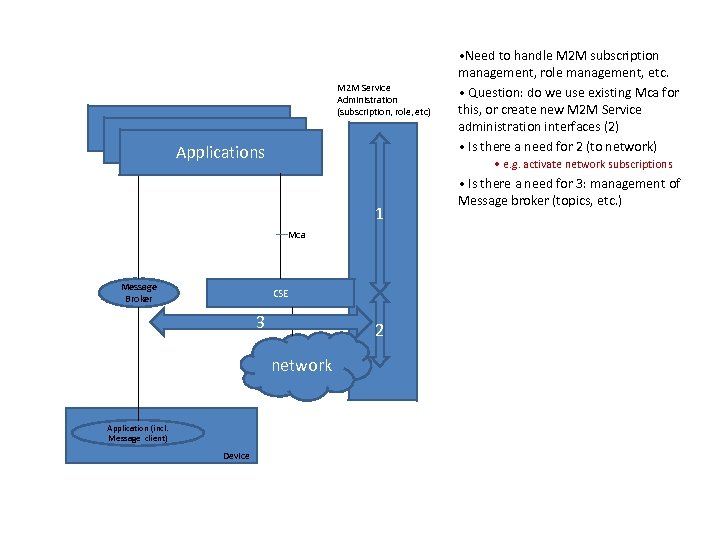 M 2 M Service Administration (subscription, role, etc) Applications • e. g. activate network subscriptions 1 Mca Message Broker CSE 3 Mcn network Application (incl. Message client) Device • Need to handle M 2 M subscription management, role management, etc. • Question: do we use existing Mca for this, or create new M 2 M Service administration interfaces (2) • Is there a need for 2 (to network) 2 • Is there a need for 3: management of Message broker (topics, etc. )
M 2 M Service Administration (subscription, role, etc) Applications • e. g. activate network subscriptions 1 Mca Message Broker CSE 3 Mcn network Application (incl. Message client) Device • Need to handle M 2 M subscription management, role management, etc. • Question: do we use existing Mca for this, or create new M 2 M Service administration interfaces (2) • Is there a need for 2 (to network) 2 • Is there a need for 3: management of Message broker (topics, etc. )


