a829709aa076886fde7fa997ca1bcf84.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 1
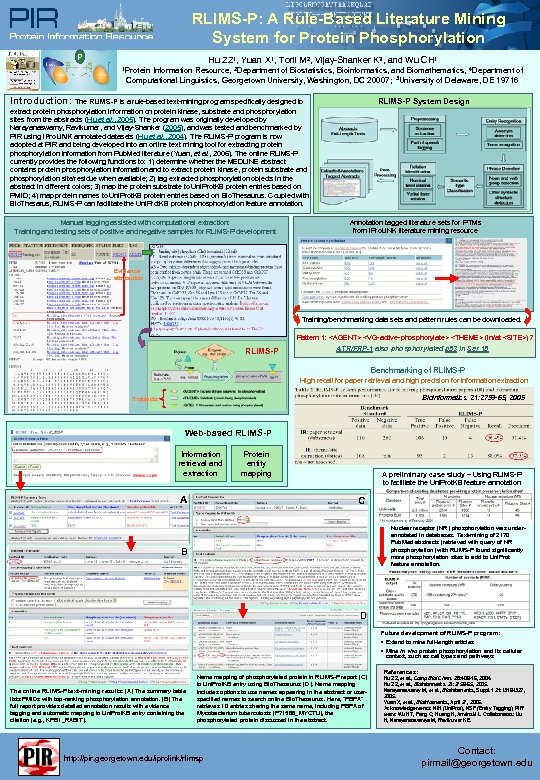
RLIMS-P: A Rule-Based Literature Mining System for Protein Phosphorylation P Hu ZZ 1, Yuan X 1, Torii M 2, Vijay-Shanker K 3, and Wu CH 1 1 Protein Information Resource, 2 Department of Biostatistics, Bioinformatics, and Biomathematics, 4 Department of Computational Linguistics, Georgetown University, Washington, DC 20007; 3 University of Delaware, DE 19716 Introduction: The RLIMS-P is a rule-based text-mining program specifically designed to RLIMS-P System Design extract protein phosphorylation information on protein kinase, substrate and phosphorylation sites from the abstracts (Hu et al. , 2005). The program was originally developed by Narayanaswamy, Ravikumar, and Vijay-Shanker (2005), and was tested and benchmarked by PIR using i. Pro. LINK annotated datasets (Hu et al. , 2004). The RLIMS-P program is now adopted at PIR and being developed into an online text mining tool for extracting protein phosphorylation information from Pub. Med literature (Yuan, et al. , 2006). The online RLIMS-P currently provides the following functions to: 1) determine whether the MEDLINE abstract contains protein phosphorylation information and to extract protein kinase, protein substrate and phosphorylation site/residue when available; 2) tag extracted phosphorylation objects in the abstract in different colors; 3) map the protein substrate to Uni. Prot. KB protein entries based on PMID; 4) map protein names to Uni. Prot. KB protein entries based on Bio. Thesaurus. Coupled with Bio. Thesarus, RLIMS-P can facilitate the Uni. Prot. KB protein phosphorylation feature annotation. Manual tagging assisted with computational extraction: Training and testing sets of positive and negative samples for RLIMS-P development Annotation tagged literature sets for PTMs from i. Pro. LINK literature mining resource Evidence attribution Training/benchmarking data sets and pattern rules can be downloaded. Pattern 1: <AGENT> <VG-active-phosphorylate> <THEME> (in/at <SITE>)? RLIMS-P ATR/FRP-1 also phosphorylated p 53 in Ser 15 Benchmarking of RLIMS-P High recall for paper retrieval and high precision for information extraction Bioinformatics. 21: 2759 -65, 2005 3 objects Web-based RLIMS-P Information retrieval and extraction A Protein entity mapping A preliminary case study – Using RLIMS-P to facilitate the Uni. Prot. KB feature annotation C Nuclear receptor (NR) phosphorylation was underannotated in databases. Text-mining of 2170 Pub. Med abstracts (retrieved with query of NR phosphorylation) with RLIMS-P found significantly more phosphorylation sites to add to Uni. Prot feature annotation. B D Future development of RLIMS-P program: • Extend to mine full-length articles • Mine in vivo protein phosphorylation and its cellular context, such as cell types and pathways The online RLIMS-P text-mining results: (A) The summary table lists PMIDs with top-ranking phosphorylation annotation. (B) The full report provides detailed annotation results with evidence tagging and automatic mapping to Uni. Prot. KB entry containing the citation (e. g. , KPB 1_RABIT). Name mapping of phosphorylated protein in RLIMS-P report (C) to Uni. Prot. KB entry using Bio. Thesaurus (D). Name mapping includes options to use names appearing in the abstract or userspecified names to search online Bio. Thesaurus. Here, “PBPA” retrieves 10 entries sharing the same name, including PBPA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (P 71586_MYCTU), the phosphorylated protein discussed in the abstract. http: //pir. georgetown. edu/iprolink/rlimsp References: Hu ZZ, et al. , Comp Biol Chem. 28: 409 -16, 2004. Hu ZZ, et al. , Bioinformatics. 21: 2759 -65, 2005. Narayanaswamy M, et al. , Bioinformatics, Suppl. 1 21: i 319 -i 327, 2005. Yuan X, et al. , Bioinformatics, April 27, 2006. Acknowledgements: NIH (Uni. Prot), NSF (Entity Tagging). PIR team: Wu HT, Fang C, Huang H, Arminski L. Collaborators: Liu H, Narayanaswamya M, Ravikumar KE. Contact: pirmail@georgetown. edu
a829709aa076886fde7fa997ca1bcf84.ppt