277f23c82b3d51f28317614cec458e15.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Rivier College CS 575: Advanced LANs Chapter 10: Wireless LANs Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Rivier College CS 575: Advanced LANs Chapter 10: Wireless LANs Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
 Wireless LANs 0 0 0 0 Wireless LANs Applications Wireless LAN Requirements Wireless LAN Technology Infrared LANs: Transmission Techniques Spread Spectrum Communications Spread Spectrum LAN Design Licensed and Unlicensed Narrowband RF Microwave LANs Wireless LAN Standards: * IEEE 802. 11 Services * Physical Medium Specification * Medium Access Control Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Wireless LANs 0 0 0 0 Wireless LANs Applications Wireless LAN Requirements Wireless LAN Technology Infrared LANs: Transmission Techniques Spread Spectrum Communications Spread Spectrum LAN Design Licensed and Unlicensed Narrowband RF Microwave LANs Wireless LAN Standards: * IEEE 802. 11 Services * Physical Medium Specification * Medium Access Control Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
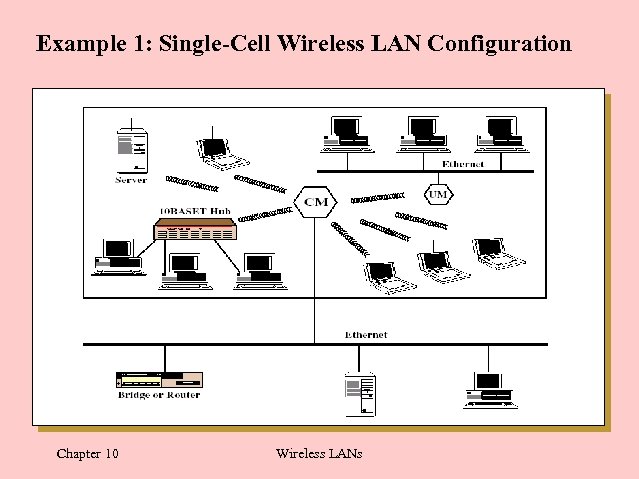 Example 1: Single-Cell Wireless LAN Configuration Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Example 1: Single-Cell Wireless LAN Configuration Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
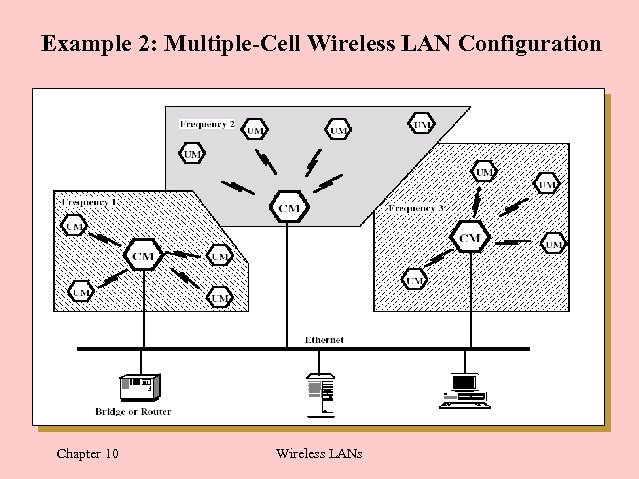 Example 2: Multiple-Cell Wireless LAN Configuration Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Example 2: Multiple-Cell Wireless LAN Configuration Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
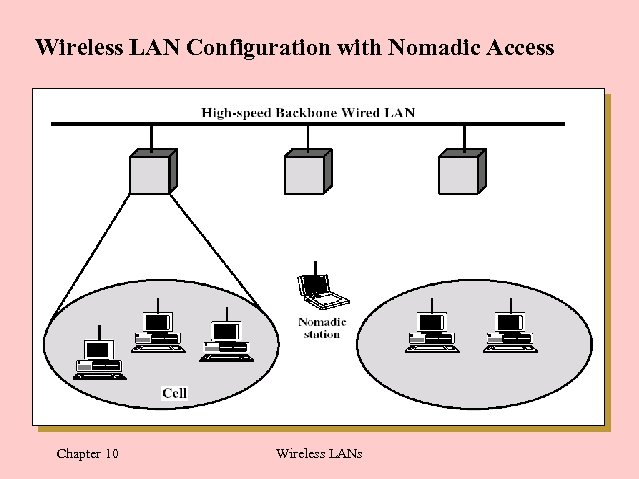 Wireless LAN Configuration with Nomadic Access Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Wireless LAN Configuration with Nomadic Access Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
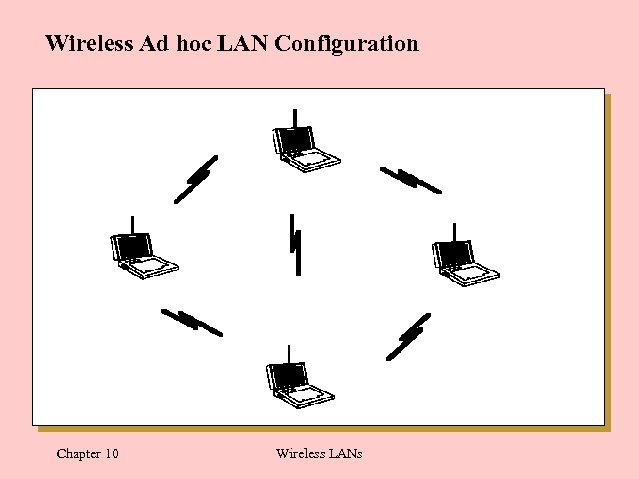 Wireless Ad hoc LAN Configuration Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Wireless Ad hoc LAN Configuration Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
 Wireless LAN Requirements 0 Throughput: The medium access control protocol should make as 0 0 efficient use as possible of the wireless medium to maximize capacity. Number of nodes: Wireless LANs may need to support hundreds of nodes across multiple cells. Connection to backbone LAN: Interconnection with stations on a wired backbone LAN is required. This is accomplished through the use of Control Modules that connect to both types of LANs. Also it may be accommodated for mobile users and ad hoc wireless networks. Service area: A typical coverage area for a wireless LAN has a diameter of 100 to 300 m. Battery power consumption: Long-life battery-powered workstations require wireless adapters. Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Wireless LAN Requirements 0 Throughput: The medium access control protocol should make as 0 0 efficient use as possible of the wireless medium to maximize capacity. Number of nodes: Wireless LANs may need to support hundreds of nodes across multiple cells. Connection to backbone LAN: Interconnection with stations on a wired backbone LAN is required. This is accomplished through the use of Control Modules that connect to both types of LANs. Also it may be accommodated for mobile users and ad hoc wireless networks. Service area: A typical coverage area for a wireless LAN has a diameter of 100 to 300 m. Battery power consumption: Long-life battery-powered workstations require wireless adapters. Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
 Wireless LAN Requirements (continued) 0 Transmission robustness and security: A wireless LAN may be interference prone and easily eavesdropped. It must permit reliable transmission even in a noisy environment and should provide some level of security from eavesdropping. 0 Collocated network operation: Two or more wireless LANs can operate in the same area and in some areas the interference between the LANs is possible. Such interference may thwart the normal operation of a MAC algorithm and may allow unauthorized access to a particular LAN. 0 License-free operation: Users would prefer to buy and operate wireless LAN products without having to secure a license for the frequency band used by the LAN. 0 Handoff-roaming: The MAC protocol used in the wireless LAN should enable mobile stations to move from one cell to another. 0 Dynamic configuration: The MAC addressing and network management aspects of the LAN should permit dynamic and automatic addition, deletion, and relocation of end systems without disruption to other users. Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Wireless LAN Requirements (continued) 0 Transmission robustness and security: A wireless LAN may be interference prone and easily eavesdropped. It must permit reliable transmission even in a noisy environment and should provide some level of security from eavesdropping. 0 Collocated network operation: Two or more wireless LANs can operate in the same area and in some areas the interference between the LANs is possible. Such interference may thwart the normal operation of a MAC algorithm and may allow unauthorized access to a particular LAN. 0 License-free operation: Users would prefer to buy and operate wireless LAN products without having to secure a license for the frequency band used by the LAN. 0 Handoff-roaming: The MAC protocol used in the wireless LAN should enable mobile stations to move from one cell to another. 0 Dynamic configuration: The MAC addressing and network management aspects of the LAN should permit dynamic and automatic addition, deletion, and relocation of end systems without disruption to other users. Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
 Wireless LAN Technologies 0 Infrared (IR) LANs: An individual cell of an IR LAN is limited to a single room because infrared light does not penetrate opaque walls (providing secured noninterfering communication). The unregulated world-wide IR spectrum is virtually unlimited, which represents the possibility of achieving extremely high data rates. IR equipment is inexpensive and simple. The ambient radiation (noise) requires the use of higher-power transmitters. 0 Spread spectrum LANs: This type of LAN makes use of spread spectrum transmission technology. They operate in the industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) bands so that no FCC licensing is required for their use in the United States. 0 Narrowband microwave: These LANs operate at microwave frequencies but do not use spread spectrum. Products operate at frequencies that require FCC licensing, while others use one of the unlicensed ISM bands. Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Wireless LAN Technologies 0 Infrared (IR) LANs: An individual cell of an IR LAN is limited to a single room because infrared light does not penetrate opaque walls (providing secured noninterfering communication). The unregulated world-wide IR spectrum is virtually unlimited, which represents the possibility of achieving extremely high data rates. IR equipment is inexpensive and simple. The ambient radiation (noise) requires the use of higher-power transmitters. 0 Spread spectrum LANs: This type of LAN makes use of spread spectrum transmission technology. They operate in the industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) bands so that no FCC licensing is required for their use in the United States. 0 Narrowband microwave: These LANs operate at microwave frequencies but do not use spread spectrum. Products operate at frequencies that require FCC licensing, while others use one of the unlicensed ISM bands. Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
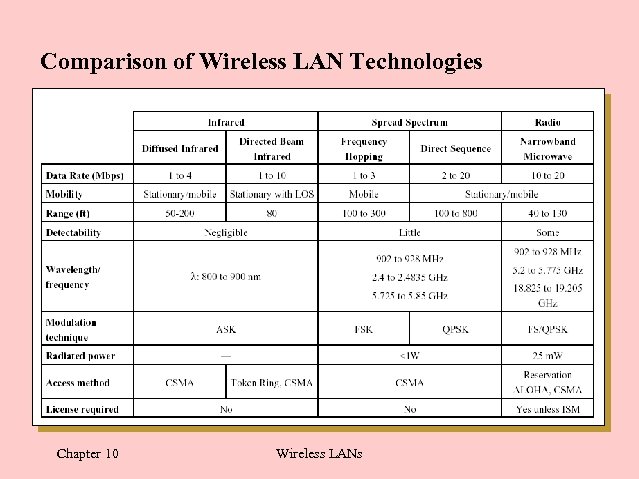 Comparison of Wireless LAN Technologies Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Comparison of Wireless LAN Technologies Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
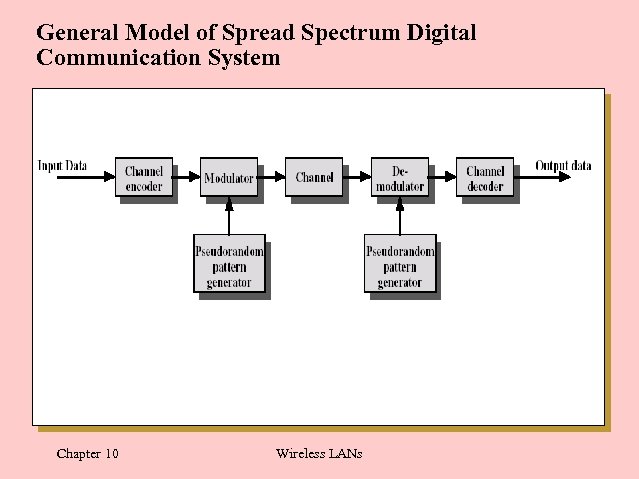 General Model of Spread Spectrum Digital Communication System Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
General Model of Spread Spectrum Digital Communication System Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
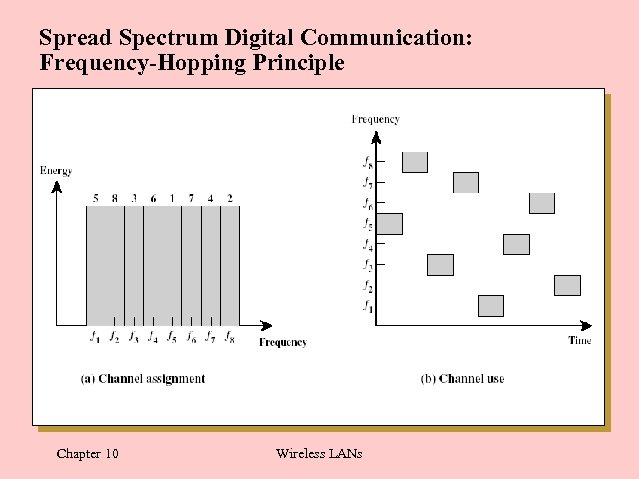 Spread Spectrum Digital Communication: Frequency-Hopping Principle Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Spread Spectrum Digital Communication: Frequency-Hopping Principle Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
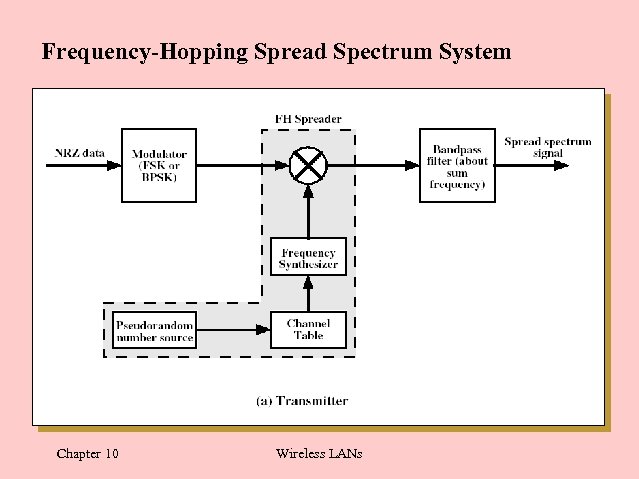 Frequency-Hopping Spread Spectrum System Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Frequency-Hopping Spread Spectrum System Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
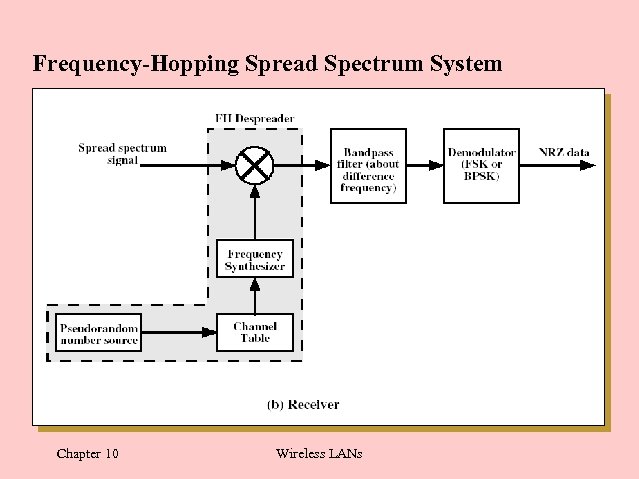 Frequency-Hopping Spread Spectrum System Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Frequency-Hopping Spread Spectrum System Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
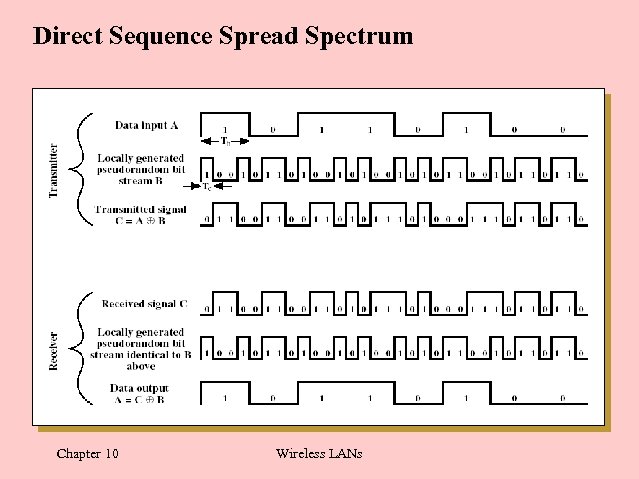 Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
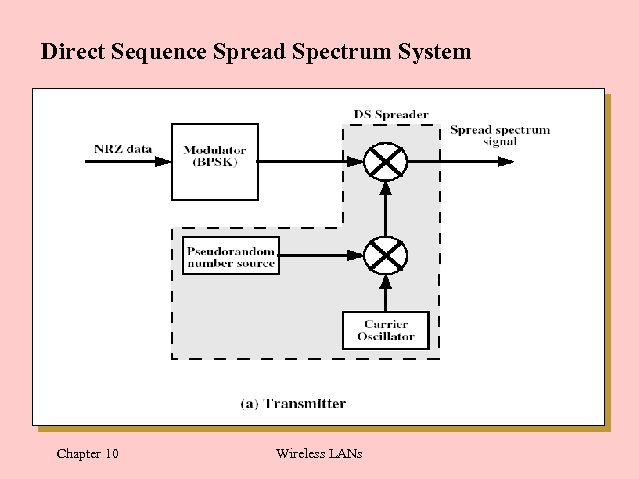 Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum System Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum System Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
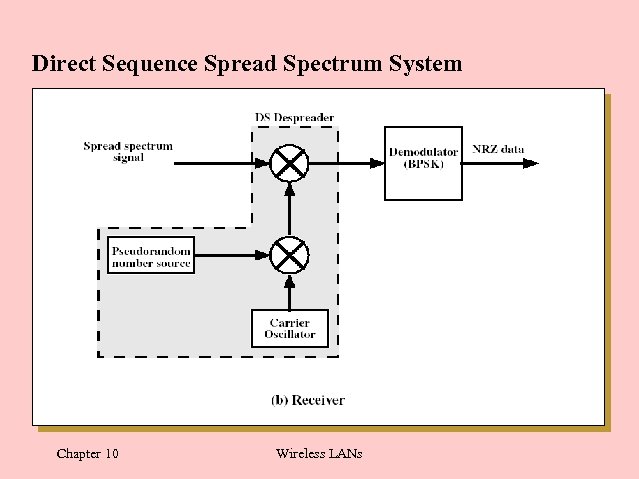 Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum System Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum System Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
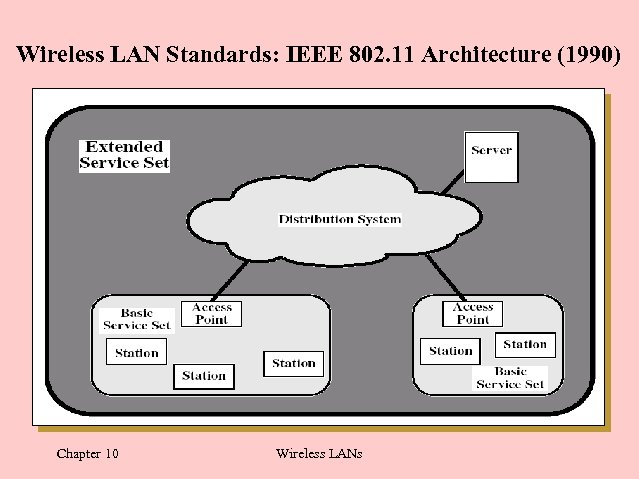 Wireless LAN Standards: IEEE 802. 11 Architecture (1990) Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Wireless LAN Standards: IEEE 802. 11 Architecture (1990) Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
 Wireless LAN Standards: Mobility Station Types 0 No transition: A station is either stationary or moves only within the direct communication range of the communicating stations of a single Basic Service Set (BSS). 0 BSS transition: This is defined as a station movement from one BSS to another BSS within the same Extended Service Set (ESS). Delivery of data to the station requires that the addressing capability be able to recognize the new location of the station. 0 EES transition: This is defined as a station movement from a BSS in one ESS to a BSS within another ESS. This case is supported only in the sense that the station can move. Maintenance of upper-layer connections supported by 802. 11 cannot be guaranteed. Disruption of service is likely to occur. Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
Wireless LAN Standards: Mobility Station Types 0 No transition: A station is either stationary or moves only within the direct communication range of the communicating stations of a single Basic Service Set (BSS). 0 BSS transition: This is defined as a station movement from one BSS to another BSS within the same Extended Service Set (ESS). Delivery of data to the station requires that the addressing capability be able to recognize the new location of the station. 0 EES transition: This is defined as a station movement from a BSS in one ESS to a BSS within another ESS. This case is supported only in the sense that the station can move. Maintenance of upper-layer connections supported by 802. 11 cannot be guaranteed. Disruption of service is likely to occur. Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
 IEEE 802. 11 Services 0 Association: Establishes an initial association between a station and an access 0 0 point within a particular BSS. The access point can then communicate information (station identity, its address) to other access points within the ESS to facilitate routing and delivery of addressed frames. Reassociation: Enables an established association to be transferred from one access point to another, allowing a mobile station to move from one BSS to another. Disassociation: A notification from either a station or an access point that an existing association is terminated. Authentication: Used to establish the identity of stations to each other. The standard does not mandate any particular authentication scheme, which could range from insecure handshaking to public-key encryption schemes. Privacy: Used to prevent the contents of messages from being read by other than the intended recipient. The standard provides for the optional use of encryption to assure privacy. Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
IEEE 802. 11 Services 0 Association: Establishes an initial association between a station and an access 0 0 point within a particular BSS. The access point can then communicate information (station identity, its address) to other access points within the ESS to facilitate routing and delivery of addressed frames. Reassociation: Enables an established association to be transferred from one access point to another, allowing a mobile station to move from one BSS to another. Disassociation: A notification from either a station or an access point that an existing association is terminated. Authentication: Used to establish the identity of stations to each other. The standard does not mandate any particular authentication scheme, which could range from insecure handshaking to public-key encryption schemes. Privacy: Used to prevent the contents of messages from being read by other than the intended recipient. The standard provides for the optional use of encryption to assure privacy. Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
 IEEE 802. 11 Physical Media 0 Infrared at 1 Mbps and 2 Mbps operating at a wavelength between 850 and 950 nm. 0 Direct-sequence spread spectrum operating in the 2. 4 GHz ISM band. Up to seven channels, each with a data rate of 1 Mbps and 2 Mbps, can be used. 0 Frequency-hopping spread spectrum operating in the 2. 4 GHz ISM band, at data rates of 1 Mbps and 2 Mbps. Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
IEEE 802. 11 Physical Media 0 Infrared at 1 Mbps and 2 Mbps operating at a wavelength between 850 and 950 nm. 0 Direct-sequence spread spectrum operating in the 2. 4 GHz ISM band. Up to seven channels, each with a data rate of 1 Mbps and 2 Mbps, can be used. 0 Frequency-hopping spread spectrum operating in the 2. 4 GHz ISM band, at data rates of 1 Mbps and 2 Mbps. Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
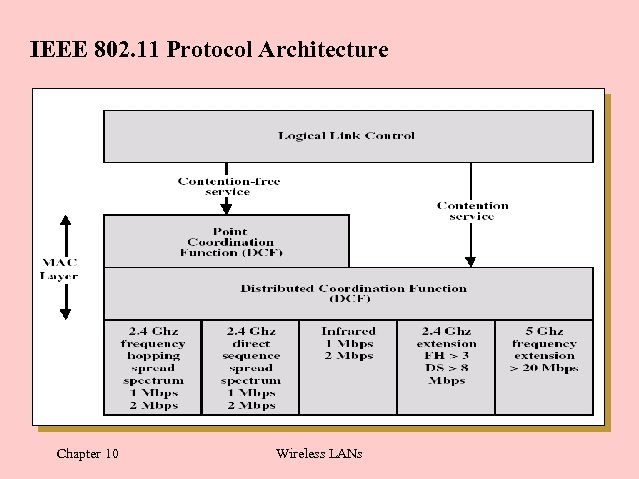 IEEE 802. 11 Protocol Architecture Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
IEEE 802. 11 Protocol Architecture Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
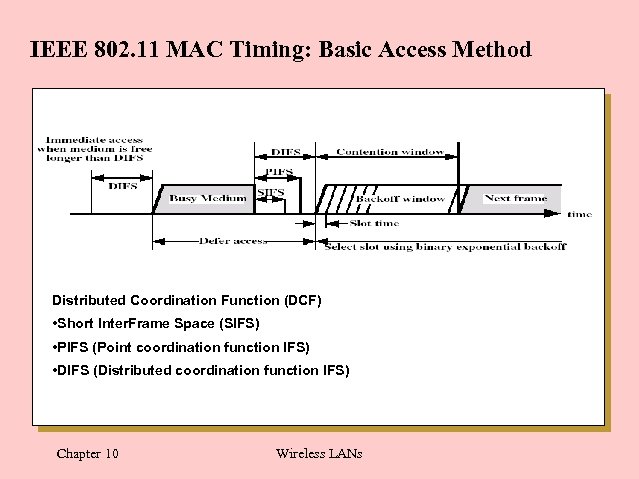 IEEE 802. 11 MAC Timing: Basic Access Method Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) • Short Inter. Frame Space (SIFS) • PIFS (Point coordination function IFS) • DIFS (Distributed coordination function IFS) Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
IEEE 802. 11 MAC Timing: Basic Access Method Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) • Short Inter. Frame Space (SIFS) • PIFS (Point coordination function IFS) • DIFS (Distributed coordination function IFS) Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
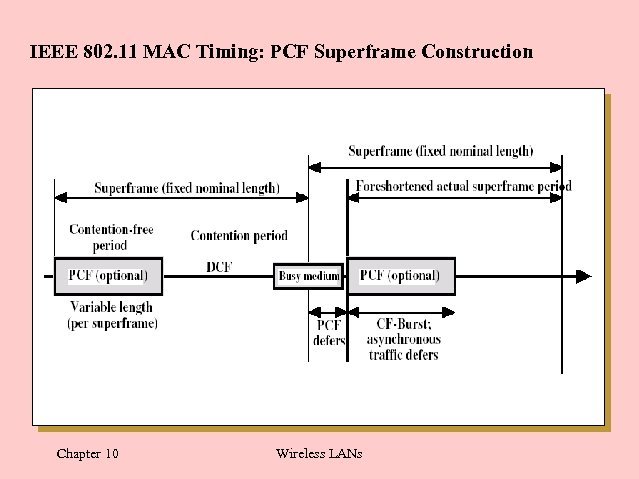 IEEE 802. 11 MAC Timing: PCF Superframe Construction Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
IEEE 802. 11 MAC Timing: PCF Superframe Construction Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
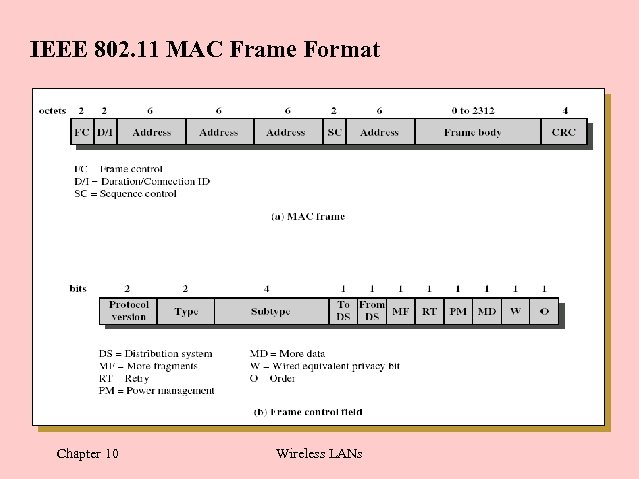 IEEE 802. 11 MAC Frame Format Chapter 10 Wireless LANs
IEEE 802. 11 MAC Frame Format Chapter 10 Wireless LANs


