7de3c90d1bf9ab49e81cc171f04e2e13.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56

River Civilizations (An Research Overview) Submitted by C. Stephen Ingraham 2008

Performance Assessment • Create a tri-fold travel brochure and present it to the class. Your project must include the natural characteristics that define the region known as the Middle East (either past or present), relative and absolute location, climate. Culture. Ecosystems, and technology. CSI 07
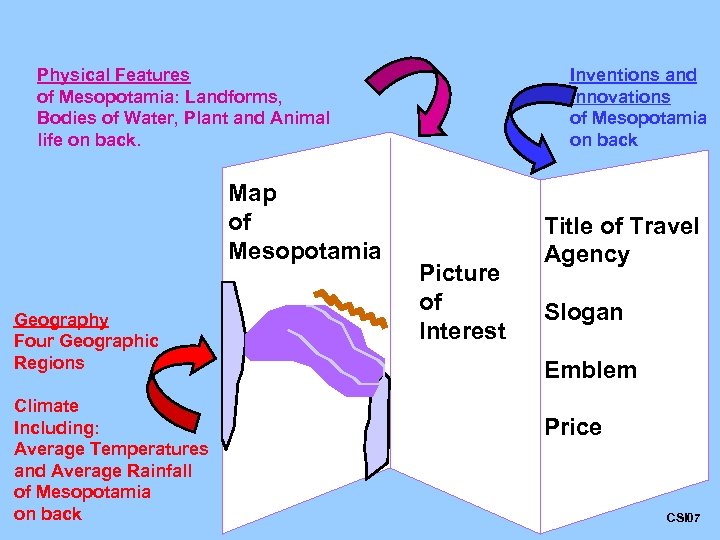
Physical Features of Mesopotamia: Landforms, Bodies of Water, Plant and Animal life on back. Map of Mesopotamia Geography Four Geographic Regions Climate Including: Average Temperatures and Average Rainfall of Mesopotamia on back Inventions and Innovations of Mesopotamia on back Picture of Interest Title of Travel Agency Slogan Emblem Price CSI 07
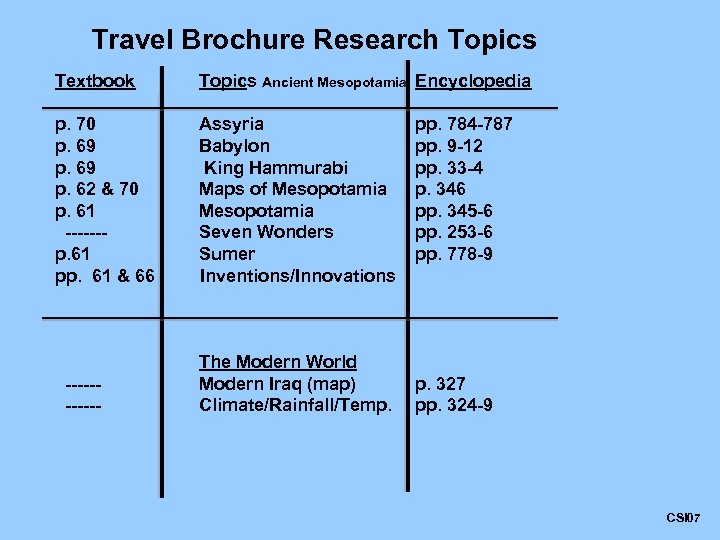
Travel Brochure Research Topics Textbook Topics Ancient Mesopotamia Encyclopedia p. 70 p. 69 p. 62 & 70 p. 61 ------p. 61 pp. 61 & 66 Assyria Babylon King Hammurabi Maps of Mesopotamia Seven Wonders Sumer Inventions/Innovations ------ The Modern World Modern Iraq (map) Climate/Rainfall/Temp. pp. 784 -787 pp. 9 -12 pp. 33 -4 p. 346 pp. 345 -6 pp. 253 -6 pp. 778 -9 p. 327 pp. 324 -9 CSI 07

The Middle East Climate: In contrast to the comfortable areas bordering the Mediterranean and Arabian Seas the inland regions are desert and almost uninhabitable. This same climate extends from the Arabian peninsula into northern Iraq, Jordan, Syria, Iran, and further to the East in Afghanistan. Rainfall: five to ten inches per year. Usually in the form of a downpour for just a very short period in winter. Temperatures: Average 130 degrees during a summer day but as low as 40 degrees at night. Agriculture: With irrigation wheat, barley, olives, figs, nuts, and grapes can be cultivated in the steppe regions. Sheep, goats, donkeys, and camels can be raised even in the desert regions. Natural Resources: (Scattered throughout the region) North Africa- Iron Ore & Phosphates Israel- Salt Turkey- chromium and molybdenum CSI 07 Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Iraq, Iran- Oil

Iraq – Ancient Land of Mesopotamia Four Geographic Regions: 1) Mountains in Northeast and Eastern sections. This area has good pastures and a few fertile plateaus. 2) Central Desert Area doted with few oasis. 3) Upper Plains – dry grassland savannah 4) Lower Plains -Irrigated valley between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. Iran – Once known as Persia Geography: High plateau much of it desert Climate: dry continental Natural Resources: coal, iron, copper, lead, borax, manganese, nickel, cobalt, and oil. 1) Agriculture: tobacco, cotton, corn, rice all grown on small farms. CSI 07

Essential Questions • Where and how did ancient civilizations begin? • In what ways are ancient civilizations similar? In what ways are they different? • What impact did cultural beliefs have on the formation of religions? • How did religion and philosophical thinking affect the development of civilization? • For what reasons do religious and philosophical differences cause conflict among cultures? • How did the agricultural revolution change civilizations? • What economic systems existed in ancient civilization? • What governmental structures emerged in ancient civilizations? • What evidence of culture clashes exist today? • What constitutes a civilization?
Social Studies Block # ___ Name ____________ Mr. Ingraham & Ms. Holmes Date ______ RIVER CIVILIZATIONS Table of Contents

This is how Mullen students roll…. We are always on time to class We come prepared to learn. We always allow other students to learn. We respect the personal space of others.

The Fertile Crescent Song Let me tell you of a civilization Sung to the tune of “The Brady Bunch” Sumer, Sumer was its name It was between the Tigris and Euphrates, but it was not alone. There came along a mighty king, Sargon, the Akkadian was the name. He united all who feared him. You join or you’re insane. Still later came King Hammurabi With his mighty long code of laws. Even later came the Assyrian Army Led by Sennacherib the “destroyer”, Who crushed and killed And stole until the Persians came along and conquered him. CSI 07
Prime Meridian 40 O N 23 30’ N Tropic of Cancer O 20 N Equator 20 S CSI 07 23 30’ S Tropic of Capricorn
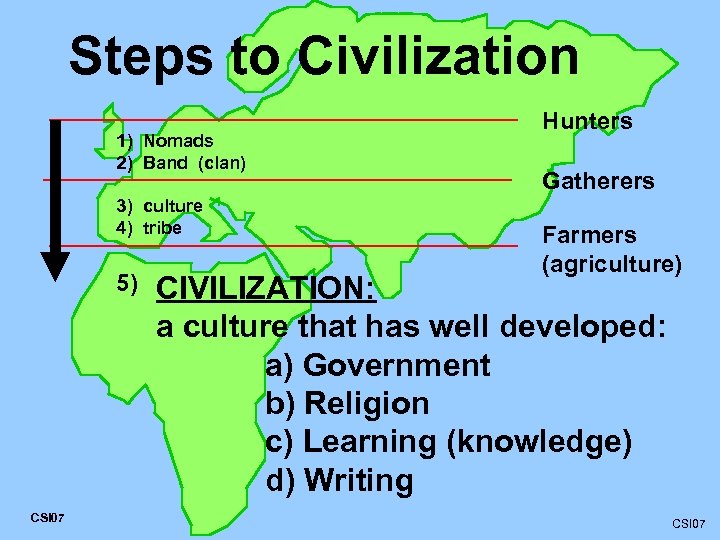
Steps to Civilization 1) Nomads 2) Band (clan) 3) culture 4) tribe 5) CSI 07 Hunters Gatherers Farmers (agriculture) CIVILIZATION: a culture that has well developed: a) Government b) Religion c) Learning (knowledge) d) Writing CSI 07

ian sp Black Sea Tig ris gr os e Me A h * Rive sopssur * r ota mia E Je r us ale m Mediterranean Sea up hra tes Riv er * Syrian Desert a Za Se Taurus Mountains Ninev Ca Asia M ou n nt ai ns lo aby B * Ur Persian Gulf Africa CSI 07

Mesopotamian Vocabulary • Civilization – a culture with well developed forms of government, religion, writing, and learning. • Technology- the use of tools and skills to make a product or achieve a goal. • Ziggurat- a huge mud-brick temple in each city-state. • Government- an organized system that groups use to make laws and decisions. • City-state- a city or village and the farm lands around it with its own leaders and government. • Monarchy- a government which has one person with complete right to rule in peacetime and in war. • Authority- right to rule. • Surplus- extra supply. • Merchant- a person who buys and sells goods for a living • Social class- groups within a civilization with different levels of importance. • Scribe- a person who knows how to read and write. . • Innovation- new ways of doing things.

Mesopotamian Vocabulary #2 • Conquer – to take over the land of others. • Empire- a land of many conquered people and places governed by one ruler. • Emperor- the ruler of an empire. • Taxation- the support of a government where people were required to pay taxes in crops or other goods or services they produced. • Code of Hammurabi- a collection of 282 laws that dealt with almost every aspect of Mesopotamian life. • Equal Justice- fair treatment under the law within each social class. • Polytheism – The belief in many supreme beings or gods • Monotheism- the belief in one supreme being or god. • Covenant- an agreement. • Ten Commandments- a set of laws for responsible behavior. • Judaism the religion of the Jewish people. • Torah- The first five books of the Bible of the Israelites. • Colony- a settlement separated from, but under the control of, a home country. • Cultural diffusion- the spreading of new ideas to other places. • Barter- the exchange of one good or service for another. • Money economy- an economic system based on the use of money rather than on barter.

Mesopotamia A. The Fertile Crescent- the land between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. 1) Villages became cities and societies became more complex 2) Cultures form Civilizations- society with developed under one Government, Religious belief, writing system, and Learning A/F. New Inventions & Innovations: canals, dikes, wheel, cart, domestication of animals, igu (acre), cargo ships with sails, & cuneiform E. Changing Economy 1) About 3000 B. C. Sumerian city-states had huge populations. 2) Ur – had 30, 000 people. 3) Successful agriculture = surplus, or extra supply (of food). Therefore: a) not everyone had to grow or find food. b) This allowed a division of labor. Besides farmers, there were managers, craftworkers, and merchants. 4) Merchants – people who bought and sold goods for a living. They traded surplus wheat, barley, and copper tools for wood, salt, precious stones, & raw copper.

F. Divisions in Society 1) Social Classes – groups with different levels of importance King Nobles – Priests & Leaders Middle Class Merchants, Craftworkers, Managers, carpenters, potters, bricklayers, & scribes 2) Scribe, or a person who could write, kept records, wrote letters for others, copied songs, & stories. Lowest Class Laborers, Unskilled workers, and Slaves 3) Men owned most of the property & held positions of leadership. A. Causes and Effects of Conflict. 1) Because the city-states grew in size and population, agricultural societies wage war to protect farmland & water rights. 2) Because the Tigris & Euphrates river valley is flat with no natural boundaries, city-states put up pillars. 3) Because powerful city-states destroy or move the pillars, more wars are fought. 4) Because more wars are being fought, new technology or better weapons are needed. (Example: War Chariot – two wheel cart pulled by horses. )

B. Sargon the Conqueror War & Peace in the Fertile Crescent 1) The Warrior Sargon from the city-state of Kish is the first to conquer, or take over, the land of others. 2) He established a vast empire, or a conquered land of many peoples and places governed by one ruler, or emperor. 3) Sargon a) built a capital city called Akkad and ruled for 55 years. b) maintained a standing army. c) appointed loyal nobles as governors to maintain control of all 12 city-states C. Hammurabi the Lawgiver 1) Hammurabi becomes king of the city-state of Babylon. 2) He promoted trade by building dikes and canals and established taxation, or people supporting government by payment in crops or other goods. 3) Hammurabi’s most important contribution was a collection of laws, given to him by the sun god Shamash called the Code of Hammurabi (282 laws) a) “The code said that whoever caused an injury should be punished by being given that same injury”. b) Equal Justice, or fair treatment was limited to equality within each social class.

Religious & Philosophical Thinking of Mesopotamia Code of Hammurabi : 282 laws providing equal justice. Teaches: An eye for an eye and a tooth for a tooth. Ten Commandments: a set of laws given to Moses for responsible behavior for Judaism. Teaches: To obey one god and how to live justly and keep families strong. Polytheism of the Ancient Mesopotamians: Many gods of nature Teaches: If bad things happen the gods are angry; if good thing happen they aren’t. Judaism: The religion of the Jewish people based on the belief of the one god, Yahweh. Teaches: God’s good qualities must be imitated by his people. Islam: The religion of the Muslims based on the belief of the one god, Allah. Teaches: Muslim must submit to god’s will and follow the Qur’an and Muhammad’s example. Christianity: a religion based to the life and teaching of Jesus Christ, a Jewish Rabi. Teaches: To love your neighbor as yourself. CSI 07

Early Egypt Song Sung to “Mary has a little Lamb” The Nile River gives Egypt life Water for the crops And fertile silt King Narmer unites us all Upper and lower Egypt Our pharaoh is the son of Ra Pharaoh Zoser asked Imhotep To build a pyramid For his tomb and decorate it with Hieroglyphics and gold. Amenemhet becomes the pharaoh He conquers Nubia and Kush is tamed. Merchants and craftworkers Form the middle class. Pharaoh Thutmose crushed the Hyksos. Egypt extends to the Fertile Crescent But Amenhotep and Nefertiti Want all to worship the one god, Aton, But the boy King Tut changes that (and that’s a chapter three fact. ) By Mr. Ingraham
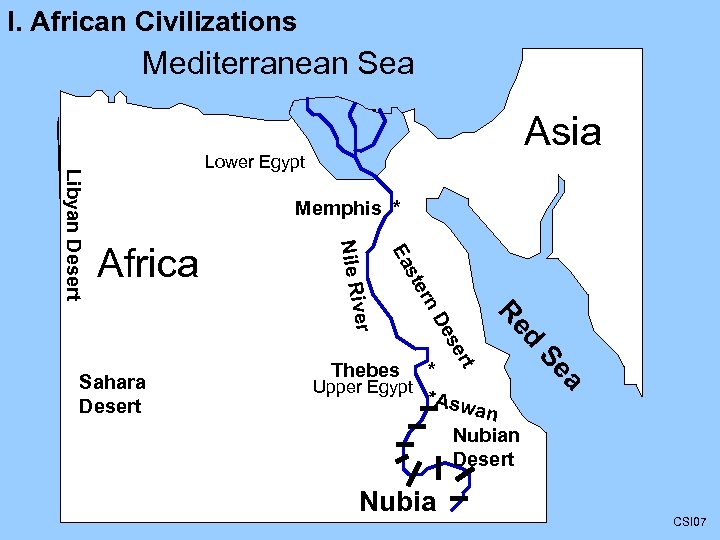
I. African Civilizations Mediterranean Sea Asia Memphis * d * Upper Egypt *Asw a a Se Thebes Re Sahara Desert rt se De ver rn ste Ea Africa Nile Ri Libyan Desert Lower Egypt n Nubian Desert Nubia CSI 07

Egyptian Vocabulary • desertification – Any change of fertile land into desert, whether caused by climate or human actions. . • silt- fine bits of rock and soil. • Irrigate – to supply land with water by artificial means. • predict- to tell ahead of time. • dynasty- a series of rulers from the same family. • pharaoh -an Egyptian King. • edicts – the commands or directions of one. in authority. • Hieroglyphics –an Egyptian picture writing system • papyrus- a paper like material. • pyramid- a tomb for a dead Egyptian ruler or noble. • mummy a dead body which has been preserved. • peasants people who farmed the land. • obelisk- an ancient monument consisting of a single pillar of stone. • annex- to take over. • independence –complete freedom. • Trading network- a group of buyers and sellers working together.
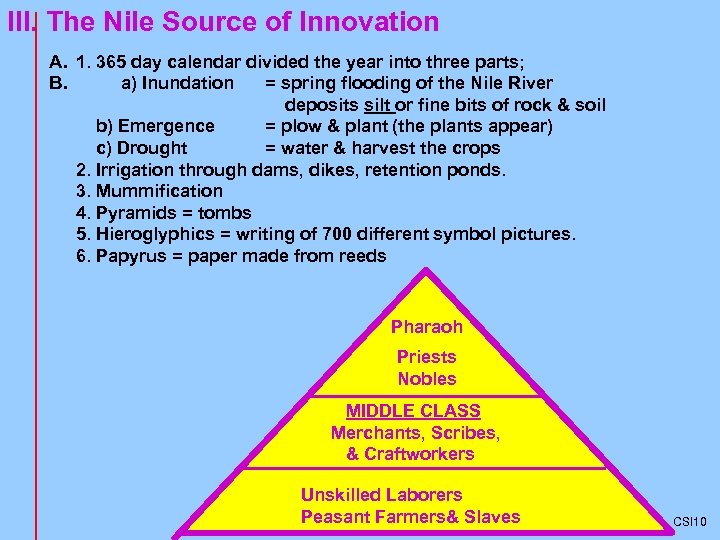
III. The Nile Source of Innovation A. 1. 365 day calendar divided the year into three parts; B. a) Inundation = spring flooding of the Nile River deposits silt or fine bits of rock & soil b) Emergence = plow & plant (the plants appear) c) Drought = water & harvest the crops 2. Irrigation through dams, dikes, retention ponds. 3. Mummification 4. Pyramids = tombs 5. Hieroglyphics = writing of 700 different symbol pictures. 6. Papyrus = paper made from reeds Pharaoh Priests Nobles MIDDLE CLASS Merchants, Scribes, & Craftworkers Unskilled Laborers Peasant Farmers& Slaves CSI 10

Religious & Philosophical Thinking of Egypt 1. Religion: Polytheism: Like many ancient peoples the Egyptians used stories about their gods to explain nature. For example: a) Amon-Ra was the sun god who was born each day and died each night. b) Osiris taught the Egyptians farming. c) Horus, the son of Osiris, ruled the sky. d) Isis, was the wife of Horus. 2. The Egyptians also believed their pharaoh, or king, was a god in human form. 3. Change during the New Kingdom 1686 - 1085 Pharaoh Amenhotep & Queen Nefertiti worship one god, Aton – monotheism King Tutankhamen (Tut) returns to polytheism.
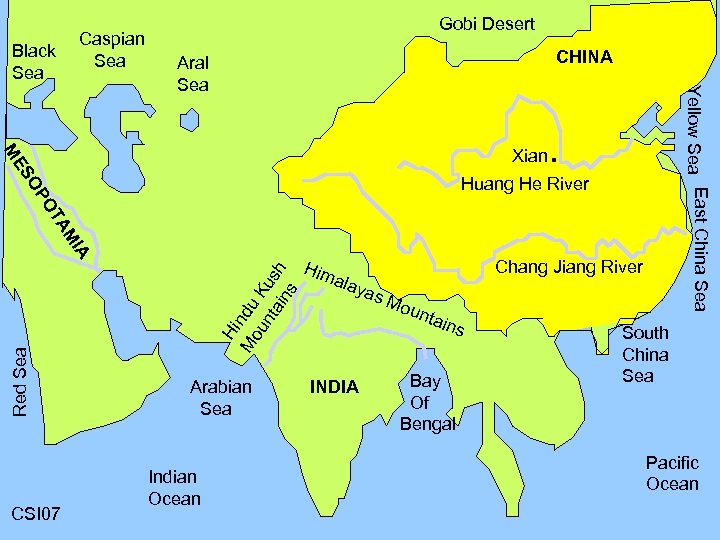
Caspian Sea Black Sea Gobi Desert CHINA ME Xian SO Yellow Sea East China Sea Aral Sea . MI TA PO Huang He River Hi M ndu ou K nt us ain h s Red Sea A CSI 07 Arabian Sea Indian Ocean Him Chang Jiang River alay a s. M oun tain s INDIA Bay Of Bengal South China Sea Pacific Ocean

China Song (Chapter 5) The Zhou claimed the mandate the peasant-farmers can’t wait to use their iron weapons to seal the Shang dynasty’s fate. Roads, … Dams, … Canals! Sung to “The Adams Family” Confucius says a guide for society is just like anyone’s family. No matter what you happen to be everyone has responsibility Courtesy, … Kindness, … Charity! The Legalism of the Qin Shi Huangdi says everyone should fear me. My great wall shows my authority built upon the peasant’s misery. Tears, … Cruelty, … Punishment! CSI 07

China Song (Continued) Sung to “The Adams Family” The Han Gao Zu said he knew to be respected & keep the people true. No harsh law or treatment cruel and all the people will follow you. Trade, … Exports, … Profits! The Daoism is taught by Emperor Wu Di to accept whatever life gives to thee. Now cause and effect is history and trade brings new technology. Wheelbarrow, … seismograph, … Paper! Ancient China always tried to strive to keep the peasants working and alive and every way each dynasty tried is all contained in chapter five!!!! CSI 07

Vocabulary of China • legends – stories handed down from earlier times. • mandate- or order to rule. • Mandate of Heaven- the right of a Chinese leader to rule given to him by the gods. • ancestors- dead relatives further back than grandparents. • oracles –a person who gives wise advise. • pictographs – drawings that were combined to make thousands of Chinese words. • heritage –a set of ideas that has been passed down from one generation to another. • militia- a group made of volunteer soldiers. • virtues- good qualities. • Public works –structures built by the government for everyone’s use. • philosopher –a person who studies the meaning of life. • responsibilities- a person’s duties. • Confucianism- the ideas and teaching of the philosopher Confucius.

Vocabulary of China #2 • Legalism – the idea that people obey their rulers out of fear and not out of respect. • standardization- the making of all things of a certain type alike. • bureaucracy –a network of appointed government officials. • Civil war- when groups of people from the same place or country fight one another. • ambassadors –a person who represents a government. • Civil Service – the part of a bureaucracy that oversees the day - to-day business of running a government. • Daoism –the idea that the key to long life and happiness is to accept life as it is. . • import- to bring in goods for sale. • export- to send out goods to be sold in other places. • caravan –a group of traders traveling with goods to be sold. • profits –money gained over the price of goods sold. • Silk Road- the trade route that stretched 5, 000 miles from China to the Mediterranean Sea.
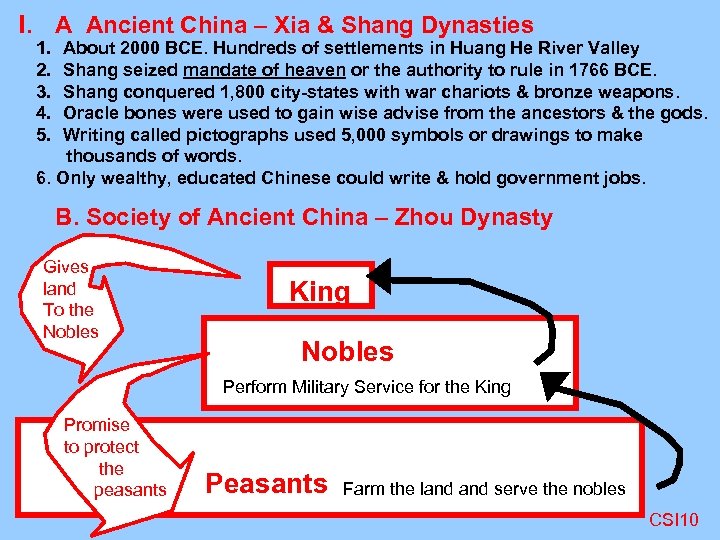
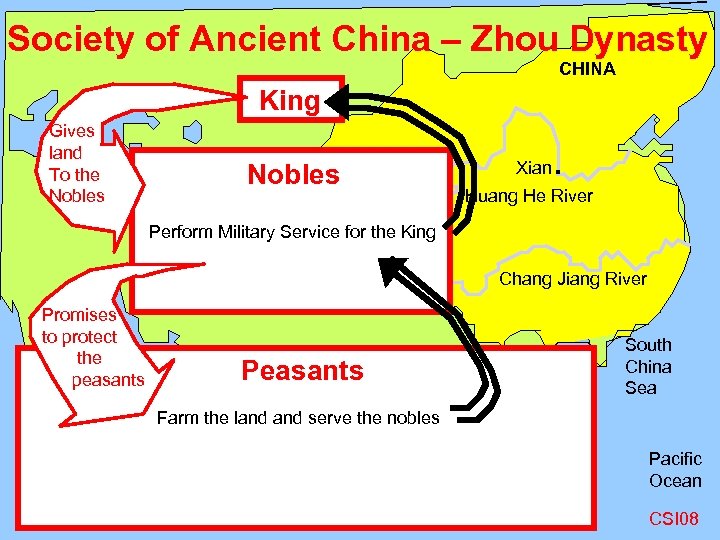
I. A Ancient China – Xia & Shang Dynasties 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. About 2000 BCE. Hundreds of settlements in Huang He River Valley Shang seized mandate of heaven or the authority to rule in 1766 BCE. Shang conquered 1, 800 city-states with war chariots & bronze weapons. Oracle bones were used to gain wise advise from the ancestors & the gods. Writing called pictographs used 5, 000 symbols or drawings to make thousands of words. 6. Only wealthy, educated Chinese could write & hold government jobs. B. Society of Ancient China – Zhou Dynasty Gives land To the Nobles King Nobles Perform Military Service for the King Promise to protect the peasants Peasants Farm the land serve the nobles CSI 10

C. Religious & Philosophical Thinking of China 1. Legalism : used by Qin Shi Huangdi as a basis for the government of his dynasty. Teaches: People obey their rulers out of fear of punishment and not respect. Harsh treatment is the only way to bring peace and wealth to China 2. Confucianism: Kung Fu Zi (Confucius) There are five virtues: charity, kindness, hardwork, good faith, and courtesy. Teaches: A good society is like a family where all members know their responsibilities. 3. Daoism: used by Emperor Wu Di with the ideas of Confucianism. Teaches: the key to long life and happiness is to accept life as it is. D. The Han Dynasty’s Golden Age & The Silk Road 1. Peace brought new technology & inventions: wheelbarrow, seismograph, paper, printing, crossbow, gunpowder, fireworks, crossbow 2. Caravans traded with other “civilized” people. a) exported silk, apricots, iron, & bronze goods b) imported gold, ivory, wool, linen, grapevines, & horses
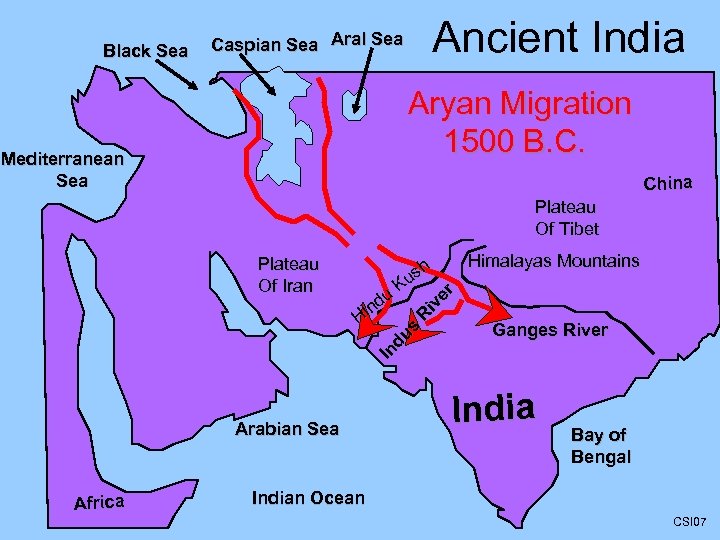
Black Sea Ancient India Caspian Sea Aral Sea Aryan Migration 1500 B. C. Mediterranean Sea China Plateau Of Tibet Arabian Sea Africa Himalayas Mountains R iv er u nd Hi h us K In du s Plateau Of Iran Ganges River India Bay of Bengal Indian Ocean CSI 07

India’s Chapter 6 Song The Aryans migrate South Through the mountain pass of Hindu Kush. Into the Indus Valley Using their horses to fight for land. Believing in Hinduism’s reincarnation means rebirth. The next life’s social position show your worth, But now your caste is unchanging. So don’t associate with the low one. Being an Untouchable is no fun!!!! Unless you’re a believer in Buddha and seek love, truth, and knowledge. What’s it to ya? Unselfish behavior all the time. (Bomb Ba Bomba Chorus) “Now I know these chapter 6 facts, I’ll be fine”. By Mr. Ingraham Sung to “Meet the Flintstones”

India’s Chapter 6 (Song verse 2) The Rajahs rule the Indian city-states Until a young Chandragupta Maurya, Like the Qin Shi Huangdi the young Chandragupta’s known for cruelty. Father and son rule with a firm hand, but grandson Asoka discovers wars don’t make the man. Non-violence and no caste system Becomes his new plan. The Gupta unites India once again. India’s golden age soon begins. Arabic numerals make math now base 10. Do you believe in Buddha? Seeking love, truth, and knowledge. What’s it to ya? Unselfish behavior all the time. (Bomb Ba Bomba Chorus) “Now I know these chapter 6 facts, I’ll be fine”. By Mr. Ingraham

Vocabulary of India • subcontinent – A large land area isolated from the rest of a continent • inscription- a written message. • Aryans- the earliest warriors and herders who immigrated from central Asia to India. • Sanskrit-the Aryan language. • Vedas –the Aryan holy books. • reincarnation – the belief that the soul lives on after death and returns to life in a new body. • Hinduism –a religion that believes in three gods: Brahma, the creator; Vishnu, the preserver; and Shiva, the destroyer. • caste- an unchanging group within a society. • untouchables- the people thought to be impure and below all of Indian castes. • Buddhism – the religion based on the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama.

The Caste System & India Society 1. The Vedas, the belief in reincarnation, and the caste system gave order to Aryan society. 2. A caste is an unchanging group within a society. A person lives, works, marries within the caste they are born into. 3. The Caste System is like a human body. SHIVA – The Destroyer a) The Brahmans are the head ( priest & scholars) b) The Kshatriyas are the arms (rulers & soldiers) c) The Vaisyas are the legs (farmers & merchants) d) The Sudras are the feet (laborers, craftworkers, & servants) 4. Below all castes were the untouchables. They were thought to be impure and had to avoid all contact with the rest of society. These people did all the unpleasant jobs.

Vocabulary of India #2 • • rajahs – Indian princes who ruled over large city-states assassination – murder for a political reason. Turning point – a time of important change. missionaries – religious teachers who help spread ideas to other areas. • Arabic numerals – a base ten number system using 1 -9 and zero. • inoculation – giving people a mild form of a disease to prevent them from getting sick with a more serious form. Persian Bonus Vocabulary • Cavalry – soldiers who rode horses and camels to make swift attacks. • Tribute – yearly payments to a king or an emperor. • Couriers – pony-express-like riders for delivering messages. • Prophet – a person who others believe speaks or writes with a divine message from god. • Zoroastrianism – the belief in two gods: Ahura Mazda, the god of truth and Ahriman, the evil enemy.

Religious & Philosophical Thinking of India Hinduism: Ancient Aryan Religion which worships three main gods: Brahma, the creator; Vishnu, the preserver; and Shiva, the destroyer. Teaches: People are born into an unchanging group within society. They can only associate with members of the same caste. If they live a good life they will be reincarnated, or come to life in a new body, in a higher caste. Buddhism: Siddhartha Gautama – reaction to the Caste System and harsh treatment under Hinduism. Teaches: People should seek love, truth, the joy of knowledge, and a calm mind.
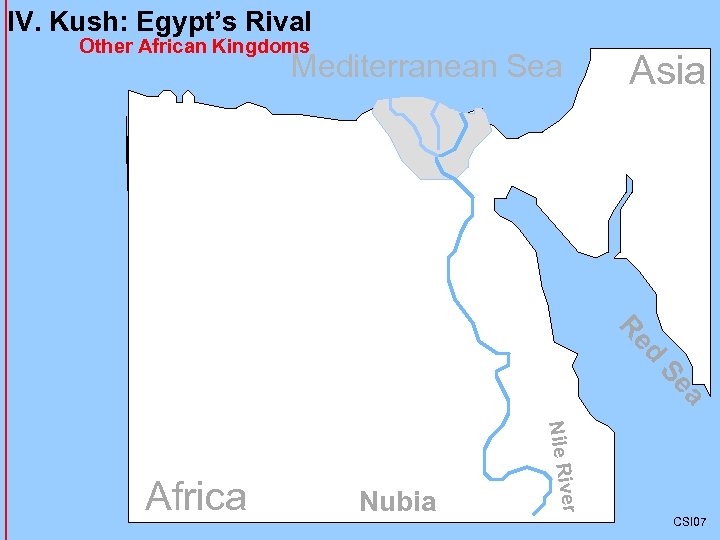
IV. Kush: Egypt’s Rival Other African Kingdoms Mediterranean Sea Asia d Re a Se er Nubia Nile Riv Africa CSI 07

IV. Kush: Egypt’s Rival A. Early People of Nubia 1. Nubia extends along Egypt’s southern border into modern Sudan. 2. The people of Nubia lived like the Egyptians. a) About 6, 000 BC. They lived in clans as herders and farmers. b) The Nubians worshipped Egyptian gods. 3. About 2000 BC. they developed into a civilization and built canals. a) They traded gold, hardwoods, animal tusks, and huge granite blocks for Egyptians goods. b) These blocks were used to build obelisks, or ancient towering monuments made of a single stone of granite. 4. During the Egyptian Middle Kingdom the pharaoh moved to annex, or take over, northern Nubia and make it part of Egypt. B. Kush 1. When the Hyksos took over upper Egypt, Nubia gained its independence, or complete freedom, from Egypt. 2. Kerma becomes the capital of the Kushite government. 3. It also becomes a trading center for central and southern Africa. a) To the North they traded for Egyptians goods. b) To the South they traded for gold, salt, elephants, rhinoceros horns, spices, and slaves. Nubia CSI 07 c) Kermas’s busy markets made the government wealthy. Mediterranean Sea Asia d Re a Se er Nile Riv Africa
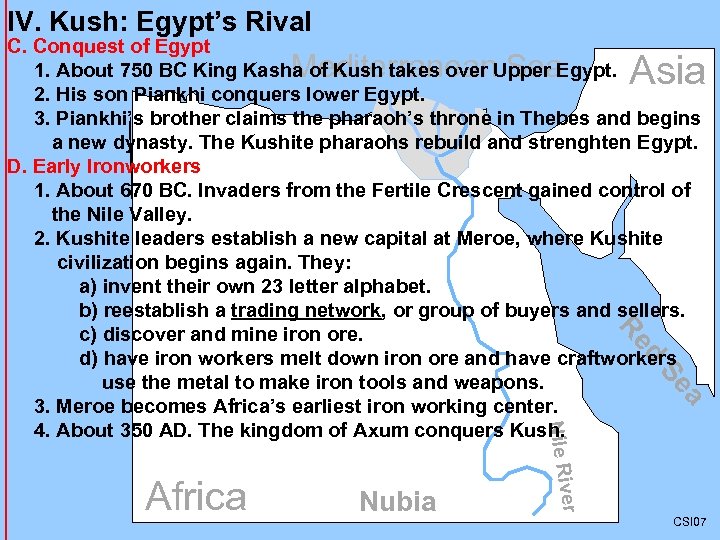
IV. Kush: Egypt’s Rival C. Conquest of Egypt 1. About 750 BC King Kasha of Kush takes over Upper Egypt. 2. His son Piankhi conquers lower Egypt. 3. Piankhi’s brother claims the pharaoh’s throne in Thebes and begins a new dynasty. The Kushite pharaohs rebuild and strenghten Egypt. D. Early Ironworkers 1. About 670 BC. Invaders from the Fertile Crescent gained control of the Nile Valley. 2. Kushite leaders establish a new capital at Meroe, where Kushite civilization begins again. They: a) invent their own 23 letter alphabet. b) reestablish a trading network, or group of buyers and sellers. c) discover and mine iron ore. d) have iron workers melt down iron ore and have craftworkers use the metal to make iron tools and weapons. 3. Meroe becomes Africa’s earliest iron working center. 4. About 350 AD. The kingdom of Axum conquers Kush. Mediterranean Sea Asia d Re a Se er Nubia Nile Riv Africa CSI 07

Religious development of the Middle East Abram breaks with the religious thinking of his neighbors and begins worshipping one supreme god (Monotheism). He changes his name to Abraham, which means “father of many nations”. a) Abraham’s son Isaac is the father of the Jewish people. 1) Judaism: The religion of the Jewish people based on the belief of the one god, Yahweh. Teaches: God’s good qualities must be imitated by his people. 2) Christianity: a religion based to the life and teaching of Jesus Christ, a Jewish Rabi. Teaches: To love your neighbor as yourself. b) Abraham’s son Ishmael is the father of the Arab people. Muhammad, an Arab, is the founder of Islam. Muslims are his followers. Islam: The religion of the Muslims based on the belief of the one god, Allah. Teaches: Muslim must submit to god’s will and follow their holy book the Qur’an and Muhammad’s example. The religious successors to Muhammad are called caliphs, but whom to follow caused divisions. • Shiite Muslims stayed loyal to the descendants of the fourth caliph, Ali’s dynasty • Sunni Muslims accepted the changing dynasties of Muhammad’s successors.
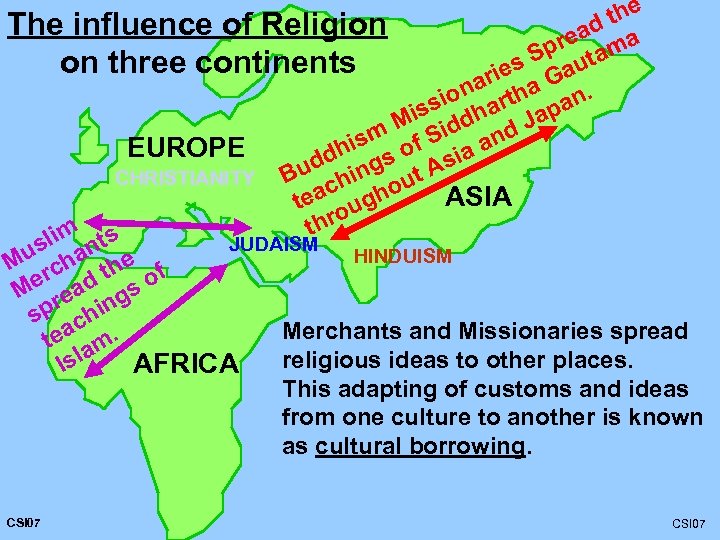
the The influence of Religion ead ma r Sp uta on three continents ies Ga r na tha n. a sio har is d ap M m f Sid and J EUROPE his s o sia dd ng A CHRISTIANITY Bu chi ut o ASIA tea ough thr m ts JUDAISM sli an u h HINDUISM e f M rc h e ad t s o M re p hing s c Merchants and Missionaries spread tea am. religious ideas to other places. AFRICA Isl This adapting of customs and ideas from one culture to another is known as cultural borrowing. CSI 07

Chinese Silk Road TRADE By 106 B. C. E. the first camel caravan headed west from China with a load of Silk. No one knew the secrets of making Silk, which gave the Chinese a monopoly. They made huge profits in gold, ivory, wool, linen, grapevines, And horses. African Salt Trade By 700 C. E. an African tribe, the Soninkes, had taken over much of the West African grasslands. To the south they traded with another tribe the Wangaras for gold. Then they traded with Muslim merchants the gold for salt. Salt was important to season and preserve food. Some of the salt they traded back to the Wangaras for more gold. Other European goods such as paper, woven cloth, and perfumes were also traded. With this trading network the Soninkes made a profit at both ends of the trading cycle and they grew rich and powerful.
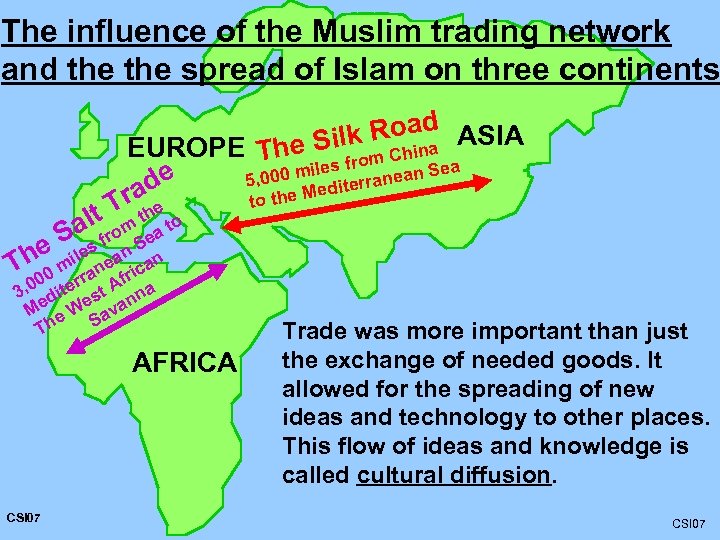
The influence of the Muslim trading network and the spread of Islam on three continents Road ASIA ina he Silk EUROPE T h from C Sea iles e 5, 000 m diterranean ad the Me r lt T the to Sas from. Sea he mile neanican T 00 rra fr 3, 0 dite st A nna e Me e W ava S Th AFRICA CSI 07 to Trade was more important than just the exchange of needed goods. It allowed for the spreading of new ideas and technology to other places. This flow of ideas and knowledge is called cultural diffusion. CSI 07
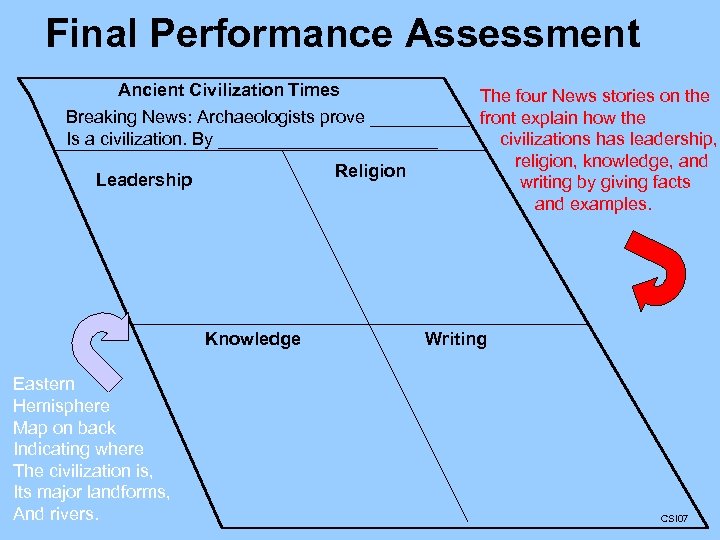
Final Performance Assessment Ancient Civilization Times The four News stories on the Breaking News: Archaeologists prove _____ front explain how the Is a civilization. By ___________ civilizations has leadership, religion, knowledge, and Religion Leadership writing by giving facts and examples. Knowledge Eastern Hemisphere Map on back Indicating where The civilization is, Its major landforms, And rivers. Writing CSI 07

Performance Assessment A News Presentation to the class Your presentation will take the form of a TV news cast. This is what is needed: 1) A large map locating your presentation’s civilization. 2) An explanation of your civilization’s government proving it had leadership. 3) An explanation of your civilization’s beliefs proving it had religion. 4) An explanation of your civilization’s innovations and inventions proving it had knowledge. 5) An explanation and description of your civilization’s writing system. Remember: Your groups 5 questions must be covered in your presentation.
How to set up your notebook for research Leadership Religion Knowledge (Learning) Writing
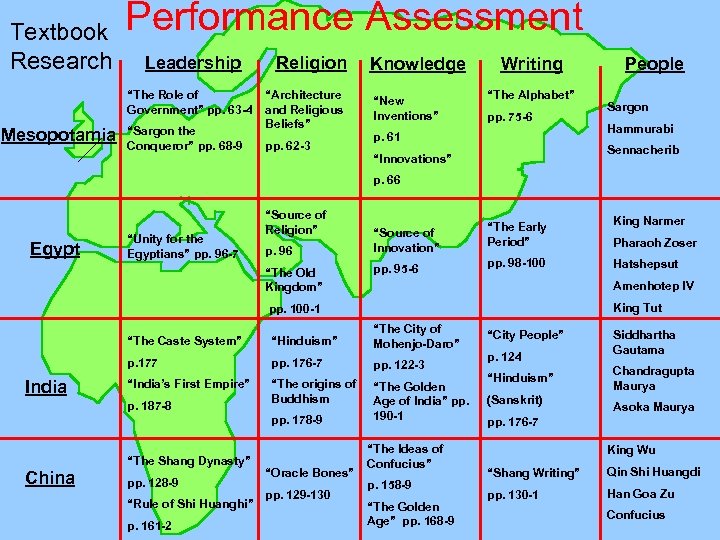
Textbook Research Performance Assessment Leadership “The Role of Government” pp. 63 -4 Mesopotamia “Sargon the Conqueror” pp. 68 -9 Religion “Architecture and Religious Beliefs” pp. 62 -3 Knowledge “New Inventions” Writing “The Alphabet” pp. 75 -6 p. 61 People Sargon Hammurabi Sennacherib “Innovations” p. 66 Egypt “Unity for the Egyptians” pp. 96 -7 “Source of Religion” p. 96 “The Old Kingdom” “Source of Innovation” “The Early Period” King Narmer pp. 95 -6 pp. 98 -100 Hatshepsut Amenhotep IV King Tut pp. 100 -1 “The Caste System” “Hinduism” “The City of Mohenjo-Daro” p. 177 India pp. 176 -7 pp. 122 -3 “India’s First Empire” p. 187 -8 “The origins of Buddhism pp. 178 -9 “The Shang Dynasty” China pp. 128 -9 “Rule of Shi Huanghi” p. 161 -2 “Oracle Bones” pp. 129 -130 Pharaoh Zoser “The Golden Age of India” pp. 190 -1 “The Ideas of Confucius” p. 158 -9 “The Golden Age” pp. 168 -9 “City People” p. 124 “Hinduism” (Sanskrit) Siddhartha Gautama Chandragupta Maurya Asoka Maurya pp. 176 -7 King Wu “Shang Writing” Qin Shi Huangdi pp. 130 -1 Han Goa Zu Confucius

Synergy The product of a group is greater than any individual of that group. . • 1) The Leader reads his/her “Leadership” notes while the other group members copy any items mentioned they don’t have. • 2) Another member of the group then reads his/her “Leadership” notes and the other group members copy any items they don’t have. • 3) Rotation continues until all members have read their “Leadership” notes.
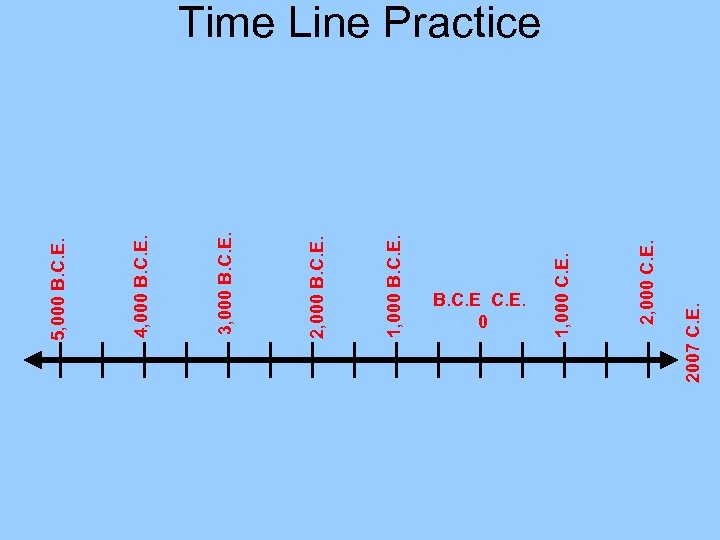
1, 000 B. C. E. 2, 000 B. C. E. 3, 000 B. C. E. 4, 000 B. C. E. 5, 000 B. C. E. 0 2007 C. E. 2, 000 C. E. 1, 000 C. E. Time Line Practice

Time Line Practice Place the following on this timeline: 2007 C. E. 2, 000 C. E. B. C. E. 0 1, 000 C. E. 1, 000 B. C. E. 2, 000 B. C. E. 3, 000 B. C. E. 4, 000 B. C. E. 5, 000 B. C. E. 1) 5, 100 years ago King Narmer unites Upper and Lower Egypt 2) 4, 650 years ago the Egyptians built the first pyramid. 3) 4, 500 years ago cities rise in the Indus Valley. 4) 4, 300 years ago merchants trade between the Indus Valley and Mesopotamia. 5) 3, 800 years ago the Shang Dynasty gains control of China. 6) 3, 465 years ago the Egyptian Empire expands to its largest size. 7) 2, 750 years ago Kush conquers upper Egypt. Hint: Remember it is now 2007 C. E. , but why not use 2, 000?
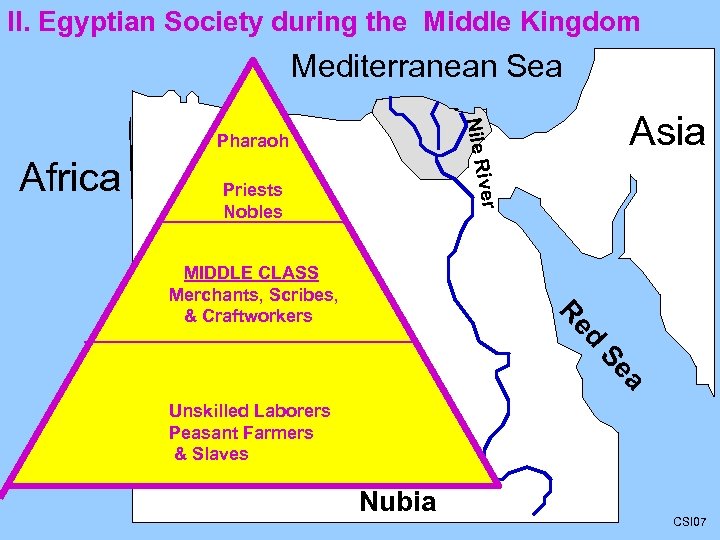
II. Egyptian Society during the Middle Kingdom Mediterranean Sea ver Africa Asia Nile Ri Pharaoh Priests Nobles d Re MIDDLE CLASS Merchants, Scribes, & Craftworkers a Se Unskilled Laborers Peasant Farmers & Slaves Nubia CSI 07
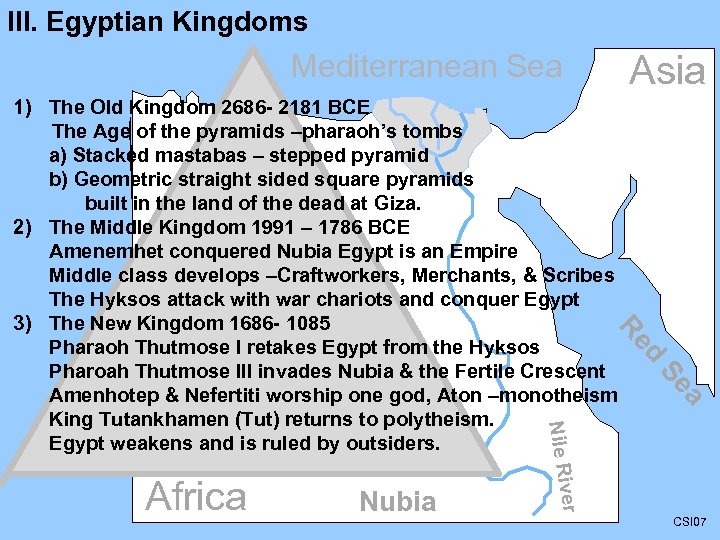
III. Egyptian Kingdoms Mediterranean Sea Asia a Se er Nubia Nile Riv Africa d Re 1) The Old Kingdom 2686 - 2181 BCE The Age of the pyramids –pharaoh’s tombs a) Stacked mastabas – stepped pyramid b) Geometric straight sided square pyramids built in the land of the dead at Giza. 2) The Middle Kingdom 1991 – 1786 BCE Amenemhet conquered Nubia Egypt is an Empire Middle class develops –Craftworkers, Merchants, & Scribes The Hyksos attack with war chariots and conquer Egypt 3) The New Kingdom 1686 - 1085 Pharaoh Thutmose I retakes Egypt from the Hyksos Pharoah Thutmose III invades Nubia & the Fertile Crescent Amenhotep & Nefertiti worship one god, Aton –monotheism King Tutankhamen (Tut) returns to polytheism. Egypt weakens and is ruled by outsiders. CSI 07
Society of Ancient China – Zhou Dynasty CHINA King Gives land To the Nobles Xian . Huang He River Perform Military Service for the King Chang Jiang River Promises to protect the peasants Peasants South China Sea Farm the land serve the nobles Pacific Ocean CSI 08

Bonus Question 5 Points What is the belief in two gods: Ahura Mazda, the god of truth and Ahriman, the evil enemy called. w) Hinduism x) Buddhism y) Judaism z) Zoroastrianism
7de3c90d1bf9ab49e81cc171f04e2e13.ppt