
RISK

Risk can be involved in any human activity which is connected with great number of factors that determinate positive or negative outcome.

1. Risk is presented in the form of possible failure, risk, financial and other losses that may occur as a result of implementing the chosen solution. 2. Risk is understood as a "way of action in unclear environment" or as "situational characteristics of its outcomes and possible adverse effects in case of failure. " Thus risk is understood as a loss, or “act for good luck. " 3. Risk is defined as a positive opportunity (chance) and negative (loss, damage) in the process of rejection of the expected values
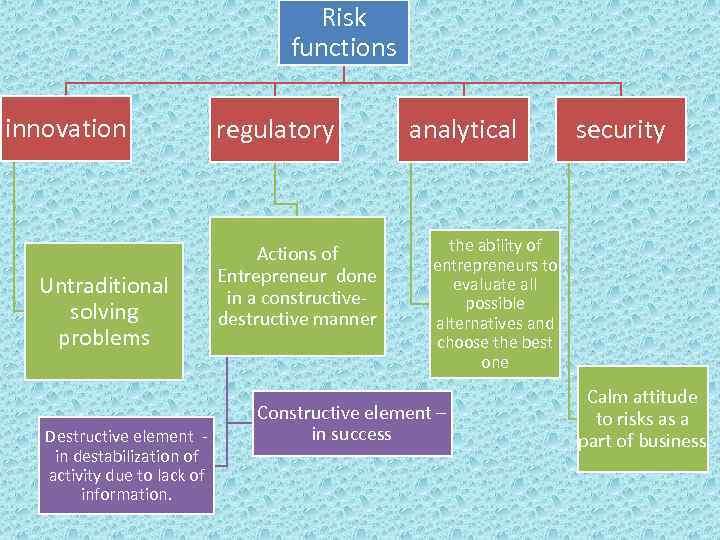
Risk functions innovation Untraditional solving problems Destructive element in destabilization of activity due to lack of information. regulatory Actions of Entrepreneur done in a constructivedestructive manner analytical security the ability of entrepreneurs to evaluate all possible alternatives and choose the best one Constructive element – in success Calm attitude to risks as a part of business
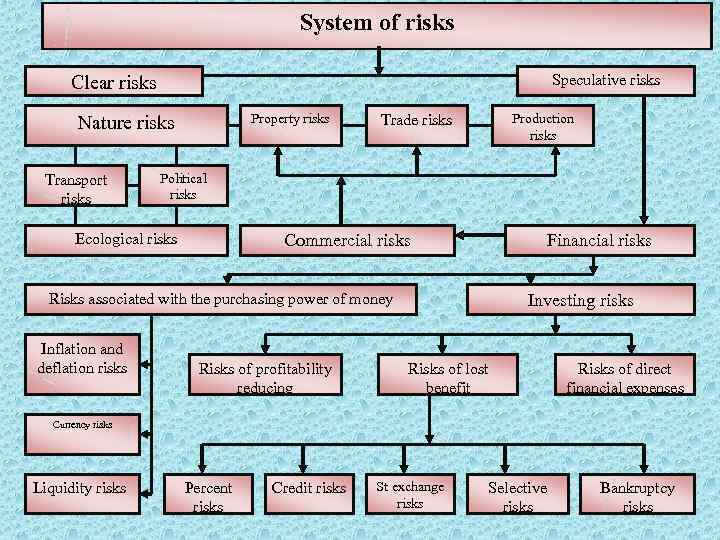
System of risks Speculative risks Clear risks Property risks Nature risks Transport risks Trade risks Political risks Ecological risks Commercial risks Risks associated with the purchasing power of money Inflation and deflation risks Production risks Risks of profitability reducing Financial risks Investing risks Risks of lost benefit Risks of direct financial expenses Currency risks Liquidity risks Percent risks Credit risks St exchange risks Selective risks Bankruptcy risks

Risk management is a set of methods and measures that allow to some extent predict the occurrence of risk events and to take measures for their reduction

Basic principles of risk to manage risky situations successfully 1. Do not risk more than you own capital. 2. Do not risk large for small. 3. You must think about the consequences of risk.
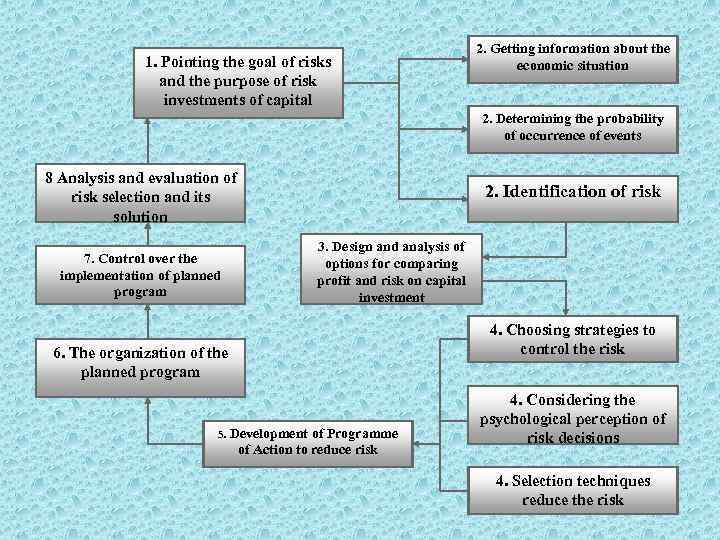
1. Pointing the goal of risks and the purpose of risk investments of capital 2. Getting information about the economic situation 2. Determining the probability of occurrence of events 8 Analysis and evaluation of risk selection and its solution 7. Control over the implementation of planned program 2. Identification of risk 3. Design and analysis of options for comparing profit and risk on capital investment 4. Choosing strategies to control the risk 6. The organization of the planned program 5. Development of Programme of Action to reduce risk 4. Considering the psychological perception of risk decisions 4. Selection techniques reduce the risk

Risk analysis involves collecting and processing data on aspects of risk, and quantitative and qualitative analysis. The main task of qualitative analysis is to obtain information about the structure and properties of the object and the risks, identifying risk factors and circumstances that lead to risky situations

Qualitative analysis - is to identify the sources, causes, risk factors, establish potential areas of risk types. Quantitative analysis - a numerical definition of certain types of risk and risk of the project

In the analysis of risk commonly used following assumptions: - Loss of one line of business does not necessarily increase the probability of loss to another, with the exception of force majeure; - Loss of risk independent from one another; - The maximum possible loss should not exceed the financial capabilities of the participant.