1e69931163423eb22308c332e3f98c90.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Risk Management § May 26, 2011 Bates Richmond, Director of Risk Management, Texas Instruments JT Fisher, CFO, Austin Industries Jeff Fritts, SVP, Willis Group Moderator: Todd Hickerson 1
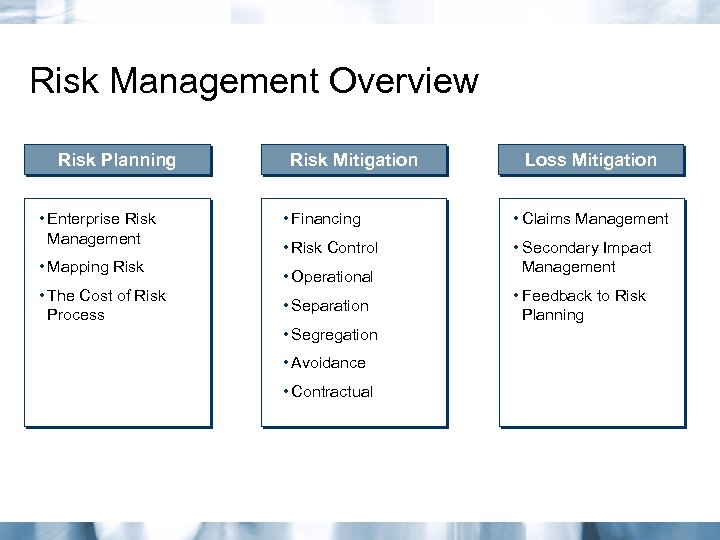
Risk Management Overview Risk Planning • Enterprise Risk Management • Mapping Risk • The Cost of Risk Process Risk Mitigation Loss Mitigation • Financing • Claims Management • Risk Control • Secondary Impact Management • Operational • Separation • Segregation • Avoidance • Contractual • Feedback to Risk Planning

Risk Management – Why? Stuff Happens!

What Is “Risk Management”? Speculative Pure § Positive and Negative Outcomes § Negative Outcomes (almost always) § Typically Uninsurable § Often Insurable § Sometimes Hedged § Not Hedged ERM § Management of risks that can take your company down
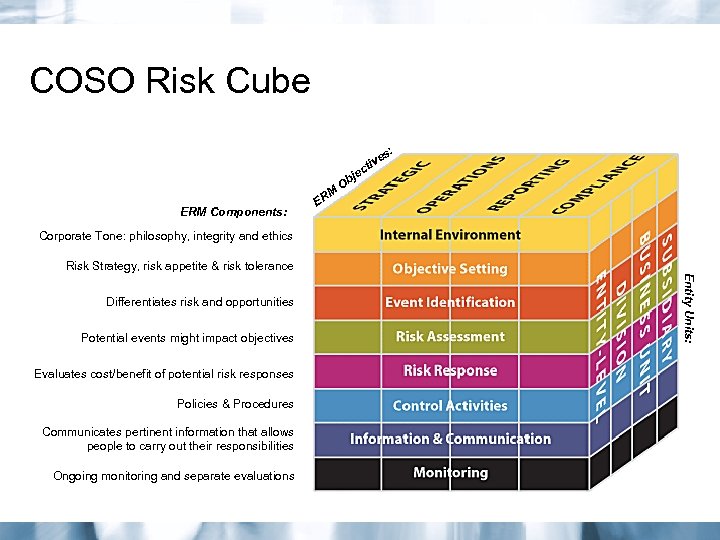
COSO Risk Cube s: e tiv ec M ERM Components: ER j Ob Corporate Tone: philosophy, integrity and ethics Risk Strategy, risk appetite & risk tolerance Potential events might impact objectives Evaluates cost/benefit of potential risk responses Policies & Procedures Communicates pertinent information that allows people to carry out their responsibilities Ongoing monitoring and separate evaluations Entity Units: Differentiates risk and opportunities

Who Does Risk Management Highly Interdisciplinary – Chief Risk Officer/Risk Management/ER Manager – Operations – Supply Chain Management – HR – Finance – Legal Across Entities – Holding Co. , Subsidiaries, Stakeholders Cultural Aspect – everyone can contribute
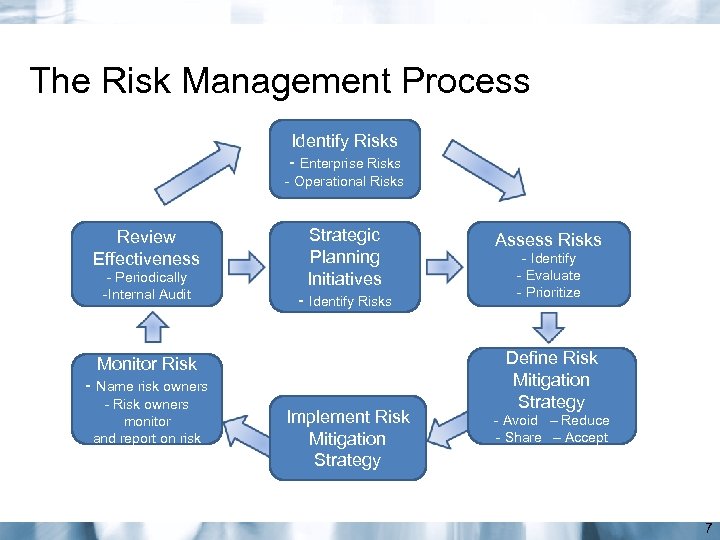
The Risk Management Process Identify Risks - Enterprise Risks - Operational Risks Review Effectiveness - Periodically -Internal Audit Strategic Planning Initiatives - Identify Risks Monitor Risk - Name risk owners - Risk owners monitor and report on risk Implement Risk Mitigation Strategy Assess Risks - Identify - Evaluate - Prioritize Define Risk Mitigation Strategy - Avoid – Reduce - Share – Accept 7

Role of US Corporate Boards 1 § Evolving legal developments make robust ERM oversight prudent – Revised NYSE listing standards require risk assessment and risk management policies – SEC endorses COSO 1992 Internal Control – Integrated Framework to manage financial risk § Rating Agencies more attuned to company’s ERM system § Increasing number of directors acknowledge they must oversee business risk as part of strategy setting role 1 The Conference Board 2006 Report R-1390 -06 -RR

Mercer’s Grouping of Causes The implied causes behind the stock drops were grouped into four different areas: hazard, financial, operational, and strategic risks. HAZARD FINANCIAL • Lawsuits – Lawsuits that are not related to accounting practices • Foreign Macro-economic – Changes in foreign interest rates and/or currency exchange rates which affects a company’s earnings • Natural Disaster – Act of God and other natural phenomena • High input commodity price – Significant increase in commodity price of a major input causing an earnings decrease • Interest rate fluctuation - Changes in interest rates negatively affect company’s earnings OPERATIONAL STRATEGIC • Accounting irregularities – Misrepresentation of financial statements and/or fraud • Competitive pressure – Loss of revenue due to pricing and/or volume pressures from competitors • Cost overruns – Higher than expected overhead or other operating costs, extraordinary charges, and/or heavy investment • Customer demand shortfall – Lower than expected industry-wide demand from customers • Ineffective Management – Poor operating decisions made by executives within the company leading to an earnings shortfall • Loss of key customer – Loss or major reduction of business from key customers • Supply chain issues – Problems with the inventory and delivery systems leading to revenue shortfalls or cost overruns • Customer pricing pressure – Strong customers negotiate price discounts • Misaligned Products/Channels – Product selection/design does not meet customer requirements • M&A integration problems – M&A activities viewed unsound by investors; cost savings and/or synergies from M&A not achieved • Regulatory problems – Regulatory changes affect long-term earnings potential • R&D Delays – Problems with research and development • Supplier Problems – Suppliers oppose company’s strategy
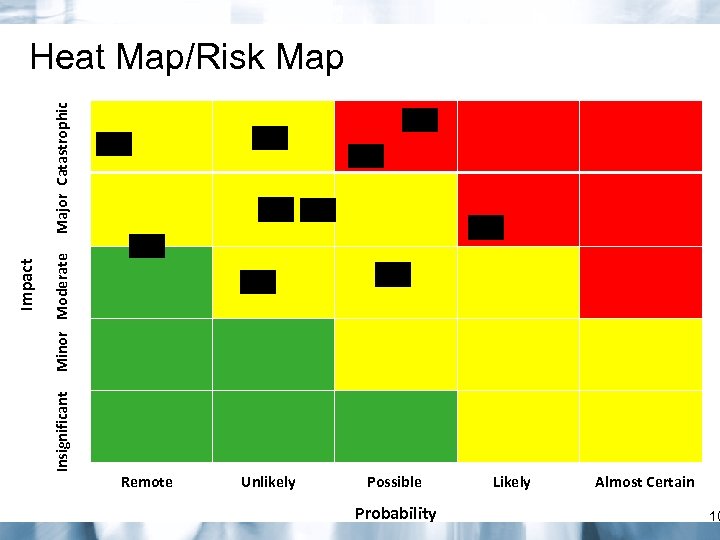
Minor Moderate Insignificant Impact Major Catastrophic Heat Map/Risk Map Remote Unlikely Possible Probability Likely Almost Certain 10
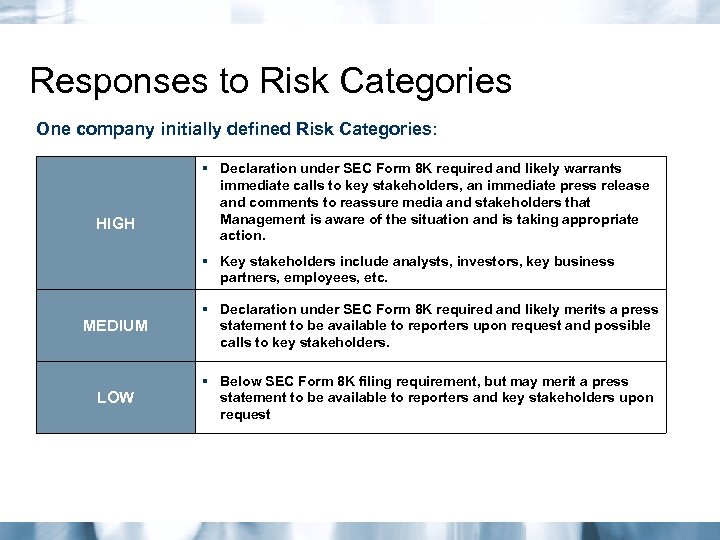
Responses to Risk Categories One company initially defined Risk Categories: HIGH § Declaration under SEC Form 8 K required and likely warrants immediate calls to key stakeholders, an immediate press release and comments to reassure media and stakeholders that Management is aware of the situation and is taking appropriate action. § Key stakeholders include analysts, investors, key business partners, employees, etc. MEDIUM § Declaration under SEC Form 8 K required and likely merits a press statement to be available to reporters upon request and possible calls to key stakeholders. LOW § Below SEC Form 8 K filing requirement, but may merit a press statement to be available to reporters and key stakeholders upon request

ERM Definitions COSO (2004) Enterprise risk management is a process, effected by an entity’s board if directors, management and other personnel, applied in strategy setting and across the enterprise, designed to identify potential events that may affect the entity, and manage risk to be within its risk appetite, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of entity objectives.

Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) § What is ERM, and what is it NOT? – ERM is: Managing the risks that can kill your company – ERM isn’t: Managing all the sundry risks encountered in operating your business § The amount of “E” risks already within your business describes your Erisk tolerance – What is the smallest $ size of risk event could cripple or kill your organization? – How many of risks of that size or larger already exist in your business today? – a (sizes of those) x b (number of those) = your real risk tolerance

Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) § How can an organization really benefit from ERM – beyond “checking the box? ” – Clearly define the E risks – Get buy-in on definition from management & board – Inventory those within your business today – Utilize multiple sets of eyes looking for potential new E-risks on the horizon, – Have a clear process for how/where to bring those to management’s attention – Define “go/no go” criteria & management’s responsibilities for reviewing, disposing, and periodically reporting to the board – Do it § Examples…
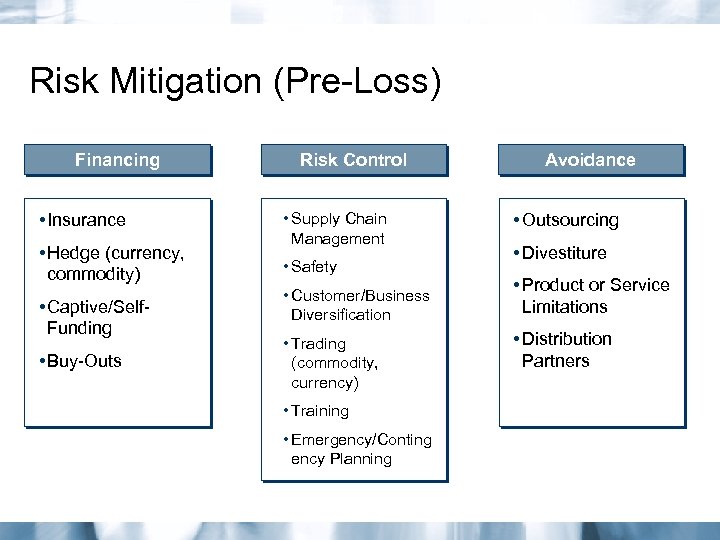
Risk Mitigation (Pre-Loss) Financing • Insurance • Hedge (currency, commodity) • Captive/Self. Funding • Buy-Outs Risk Control • Supply Chain Management • Safety • Customer/Business Diversification • Trading (commodity, currency) • Training • Emergency/Conting ency Planning Avoidance • Outsourcing • Divestiture • Product or Service Limitations • Distribution Partners
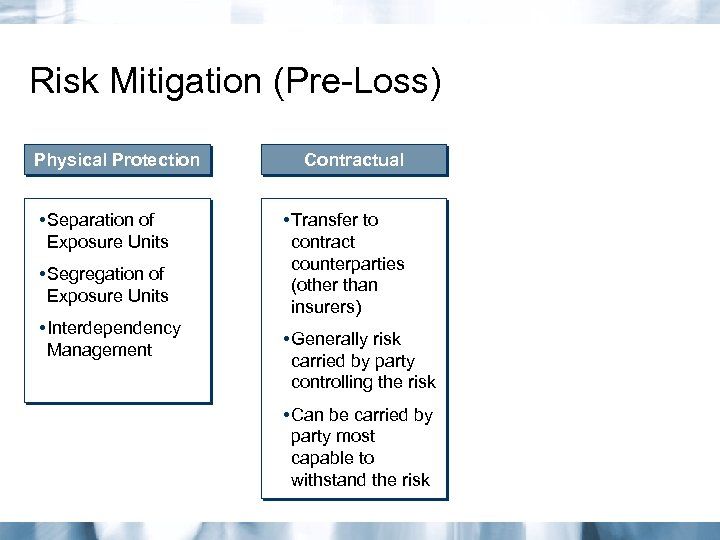
Risk Mitigation (Pre-Loss) Physical Protection • Separation of Exposure Units • Segregation of Exposure Units • Interdependency Management Contractual • Transfer to contract counterparties (other than insurers) • Generally risk carried by party controlling the risk • Can be carried by party most capable to withstand the risk
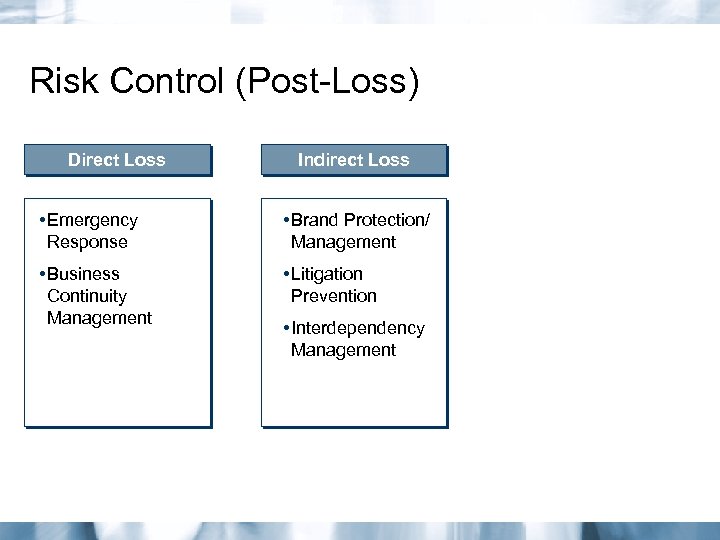
Risk Control (Post-Loss) Direct Loss Indirect Loss • Emergency Response • Brand Protection/ Management • Business Continuity Management • Litigation Prevention • Interdependency Management
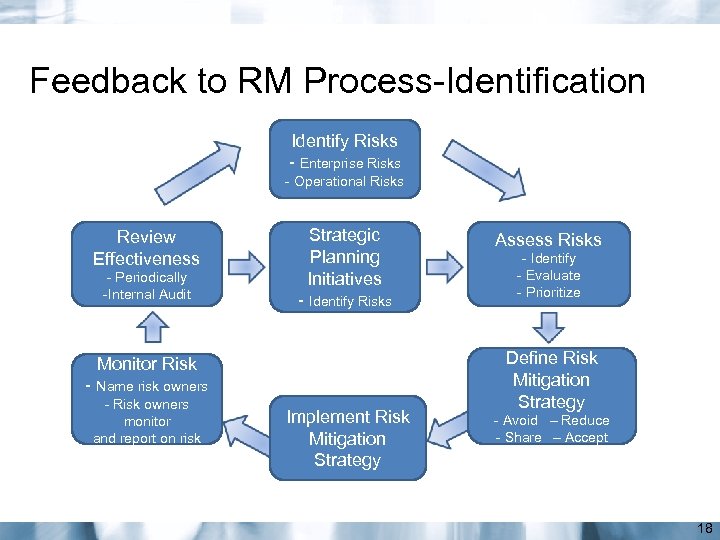
Feedback to RM Process-Identification Identify Risks - Enterprise Risks - Operational Risks Review Effectiveness - Periodically -Internal Audit Strategic Planning Initiatives - Identify Risks Monitor Risk - Name risk owners - Risk owners monitor and report on risk Implement Risk Mitigation Strategy Assess Risks - Identify - Evaluate - Prioritize Define Risk Mitigation Strategy - Avoid – Reduce - Share – Accept 18
1e69931163423eb22308c332e3f98c90.ppt