ec5c69615282097e5ae10dbd156ea90e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Risk Management Lecture 1 Introduction: Financial System, Institutions & Instruments Nadir Khan
Risk Management Lecture 1 Introduction: Financial System, Institutions & Instruments Nadir Khan
 Risk Management Financial Markets • A market is a venue where goods and services are exchanged. • A financial market is a place where individuals and organizations needing funds are brought together with those having surplus of funds. Nadir Khan
Risk Management Financial Markets • A market is a venue where goods and services are exchanged. • A financial market is a place where individuals and organizations needing funds are brought together with those having surplus of funds. Nadir Khan
 Risk Management Types of Markets • Physical Assets Market • Physical markets deal with real assets such as wheat, automobiles, computers, etc. • Financial Assets Market • Financial markets deal with stocks, bonds, derivative securities, etc. • Money Market • Money markets are for short-term, highly liquid debt securities. • Capital Market • Capital markets are for intermediate, long-term debt etc. • Primary Market • Primary markets are markets where corporations raise new capital. • Secondary Market • Secondary markets are where existing shares are traded among investors. Nadir Khan
Risk Management Types of Markets • Physical Assets Market • Physical markets deal with real assets such as wheat, automobiles, computers, etc. • Financial Assets Market • Financial markets deal with stocks, bonds, derivative securities, etc. • Money Market • Money markets are for short-term, highly liquid debt securities. • Capital Market • Capital markets are for intermediate, long-term debt etc. • Primary Market • Primary markets are markets where corporations raise new capital. • Secondary Market • Secondary markets are where existing shares are traded among investors. Nadir Khan
 Risk Management Types of Markets (Con’t …) • Spot Markets • Spot markets are markets where assets are bought or sold for ‘on the spot’ delivery. • Futures Markets • Futures markets are markets in which participants agree to buy or sell an asset at some future date. • Private Markets • Private markets are markets where transaction occurs between two parties. • Public Markets • Public markets are markets where standardized contracts are traded on organized exchange. Nadir Khan
Risk Management Types of Markets (Con’t …) • Spot Markets • Spot markets are markets where assets are bought or sold for ‘on the spot’ delivery. • Futures Markets • Futures markets are markets in which participants agree to buy or sell an asset at some future date. • Private Markets • Private markets are markets where transaction occurs between two parties. • Public Markets • Public markets are markets where standardized contracts are traded on organized exchange. Nadir Khan
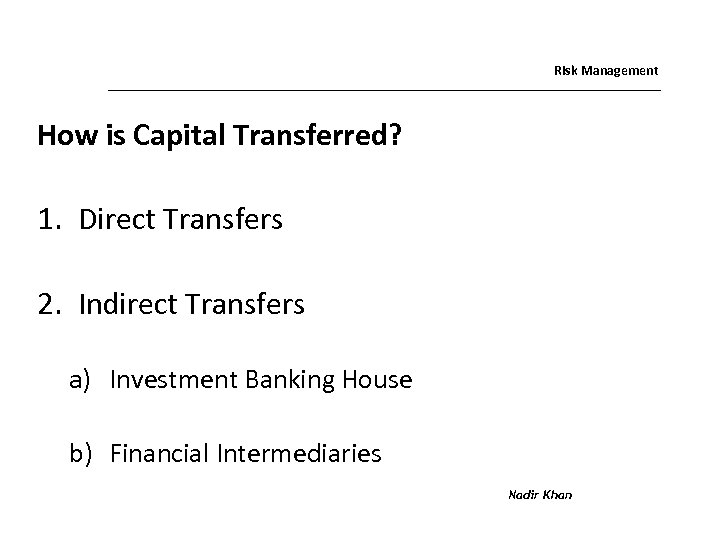 Risk Management How is Capital Transferred? 1. Direct Transfers 2. Indirect Transfers a) Investment Banking House b) Financial Intermediaries Nadir Khan
Risk Management How is Capital Transferred? 1. Direct Transfers 2. Indirect Transfers a) Investment Banking House b) Financial Intermediaries Nadir Khan
 Risk Management • Direct Finance – Borrowers borrow funds directly from lenders in financial markets by selling them securities (also called financial instruments) which are claims on borrower’s future income or assets. – Securities are assets for the person who buys them but liabilities for the individual or firm that sells them. – For example, if Toyota Indus needs to borrow funds to pay for a new factory to manufacture electric cars, it might borrow funds from savers by selling them bonds, debt securities that promise to make payments periodically for a specified period of time. • Indirect Finance – Borrowers borrow funds from a financial institution (commercial bank etc) where the savings are deposited, i. e. they borrow through financial intermediaries and these borrowings are backed by their portfolio of assets which are claims on the borrowers. – Or hire a financial advisor (investment bank) to arrange capital for them. Nadir Khan
Risk Management • Direct Finance – Borrowers borrow funds directly from lenders in financial markets by selling them securities (also called financial instruments) which are claims on borrower’s future income or assets. – Securities are assets for the person who buys them but liabilities for the individual or firm that sells them. – For example, if Toyota Indus needs to borrow funds to pay for a new factory to manufacture electric cars, it might borrow funds from savers by selling them bonds, debt securities that promise to make payments periodically for a specified period of time. • Indirect Finance – Borrowers borrow funds from a financial institution (commercial bank etc) where the savings are deposited, i. e. they borrow through financial intermediaries and these borrowings are backed by their portfolio of assets which are claims on the borrowers. – Or hire a financial advisor (investment bank) to arrange capital for them. Nadir Khan
 Investment Analysis INDIRECT FINANCE FUNDS Financial Intermediaries FUNDS 1. 2. 3. 4. Lenders-Savers Households Business Firms Government Foreigners FUNDS Financial Markets FUNDS Borrowers-Spenders 1. Business Firms 2. Government 3. Households 4. Foreigners DIRECT FINANCE Nadir Khan
Investment Analysis INDIRECT FINANCE FUNDS Financial Intermediaries FUNDS 1. 2. 3. 4. Lenders-Savers Households Business Firms Government Foreigners FUNDS Financial Markets FUNDS Borrowers-Spenders 1. Business Firms 2. Government 3. Households 4. Foreigners DIRECT FINANCE Nadir Khan
 Investment Analysis Financial Institutions (FIs) • A financial institution acts as an agent that provides financial services to its clients or members. • FIs perform the essential function of arranging funds from those with surplus funds to those with shortage of funds. • FIs generally fall under financial regulation from a government. Nadir Khan
Investment Analysis Financial Institutions (FIs) • A financial institution acts as an agent that provides financial services to its clients or members. • FIs perform the essential function of arranging funds from those with surplus funds to those with shortage of funds. • FIs generally fall under financial regulation from a government. Nadir Khan
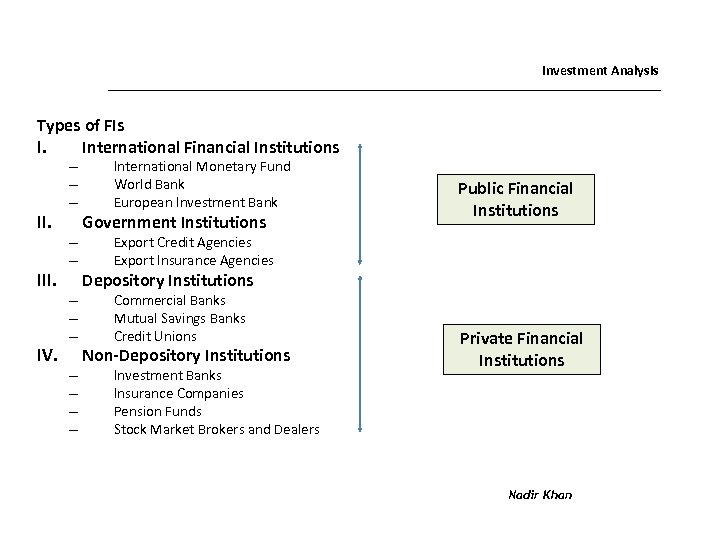 Investment Analysis Types of FIs I. International Financial Institutions – – – II. III. IV. – – – – – International Monetary Fund World Bank European Investment Bank Government Institutions Public Financial Institutions Export Credit Agencies Export Insurance Agencies Depository Institutions Commercial Banks Mutual Savings Banks Credit Unions Non-Depository Institutions Investment Banks Insurance Companies Pension Funds Stock Market Brokers and Dealers Private Financial Institutions Nadir Khan
Investment Analysis Types of FIs I. International Financial Institutions – – – II. III. IV. – – – – – International Monetary Fund World Bank European Investment Bank Government Institutions Public Financial Institutions Export Credit Agencies Export Insurance Agencies Depository Institutions Commercial Banks Mutual Savings Banks Credit Unions Non-Depository Institutions Investment Banks Insurance Companies Pension Funds Stock Market Brokers and Dealers Private Financial Institutions Nadir Khan
 Risk Management Three Main Services • Risk Sharing – For savers steady return (profit, interest) – For borrowers predictable cost (interest payable by borrower) • Liquidity – Enhance liquidity of financial system • Solve asymmetric information problem – Information can be easily and at less cost available on borrower’s credit worthiness etc. through banks/financial system Nadir Khan
Risk Management Three Main Services • Risk Sharing – For savers steady return (profit, interest) – For borrowers predictable cost (interest payable by borrower) • Liquidity – Enhance liquidity of financial system • Solve asymmetric information problem – Information can be easily and at less cost available on borrower’s credit worthiness etc. through banks/financial system Nadir Khan
 Risk Management Financial System • The financial system of a country consists of institutions and regulators that act on a national or regional level. • The main players are the (1) financial institutions, such as, commercial banks, (2) financial intermediaries, such as, brokers/investment banks, (3) financial markets, such as, exchanges, (4) national agencies and government departments, such as, central bank and finance ministries etc. • Financial system hence , is the channel through which savings become investments and through which money and financial claims are transferred and settled. The participants in a financial system work together for the health and stability of a nation’s economy. Nadir Khan
Risk Management Financial System • The financial system of a country consists of institutions and regulators that act on a national or regional level. • The main players are the (1) financial institutions, such as, commercial banks, (2) financial intermediaries, such as, brokers/investment banks, (3) financial markets, such as, exchanges, (4) national agencies and government departments, such as, central bank and finance ministries etc. • Financial system hence , is the channel through which savings become investments and through which money and financial claims are transferred and settled. The participants in a financial system work together for the health and stability of a nation’s economy. Nadir Khan
 Risk Management Why Regulators are needed? • FIs provide vital services to all sectors of the economy; therefore, their regulation is in public interest. • In an attempt to prevent the failure of FIs and the failure of financial markets overall and hence the whole economy. • Regulatory authorities are necessary for maintenance and financial stability of the economy and building confidence of all stake holders in the system. Nadir Khan
Risk Management Why Regulators are needed? • FIs provide vital services to all sectors of the economy; therefore, their regulation is in public interest. • In an attempt to prevent the failure of FIs and the failure of financial markets overall and hence the whole economy. • Regulatory authorities are necessary for maintenance and financial stability of the economy and building confidence of all stake holders in the system. Nadir Khan
 Risk Management Financial Instruments • Financial instruments are cash, evidence of ownership interest in an entity or a contractual right to receive or deliver cash or another financial instrument. • An instrument having monetary value or recording a monetary transaction. • In general, any financial security such as a bond, stock, check, etc. Money market securities (such as Treasury Bills, Commercial Papers) and Capital market securities (such as Certificate of Deposit, longterm bonds) are also referred to as instruments. Nadir Khan
Risk Management Financial Instruments • Financial instruments are cash, evidence of ownership interest in an entity or a contractual right to receive or deliver cash or another financial instrument. • An instrument having monetary value or recording a monetary transaction. • In general, any financial security such as a bond, stock, check, etc. Money market securities (such as Treasury Bills, Commercial Papers) and Capital market securities (such as Certificate of Deposit, longterm bonds) are also referred to as instruments. Nadir Khan
 Risk Management Types of Financial Instruments Categorized by “Asset” Class 1. Equity Based: representing ownership of the asset. 2. Debt Based: reflecting a loan the investor has made to the issuing entity. Nadir Khan
Risk Management Types of Financial Instruments Categorized by “Asset” Class 1. Equity Based: representing ownership of the asset. 2. Debt Based: reflecting a loan the investor has made to the issuing entity. Nadir Khan
 Risk Management Types of Financial Instruments Categorized by “Maturity” 1. 2. Money Market: ü ü ü Short-term (less than 1 year) Less price fluctuation Hence less risky investments Capital Market: ü ü ü Debt and equity instruments with maturities greater than 1 year Wider price fluctuation Fairly risky investments Nadir Khan
Risk Management Types of Financial Instruments Categorized by “Maturity” 1. 2. Money Market: ü ü ü Short-term (less than 1 year) Less price fluctuation Hence less risky investments Capital Market: ü ü ü Debt and equity instruments with maturities greater than 1 year Wider price fluctuation Fairly risky investments Nadir Khan
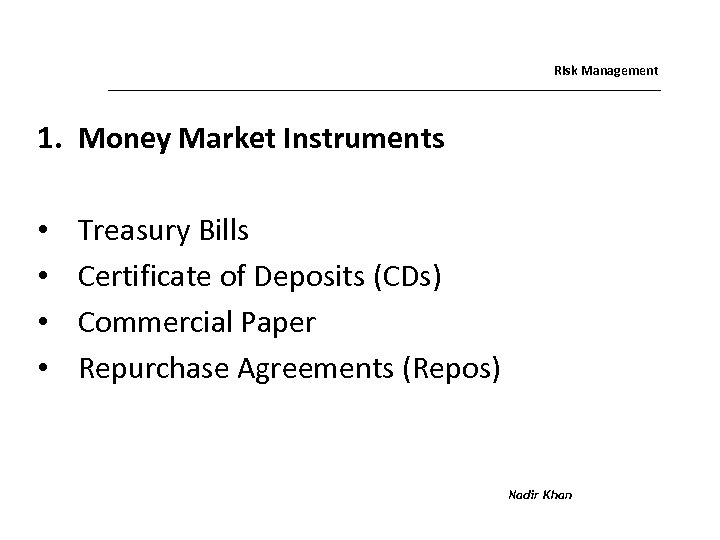 Risk Management 1. Money Market Instruments • • Treasury Bills Certificate of Deposits (CDs) Commercial Paper Repurchase Agreements (Repos) Nadir Khan
Risk Management 1. Money Market Instruments • • Treasury Bills Certificate of Deposits (CDs) Commercial Paper Repurchase Agreements (Repos) Nadir Khan
 Risk Management 2. Capital Market Instruments • • Stocks Corporate Bonds Government Securities Sukuks Nadir Khan
Risk Management 2. Capital Market Instruments • • Stocks Corporate Bonds Government Securities Sukuks Nadir Khan


