09d4ca4711f5152174381a23afd15249.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Risk and Return and the Financing Decision: Bonds vs. Stock

Bonds l are debt instruments issued by financial institutions, the municipal/state/federal government, and companies to public investors to obtain capital. l have a set maturity, e. g. 10, 20, 30 years. l carry a certain interest rate.

Sources of Capital for Growth l Profits (earnings, net income) l Issue new shares of stock l Borrowings Loan from bank l Issue bonds in bond market l

What could go wrong in the Creemee Business? l l l Weather Running out of inventory Ordering too much inventory Choosing wrong location for the day Too many/too few employees = Examples of Basic Business Risk in the Creemee Business
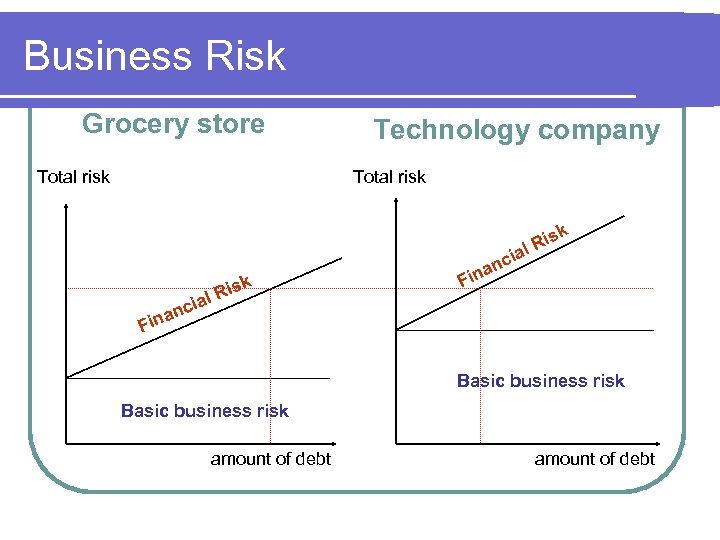
Business Risk Grocery store Total risk Technology company Total risk k is l. R ia k s l Ri a c an in F i anc in F Basic business risk amount of debt

The Financing Decision Assess the level of Basic Business Risk. 2. Determine how much Financial Risk is appropriate, given the level of Basic Business Risk. 1. l l Basic Business Risk + Financial Risk = Total Risk of the Firm Stockholders care about Total Risk.
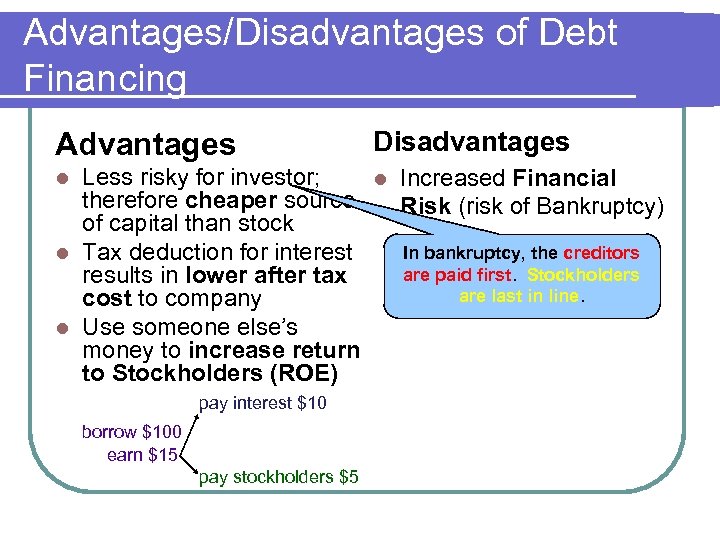
Advantages/Disadvantages of Debt Financing Advantages Disadvantages Less risky for investor; l Increased Financial therefore cheaper source Risk (risk of Bankruptcy) of capital than stock In bankruptcy, the creditors l Tax deduction for interest are paid first. Stockholders results in lower after tax are last in line. cost to company l Use someone else’s money to increase return to Stockholders (ROE) l pay interest $10 borrow $100 earn $15 pay stockholders $5
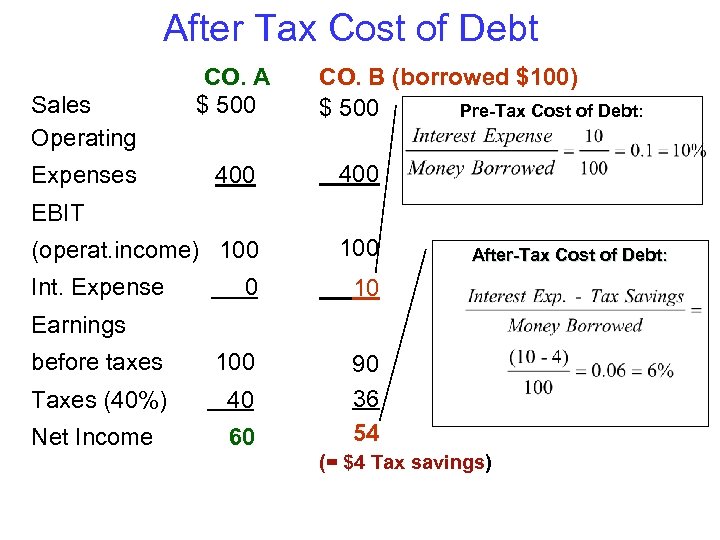
After Tax Cost of Debt Sales Operating CO. A $ 500 CO. B (borrowed $100) $ 500 Pre-Tax Cost of Debt: 400 (operat. income) 100 Expenses EBIT Int. Expense 0 10 before taxes 100 Taxes (40%) 40 Net Income 60 After-Tax Cost of Debt: 90 36 54 Earnings (= $4 Tax savings)
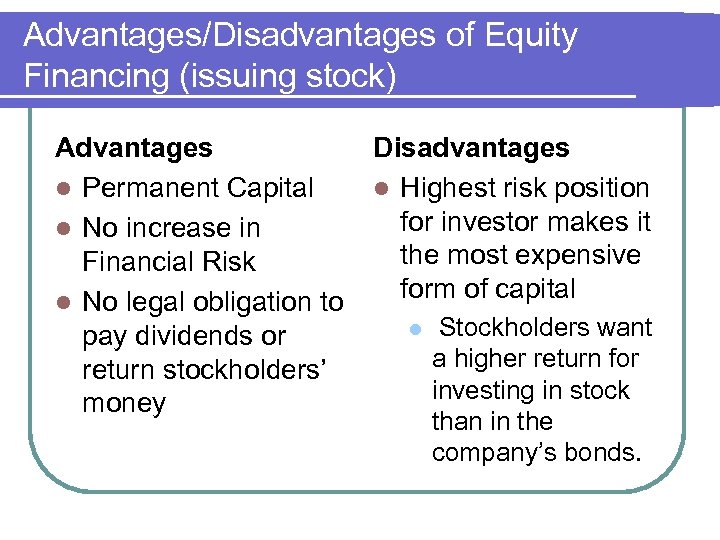
Advantages/Disadvantages of Equity Financing (issuing stock) Advantages l Permanent Capital l No increase in Financial Risk l No legal obligation to pay dividends or return stockholders’ money Disadvantages l Highest risk position for investor makes it the most expensive form of capital l Stockholders want a higher return for investing in stock than in the company’s bonds.

Why Lenders Charge Interest Default risk: risk of not getting your money back 2. Opportunity cost: You could invest your money in something else. 3. Inflation risk 1.
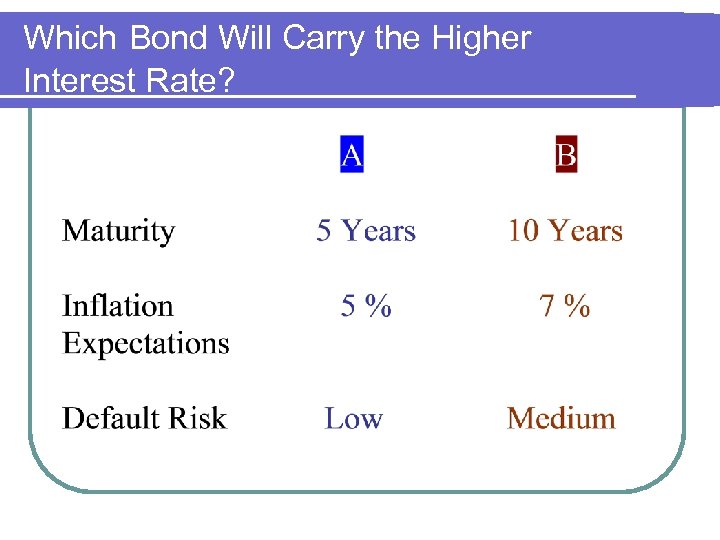
Which Bond Will Carry the Higher Interest Rate?
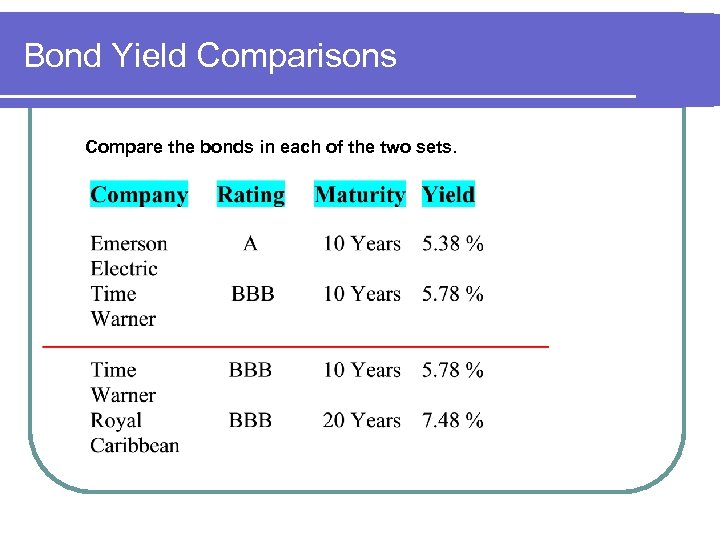
Bond Yield Comparisons Compare the bonds in each of the two sets.
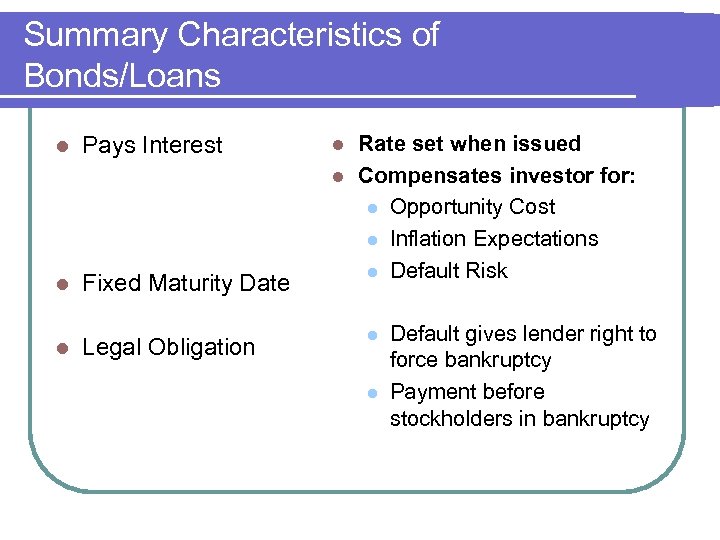
Summary Characteristics of Bonds/Loans l Pays Interest l Fixed Maturity Date l Legal Obligation Rate set when issued l Compensates investor for: l Opportunity Cost l Inflation Expectations l Default Risk l l l Default gives lender right to force bankruptcy Payment before stockholders in bankruptcy

Why Buy A Stock? l l l Become an Owner of a Company Objective: Make money Concerns: What level of return? Return related to performance of the company Forms of Return: l Dividends l Increase in Stock Price l Why would the stock price go up ? ? ?
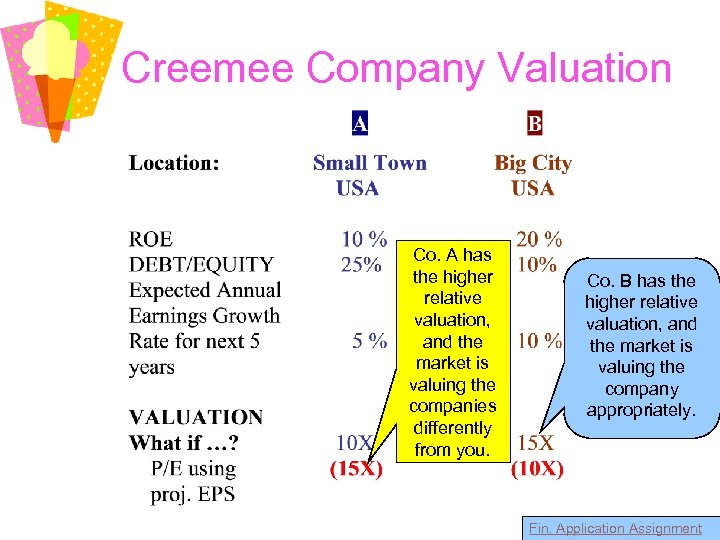
Creemee Company Valuation Co. A has the higher relative valuation, and the market is valuing the companies differently from you. Co. B has the higher relative valuation, and the market is valuing the company appropriately. Fin. Application Assignment
Summary Characteristics of Common Stock (Equity) l Stockholders can receive a return through: l l l Dividend Decision l l l Increase in Stock Price (buy low/sell high) Dividends Based on earnings performance of Company Made by the Board No requirement to pay dividends No bankruptcy if dividend declared is not paid Relative Valuation of Stock by Investors related to: l l l Future earnings growth prospects Rate of return expected to be earned by equity holders (ROE) Risk of not getting this expected return (business or financial risk)
09d4ca4711f5152174381a23afd15249.ppt