6e21f444822fc8bffb65fda056215658.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Risk Analysis COEN 250
Risk Analysis COEN 250
 Risk Management n Risk Management consists of ¨ Risk Assessment ¨ Risk Mitigation ¨ Risk Evaluation and Assessment n Risk Management allows ¨ Balance operational and economic costs of protective measures
Risk Management n Risk Management consists of ¨ Risk Assessment ¨ Risk Mitigation ¨ Risk Evaluation and Assessment n Risk Management allows ¨ Balance operational and economic costs of protective measures
 Risk Management and System Development Life Cycle n Phase 1 – Initiation Need for IT system is expressed, scope is documented ¨ Identified risks are for ¨ n Developing system requirements ¨ ¨ n Including security requirements Security strategy of operations Phase 2 – Development or Acquisition IT system is Designed, Purchased, Programmed, Developed ¨ Risks identified during this phase are used to ¨ n Support security analyses of system ¨ Might lead to architecture and design trade-offs during development
Risk Management and System Development Life Cycle n Phase 1 – Initiation Need for IT system is expressed, scope is documented ¨ Identified risks are for ¨ n Developing system requirements ¨ ¨ n Including security requirements Security strategy of operations Phase 2 – Development or Acquisition IT system is Designed, Purchased, Programmed, Developed ¨ Risks identified during this phase are used to ¨ n Support security analyses of system ¨ Might lead to architecture and design trade-offs during development
 Risk Management and System Development Life Cycle n Phase 3 – Implementation System features are configured, enabled, tested, verified ¨ Risk management supports assessment of system implementation against requirements and modeled operational environment ¨ n Phase 4 – Operation or Maintenance ¨ System performs its functions n ¨ Typically: modification on an ongoing basis Risk Management activities: n System reauthorization / reaccreditation ¨ ¨ ¨ Periodic Triggered by changes in system Triggered by changes in operational production environment
Risk Management and System Development Life Cycle n Phase 3 – Implementation System features are configured, enabled, tested, verified ¨ Risk management supports assessment of system implementation against requirements and modeled operational environment ¨ n Phase 4 – Operation or Maintenance ¨ System performs its functions n ¨ Typically: modification on an ongoing basis Risk Management activities: n System reauthorization / reaccreditation ¨ ¨ ¨ Periodic Triggered by changes in system Triggered by changes in operational production environment
 Risk Management and System Development Life Cycle n Phase 5 – Disposal ¨ Disposition of n n n ¨ Activities n n n ¨ Information Hardware Software Moving Archiving Discarding Destroying Sanitizing Risk management: n n n Ensure proper disposal of software and hardware Proper handling of residual data System migration conducted securely and systematically
Risk Management and System Development Life Cycle n Phase 5 – Disposal ¨ Disposition of n n n ¨ Activities n n n ¨ Information Hardware Software Moving Archiving Discarding Destroying Sanitizing Risk management: n n n Ensure proper disposal of software and hardware Proper handling of residual data System migration conducted securely and systematically
 Risk Management and System Development Life Cycle n Risk management is management responsibility ¨ Senior management n n ¨ Chief Information Officer (CIO) n n ¨ Ensures effective application of necessary resources to develop mission capabilities Need to asses and incorporate results of risk management into decision making process Responsible for planning, budgeting, and performance of IT Includes Information Security components Systems and Information Owners n n n Responsible for ensuring existence of proper controls Have to approve and sign off to changes in IT system Need to understand role of risk management
Risk Management and System Development Life Cycle n Risk management is management responsibility ¨ Senior management n n ¨ Chief Information Officer (CIO) n n ¨ Ensures effective application of necessary resources to develop mission capabilities Need to asses and incorporate results of risk management into decision making process Responsible for planning, budgeting, and performance of IT Includes Information Security components Systems and Information Owners n n n Responsible for ensuring existence of proper controls Have to approve and sign off to changes in IT system Need to understand role of risk management
 Risk Management and System Development Life Cycle ¨ Business and Functional Managers n n ¨ Information System Security Officer (ISSO) n n n ¨ Responsible for security program, including risk management Play leading role for methodology of risk management Act as consultant to senior management IT Security Practitioners n n n ¨ Have authority and responsibility to make trade-off decisions Need to be involved in risk management Responsible for proper implementation Must support risk management process to identify new potential risks Must implement new security controls Security Awareness Trainers n n n Proper use of systems is instrumental in risk mitigation and IT resource protection Must understand risk management Must incorporate risk assessment into training programs
Risk Management and System Development Life Cycle ¨ Business and Functional Managers n n ¨ Information System Security Officer (ISSO) n n n ¨ Responsible for security program, including risk management Play leading role for methodology of risk management Act as consultant to senior management IT Security Practitioners n n n ¨ Have authority and responsibility to make trade-off decisions Need to be involved in risk management Responsible for proper implementation Must support risk management process to identify new potential risks Must implement new security controls Security Awareness Trainers n n n Proper use of systems is instrumental in risk mitigation and IT resource protection Must understand risk management Must incorporate risk assessment into training programs
 Risk Assessment n Risk depends on ¨ Likelihood of a given threat-source exercising a particular potential vulnerability ¨ Resulting impact of the adverse event
Risk Assessment n Risk depends on ¨ Likelihood of a given threat-source exercising a particular potential vulnerability ¨ Resulting impact of the adverse event
 Hypothetical 2003 Example Polish hacker N@te upset at Polish control of Multinational Division Central South Iraq n His hacker group wants to attack www. wp. mil. pl n ¨ Finds out n www. wp. mil. pl runs Apache n Runs old version of Open. SSL vulnerable to a buffer overflow attack Bejtlich: The Tao of Network Security Monitoring
Hypothetical 2003 Example Polish hacker N@te upset at Polish control of Multinational Division Central South Iraq n His hacker group wants to attack www. wp. mil. pl n ¨ Finds out n www. wp. mil. pl runs Apache n Runs old version of Open. SSL vulnerable to a buffer overflow attack Bejtlich: The Tao of Network Security Monitoring
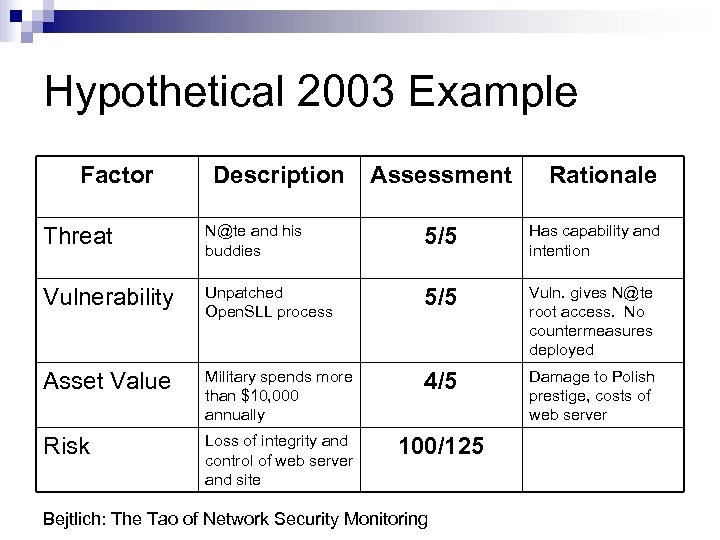 Hypothetical 2003 Example Factor Description Assessment Rationale Threat N@te and his buddies 5/5 Has capability and intention Vulnerability Unpatched Open. SLL process 5/5 Vuln. gives N@te root access. No countermeasures deployed Asset Value Military spends more than $10, 000 annually 4/5 Damage to Polish prestige, costs of web server Risk Loss of integrity and control of web server and site 100/125 Bejtlich: The Tao of Network Security Monitoring
Hypothetical 2003 Example Factor Description Assessment Rationale Threat N@te and his buddies 5/5 Has capability and intention Vulnerability Unpatched Open. SLL process 5/5 Vuln. gives N@te root access. No countermeasures deployed Asset Value Military spends more than $10, 000 annually 4/5 Damage to Polish prestige, costs of web server Risk Loss of integrity and control of web server and site 100/125 Bejtlich: The Tao of Network Security Monitoring
 Hypothetical 2003 Example Polish military does not know N@te, but knows about its exposure n Needs to know about vulnerability n Risk assessment changes dramatically once vulnerability is recognized n
Hypothetical 2003 Example Polish military does not know N@te, but knows about its exposure n Needs to know about vulnerability n Risk assessment changes dramatically once vulnerability is recognized n
 Vulnerability Threat n February 2002 SNMP vulnerability ¨ SNMP widespread network management tool. ¨ Potentially affected most network devices. ¨ However, NO exploits were discovered.
Vulnerability Threat n February 2002 SNMP vulnerability ¨ SNMP widespread network management tool. ¨ Potentially affected most network devices. ¨ However, NO exploits were discovered.
 Vulnerability Threat n Windows RPC vulnerability of 2003 ¨ Dozens of exploits ¨ Blaster worm caused > $1. 000 damage
Vulnerability Threat n Windows RPC vulnerability of 2003 ¨ Dozens of exploits ¨ Blaster worm caused > $1. 000 damage
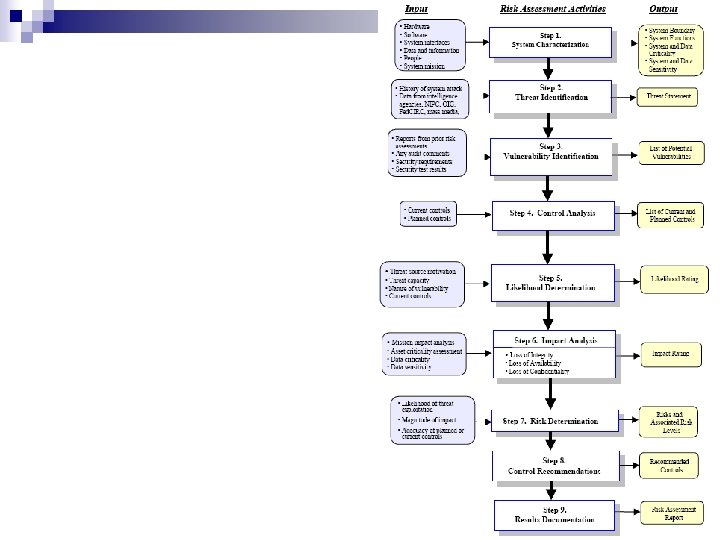
 Risk Assessment n Step 1: System Characterization ¨ Collect n n n n system related information Hardware Software Connectivity Data and information Users and support System mission System and data criticality and sensitivity …
Risk Assessment n Step 1: System Characterization ¨ Collect n n n n system related information Hardware Software Connectivity Data and information Users and support System mission System and data criticality and sensitivity …
 Risk Assessment n Step 2: Threat Identification ¨ Threat n Natural events: ¨ n Floods, fires, earthquakes, … Human threats: ¨ ¨ n Source Identification Unintentional acts Deliberate actions § Consider motivations and actions Environmental threats ¨ Long-term power failure, pollution, chemicals, liquid leakage
Risk Assessment n Step 2: Threat Identification ¨ Threat n Natural events: ¨ n Floods, fires, earthquakes, … Human threats: ¨ ¨ n Source Identification Unintentional acts Deliberate actions § Consider motivations and actions Environmental threats ¨ Long-term power failure, pollution, chemicals, liquid leakage
 Risk Assessment n Step 3: Vulnerability Identification ¨ Varies on SDLC phase ¨ Sources n n n Previous risk assessment documents IT system audits and logs Vulnerability lists (NIST I-CAT, CERT, SANS, Security. Focus. com) Security advisories Vendor advisories System software security analyses
Risk Assessment n Step 3: Vulnerability Identification ¨ Varies on SDLC phase ¨ Sources n n n Previous risk assessment documents IT system audits and logs Vulnerability lists (NIST I-CAT, CERT, SANS, Security. Focus. com) Security advisories Vendor advisories System software security analyses
 Risk Assessment n Step 3: Vulnerability Identification ¨ Security Testing Automated vulnerability scanning tools n Penetration testing n Security Test and Evaluation (ST&E) n Develop a test plan ¨ Test Effectiveness of security controls ¨ n See NIST SP 800 -42
Risk Assessment n Step 3: Vulnerability Identification ¨ Security Testing Automated vulnerability scanning tools n Penetration testing n Security Test and Evaluation (ST&E) n Develop a test plan ¨ Test Effectiveness of security controls ¨ n See NIST SP 800 -42
 Risk Assessment n Step 3: Vulnerability Identification ¨ Develop a Security Requirements n Management Security ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ Checklist Assignment of responsibilities Continuity of support Incident response capability Periodic review of security controls Personnel clearance and background investigations Risk assessment Separation of duties System authorization and reauthorization System or application security plan
Risk Assessment n Step 3: Vulnerability Identification ¨ Develop a Security Requirements n Management Security ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ Checklist Assignment of responsibilities Continuity of support Incident response capability Periodic review of security controls Personnel clearance and background investigations Risk assessment Separation of duties System authorization and reauthorization System or application security plan
 Risk Assessment n Step 3: Vulnerability Identification ¨ Develop a Security Requirements n Operational Security ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ Checklist Control of air-borne contaminants Controls to ensure the quality of the electrical power supply Data media access and disposal External data distribution and labeling Facility protection (e. g. , computer room, data center, office) Humidity control Temperature control Workstations, laptops, and stand-alone personal computers
Risk Assessment n Step 3: Vulnerability Identification ¨ Develop a Security Requirements n Operational Security ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ Checklist Control of air-borne contaminants Controls to ensure the quality of the electrical power supply Data media access and disposal External data distribution and labeling Facility protection (e. g. , computer room, data center, office) Humidity control Temperature control Workstations, laptops, and stand-alone personal computers
 Risk Assessment n Step 3: Vulnerability Identification ¨ Develop n a Security Requirements Checklist Technical Security ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ Communications (e. g. , dial-in, system interconnection, routers) Cryptography Discretionary access control Identification and authentication Intrusion detection Object reuse System audit
Risk Assessment n Step 3: Vulnerability Identification ¨ Develop n a Security Requirements Checklist Technical Security ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ Communications (e. g. , dial-in, system interconnection, routers) Cryptography Discretionary access control Identification and authentication Intrusion detection Object reuse System audit
 Risk Assessment n Step 3: Vulnerability Identification ¨ Outcome: A list of system vulnerabilities that could be exercised by a potential threat source
Risk Assessment n Step 3: Vulnerability Identification ¨ Outcome: A list of system vulnerabilities that could be exercised by a potential threat source
 Risk Assessment n Control Analysis ¨ Control n Technical methods ¨ n Methods Safeguards built into computer hardware, software, firmware Nontechnical methods ¨ Management and operational controls § Security policies § Operational procedures § Personnel security § Physical security § Environmental security
Risk Assessment n Control Analysis ¨ Control n Technical methods ¨ n Methods Safeguards built into computer hardware, software, firmware Nontechnical methods ¨ Management and operational controls § Security policies § Operational procedures § Personnel security § Physical security § Environmental security
 Risk Assessment n Control Categories ¨ Preventive controls ¨ Detective controls
Risk Assessment n Control Categories ¨ Preventive controls ¨ Detective controls
 Risk Assessment n Control Analysis ¨ Compare security requirements checklist to validate security (non)-compliance n Output: ¨ List of current or planned controls
Risk Assessment n Control Analysis ¨ Compare security requirements checklist to validate security (non)-compliance n Output: ¨ List of current or planned controls
 Risk Assessment n Step 5: Likelihood determination ¨ Governing factors Threat source motivation and capability n Nature of vulnerability n Existence and effectiveness of current controls n ¨ Assign likelihood levels
Risk Assessment n Step 5: Likelihood determination ¨ Governing factors Threat source motivation and capability n Nature of vulnerability n Existence and effectiveness of current controls n ¨ Assign likelihood levels
 Risk Assessment n Step 6: Impact Analysis ¨ Requires n System mission n System and data criticality n System and data sensitivity ¨ Can typically be described n Loss of integrity n Loss of availability n Loss of confidentiality in
Risk Assessment n Step 6: Impact Analysis ¨ Requires n System mission n System and data criticality n System and data sensitivity ¨ Can typically be described n Loss of integrity n Loss of availability n Loss of confidentiality in
 Risk Assessment n Step 6: Impact Analysis ¨ Can be done quantitatively or qualitatively
Risk Assessment n Step 6: Impact Analysis ¨ Can be done quantitatively or qualitatively
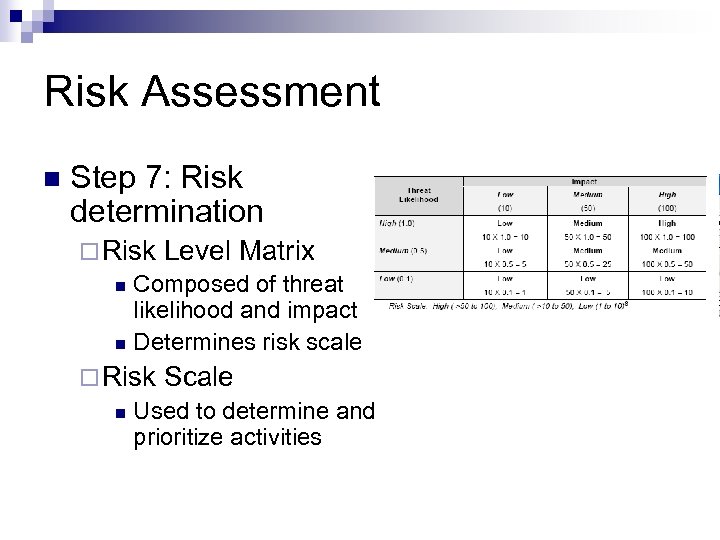 Risk Assessment n Step 7: Risk determination ¨ Risk Level Matrix n Composed of threat likelihood and impact n Determines risk scale ¨ Risk Scale n Used to determine and prioritize activities
Risk Assessment n Step 7: Risk determination ¨ Risk Level Matrix n Composed of threat likelihood and impact n Determines risk scale ¨ Risk Scale n Used to determine and prioritize activities
 Risk Assessment n Control Recommendations ¨ Reduce risks to data and system to acceptable level ¨ Base evaluation on n n Effectiveness Legislation and regulation Organizational policy Operational impact Safety and reliability ¨ Perform cost benefit analysis
Risk Assessment n Control Recommendations ¨ Reduce risks to data and system to acceptable level ¨ Base evaluation on n n Effectiveness Legislation and regulation Organizational policy Operational impact Safety and reliability ¨ Perform cost benefit analysis
 Risk Assessment n Step 9: Result Documentation ¨ Risk assessment report Describes threats and vulnerabilities n Measures risk n Provides recommendations for control implementation n
Risk Assessment n Step 9: Result Documentation ¨ Risk assessment report Describes threats and vulnerabilities n Measures risk n Provides recommendations for control implementation n
 Risk Mitigation Prioritizing n Evaluating n Implementing Appropriate risk-reducing controls n
Risk Mitigation Prioritizing n Evaluating n Implementing Appropriate risk-reducing controls n
 Risk Mitigation n Options ¨ Risk Assumption n ¨ Risk Avoidance n ¨ To manage risk by developing a risk mitigation plan that prioritizes, implements, and maintains controls Research and Acknowledgment n ¨ To limit the risk by implementing controls that minimize the adverse impact of a threat’s exercising a vulnerability Risk Planning n ¨ To avoid the risk by eliminating the risk cause and/or consequence Risk Limitation n ¨ To accept the potential risk and continue operating the IT system or to implement controls to lower the risk to an acceptable level To lower the risk of loss by acknowledging the vulnerability or flaw and researching controls to correct the vulnerability Risk Transference n To transfer the risk by using other options to compensate for the loss, such as purchasing insurance.
Risk Mitigation n Options ¨ Risk Assumption n ¨ Risk Avoidance n ¨ To manage risk by developing a risk mitigation plan that prioritizes, implements, and maintains controls Research and Acknowledgment n ¨ To limit the risk by implementing controls that minimize the adverse impact of a threat’s exercising a vulnerability Risk Planning n ¨ To avoid the risk by eliminating the risk cause and/or consequence Risk Limitation n ¨ To accept the potential risk and continue operating the IT system or to implement controls to lower the risk to an acceptable level To lower the risk of loss by acknowledging the vulnerability or flaw and researching controls to correct the vulnerability Risk Transference n To transfer the risk by using other options to compensate for the loss, such as purchasing insurance.
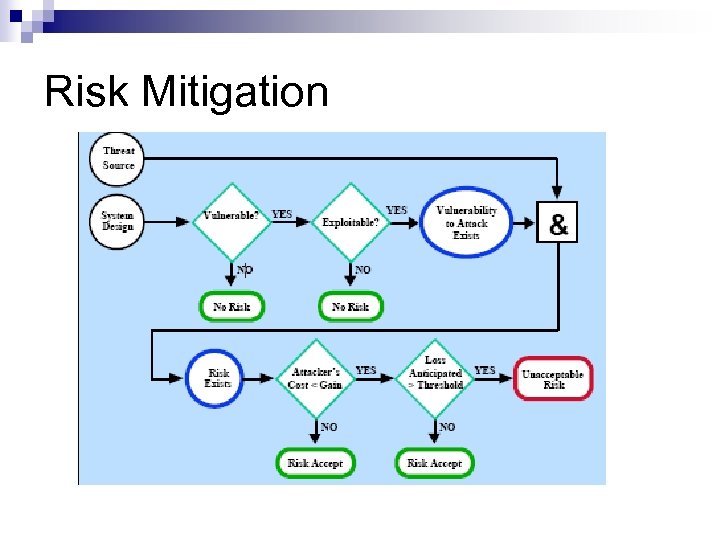 Risk Mitigation
Risk Mitigation
 Risk Mitigation n Control Implementation ¨ Prioritize Actions ¨ Evaluate Recommended Control Options ¨ Conduct Cost-Benefit Analysis ¨ Select Control ¨ Assign Responsibility ¨ Develop a Safeguard Implementation Plan ¨ Implement Selected Control(s)
Risk Mitigation n Control Implementation ¨ Prioritize Actions ¨ Evaluate Recommended Control Options ¨ Conduct Cost-Benefit Analysis ¨ Select Control ¨ Assign Responsibility ¨ Develop a Safeguard Implementation Plan ¨ Implement Selected Control(s)


